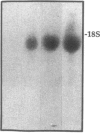
Abstract
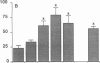
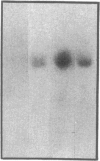
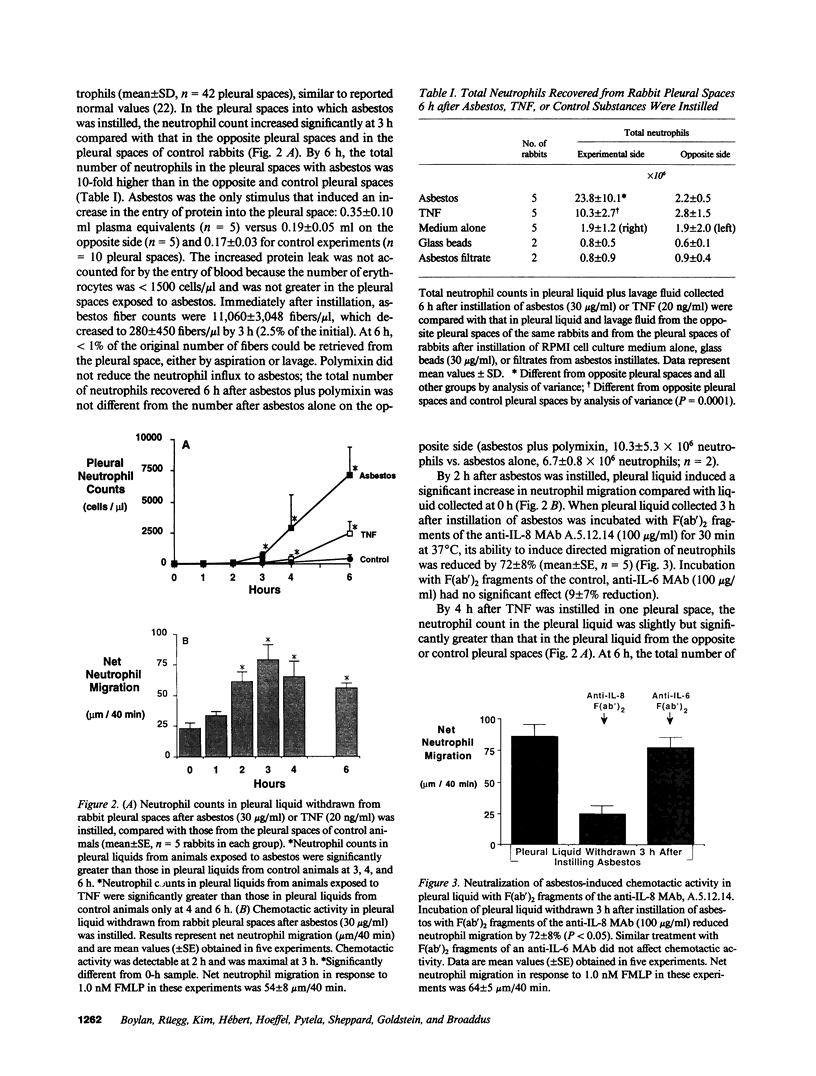
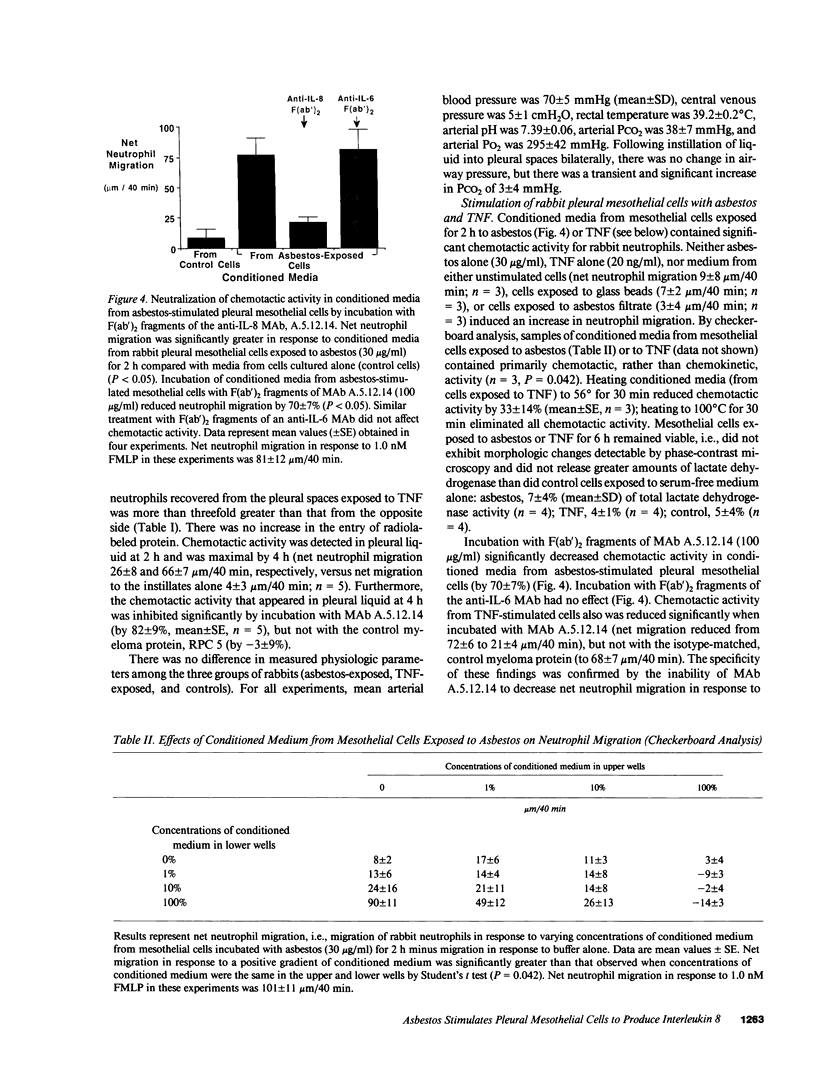
Although acute asbestos-induced pleurisy is characterized by an influx of neutrophils, the identity of the factors that attract these cells to the pleural space and the source of the factors are unknown. We found that instillation of crocidolite asbestos into the pleural space of rabbits led to the appearance in pleural liquid of chemotactic activity for neutrophils, and that this chemotactic activity was inhibited significantly by a neutralizing antibody to human interleukin 8 (IL-8). Cultured rabbit pleural mesothelial cells incubated with crocidolite asbestos also released chemotactic activity for neutrophils, which was inhibited significantly by the anti-IL-8 antibody. To determine whether rabbit pleural mesothelial cells synthesize IL-8, we generated a probe for rabbit IL-8 mRNA by amplifying cDNA prepared from stimulated pleural mesothelial cells using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and primers based on homologous sequences in human and sheep IL-8 cDNAs. Homology-based PCR yielded a single cDNA fragment with a nucleotide sequence 88% identical to that of a corresponding region of human IL-8 cDNA. With the radiolabeled PCR product as a probe, we demonstrated rapid induction of IL-8 mRNA expression in pleural mesothelial cells exposed to asbestos. As expected, tumor necrosis factor-alpha also led to the appearance of IL-8 in the rabbit pleural space and stimulated cultured pleural mesothelial cells to synthesize and release IL-8. We conclude that asbestos directly stimulates pleural mesothelial cells to synthesize IL-8 and that mesothelial cell-derived IL-8 may play an important role in mediating asbestos-induced pleural inflammation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antony V. B., Owen C. L., Hadley K. J. Pleural mesothelial cells stimulated by asbestos release chemotactic activity for neutrophils in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jan;139(1):199–206. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaubien B. C., Collins P. D., Jose P. J., Totty N. F., Hsuan J., Waterfield M. D., Williams T. J. A novel neutrophil chemoattractant generated during an inflammatory reaction in the rabbit peritoneal cavity in vivo. Purification, partial amino acid sequence and structural relationship to interleukin 8. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):797–801. doi: 10.1042/bj2710797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette E., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of asbestosis and silicosis. Possible role of tumor necrosis factor. Inflammation. 1989 Jun;13(3):329–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00914399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broaddus V. C., Araya M. Liquid and protein dynamics using a new minimally invasive pleural catheter in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Mar;72(3):851–857. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.3.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coene M. C., Van Hove C., Claeys M., Herman A. G. Arachidonic acid metabolism by cultured mesothelial cells. Different transformations of exogenously added and endogenously. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 12;710(3):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N. D., Rheinwald J. G. Regulation of the cytoskeleton in mesothelial cells: reversible loss of keratin and increase in vimentin during rapid growth in culture. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., McComb D. J., Movat H. Z. Protein synthesis dependent and independent mechanisms of neutrophil emigration. Different mechanisms of inflammation in rabbits induced by interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor alpha or endotoxin versus leukocyte chemoattractants. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):227–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmers P. A., Lo S. K., Olsen-Egbert E., Walz A., Baggiolini M., Cohn Z. A. Neutrophil-activating protein 1/interleukin 8 stimulates the binding activity of the leukocyte adhesion receptor CD11b/CD18 on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1155–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Chang D., Griffin G. L., Heinrikson R. L., Kaiser E. T. Platelet factor 4 is chemotactic for neutrophils and monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4584–4587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois C. M., Bissonnette E., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Asbestos fibers and silica particles stimulate rat alveolar macrophages to release tumor necrosis factor. Autoregulatory role of leukotriene B4. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 May;139(5):1257–1264. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.5.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatt M., Dieppe P., Willoughby D. Crystal-induced inflammation, enzyme release and the effects of drugs in the rat pleural space. J Rheumatol. 1979 May-Jun;6(3):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. B., Wood R. G., Martin T. R., Hanson-Painton O., Kinasewitz G. T. Cytokine-stimulated human mesothelial cells produce chemotactic activity for neutrophils including NAP-1/IL-8. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):457–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. A., Venaille T. J., Rose A. H., Musk A. W., Robinson B. W. Asbestos-induced release of a human alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor. Exp Lung Res. 1990 Mar-Apr;16(2):121–130. doi: 10.3109/01902149009087877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Megyeri P., Issekutz T. B. Role for macrophage products in endotoxin-induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation during inflammation. Lab Invest. 1987 Jan;56(1):49–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurand M. C., Kaplan H., Thiollet J., Pinchon M. C., Bernaudin J. F., Bignon J. Phagocytosis of chrysotile fibers by pleural mesothelial cells in culture. Am J Pathol. 1979 Mar;94(3):529–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzan S., Brody A. R., Nettesheim P., Eling T. Production of arachidonic acid metabolites by macrophages exposed in vitro to asbestos, carbonyl iron particles, or calcium ionophore. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):624–632. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J. F., Tokiwa T., LaVeck M., Benedict W. F., Banks-Schlegel S., Yeager H., Jr, Banerjee A., Harris C. C. Asbestos-associated chromosomal changes in human mesothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3884–3888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Pistorese B. P., Chi E. Y., Goodman R. B., Matthay M. A. Effects of leukotriene B4 in the human lung. Recruitment of neutrophils into the alveolar spaces without a change in protein permeability. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1609–1619. doi: 10.1172/JCI114338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miserocchi G., Agostoni E. Contents of the pleural space. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Feb;30(2):208–213. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.30.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moalli P. A., MacDonald J. L., Goodglick L. A., Kane A. B. Acute injury and regeneration of the mesothelium in response to asbestos fibers. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):426–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossman B. T., Gee J. B. Asbestos-related diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 29;320(26):1721–1730. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906293202604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oghiso Y., Kubota Y. Interleukin 1 production and accessory cell function of rat alveolar macrophages exposed to mineral dust particles. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(3):275–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuck A. S., Braude A. C. Bronchoalveolar lavage in asbestosis. Arch Intern Med. 1983 May;143(5):950–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., Musk A. W. Benign asbestos pleural effusion: diagnosis and course. Thorax. 1981 Dec;36(12):896–900. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.12.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., Rose A. H., James A., Whitaker D., Musk A. W. Alveolitis of pulmonary asbestosis. Bronchoalveolar lavage studies in crocidolite- and chrysotile-exposed individuals. Chest. 1986 Sep;90(3):396–402. doi: 10.1378/chest.90.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Gouin S., Bégin R. Asbestos-induced lung inflammation. Role of local macrophage-derived chemotactic factors in accumulation of neutrophils in the lungs. Inflammation. 1984 Mar;8(1):53–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00918353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahn S. A., Antony V. B. Pathogenesis of pleural plaques. Relationship of early cellular response and pathology. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):884–887. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B. L., Daughaday C. C., Spilberg I. Benign asbestos pleurisy in the rabbit. A model for the study of pathogenesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Sep;128(3):481–485. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Basha M. A., Chensue S. W., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Toews G. B., Westwick J., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 gene expression by a pulmonary epithelial cell line. A model for cytokine networks in the lung. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI114928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Schultz E. L., Koike K., Albertine K. H. Effect of neutrophil migration induced by leukotriene B4 on protein permeability in sheep lung. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 1):30–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer J. L., Potts D. E., Sahn S. A. Cellular content of the normal rabbit pleural space. Acta Cytol. 1978 Nov-Dec;22(6):570–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Basha M. A., Standiford T. J., Lynch J. P., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L. Human alveolar macrophage gene expression of interleukin-8 by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, lipopolysaccharide, and interleukin-1 beta. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):321–326. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Phan S. H., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Lynch J. P., Genord M., Raiford C., Eskandari M., Marks R. M., Kunkel S. L. Monokine-induced neutrophil chemotactic factor gene expression in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10621–10626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkeltaub R., Zachariae C., Santoro D., Martin J., Peveri P., Matsushima K. Monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor/interleukin-8 is a potential mediator of crystal-induced inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jul;34(7):894–903. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton A. J., Strieter R. M., Lindley I., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine-induced gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor/IL-8 in human hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2609–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Rampart M., Conings R., Decock B., Van Osselaer N., Willems J., Billiau A. The neutrophil-activating proteins interleukin 8 and beta-thromboglobulin: in vitro and in vivo comparison of NH2-terminally processed forms. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2113–2118. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinegar R., Truax J. F., Selph J. L., Voelker F. A. Pathway of onset, development, and decay of carrageenan pleurisy in the rat. Fed Proc. 1982 Jul;41(9):2588–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Peveri P., Aschauer H., Baggiolini M. Purification and amino acid sequencing of NAF, a novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90432-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. R., Gaumer H. R., Salvaggio J. E. Activation of the alternative complement pathway and generation of chemotactic factors by asbestos. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Oct;60(4):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Cerami A. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: members of a novel superfamily of cytokines. FASEB J. 1989 Dec;3(14):2565–2573. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.14.2687068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Yuhki N. Neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in rabbit. cDNA cloning and their expression in spleen cells. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3483–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]