Abstract
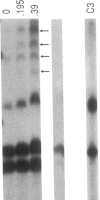
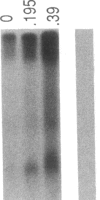
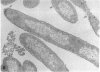
Serum-resistant organisms grown in sub-minimal inhibitory concentrations (subMICs) of antibiotics in vitro may be rendered sensitive to complement-mediated, serum bactericidal activity. We measured 125I-C3 and 125I-C9 deposition on genetically serum resistant Salmonella montevideo SH5770 (SH5770) that was rendered serum sensitive by growth in sub-MICs of cefmetazole (CMZ), a parenteral, second generation, cephamycin-group antibiotic. Three times as much C3 and over six times as much C9 bound to SH5770 grown in one-fourth the MIC of CMZ compared to broth-grown bacteria. SDS-PAGE analysis and autoradiography showed that neither the ratio of C3b:iC3b (approximately 1:2.5) nor the nature of the C3-bacterial bond was changed by growing the organisms in CMZ. Large amounts of complement membrane attack complexes containing poly-C9 were seen only on CMZ-grown SH5770 by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Poly-C9 was also detected only on CMZ-grown bacteria by indirect immunofluorescence and ELISA using a murine monoclonal antibody directed against a neoantigen of poly-C9. Bacterial hydrophobicity increased after growth in CMZ, and transmission electron micrographs of CMZ-grown SH5770 showed cell wall disruption and blebbing. These results indicate that growth in subMICs of CMZ increases bacterial hydrophobic domains available for interacting with the membrane attack complex, C5b-9, allowing formation and stable insertion of bactericidal complexes containing poly-C9.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander W. J., Cobbs C. G., Curtiss R., 3rd Modification of bacterial serum susceptibility by rifampin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):923–926. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.923-926.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Kuller G., Muhly M., Fromm S., Seibert G., Parrisius J. Formation of transmural complement pores in serum-sensitive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):206–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.206-210.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch E. F., Schmetz M. A., Foulds J., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M., Joiner K. A. Multimeric C9 within C5b-9 is required for inner membrane damage to Escherichia coli J5 during complement killing. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmasso A. P., Benson B. A., Falk R. J. Complement channels in membranes: inhibition with a monoclonal antibody to a neoantigen of polymerized C9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):1013–1019. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91384-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J. R., Esser A. F. Bacterial killing by complement. C9-mediated killing in the absence of C5b-8. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj2440393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J. R., Esser A. F. Complement-mediated killing of Escherichia coli: dissipation of membrane potential by a C9-derived peptide. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Cunningham M. D. Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of cephalosporins on the serum sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):914–921. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Kolb W. P., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular reorganization of lipid bilayers by complement: a possible mechanism for membranolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1410–1414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S. The serum bactericidal reaction. IV. Phenotypic conversion of Escherichia coli from serum-resistance to serum-sensitivity by diphenylamine. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):437–444. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S. The serum bactericidal reaction. IV. Phenotypic conversion of Escherichia coli from serum-resistance to serum-sensitivity by diphenylamine. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):437–444. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. N., Austen K. F. Reaction mechanisms of nascent C567 (reactive lysis). II. Killing of a rough form of Escherichia coli by C567, C8, and C9. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):444–450. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Miller M. F. Complement attack of altered outer membrane areas synthesized after inhibition of the 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate pathway leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):185–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Fazio M., Tomasz A. Effect of benzylpenicillin on the synthesis and structure of the cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):514–526. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Comparison of the responses of Escherichia coli and proteus mirabilis to seven beta-lactam antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):211–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman N., Schmetz M. A., Foulds J., Klima E. N., Jimenez-Lucho V. E., Leive L. L., Joiner K. A., Jiminez V. Lipopolysaccharide size and distribution determine serum resistance in Salmonella montevideo. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):856–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.856-863.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Alterations in outer membrane permeability. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:237–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Hakenbeck R., Tomasz A. Secretion of lipids induced by inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):704–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.704-717.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jit Sud I., Feingold D. S. Detection of agents that alter the bacterial cell surface. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):34–37. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A. Complement evasion by bacteria and parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:201–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Goldman R. C., Hammer C. H., Leive L., Frank M. M. Studies of the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. V. IgG and F(ab')2 mediate killing of E. coli 0111B4 by the alternative complement pathway without increasing C5b-9 deposition. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2563–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Scales R., Warren K. A., Frank M. M., Rice P. A. Mechanism of action of blocking immunoglobulin G for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1172/JCI112167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Schmetz M. A., Sanders M. E., Murray T. G., Hammer C. H., Dourmashkin R., Frank M. M. Multimeric complement component C9 is necessary for killing of Escherichia coli J5 by terminal attack complex C5b-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Tartanian A. B., Hammer C. H., Schweinle J. E. Multimeric C9 within C5b-9 deposits in unique locations in the cell wall of Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4450–4457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Warren K. A., Brown E. J., Swanson J., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. IV. C5b-9 forms high molecular weight complexes with bacterial outer membrane constituents on serum-resistant but not on serum-sensitive Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1443–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N. Cefmetazole (CS-1170), a "new" cephamycin with a decade of clinical experience. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;12(5):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N. Review of the in-vitro spectrum and characteristics of cefmetazole (CS-1170). J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Apr;23 (Suppl 500):1–12. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll H. P., Bhakdi S., Taylor P. W. Membrane changes induced by exposure of Escherichia coli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1055-1066.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. ACTINOMYCIN SENSITIVITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:13–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90874-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang-Takasaki C. J., Grossman N., Leive L. Salmonellae activate complement differentially via the alternative pathway depending on the structure of their lipopolysaccharide O-antigen. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1867–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang-Takasaki C. J., Mäkelä P. H., Leive L. Phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages: changing the carbohydrate of lipopolysaccharide alters interaction with complement and macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1229–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay S. L., Dankert J. R. Bacterial killing and inhibition of inner membrane activity by C5b-9 complexes as a function of the sequential addition of C9 to C5b-8 sites. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3367–3371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Sharon N. Role of the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidation reaction in attachment of newly synthesized peptidoglycan to cell walls of Micrococcus luteus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Palmer J. D. Neutralization of endotoxin toxicity in chick embryos by antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):815–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.815-819.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D. Studies on the interaction between endotoxin and polymyxin B. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):433–438. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweinle J. E., Ezekowitz R. A., Tenner A. J., Kuhlman M., Joiner K. A. Human mannose-binding protein activates the alternative complement pathway and enhances serum bactericidal activity on a mannose-rich isolate of Salmonella. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1821–1829. doi: 10.1172/JCI114367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Gaunt H., Unger F. M. Effect of subinhibitory concentrations of mecillinam on the serum susceptibility of Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):786–788. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Kroll H. P. Effect of lethal doses of complement on the functional integrity of target enterobacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;121:135–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45604-6_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations as outer membrane-disorganizing agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Sensitization of Gram-negative bacteria to antibiotics and complement by a nontoxic oligopeptide. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):526–528. doi: 10.1038/303526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Viljanen P., Vaara T., Mäkelä P. H. An outer membrane-disorganizing peptide PMBN sensitizes E. coli strains to serum bactericidal action. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2582–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen V. V. Mouse virulence of Salmonella strains: the effect of different smooth-type O side-chains. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):255–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer B. W., Fugate R. D., Sims P. J. Complement proteins C5b-9 induce transbilayer migration of membrane phospholipids. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):935–946. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82739-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Tawara S., Mine Y., Kikuchi H., Goto S., Kuwahara S. Synergism of cephalosporins at subinhibitory concentrations and polymorphonuclear leukocytes on phagocytic killing of Escherichia coli and its mode of action. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Feb;39(2):294–303. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]