Abstract
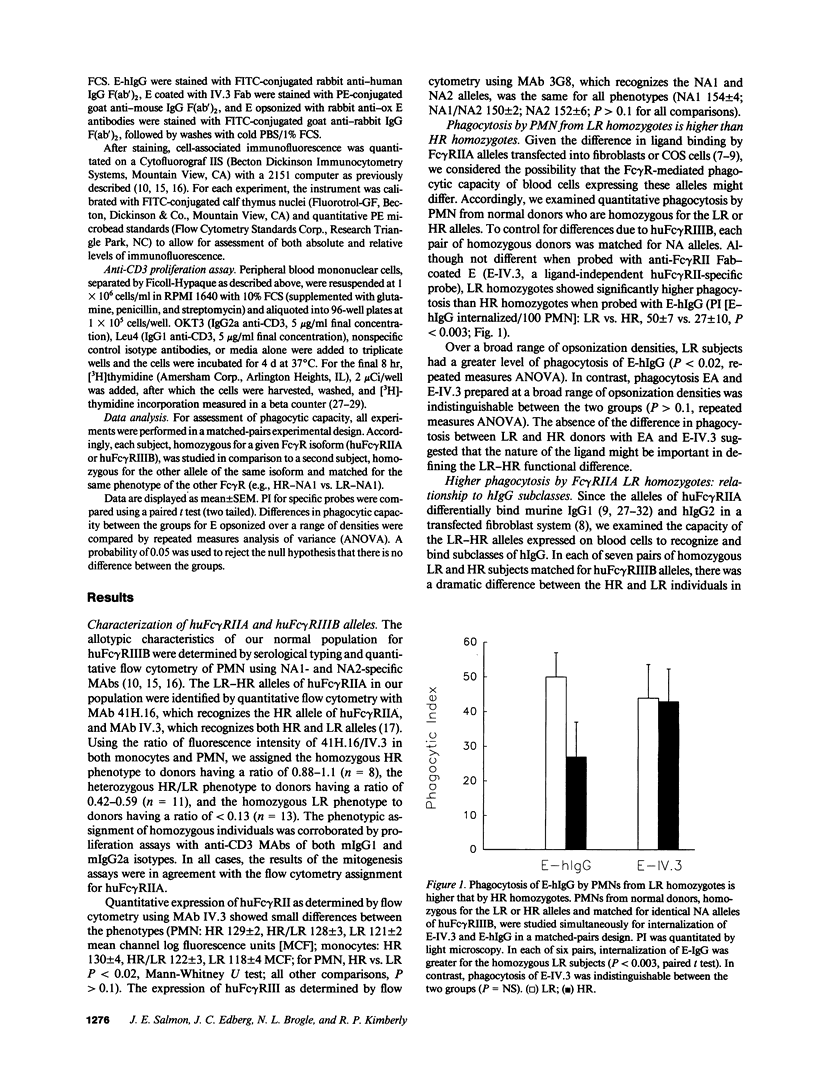
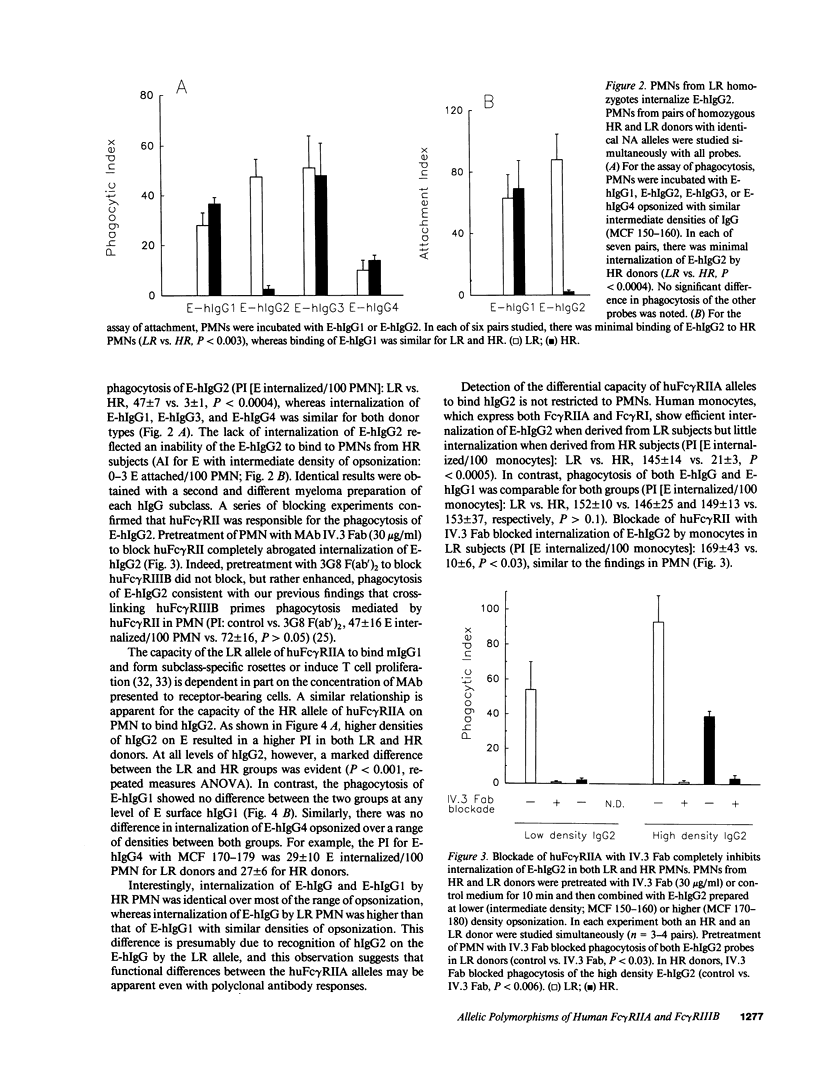
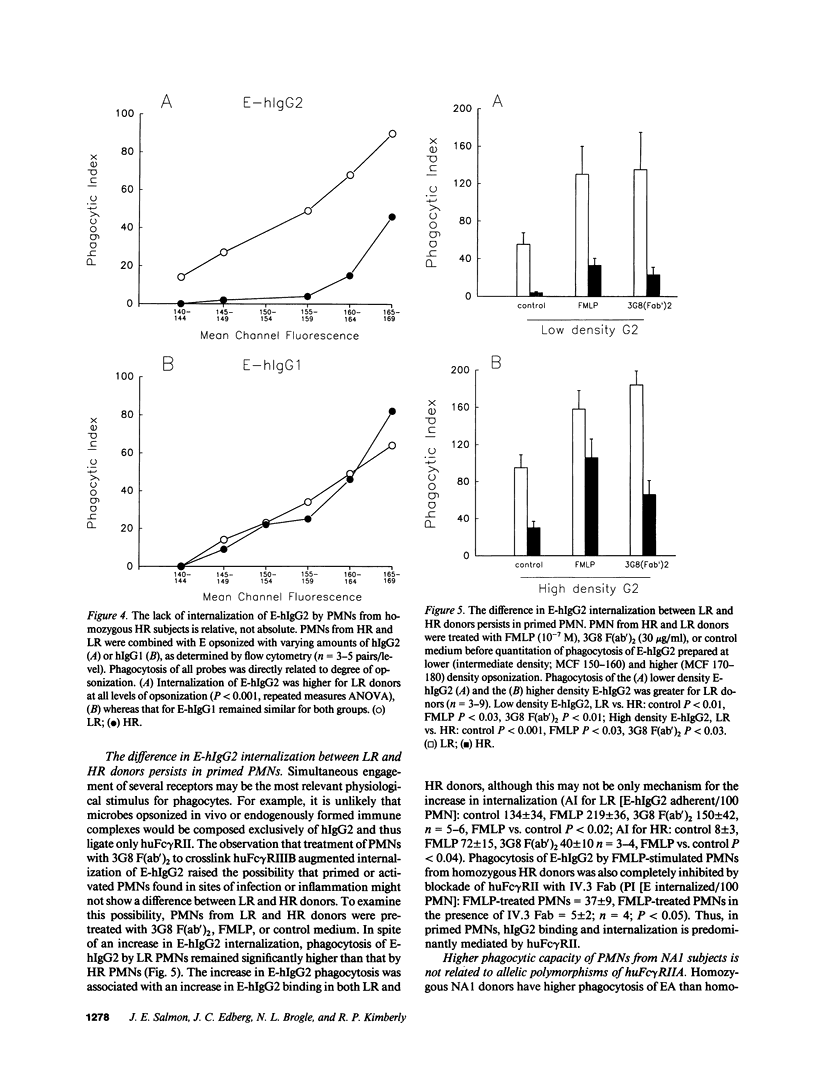
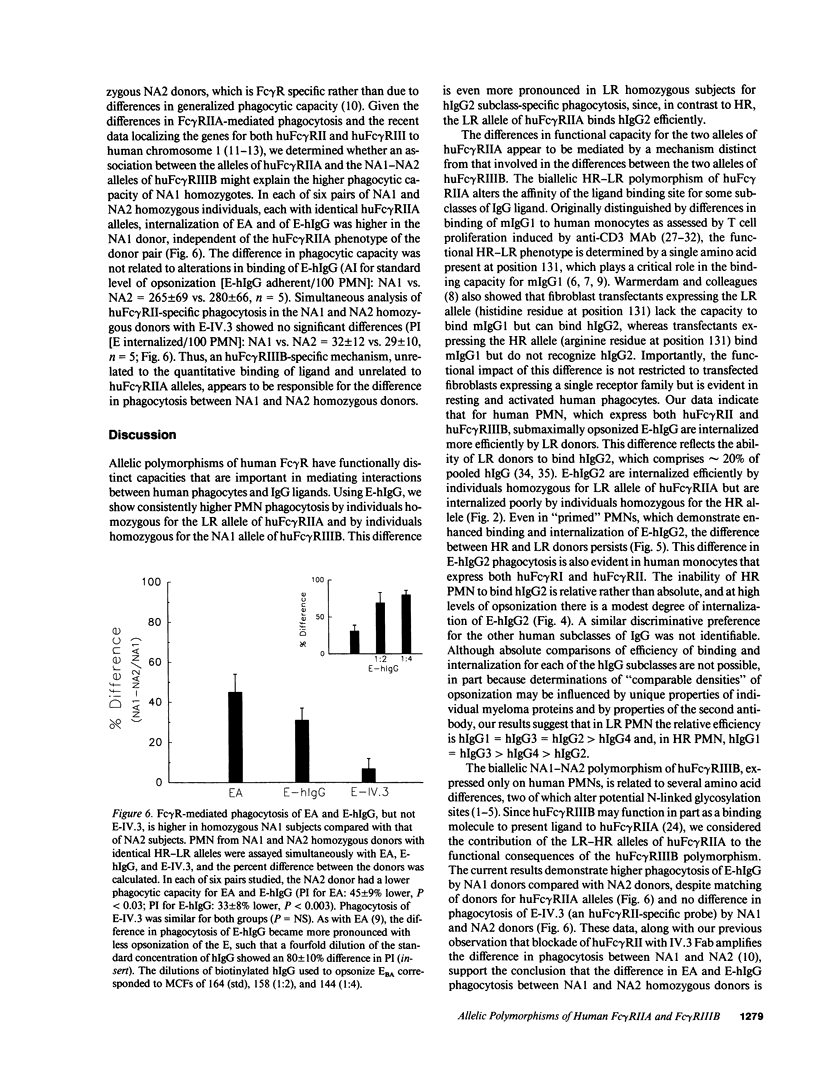
Two different allelic polymorphisms among the isoforms of human Fc gamma receptors have been defined: the low-responder (LR)-high-responder (HR) polymorphism of huFc gamma RIIA expressed on both PMN and monocytes and the NA1-NA2 polymorphism of the neutrophil Fc gamma RIII (huFc gamma RIIIB). To address the issues of whether the LR-HR polymorphism has a significant impact on Fc gamma R-mediated functions in human blood cells and whether any differences in LR-HR might be related to higher Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis in NA1 donors, we examined Fc gamma R-specific binding and internalization by donors homozygous for the two huFc gamma RIIA alleles. PMN from LR homozygotes showed consistently higher levels of internalization of erythrocytes opsonized with pooled human IgG (E-hIgG). The absence of an LR-HR phagocytic difference with erythrocytes opsonized with either anti-Fc gamma RIIA MAb IV.3 or rabbit IgG, as opposed to E-hIgG, suggested that the Fc piece of the opsonin might be important for this LR-HR difference. Accordingly, we studied HR and LR homozygotes with human IgG subclass-specific probes. Both PMN (independent of huFc gamma RIIIB phenotype) and monocytes from LR donors bound and internalized erythrocytes coated with human IgG2 (E-hIgG2) efficiently, whereas phagocytes from HR donors did so poorly. E-hIgG2 internalization was completely abrogated by blockade of the ligand binding site of huFc gamma RIIA with IV.3 Fab, indicating that huFc gamma RIIA is essential for the handling of hIgG2 and that the mechanism of the LR-HR phagocytic difference is at the level of ligand binding to huFc gamma RIIA. In contrast, the difference in internalization of E-hIgG between NA1 and NA2 homozygous donors was independent of the huFc gamma RIIA phenotype and did not manifest differences in ligand binding. Thus, the two known allelic polymorphisms of human Fc gamma R have distinct and independent mechanisms for altering receptor function, which may influence host defense and immune complex handling.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AboT, Tilden A. B., Balch C. M., Kumagai K., Troup G. M., Cooper M. D. Ethnic differences in the lymphocyte proliferative response induced by a murine IgG1 antibody, Leu-4, to the T3 molecule. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):303–309. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. L., Shen L., Eicher D. M., Wewers M. D., Gill J. K. Phagocytosis mediated by three distinct Fc gamma receptor classes on human leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1333–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoun G. R., Longenecker B. M., Zipf T. F. Comparison of the 40 kDa hematopoietic cell antigens bound by monoclonal antibodies IV.3, 41H.16 and KB61. Mol Immunol. 1989 Mar;26(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boot J. H., Geerts M. E., Aarden L. A. Functional polymorphisms of Fc receptors in human monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity towards erythrocytes induced by murine isotype switch variants. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1217–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. G., Qiu W. Q., Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Structure and expression of human IgG FcRII(CD32). Functional heterogeneity is encoded by the alternatively spliced products of multiple genes. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1369–1385. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceuppens J. L., Van Vaeck F. Direct demonstration of binding of anti-Leu 4 antibody to the 40 kDa Fc receptor on monocytes as a prerequisite for anti-Leu 4-induced T cell mitogenesis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4067–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Clarkson S. B., Ory P. A., Stollman N., Goldstein I. M. Molecular basis for a polymorphism involving Fc receptor II on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1731–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Stuart S. G., Kimberly R. P., Ory P. A., Goldstein I. M. A single amino acid distinguishes the high-responder from the low-responder form of Fc receptor II on human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Aug;21(8):1911–1916. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Tilden A. B., Dunlap N. E. Analysis of the monocyte Fc receptors and antibody-mediated cellular interactions required for the induction of T cell proliferation by anti-T3 antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):165–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg J. C., Barinsky M., Redecha P. B., Salmon J. E., Kimberly R. P. Fc gamma RIII expressed on cultured monocytes is a N-glycosylated transmembrane protein distinct from Fc gamma RIII expressed on natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4729–4734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg J. C., Redecha P. B., Salmon J. E., Kimberly R. P. Human Fc gamma RIII (CD16). Isoforms with distinct allelic expression, extracellular domains, and membrane linkages on polymorphonuclear and natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1642–1649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Cystic fibrosis pseudomonas opsonins. Inhibitory nature in an in vitro phagocytic assay. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):899–914. doi: 10.1172/JCI110345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Olchowski J., Squier S. U., Merrill W. W., Reynolds H. Y. Immunoglobulin-G subclasses in cystic fibrosis. IgG2 response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Mar;133(3):418–422. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Wright S. D., Unkeless J. C. Human neutrophil Fc gamma receptor distribution and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3275–3279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin E. J., Brown M. F., Anderson C. L., Zipf T. F., Guyre P. M. The monoclonal antibody 41H16 detects the Leu 4 responder form of human Fc gamma RII. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1817–1822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy H. O., Peltz G., Moore K. W., Golbus M. S., Jackson L. G., Lebo R. V. The polymorphic Fc gamma receptor II gene maps to human chromosome 1q. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(5):331–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00352843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick D. B., Fick R. B., Jr The immunoglobulin G subclass composition of immune complexes in cystic fibrosis. Implications for the pathogenesis of the Pseudomonas lung lesion. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1285–1292. doi: 10.1172/JCI114836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Kumararatne D. S. Selective IgG subclass deficiency: quantification and clinical relevance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Sep;81(3):357–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Ryan D. H., Takahashi K., Fleit H. B., Cohen H. J., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Identification of a second class of IgG Fc receptors on human neutrophils. A 40 kilodalton molecule also found on eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):826–836. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ory P. A., Clark M. R., Kwoh E. E., Clarkson S. B., Goldstein I. M. Sequences of complementary DNAs that encode the NA1 and NA2 forms of Fc receptor III on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1688–1691. doi: 10.1172/JCI114350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ory P. A., Goldstein I. M., Kwoh E. E., Clarkson S. B. Characterization of polymorphic forms of Fc receptor III on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1676–1681. doi: 10.1172/JCI114067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz G. A., Grundy H. O., Lebo R. V., Yssel H., Barsh G. S., Moore K. W. Human Fc gamma RIII: cloning, expression, and identification of the chromosomal locus of two Fc receptors for IgG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1013–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Perussia B. Alternative membrane forms of Fc gamma RIII(CD16) on human natural killer cells and neutrophils. Cell type-specific expression of two genes that differ in single nucleotide substitutions. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):481–497. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Brogle N. L., Edberg J. C., Kimberly R. P. Fc gamma receptor III induces actin polymerization in human neutrophils and primes phagocytosis mediated by Fc gamma receptor II. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):997–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Edberg J. C., Kimberly R. P. Fc gamma receptor III on human neutrophils. Allelic variants have functionally distinct capacities. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1287–1295. doi: 10.1172/JCI114566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Kapur S., Kimberly R. P. Opsonin-independent ligation of Fc gamma receptors. The 3G8-bearing receptors on neutrophils mediate the phagocytosis of concanavalin A-treated erythrocytes and nonopsonized Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1798–1813. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Kimberly R. P., Gibofsky A., Fotino M. Altered phagocytosis by monocytes from HLA-DR2 and DR3-positive healthy adults is Fc gamma receptor specific. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3625–3630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H. IgG subclasses--a review. Ann Allergy. 1987 Feb;58(2):89-96, 99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Guyre P. M., Anderson C. L., Fanger M. W. Heteroantibody-mediated cytotoxicity: antibody to the high affinity Fc receptor for IgG mediates cytotoxicity by human monocytes that is enhanced by interferon-gamma and is not blocked by human IgG. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3378–3382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Santosham M., Reid G. R., Thompson C., Almeido-Hill J., Morell A., deLange G., Ketcham J. K., Callahan E. H. Impaired antibody response to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide and low IgG2 and IgG4 concentrations in Apache children. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 15;323(20):1387–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011153232005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., Hermes F. F., Willems R. W., Capel P. J., Koene R. A. Fc receptors for mouse IgG1 on human monocytes: polymorphism and role in antibody-induced T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1185–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., Willems H. W., Reekers P. P., Capel P. J., Koene R. A. Polymorphism in mitogenic effect of IgG1 monoclonal antibodies against T3 antigen on human T cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):445–447. doi: 10.1038/304445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J., Brenneman G., Letson G. W., Heyward W. L. Limited efficacy of a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine in Alaska Native infants. The Alaska H. influenzae Vaccine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 15;323(20):1393–1401. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011153232006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam P. A., van de Winkel J. G., Gosselin E. J., Capel P. J. Molecular basis for a polymorphism of human Fc gamma receptor II (CD32). J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):19–25. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam P. A., van de Winkel J. G., Vlug A., Westerdaal N. A., Capel P. J. A single amino acid in the second Ig-like domain of the human Fc gamma receptor II is critical for human IgG2 binding. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1338–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Boonen G. J., Janssen P. L., Vlug A., Hogg N., Tax W. J. Activity of two types of Fc receptors, Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII, in human monocyte cytotoxicity to sensitized erythrocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jan;29(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



