Abstract
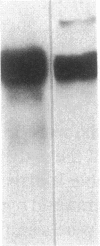
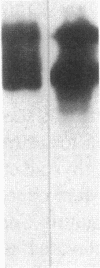
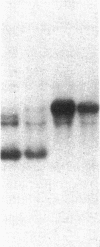
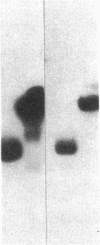
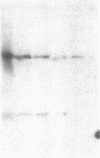
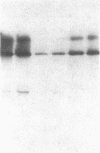
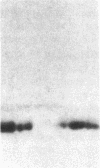
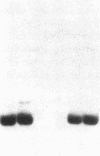
Studies of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats have demonstrated that hepatic apo B and apo E production are reduced. To determine if reductions are related to decreases in hepatic mRNAs, we performed blotting analysis of total liver RNA with rat apo B, apo E, and albumin cDNA probes. The expected reduction in albumin mRNA levels to 48% of control livers occurred in diabetic rat liver, while apo B and apo E mRNA levels were unchanged. The proportion of translational stop codon (BSTOP) mRNA averaged 43% of total in diabetic rats similar to control levels. Long-term labeling experiments using [35S]methionine in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes and specific immunoprecipitations demonstrated production of apo B and apo E, and albumin by hepatocytes from diabetic rats was reduced to 37%, 53%, and 23% of controls. Pulse-chase studies, together with mRNA analyses, suggest that reduced hepatic secretion of apo B and apo E in diabetics is primarily a result of impaired translation and not intracellular degradation. Ribosome transit studies directly confirmed the prolonged elongation rates for apo B and apo E mRNAs in hepatocytes derived from diabetic rats. This effect was more pronounced on apo BH (higher molecular weight) than on apo BL (lower molecular weight). Treatment of diabetic rats with insulin for 7 d led to normalization of hepatic albumin mRNA levels with no substantial change in apo E mRNA levels. In contrast, insulin treatment resulted in significant increases in hepatic apo B mRNA over control levels. Results suggest hepatic albumin and apo B mRNA levels are responsive to insulin in the diabetic state.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backus J. W., Eagleton M. J., Harris S. G., Sparks C. E., Sparks J. D., Smith H. C. Quantitation of endogenous liver apolipoprotein B mRNA editing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92121-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum C. L., Teng B. B., Davidson N. O. Apolipoprotein B messenger RNA editing in the rat liver. Modulation by fasting and refeeding a high carbohydrate diet. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19263–19270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry E. M., Ziv E., Bar-On H. Lipoprotein secretion by isolated perfused livers from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):402–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00252689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry E. M., Ziv E., Bar-On H. Protein and glycoprotein synthesis and secretion by the diabetic liver. Diabetologia. 1980;19(6):535–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00253181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnsson O. G., Duerden J. M., Bartlett S. M., Sparks J. D., Sparks C. E., Gibbons G. F. The role of pancreatic hormones in the regulation of lipid storage, oxidation and secretion in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Short- and long-term effects. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):381–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2810381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Aron L., Sciacca R. Radioimmunoassay studies of human apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1172/JCI109975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt R. A., Davis R. A. Intrahepatic assembly of very low density lipoproteins. Rate of transport out of the endoplasmic reticulum determines rate of secretion. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16394–16402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boström K., Wettesten M., Borén J., Bondjers G., Wiklund O., Olofsson S. O. Pulse-chase studies of the synthesis and intracellular transport of apolipoprotein B-100 in Hep G2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13800–13806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. Abnormal lipoprotein-lipase-mediated plasma triglyceride removal in untreated diabetes mellitus associated with hypertriglyceridemia. Metabolism. 1979 Sep;28(9):901–907. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Bierman E. L., Albers J. J. Regulatory role of insulin in the degradation of low density lipoprotein by cultured human skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 25;529(2):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Habib G., Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Lee B. R., Weng S. A., Silberman S. R., Cai S. J., Deslypere J. P., Rosseneu M. Apolipoprotein B-48 is the product of a messenger RNA with an organ-specific in-frame stop codon. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):363–366. doi: 10.1126/science.3659919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepin K. M., Darville M. I., Hue L., Rousseau G. G. Starvation or diabetes decreases the content but not the mRNA of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80884-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Carlos R. C., Drewek M. J., Parmer T. G. Apolipoprotein gene expression in the rat is regulated in a tissue-specific manner by thyroid hormone. J Lipid Res. 1988 Nov;29(11):1511–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Scott J. Thyroid hormone modulates the introduction of a stop codon in rat liver apolipoprotein B messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13482–13485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmer L. A., Levin M. S., Elovson J., Reuben M. A., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. Tissue-specific expression and developmental regulation of the rat apolipoprotein B gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8102–8106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillmann W. H. Diabetes mellitus-induced changes in the concentration of specific mRNAs and proteins. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Dec;4(8):789–797. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. L., Furukawa S., Ginsberg H. N. Oleate stimulates secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins from Hep G2 cells by inhibiting early intracellular degradation of apolipoprotein B. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5080–5086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerden J. M., Bartlett S. M., Gibbons G. F. Regulation of very-low-density-lipoprotein lipid secretion in hepatocyte cultures derived from diabetic animals. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):313–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2620313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerden J. M., Gibbons G. F. Secretion and storage of newly synthesized hepatic triacylglycerol fatty acids in vivo in different nutritional states and in diabetes. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):929–935. doi: 10.1042/bj2550929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge S. B., Hoeg J. M., Schneider P. D., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein B synthesis in humans: liver synthesizes only apolipoprotein B-100. Metabolism. 1985 Aug;34(8):726–730. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Chatterton J. E., Bell G. T., Schumaker V. N., Reuben M. A., Puppione D. L., Reeve J. R., Jr, Young N. L. Plasma very low density lipoproteins contain a single molecule of apolipoprotein B. J Lipid Res. 1988 Nov;29(11):1461–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Huang Y. O., Baker N., Kannan R. Apolipoprotein B is structurally and metabolically heterogeneous in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Boguski M. S., Liao W. S., Jefferson L. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. A., Carroll R. D., Cortner J. A., Surrey S. Transcriptional activity of the genes for apoproteins A-I and E in neonatal rat liver. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Dec;68(3):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. F. Assembly and secretion of hepatic very-low-density lipoprotein. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2680001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. F. Hyperlipidaemia of diabetes. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 Nov;71(5):477–486. doi: 10.1042/cs0710477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., Caskey C. T. Detection of single DNA base differences by competitive oligonucleotide priming. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2437–2448. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. P., Chait A., Brunzell J. D. Postprandial adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase activity in primary hypertriglyceridemia. Metabolism. 1980 Mar;29(3):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Levy R. I., John K., Fredrickson D. S. On the protein defect in abetalipoproteinemia. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):813–818. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Stratowa C., Rutter W. J. Isolation of full-length putative rat lysophospholipase cDNA using improved methods for mRNA isolation and cDNA cloning. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1617–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hospattankar A. V., Higuchi K., Law S. W., Meglin N., Brewer H. B., Jr Identification of a novel in-frame translational stop codon in human intestine apoB mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V. Lipoprotein metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):613–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui Y., Kawata S., Matsuzawa Y., Tokunaga K., Fujioka S., Tamura S., Kobatake T., Keno Y., Tarui S. Increased level of apolipoprotein B mRNA in the liver of ventromedial hypothalamus lesioned obese rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):1107–1112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. Apolipoprotein B: structural and metabolic heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:637–650. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazumi T., Vranic M., Bar-On H., Steiner G. Portal v peripheral hyperinsulinemia and very low density lipoprotein triglyceride kinetics. Metabolism. 1986 Nov;35(11):1024–1028. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazumi T., Vranic M., Steiner G. Changes in very low density lipoprotein particle size and production in response to sucrose feeding and hyperinsulinemia. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):1145–1150. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaiah K. V., Walker L. F., Borensztajn J., Schonfeld G., Getz G. S. Apolipoprotein B variant derived from rat intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. E., Sells B. H. The function of proteins that interact with mRNA. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Mar;74(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00221907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledford B. E., Davis D. F. Ayalysis of translational parameters in cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 22;519(1):204–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton J. K., Joyner J., Zamarripa J., Deines M., Davis R. A. Fasting decreases apolipoprotein B mRNA editing and the secretion of small molecular weight apoB by rat hepatocytes: evidence that the total amount of apoB secreted is regulated post-transcriptionally. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1663–1668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Shafrir E., Ziv E., Bar-On H. Composition, removal and metabolic fate of chylomicrons derived from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 17;834(3):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C. Effects of hormones on apolipoprotein secretion in cultured rat hepatocytes. Metabolism. 1988 Aug;37(8):745–751. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Isolation and characterization of apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), a plasma high density apolipoprotein containing two identical polypeptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7510–7518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. L., Treat D. E., Fridd B., Wemett D. Effects of streptozotocin diabetes in the rat on blood levels of ten specific plasma proteins and on their net biosynthesis by the isolated perfused liver. Hepatology. 1990 Apr;11(4):635–645. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Looney P., Irwin D., Briscoe P., Vahouny G. V. Lipoprotein composition as a component in the lipoprotein clearance defect in experimental diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):428–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Regulation of protein synthesis in chick oviduct. II. Modulation of polypeptide elongation and initiation rates by estrogen and progesterone. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6770–6780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandurò A., Lin-Lee Y. C., Chan L., Shafritz D. A. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of apolipoprotein E, A-I, and A-II gene expression in normal rat liver and during several pathophysiologic states. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8430–8435. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Franz S., Schonfeld G. Role of insulin in lipoprotein secretion by cultured rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1161–1174. doi: 10.1172/JCI110865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Gotto A. M., Jr, Patsch J. R. Effects of insulin on lipoprotein secretion in rat hepatocyte cultures. The role of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9603–9606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. E., Taylor J. M., Jefferson L. S. Time course of changes in albumin synthesis and mRNA in diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):E656–E663. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.6.E656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. T., Alford F. P., Reaven E. P., Ueyama I., Reaven G. M. Characteristics of membrane-bound and free hepatic ribosomes from insulin-deficient rats. I. Acute experimental diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3201–3211. doi: 10.1172/JCI107520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rash J. M., Rothblat G. H., Sparks C. E. Lipoprotein apolipoprotein synthesis by human hepatoma cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 23;666(2):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Reaven G. M. Mechanisms for development of diabetic hypertriglyceridemia in streptozotocin-treated rats. Effect of diet and duration of insulin deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1167–1178. doi: 10.1172/JCI107860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Mondon C. E. Effect of in vivo plasma insulin levels on the relationship between perfusate free fatty acid concentration and triglyceride secretion by perfused rat livers. Horm Metab Res. 1984 May;16(5):230–232. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato R., Imanaka T., Takatsuki A., Takano T. Degradation of newly synthesized apolipoprotein B-100 in a pre-Golgi compartment. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11880–11884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall R. F., Jr, Fraser A. S., Hansen H. W., Kern C. W., Tenoso H. J. A sensitive manual enzyme immunoassay for thyroxine. Clin Chem. 1978 Oct;24(10):1801–1804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Kuo S. R., Backus J. W., Harris S. G., Sparks C. E., Sparks J. D. In vitro apolipoprotein B mRNA editing: identification of a 27S editing complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1489–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Hnatiuk O., Marsh J. B. Hepatic and intestinal contribution of two forms of apolipoprotein B to plasma lipoprotein fractions in the rat. Can J Biochem. 1981 Aug;59(8):693–699. doi: 10.1139/o81-096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Marsh J. B. Analysis of lipoprotein apoproteins by SDS-gel filtration column chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):514–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Marsh J. B. Metabolic heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Rader D. J., Marsh J. B. Metabolism of two forms of apolipoprotein B of VLDL by rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):156–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Sparks J. D., Bolognino M., Salhanick A., Strumph P. S., Amatruda J. M. Insulin effects on apolipoprotein B lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Metabolism. 1986 Dec;35(12):1128–1136. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. D., Bolognino M., Trax P. A., Sparks C. E. The production and utility of monoclonal antibodies to rat apolipoprotein B lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Sep;61(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. D., Sparks C. E., Bolognino M., Roncone A. M., Jackson T. K., Amatruda J. M. Effects of nonketotic streptozotocin diabetes on apolipoprotein B synthesis and secretion by primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):37–43. doi: 10.1172/JCI113597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. D., Sparks C. E. Insulin modulation of hepatic synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein B by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8854–8862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. D., Sparks C. E., Miller L. L. Insulin effects on apolipoprotein B production by normal, diabetic and treated-diabetic rat liver and cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):83–88. doi: 10.1042/bj2610083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. D., Sparks C. E., Roncone A. M., Amatruda J. M. Secretion of high and low molecular weight phosphorylated apolipoprotein B by hepatocytes from control and diabetic rats. Phosphorylation of APO BH and APO BL. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5001–5004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner G., Haynes F. J., Yoshino G., Vranic M. Hyperinsulinemia and in vivo very-low-density lipoprotein-triglyceride kinetics. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):E187–E192. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.2.E187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. S., Dahl H. H., Mercer J. F., Green A. K., Fisher M. J. The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on phenylalanine hydroxylase expression in rat liver. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):185–190. doi: 10.1042/bj2640185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland D., Mondon C. E., Reaven G. M. Evidence for multiple causality in the development of diabetic hypertriglyceridaemia. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):335–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00251016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]