Abstract
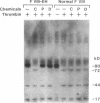
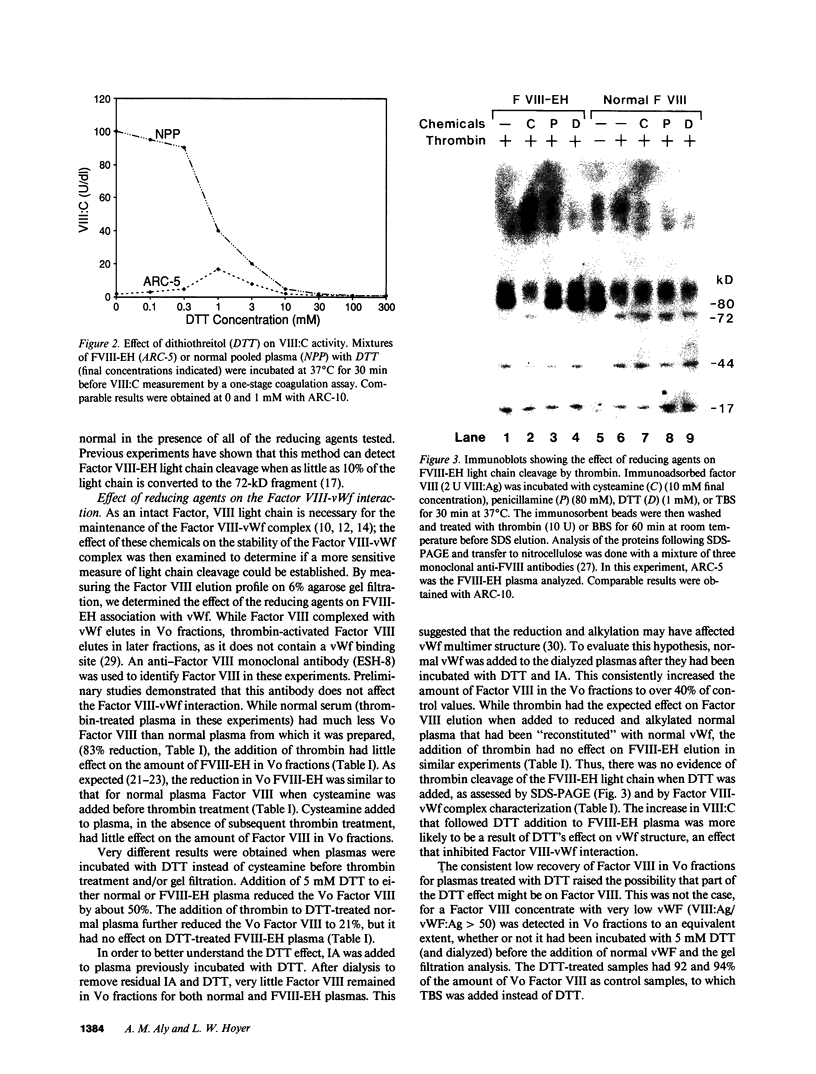
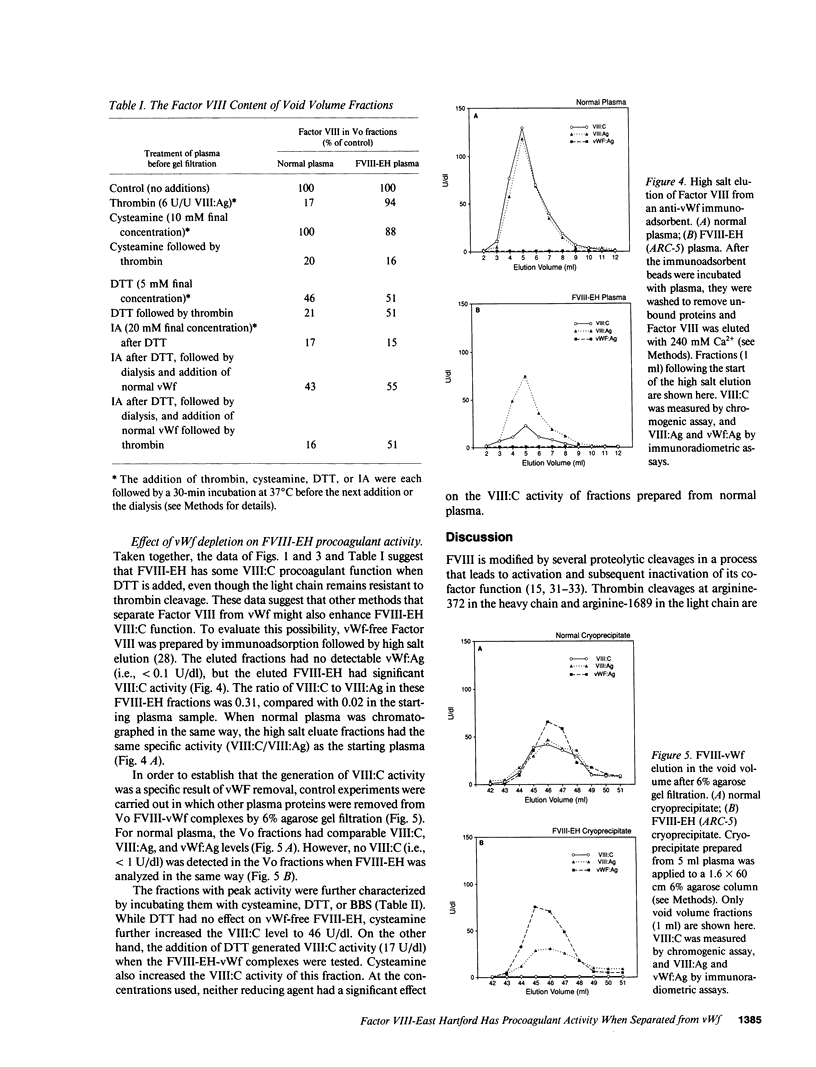
Factor VIII East Hartford (FVIII-EH) procoagulant activity is reduced because the substitution of cysteine for arginine 1689 abolishes an essential Factor VIII light chain thrombin cleavage site. Incubation of FVIII-EH plasma with penicillamine or DTT causes a five- to sixfold increase in FVIII-EH VIII:C, at 80 and 1 mM, respectively. While there is no FVIII-EH light chain cleavage when thrombin is added in the presence of penicillamine or DTT, these reducing agents disrupt the FVIII-vWf complex. For example, the addition of 5 mM DTT to normal or FVIII-EH plasma causes a 50% reduction in Factor VIII binding to vWf. These observations suggested that DTT increases FVIII-EH VIII:C by partial dissociation of FVIII-EH from vWf. This was verified by showing that vWf-free FVIII-EH had VIII:C activity of 21 U/dl, while the starting plasma level was 2.5 U/dl. Removal of other FVIII-EH plasma proteins by agarose gel filtration had no effect on VIII:C activity. The demonstration that this mutant Factor VIII has cofactor function when separated from vWf indicates that the dissociation of Factor VIII from vWf is an essential effect of Factor VIII light chain cleavage at arginine-1689.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai M., Higuchi M., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Phillips J. A., 3rd, Janco R. L., Hoyer L. W. Characterization of a thrombin cleavage site mutation (Arg 1689 to Cys) in the factor VIII gene of two unrelated patients with cross-reacting material-positive hemophilia A. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):384–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai M., Inaba H., Higuchi M., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Fujimaki M., Hoyer L. W. Direct characterization of factor VIII in plasma: detection of a mutation altering a thrombin cleavage site (arginine-372----histidine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4277–4281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE R. T., RATNOFF C. D. Studies on the nature of the circulating anticoagulant directed against antihemophilic factor: with notes on an assay for anthemophilic factor. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Reisner F. F., Hall M., Wagner R. H. Effects of thrombin treatment of preparations of factor VIII and the Ca2+-dissociated small active fragment. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):751–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI108146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts R. B., Paskell S. L., Elgee S. K. Disulfide bonds and the quaternary structure of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):702–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI109178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. L., Furlong R. A., Peake I. R. Studies on the relationship between factor VIII related antigen (VIIIRAg) and factor VIII clotting antigen (VIIICAg) by immunoelectrophoresis and autoradiography using 125I anti VIIICAg. Thromb Res. 1981 Apr 1;22(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D., Rodriguez H., Vehar G. A. Proteolytic processing of human factor VIII. Correlation of specific cleavages by thrombin, factor Xa, and activated protein C with activation and inactivation of factor VIII coagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):505–512. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Houghten R. A., Zimmerman T. S. A synthetic factor VIII peptide of eight amino acid residues (1677-1684) contains the binding region of an anti-factor VIII antibody which inhibits the binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):403–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Houghten R. A., Zimmerman T. S. An immunogenic region within residues Val1670-Glu1684 of the factor VIII light chain induces antibodies which inhibit binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5230–5234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Holland L. Z., Zimmerman T. S. Human factor VIII procoagulant protein. Monoclonal antibodies define precursor-product relationships and functional epitopes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI111933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Zimmerman T. S. Thrombin proteolysis of purified factor viii procoagulant protein: correlation of activation with generation of a specific polypeptide. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Kogan S., Levinson B., Tuddenham E. G. Mutations of factor VIII cleavage sites in hemophilia A. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1022–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer R. J., Koedam J. A., Beeser-Visser N. H., Bertina R. M., Van Mourik J. A., Sixma J. J. Factor VIII binds to von Willebrand factor via its Mr-80,000 light chain. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):37–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer R. J., Koedam J. A., Beeser-Visser N. H., Sixma J. J. The effect of thrombin on the complex between factor VIII and von Willebrand factor. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 1;167(2):253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill-Eubanks D. C., Parker C. G., Lollar P. Differential proteolytic activation of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor complex by thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6508–6512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Breckenridge R. T. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII): cross-reacting material in a genetic variant of hemophilia A. Blood. 1968 Dec;32(6):962–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). IV. Radioimmunoassay of AHF antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):822–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Nemerson Y. Activation of factor X by factors IXa and VIII; a specific assay for factor IXa in the presence of thrombin-activated factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):928–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Davies M. V., Wise R. J., Israel D. I., Dorner A. J. Effect of von Willebrand factor coexpression on the synthesis and secretion of factor VIII in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1233–1242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Hoyer L. W. Immunoradiometric measurement of the factor VIII procoagulant antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1048–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI109209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Hill-Eubanks D. C., Parker C. G. Association of the factor VIII light chain with von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10451–10455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien D. P., Tuddenham E. G. Purification and characterization of factor VIII 1,689-Cys: a nonfunctional cofactor occurring in a patient with severe hemophilia A. Blood. 1989 Jun;73(8):2117–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C. A., Jr, Bowie E. J., Fass D. N. Generation of factor VIII coagulant activity by isolated, perfused neonatal pig livers and adult rat livers. Br J Haematol. 1979 Oct;43(2):307–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J. Proteolytic requirements for thrombin activation of anti-hemophilic factor (factor VIII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J. Structure-function relationships of factor VIII elucidated through recombinant DNA technology. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Apr 25;61(2):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Precup J. W., Kline B. C., Fass D. N. A monoclonal antibody to factor VIII inhibits von Willebrand factor binding and thrombin cleavage. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1929–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotblat F., O'Brien D. P., O'Brien F. J., Goodall A. H., Tuddenham E. G. Purification of human factor VIII:C and its characterization by Western blotting using monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4294–4300. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seghatchian M. J., Miller-Andersson M. A colorimetric evaluation of factor VIII: C potency. Med Lab Sci. 1978 Oct;35(4):347–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham E. G., Lane R. S., Rotblat F., Johnson A. J., Snape T. J., Middleton S., Kernoff P. B. Response to infusions of polyelectrolyte fractionated human factor VIII concentrate in human haemophilia A and von Willebrand's disease. Br J Haematol. 1982 Oct;52(2):259–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb03888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham E. G., Trabold N. C., Collins J. A., Hoyer L. W. The properties of factor VIII coagulant activity prepared by immunoadsorbent chromatography. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jan;93(1):40–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Sussman I. I., Hoyer L. W. Stabilization of factor VIII in plasma by the von Willebrand factor. Studies on posttransfusion and dissociated factor VIII and in patients with von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):390–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI108788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]