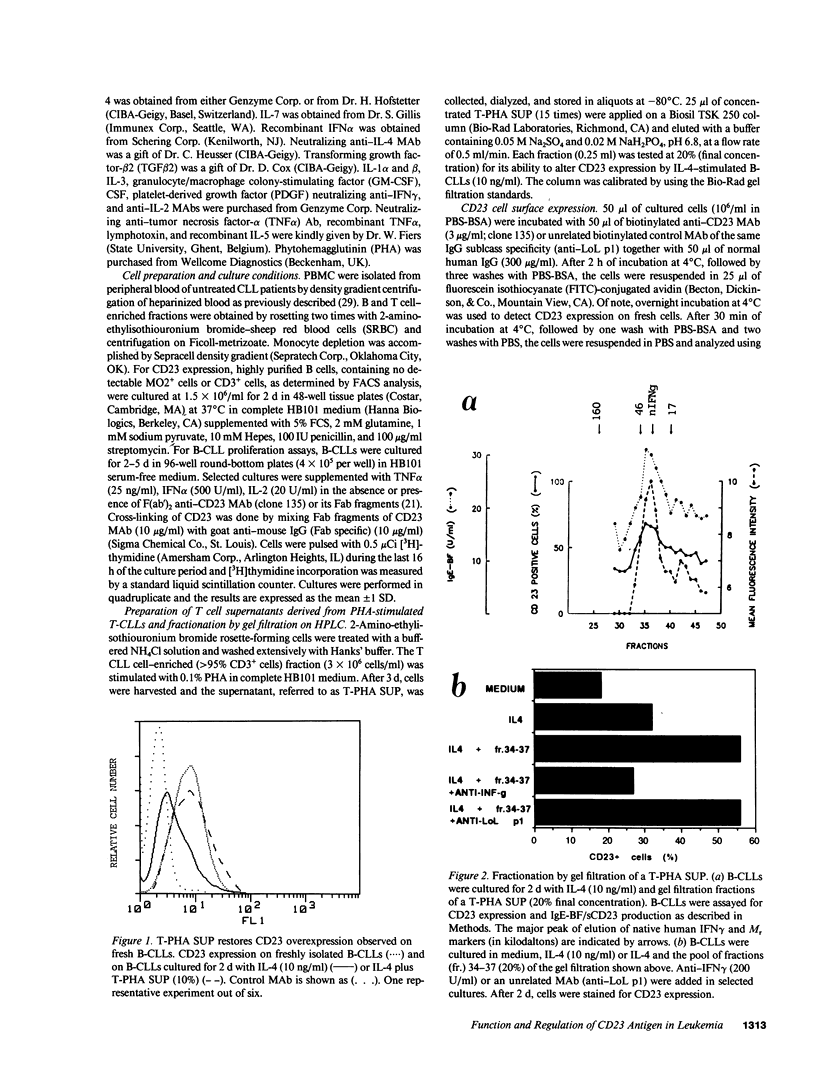
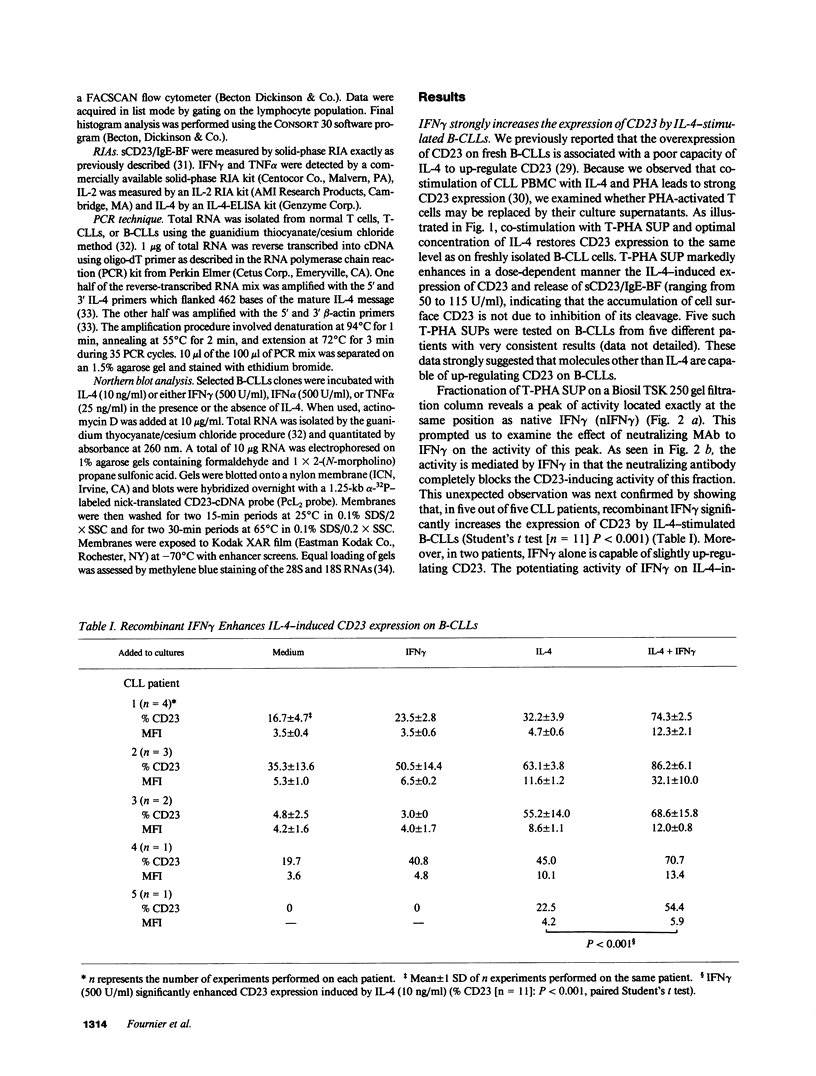
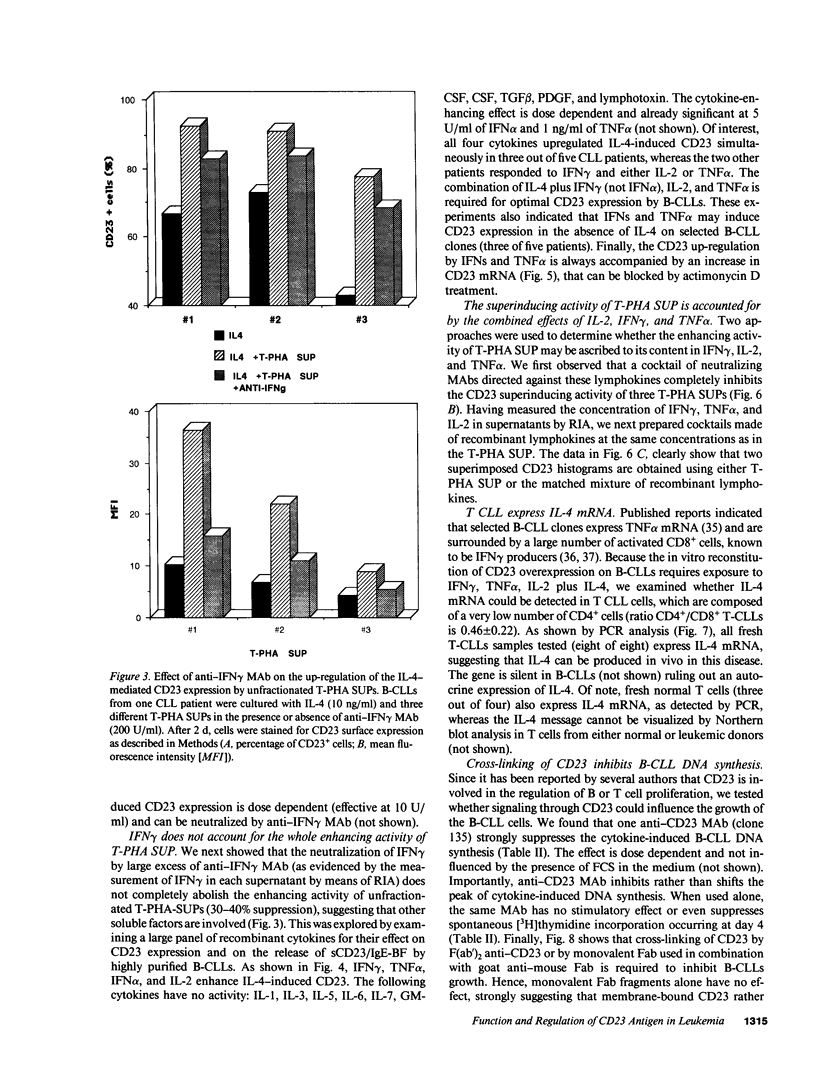
Abstract
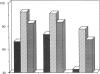
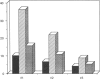
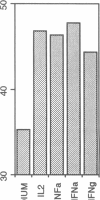
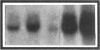
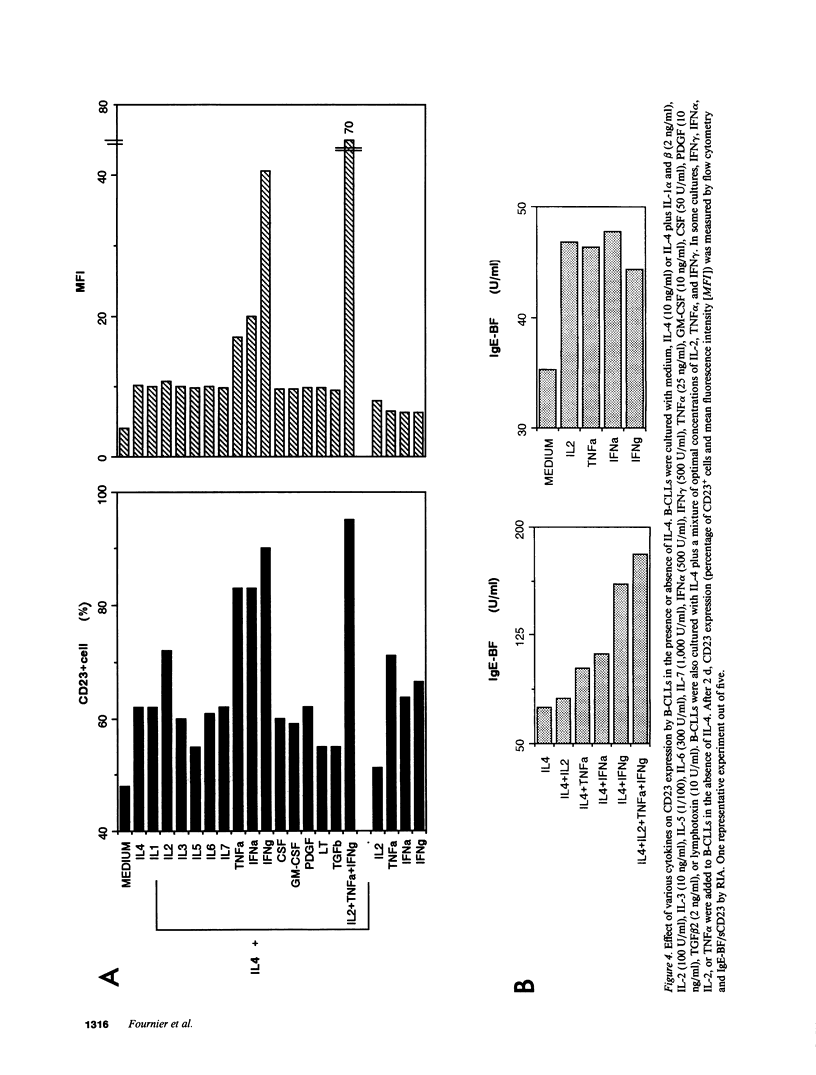
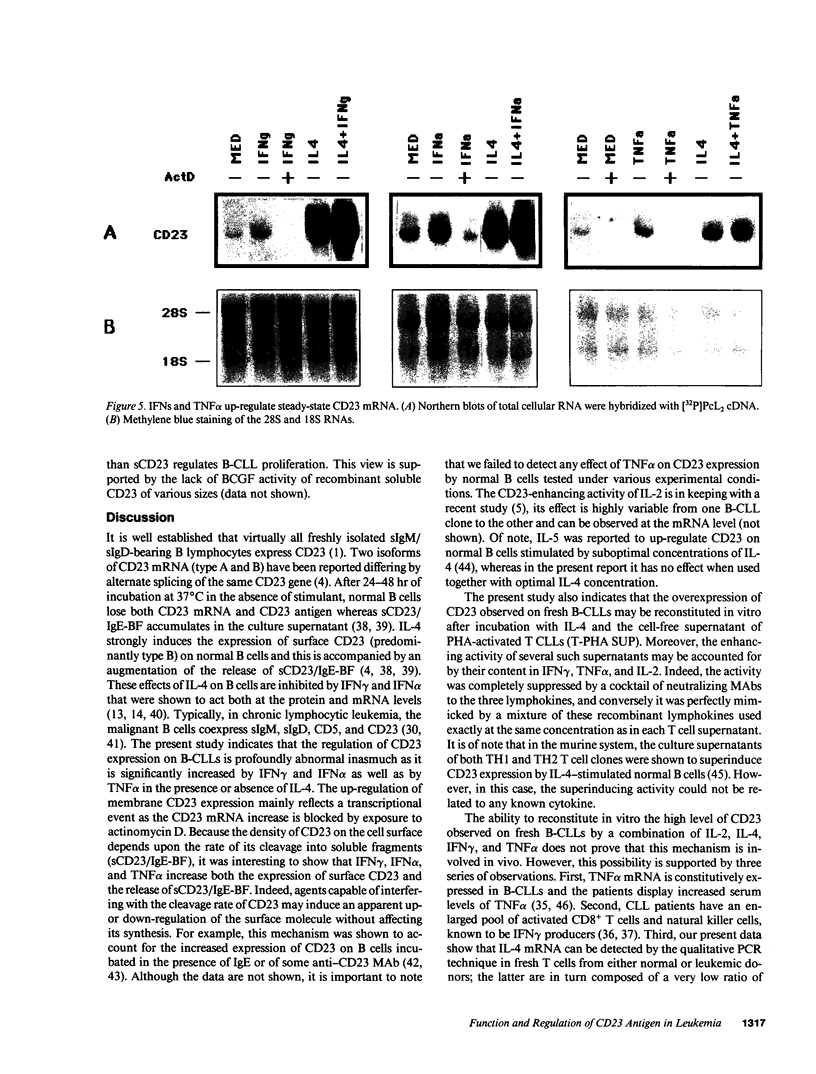
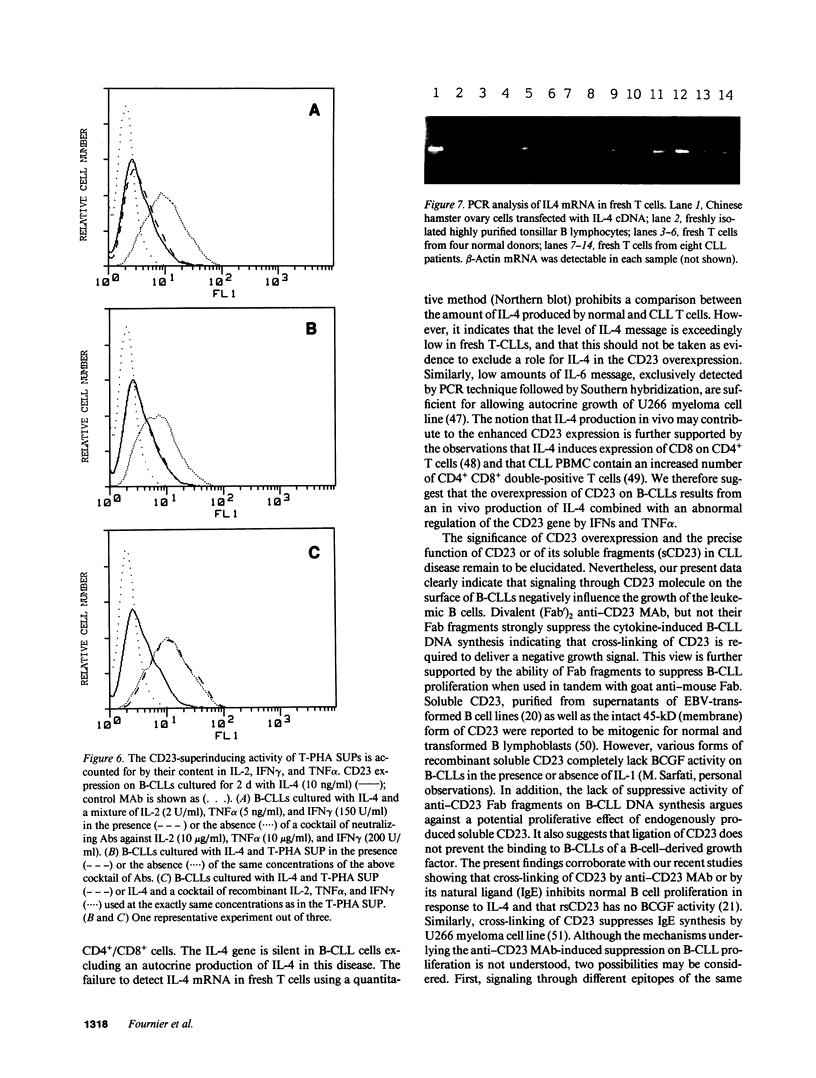
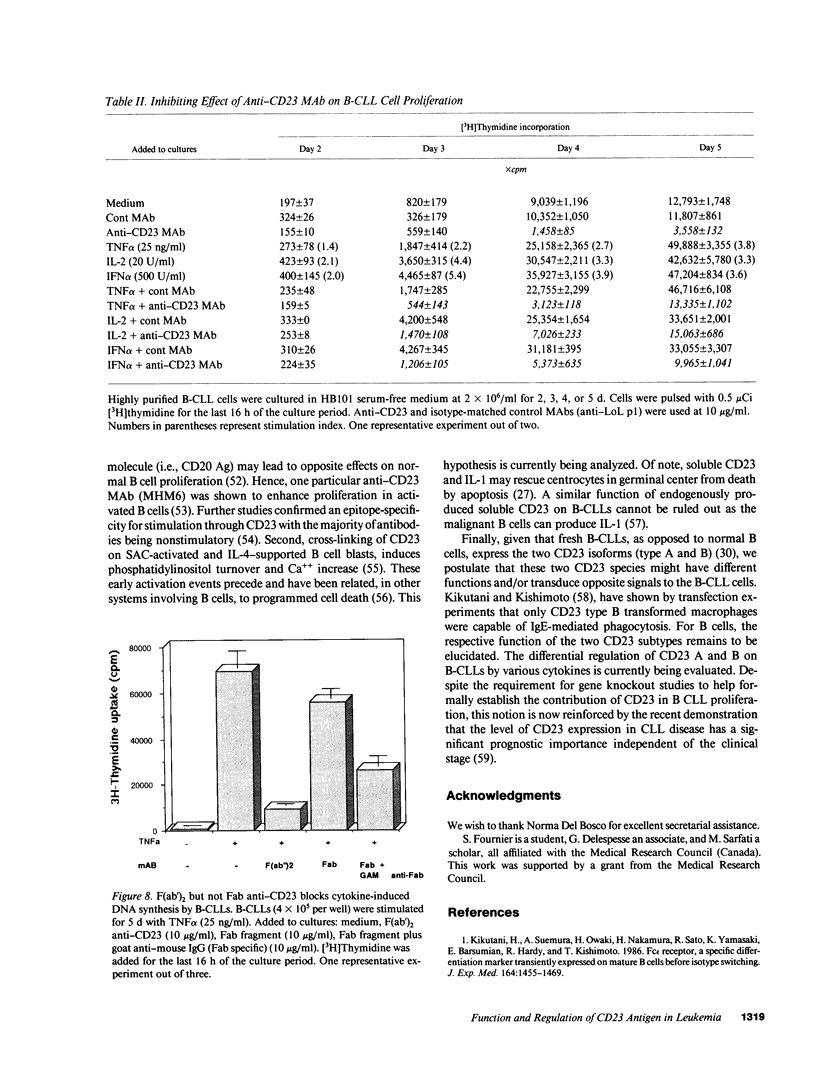
B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLLs), strongly express the CD23 antigen, a surface marker with significant prognostic importance in this disease. Because we previously reported that IL-4 shows a poor capacity for CD23 expression on B-CLLs, we first examined the possible mechanisms underlying CD23 overexpression on B-CLLs and found that mitogen-activated CLL T cells release soluble factors that are capable, in synergy with IL-4, of strongly inducing CD23. Using neutralizing Abs, we noticed that the T-cell-derived enhancing activity is entirely ascribed to the combined effects of IFN gamma (potent inhibitor of CD23 on normal B cells), TNF alpha (which has no effect on normal B cells), and IL-2 (which has a slight enhancing effect on both CLL and normal B cells). Furthermore, recombinant IFN gamma as well as IFN alpha, TNF alpha, and IL-2 (but not IL-3, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, and lymphotoxin) significantly enhance CD23 protein and mRNA expression on B-CLLs, in the presence or absence of IL-4. Inasmuch as optimal CD23 expression absolutely requires the combination of IFN gamma, IL-2, TNF alpha (the production of which is increased in CLL disease), and IL-4, it was relevant to show that IL-4 mRNA is indeed expressed in fresh T-CLL cells. We next examined the possible role of CD23 in the regulation of B-CLL proliferation. Signaling through CD23 via ligation of the antigen by F(ab')2 anti-CD23 MAb but not Fab fragments inhibits the cytokine-induced B-CLL DNA synthesis. It is concluded that the CD23 gene is abnormally regulated in B-CLL disease and that cross-linking of CD23 molecule delivers a negative growth signal to the leukemic B cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage R. J., Goff L. K., Beverley P. C. Expression and functional role of CD23 on T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):31–35. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieber T., Rieger A., Neuchrist C., Prinz J. C., Rieber E. P., Boltz-Nitulescu G., Scheiner O., Kraft D., Ring J., Stingl G. Induction of Fc epsilon R2/CD23 on human epidermal Langerhans cells by human recombinant interleukin 4 and gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):309–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Shields J., Mermod J. J. Inhibition of human interleukin 4-induced IgE synthesis by a subset of anti-CD23/Fc epsilon RII monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C. A., Tam A. W., Nelson P. A., Engleman E. G., Suzuki N., Fry K. E., Larrick J. W. Message amplification phenotyping (MAPPing): a technique to simultaneously measure multiple mRNAs from small numbers of cells. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1096–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J. A., Gordon J. Intact, 45-kDa (membrane) form of CD23 is consistently mitogenic for normal and transformed B lymphoblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):539–543. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Jouault T., Prin L., Joseph M., Ameisen J. C., Butterworth A. E., Papin J. P., Kusnierz J. P., Capron A. Functional study of a monoclonal antibody to IgE Fc receptor (Fc epsilon R2) of eosinophils, platelets, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):72–89. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien I., Pène J., Brière F., De Waal Malefijt R., Rousset F., De Vries J. E. Regulation of human IgE synthesis. I. Human IgE synthesis in vitro is determined by the reciprocal antagonistic effects of interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):243–251. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. Structure, function, and genetics of human B cell-associated surface molecules. Adv Cancer Res. 1989;52:81–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley F. T., Bianchi A., Hoffbrand A. V., Reittie J. E., Heslop H. E., Vyakarnam A., Turner M., Meager A., Brenner M. K. Tumour necrosis factor as an autocrine tumour growth factor for chronic B-cell malignancies. Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):969–971. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91782-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Aubry J. P., Rousset F., Vanbervliet B., Bonnefoy J. Y., Arai N., Takebe Y., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Human recombinant interleukin 4 induces Fc epsilon receptors (CD23) on normal human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1459–1467. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Suter U., Nakajima T., Frost H., Letellier M., Peleman R., Kilchherr E. Human Fc epsilon RII. Molecular, biological and clinical aspects. Chem Immunol. 1989;47:79–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Hofstetter H. Human IgE-binding factors. Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Peleman R. Influence of recombinant IL-4, IFN-alpha, and IFN-gamma on the production of human IgE-binding factor (soluble CD23). J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Rubio-Trujillo M., Wolowiec T. IgE receptors on human lymphocytes. III. Expression of IgE receptors on mitogen-stimulated human mononuclear cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1043–1047. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoroy M. C., Yodoi J., Banchereau J. Interleukin 4 and interferons alpha and gamma regulate Fc epsilon R2/CD23 mRNA expression on normal human B cells. Mol Immunol. 1990 Feb;27(2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90107-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digel W., Schöniger W., Stefanic M., Janssen H., Buck C., Schmid M., Raghavachar A., Porzsolt F. Receptors for tumor necrosis factor on neoplastic B cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia are expressed in vitro but not in vivo. Blood. 1990 Oct 15;76(8):1607–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugas B., Paul-Eugene N., Cairns J., Gordon J., Calenda A., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Braquet P. Leukotriene B4 potentiates the expression and release of Fc epsilon RII/CD23, and proliferation and differentiation of human B lymphocytes induced by IL-4. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3406–3411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foa R., Massaia M., Cardona S., Tos A. G., Bianchi A., Attisano C., Guarini A., di Celle P. F., Fierro M. T. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: a possible regulatory role of TNF in the progression of the disease. Blood. 1990 Jul 15;76(2):393–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier S., Tran I. D., Suter U., Biron G., Delespesse G., Sarfati M. The in vivo expression of type B CD23 mRNA in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemic cells is associated with an abnormally low CD23 upregulation by IL-4: comparison with their normal cellular counterparts. Leuk Res. 1991;15(7):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(91)90030-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler C. H., Larsen J. K., Hansen N. E., Hansen M. M., Christensen B. E., Lund B., Nielsen H., Plesner T., Thorling K., Andersen E. Prognostic importance of flow cytometric immunophenotyping of 540 consecutive patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1795–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Rowe M., Walker L., Guy G. Ligation of the CD23,p45 (BLAST-2,EBVCS) antigen triggers the cell-cycle progression of activated B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Webb A. J., Guy G. R., Walker L. Triggering of B lymphocytes through CD23: epitope mapping and studies using antibody derivatives indicate an allosteric mechanism of signalling. Immunology. 1987 Apr;60(4):517–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hivroz C., Vallé A., Brouet J. C., Banchereau J., Grillot-Courvalin C. Regulation by interleukin 2 of CD23 expression of leukemic and normal B cells: comparison with interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jun;19(6):1025–1030. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoda M., Makino S., Kawabe T., Maeda Y., Satoh S., Takami M., Mayumi M., Arai K., Saitoh H., Yodoi J. Differential regulation of the low affinity Fc receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon R2/CD23) and the IL-2 receptor (Tac/p55) on eosinophilic leukemia cell line (EoL-1 and EoL-3). J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Takami M., Hosoda M., Maeda Y., Sato S., Mayumi M., Mikawa H., Arai K., Yodoi J. Regulation of Fc epsilon R2/CD23 gene expression by cytokines and specific ligands (IgE and anti-Fc epsilon R2 monoclonal antibody). Variable regulation depending on the cell types. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1376–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan A. D., Snapper C. M., Van Dusen R., Paul W. E., Conrad D. H. Superinduction of the murine B cell Fc epsilon RII by T helper cell clones. Role of IL-4. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3868–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Kishimoto T. Molecular genetics and biology of two different species of Fc epsilon RII. Res Immunol. 1990 Mar-Apr;141(3):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(90)90116-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Suemura M., Owaki H., Nakamura H., Sato R., Yamasaki K., Barsumian E. L., Hardy R. R., Kishimoto T. Fc epsilon receptor, a specific differentiation marker transiently expressed on mature B cells before isotype switching. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1455–1469. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb J. P., Renard D., Dugas B., Genot E., Petit-Koskas E., Sarfati M., Delespesse G., Poggioli J. Monoclonal anti-CD23 antibodies induce a rise in [Ca2+]i and polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in human activated B cells. Involvement of a Gp protein. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letellier M., Sarfati M., Delespesse G. Mechanisms of formation of IgE-binding factors (soluble CD23)--I. Fc epsilon R II bearing B cells generate IgE-binding factors of different molecular weights. Mol Immunol. 1989 Dec;26(12):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Cairns J. A., Holder M. J., Abbot S. D., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y., Gordon J., MacLennan I. C. Recombinant 25-kDa CD23 and interleukin 1 alpha promote the survival of germinal center B cells: evidence for bifurcation in the development of centrocytes rescued from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H. Y., Hofstetter H., Banchereau J., Delespesse G. Cross-linking of CD23 antigen by its natural ligand (IgE) or by anti-CD23 antibody prevents B lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2122–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morabito F., Prasthofer E. F., Dunlap N. E., Grossi C. E., Tilden A. B. Expression of myelomonocytic antigens on chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells correlates with their ability to produce interleukin 1. Blood. 1987 Dec;70(6):1750–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossalayi M. D., Arock M., Bertho J. M., Blanc C., Dalloul A. H., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Delespesse G., Debré P. Proliferation of early human myeloid precursors induced by interleukin-1 and recombinant soluble CD23. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):1924–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossalayi M. D., Lecron J. C., Dalloul A. H., Sarfati M., Bertho J. M., Hofstetter H., Delespesse G., Debre P. Soluble CD23 (Fc epsilon RII) and interleukin 1 synergistically induce early human thymocyte maturation. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):959–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Sarfati M., Delespesse G. Relationship between human IgE-binding factors (IgE-BF) and lymphocyte receptors for IgE. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):848–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul-Eugène N., Dugas B., Picquot S., Lagente V., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Braquet P. Influence of interleukin-4 and platelet-activating factor on the Fc epsilon RII/CD23 expression on human monocytes. J Lipid Mediat. 1990 Mar-Apr;2(2):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Galinski M., Kempin S., Reich L., Clarkson B., Good R. A. Abnormal T lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an analysis by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2305–2312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz J. C., Baur X., Mazur G., Rieber E. P. Allergen-directed expression of Fc receptors for IgE (CD23) on human T lymphocytes is modulated by interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1259–1264. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Bonnefoy J. Y., Spits H., Yokota T., Arai N., Arai K., Banchereau J. IgE production by normal human lymphocytes is induced by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferons gamma and alpha and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Wideman J., Bonnefoy J. Y., De Vries J. E. Interleukin 5 enhances interleukin 4-induced IgE production by normal human B cells. The role of soluble CD23 antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):929–935. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Malefijt R. W., Slierendregt B., Aubry J. P., Bonnefoy J. Y., Defrance T., Banchereau J., de Vries J. E. Regulation of Fc receptor for IgE (CD23) and class II MHC antigen expression on Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines by human IL-4 and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2625–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Bron D., Lagneaux L., Fonteyn C., Frost H., Delespesse G. Elevation of IgE-binding factors in serum of patients with B cell-derived chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Delespesse G. Possible role of human lymphocyte receptor for IgE (CD23) or its soluble fragments in the in vitro synthesis of human IgE. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2195–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Fournier S., Christoffersen M., Biron G. Expression of CD23 antigen and its regulation by IL-4 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Res. 1990;14(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90145-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Nutman T., Fonteyn C., Delespesse G. Presence of antigenic determinants common to Fc IgE receptors on human macrophages, T and B lymphocytes and IgE-binding factors. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):569–575. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthou P., Henry-Toulmé N., Cazenave P. A. Membrane IgM cross-linking is not coupled to protein kinase C translocation in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1247–1252. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab G., Siegall C. B., Aarden L. A., Neckers L. M., Nordan R. P. Characterization of an interleukin-6-mediated autocrine growth loop in the human multiple myeloma cell line, U266. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):587–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Pezzutto A., Foa R., Lauria F., Raimondi R. T lymphocytes in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: characterization by monoclonal antibodies and correlation with Fc receptors. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Feb;26(2):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr E., Macy E., Kimata H., Gilly M., Saxon A. Binding the low affinity Fc epsilon R on B cells suppresses ongoing human IgE synthesis. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendeman S., Thorley-Lawson D. A. The activation antigen BLAST-2, when shed, is an autocrine BCGF for normal and transformed B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1637–1642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman T. H., Carlsson M., Simonsson B., Bengtsson M., Nilsson K. T-cell activation and subset patterns are altered in B-CLL and correlate with the stage of the disease. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):786–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Lee B. W., Woodland N., Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Human recombinant interleukin 4 induces Fc epsilon R2/CD23 on normal human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1406–1416. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Y., Sarfati M., Heusser C., Fournier S., Rubio-Trujillo M., Peleman R., Delespesse G. Glucocorticoids increase the synthesis of immunoglobulin E by interleukin 4-stimulated human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):870–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI115092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota A., Kikutani H., Tanaka T., Sato R., Barsumian E. L., Suemura M., Kishimoto T. Two species of human Fc epsilon receptor II (Fc epsilon RII/CD23): tissue-specific and IL-4-specific regulation of gene expression. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Velde A. A., Rousset F., Peronne C., De Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma have different regulatory effects on IL-4-induced membrane expression of Fc epsilon RIIb and release of soluble Fc epsilon RIIb by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3052–3059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]