Abstract
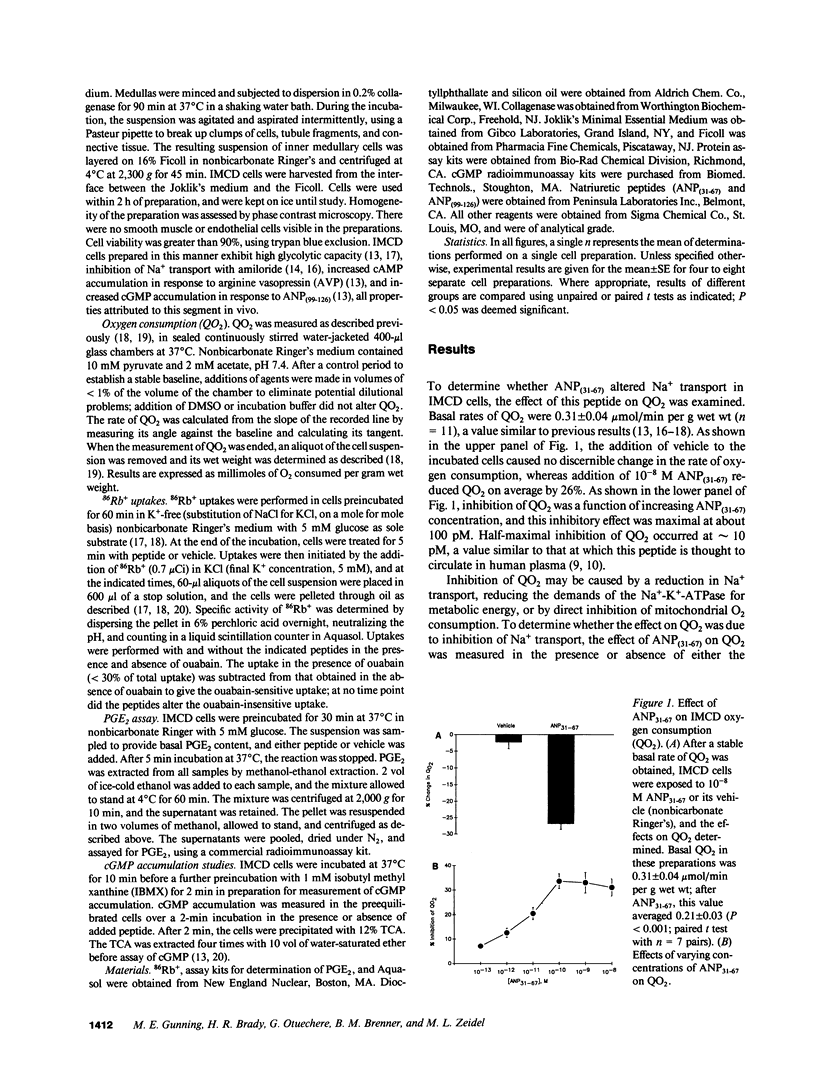
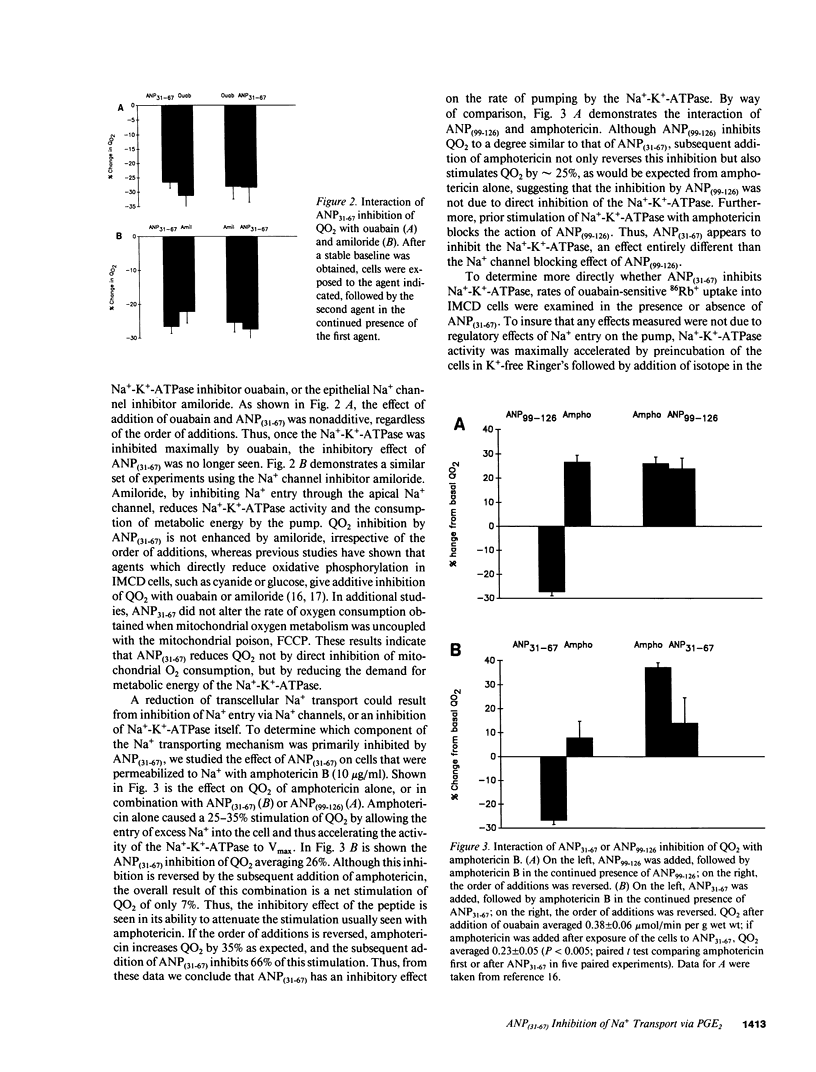
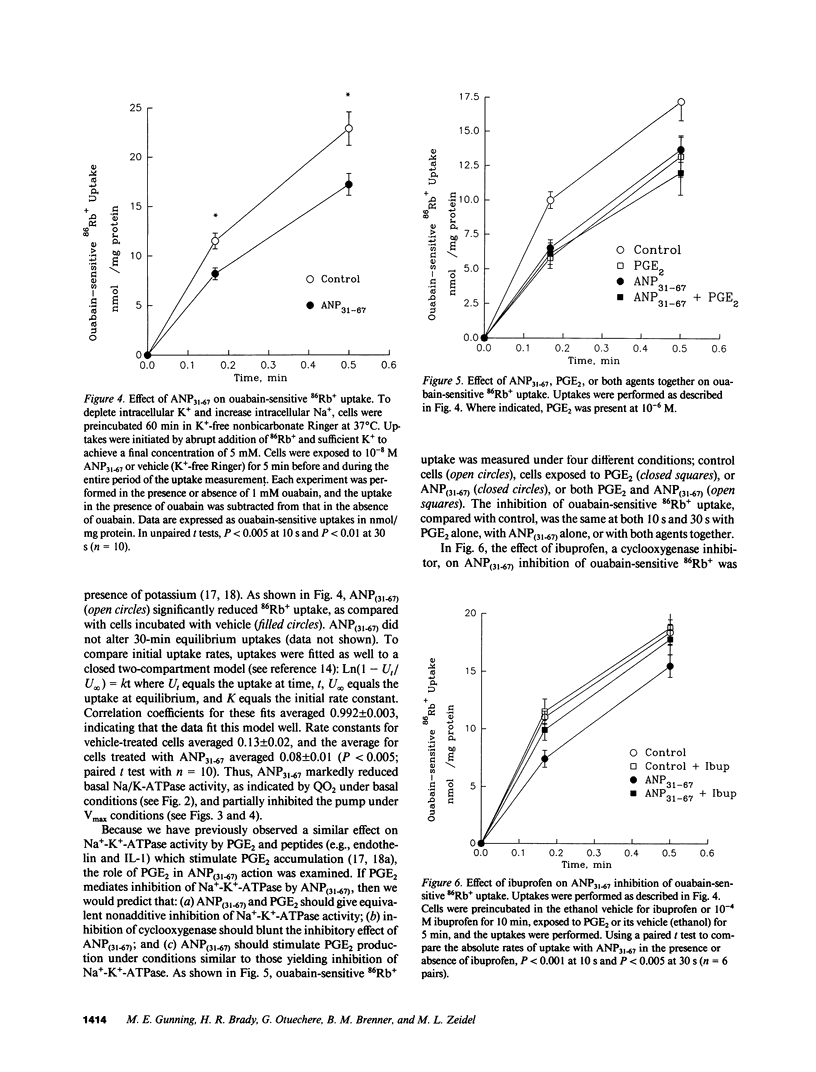
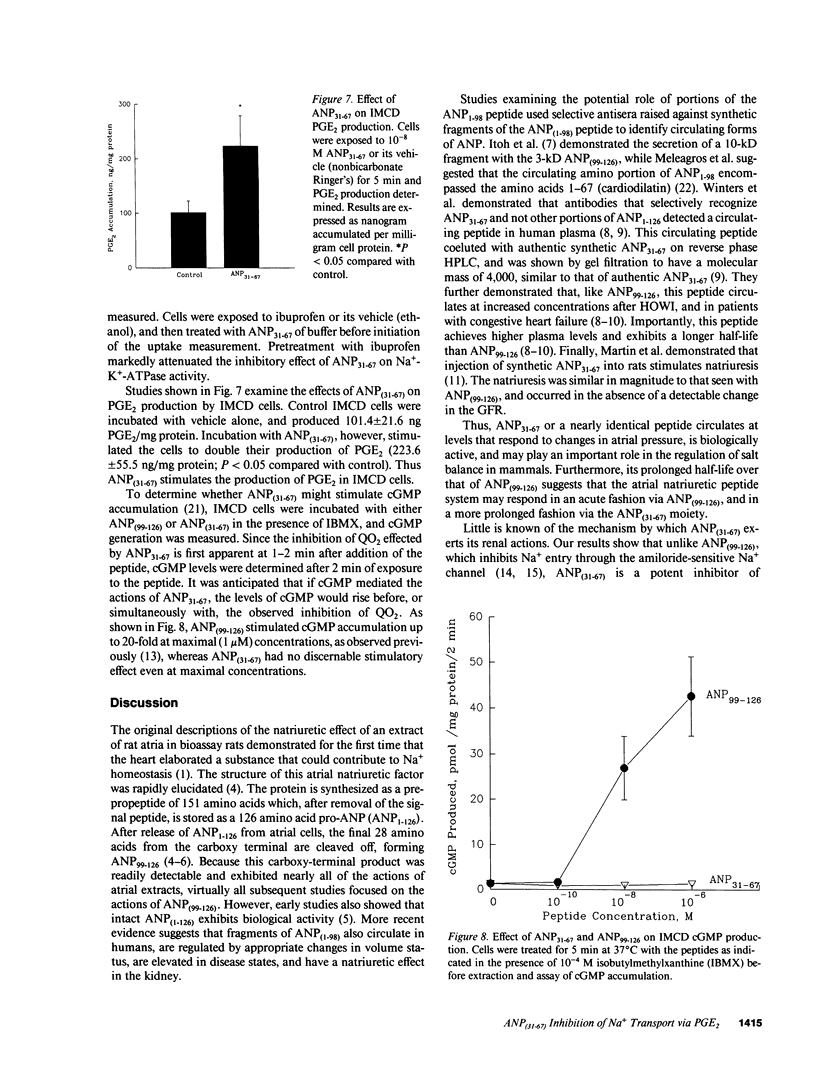
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)(31-67), a portion of the atrial peptide prohormone, circulates in humans, and its plasma level varies with atrial pressure. Like the more widely studied carboxy-terminal fragment ANP(99-126), ANP(31-67) stimulates natriuresis and diuresis. We examined the mechanism of this natriuresis by measuring the effects of ANP(31-67) on Na+ transport in cells of the rabbit inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD). ANP(31-67) (10(-8) M) caused a 26 +/- 4% inhibition of oxygen consumption (QO2); half-maximal inhibition occurred at 10(-11) M, suggesting a physiologic effect. This effect was not additive with either ouabain or amiloride, suggesting that it reflected inhibition of Na+ transport-dependent QO2. ANP(31-67) reduced the amphotericin-induced stimulation of QO2 consistent with inhibition by this peptide of the Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. In addition, ANP(31-67) reduced ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake under Vmax conditions. Several lines of evidence indicated that PGE2, a known endogenous IMCD Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase inhibitor, mediates pump inhibition by ANP(31-67). Thus, ANP(31-67) inhibits Na+ transport by inhibiting the Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase of IMCD cells, an effect mediated by the generation of PGE2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Renal actions of prostacyclin. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):467–469. doi: 10.1038/271467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Ballermann B. J., Gunning M. E., Zeidel M. L. Diverse biological actions of atrial natriuretic peptide. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):665–699. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M., Lifschitz M. D., Hoffman D. S., Stein J. H. Relationship between renal prostaglandin E and renal sodium handling during water immersion in normal man. Circ Res. 1979 Jul;45(1):71–80. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning M. E., Ballermann B. J., Silva P., Brenner B. M., Zeidel M. L. Characterization of ANP receptors in rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F324–F330. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning M., Silva P., Brenner B. M., Zeidel M. L. Characteristics of ANP-sensitive guanylate cyclase in inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F766–F775. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Imai M. Effects of prostaglandins on Na transport in isolated collecting tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Feb 22;373(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00584850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs K., Zeidel M. L., Silva P. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits Na+-K+-ATPase activity in the inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):F424–F430. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.3.F424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Fukuda A., Matsuo H. Structural identification of beta- and gamma-human atrial natriuretic polypeptides. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):397–400. doi: 10.1038/313397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kone B. C., Kikeri D., Zeidel M. L., Gullans S. R. Cellular pathways of potassium transport in renal inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C823–C830. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Schwiebert E. M., Karlson K. H., Stanton B. A. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits a cation channel in renal inner medullary collecting duct cells. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):383–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2463673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R., Pevahouse J. B., Trigg D. J., Vesely D. L., Buerkert J. E. Three peptides from the ANF prohormone NH(2)-terminus are natriuretic and/or kaliuretic. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1401–F1408. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meleagros L., Gibbs J. S., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Increase in plasma concentrations of cardiodilatin (amino terminal pro-atrial natriuretic peptide) in cardiac failure and during recumbency. Br Heart J. 1988 Jul;60(1):39–44. doi: 10.1136/hrt.60.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Geller D. M., Manning P. T., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Smith C. E., Needleman P. Ser-Leu-Arg-Arg-atriopeptin III: the major circulating form of atrial peptide. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):397–400. doi: 10.1126/science.3160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Cupples W. A., de Bold A. J., Veress A. T. Intrarenal localization of the natriuretic effect of cardiac atrial extract. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;60(9):1149–1152. doi: 10.1139/y82-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Honrath U., Chong C. K., Wilson D. R. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits sodium transport in medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):F963–F966. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.6.F963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P. Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1172/JCI108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange K. Volume regulation following Na+ pump inhibition in CCT principal cells: apical K+ loss. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F732–F740. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesely D. L., Bayliss J. M., Sallman A. L. Human prepro atrial natriuretic factors 26-55, 56-92, and 104-123 increase renal guanylate cyclase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 27;143(1):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90648-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesely D. L., Norsk P., Winters C. J., Rico D. M., Sallman A. L., Epstein M. Increased release of the N-terminal and C-terminal portions of the prohormone of atrial natriuretic factor during immersion-induced central hypervolemia in normal humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Dec;192(3):230–235. doi: 10.3181/00379727-192-42990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C. J., Sallman A. L., Baker B. J., Meadows J., Rico D. M., Vesely D. L. The N-terminus and a 4,000-MW peptide from the midportion of the N-terminus of the atrial natriuretic factor prohormone each circulate in humans and increase in congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1989 Sep;80(3):438–449. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.3.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C. J., Sallman A. L., Meadows J., Rico D. M., Vesely D. L. Two new hormones: prohormone atrial natriuretic peptides 1-30 and 31-67 circulate in man. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90510-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Kikeri D., Silva P., Burrowes M., Brenner B. M. Atrial natriuretic peptides inhibit conductive sodium uptake by rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1172/JCI113663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L. Renal actions of atrial natriuretic peptide: regulation of collecting duct sodium and water transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:747–759. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Seifter J. L., Lear S., Brenner B. M., Silva P. Atrial peptides inhibit oxygen consumption in kidney medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):F379–F383. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.2.F379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Silva P., Brenner B. M., Seifter J. L. cGMP mediates effects of atrial peptides on medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):F551–F559. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.3.F551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



