Abstract
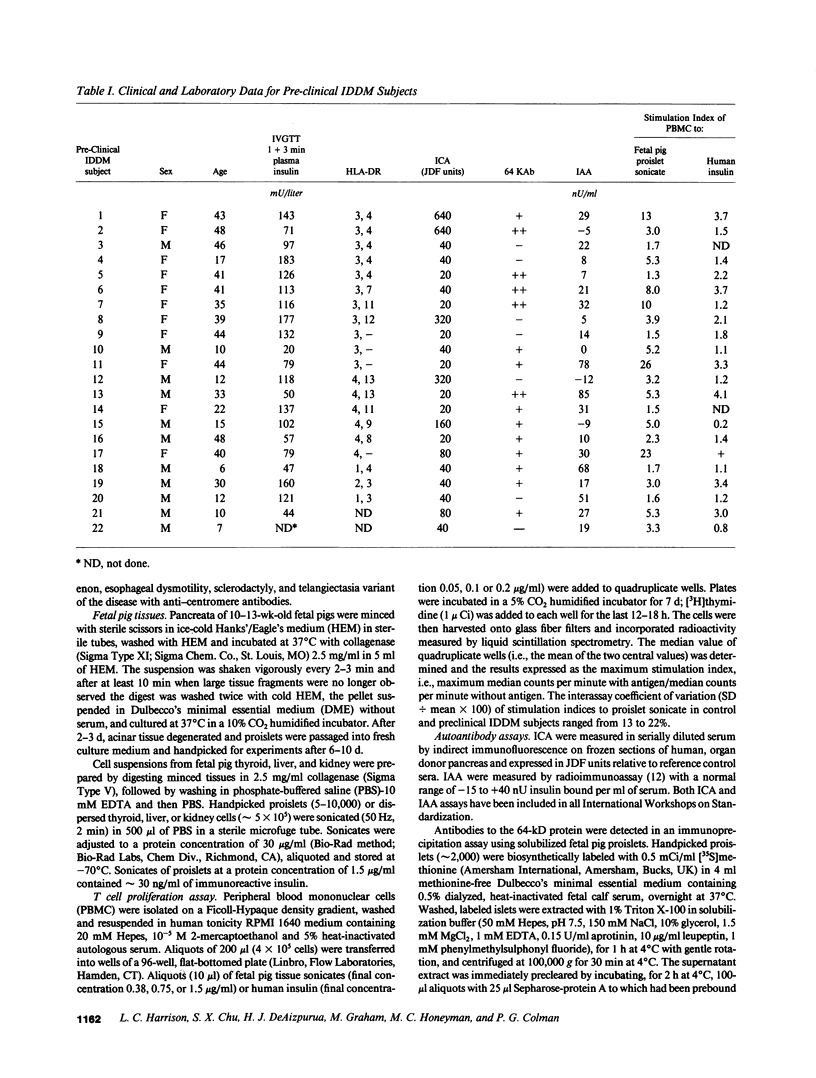
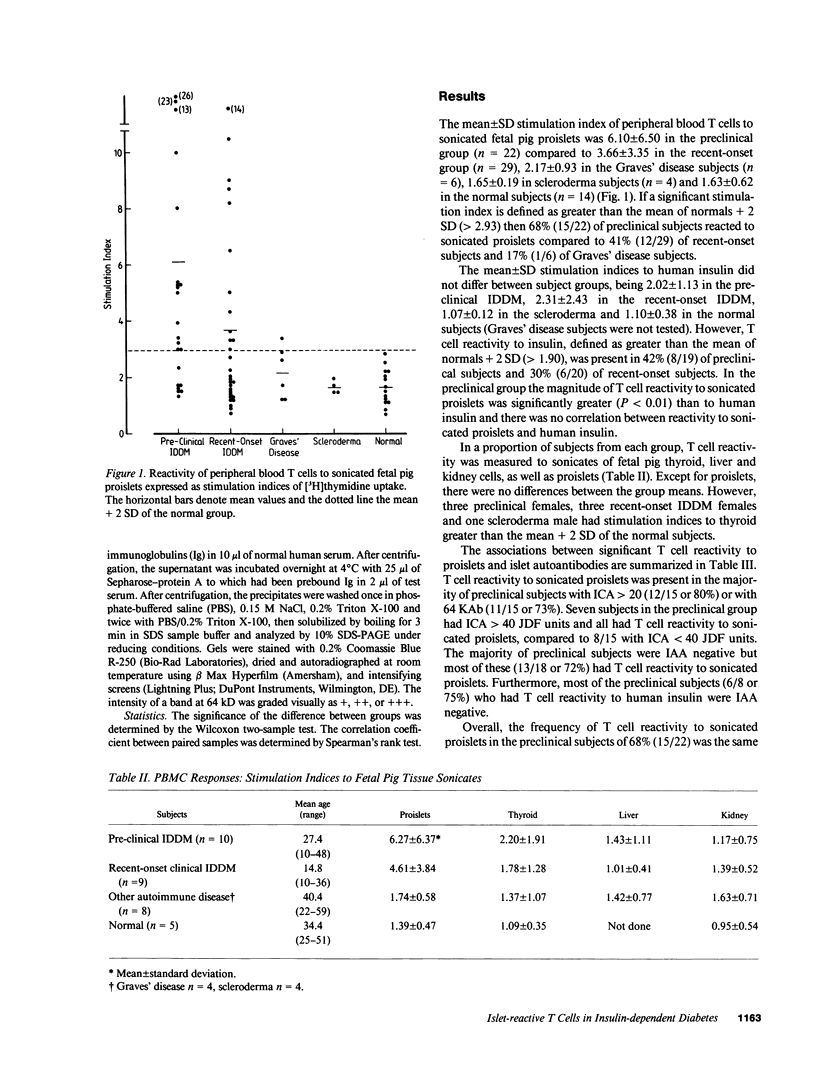
The destruction of pancreatic islet beta cells in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is thought to be T cell mediated. To directly identify islet-reactive T cells in asymptomatic, "preclinical" IDDM individuals with islet cell antibodies (ICA), proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) was measured in the presence of sonicated fetal pig proislets. Stimulation indices (mean +/- SD) for [3H]thymidine uptake by PBMC cultured with sonicated proislets were: preclinical IDDM subjects (n = 22) 6.10 +/- 6.50, recent-onset IDDM subjects (n = 29) 3.66 +/- 3.35, Graves' disease subjects (n = 6) 2.17 +/- 0.93, scleroderma subjects (n = 4) 1.65 +/- 0.19 and normal control subjects (n = 14) 1.63 +/- 0.62. 68% (15/22) of preclinical IDDM, 41% (12/29) of recent-onset IDDM and 17% (1/6) of Graves' disease subjects had T cell reactivity greater than the mean + 2 SD of controls. T cell reactivity to proislets was tissue specific, and greater in magnitude and frequency than to human insulin. The majority of preclinical subjects with ICA greater than 20 Juvenile Diabetes Foundation (JDF) units (12/15, 80%) or antibodies to a 64-kD islet autoantigen (11/15, 73%) had significant T cell reactivity to proislets. ICA greater than 40 JDF units, a strong prognostic marker for progression to clinical IDDM, was an absolute index of T cell reactivity. Overall, the frequency of T cell reactivity in preclinical subjects, 68% (15/22), was comparable to that of ICA greater than 20 JDF units or 64-kD antibodies. Greater T cell reactivity to proislets in preclinical subjects accords with the natural history of autoimmune beta cell destruction. The direct assay of islet-reactive T cells in peripheral blood may have prognostic significance for the development of clinical IDDM and should facilitate identification of the primary target autoantigen(s).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Riley W. J. 64,000 Mr autoantibodies as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jun 9;335(8702):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Bingley P. J., Shattock M., Dean B. M., Dunger D., Gale E. A., Bottazzo G. F. Quantification of islet-cell antibodies and prediction of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jan 20;335(8682):147–149. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90013-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram D. S., Barnett L. D., Joseph J. L., Harrison L. C. Cloning and partial nucleotide sequence of human glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA from brain and pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1239–1244. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke E., Marchetti P., Falqui L., Swanson C., McLear M., Olack B., Scharp D., Lacy P. Large scale isolation, function, and transplantation of islets of Langerhans from the adult pig pancreas. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):772–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., De Aizpurua H., Loudovaris T., Campbell I. L., Cebon J. S., Tait B. D., Colman P. G. Reactivity to human islets and fetal pig proislets by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from subjects with preclinical and clinical insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Sep;40(9):1128–1133. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.9.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay T. W., Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C. Characterization of pancreatic T lymphocytes associated with beta cell destruction in the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse. J Autoimmun. 1991 Apr;4(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koevary S., Rossini A., Stoller W., Chick W., Williams R. M. Passive transfer of diabetes in the BB/W rat. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):727–728. doi: 10.1126/science.6836309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Morahan G., Allison J. Immunological tolerance: new approaches using transgenic mice. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90306-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordes J. P., Desemone J., Rossini A. A. The BB rat. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jul;3(3):725–750. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly L. A., Hutchings P. R., Crocker P. R., Simpson E., Lund T., Kioussis D., Takei F., Baird J., Cooke A. Characterization of pancreatic islet cell infiltrates in NOD mice: effect of cell transfer and transgene expression. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1171–1180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roep B. O., Kallan A. A., Hazenbos W. L., Bruining G. J., Bailyes E. M., Arden S. D., Hutton J. C., de Vries R. R. T-cell reactivity to 38 kD insulin-secretory-granule protein in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 1991 Jun 15;337(8755):1439–1441. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93127-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardi P., Dib S. A., Tuttleman M., Connelly J. E., Grinbergs M., Radizabeh A., Riley W. J., Maclaren N. K., Eisenbarth G. S., Soeldner J. S. Competitive insulin autoantibody assay. Prospective evaluation of subjects at high risk for development of type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1987 Nov;36(11):1286–1291. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.11.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Miller B. J., Mullen Y. Transfer of autoimmune diabetes mellitus with splenocytes from nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes. 1986 Aug;35(8):855–860. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.8.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Berardinis P., Londei M., James R. F., Lake S. P., Wise P. H., Feldmann M. Do CD4-positive cytotoxic T cells damage islet beta cells in type 1 diabetes? Lancet. 1988 Oct 8;2(8615):823–824. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92785-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



