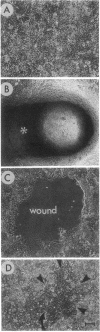
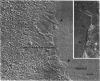
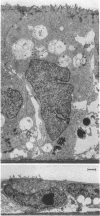
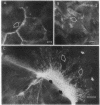
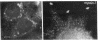
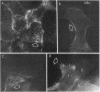
Abstract
Closure of superficial wounds in epithelia occurs by migration of cells shouldering the wound. We describe an in vitro model of such restitution using a human intestinal epithelial cell line, T84. T84 cells were grown on novel optically transparent type 1 collagen membranes without underlying filter supports. Monolayers so grown display substantial barrier function (400-500 ohm.cm2; 1.3 +/- 0.4 nmol.h-1.cm-2 mannitol flux). Wounds made with micropipettes were accompanied by a fall in resistance and rise in monolayer permeability to mannitol and inulin. After injury, cells shouldering wounds migrated, by extension of lamellipodia-like processes, to reseal wounds as defined by structural and functional criteria. F actin arcs crossed the base of the lamellipodia-like extensions and F actin microspikes projected from the leading edge of these extensions. Villin, an epithelial-specific cytoskeletal protein with both F actin bundling and severing capacities, was also expressed at the leading edge in a pattern consistent with a regulatory role in the dynamic restructuring of lamellipodia. Lastly, myosin II was predominantly localized to the basal regions of lamellipodia, though occasional staining was seen close to the advancing edge. Myosin I, a recently recognized myosin family member considered to be essential for fibroblast and slime mold motility, was present throughout lamellipodia in punctate fashion, but was not concentrated at the leading edge.
Full text
PDF
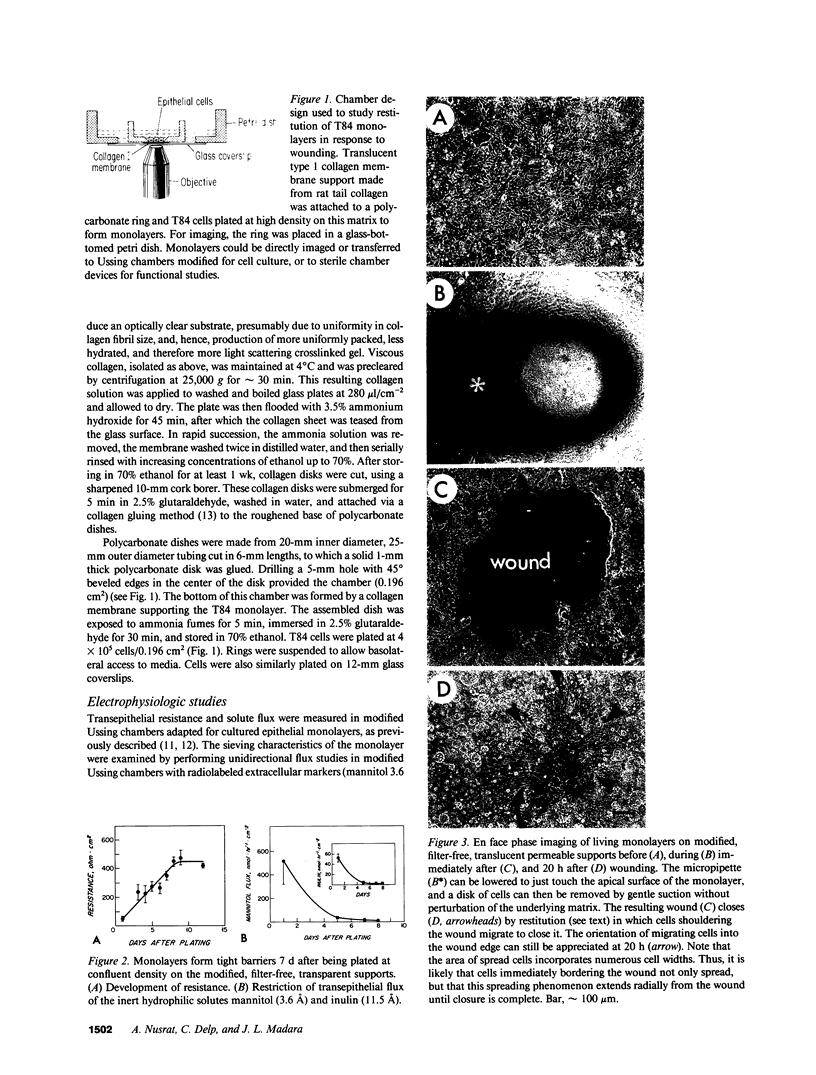

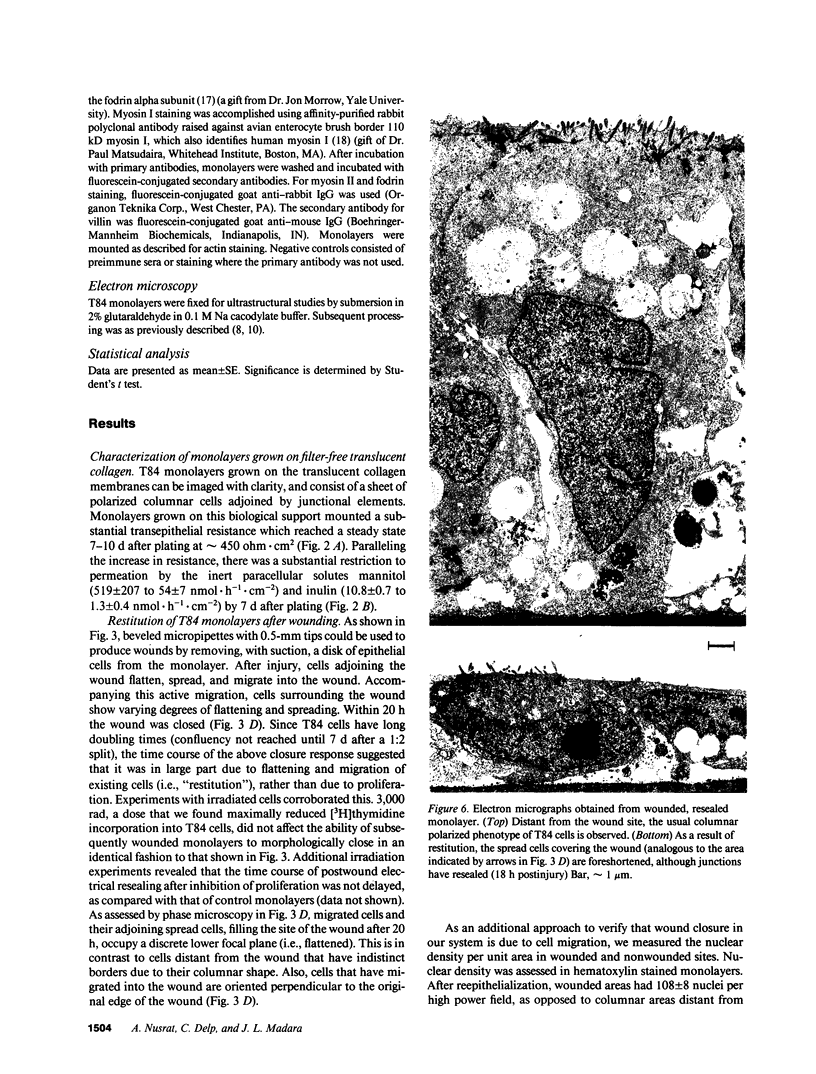


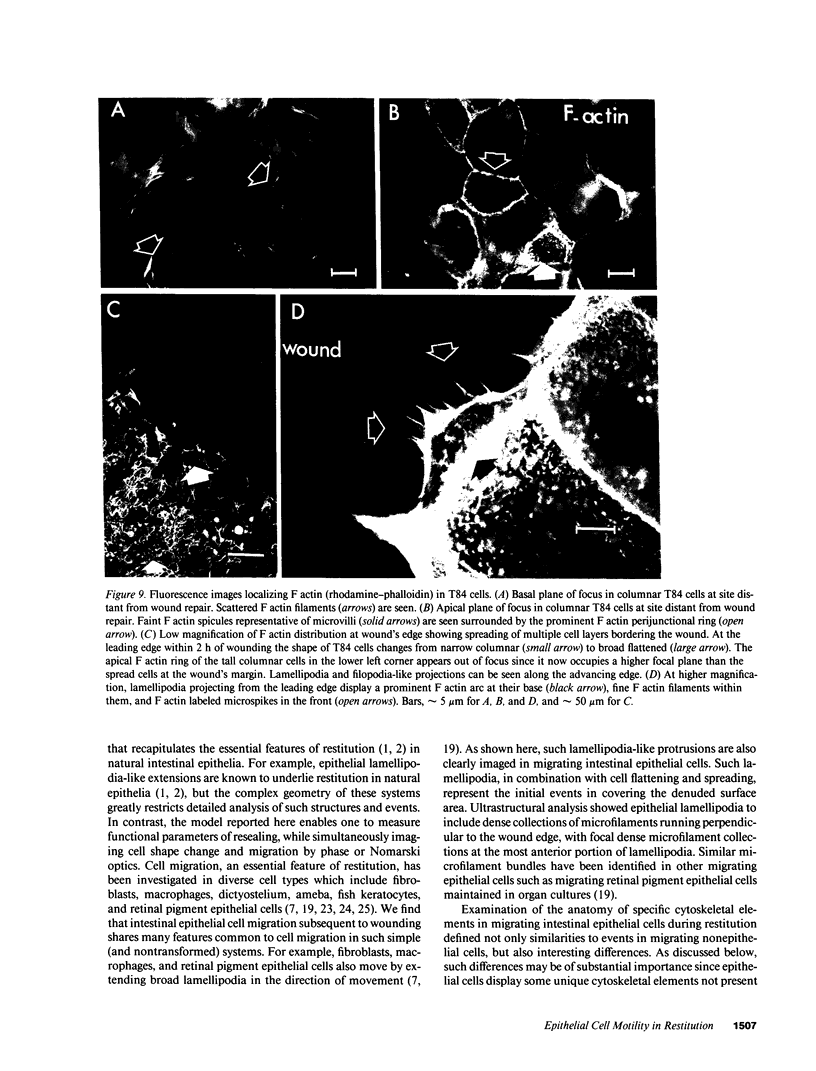
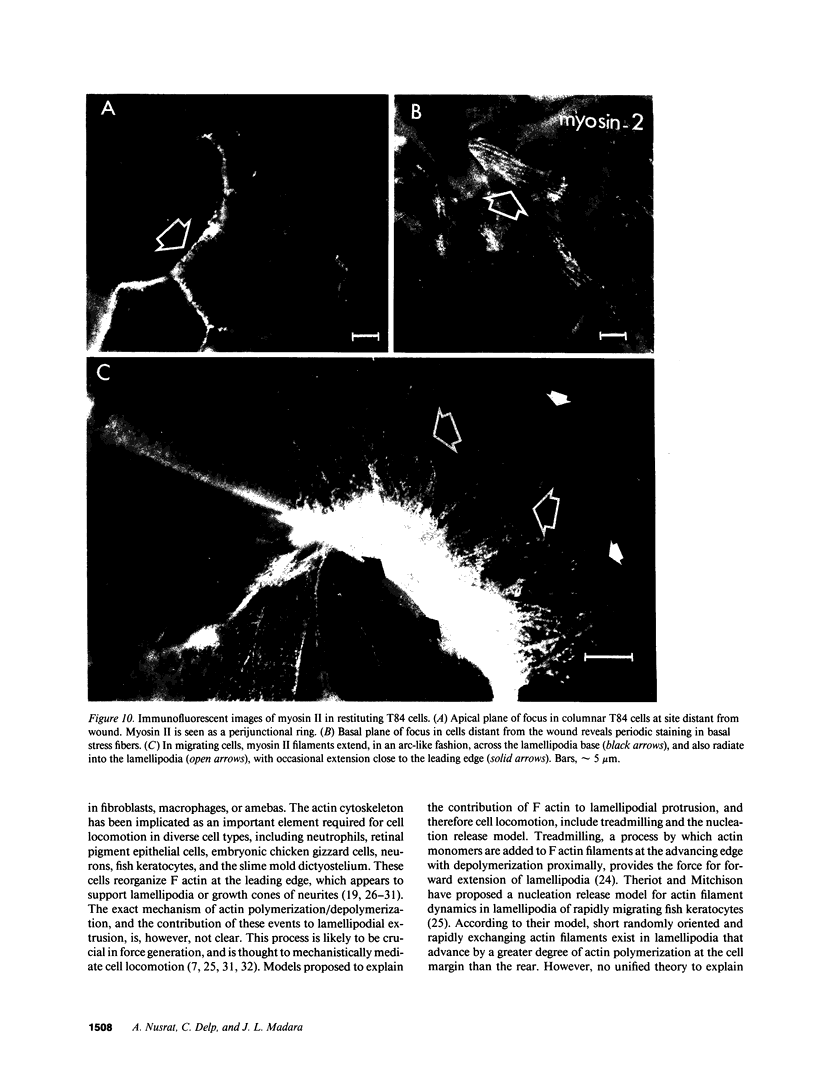

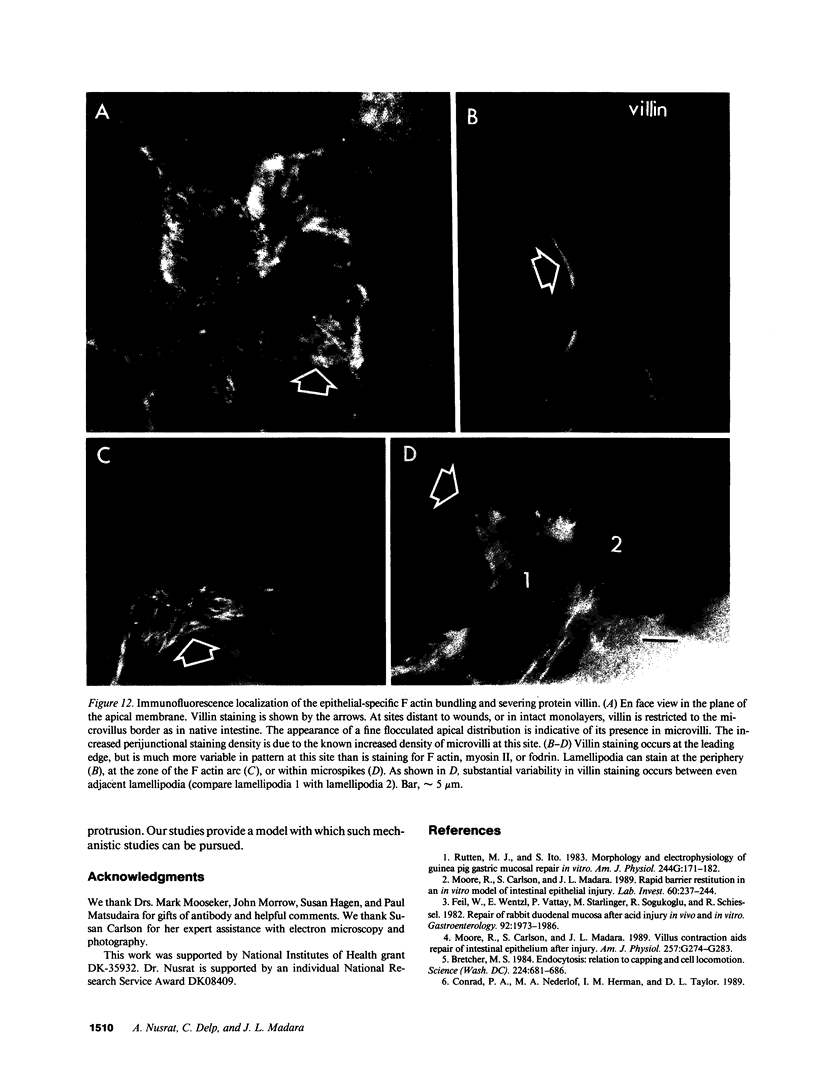

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergmann J. E., Kupfer A., Singer S. J. Membrane insertion at the leading edge of motile fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1367–1371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Bretcher M. S. Fibroblasts on the move. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):235–237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M. Living with clathrin: its role in intracellular membrane traffic. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1396–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.2904698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Robbins E. S., Dolan W. J., Rotunno C. A., Sabatini D. D. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):853–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K., Sellers J. R., Matsudaira P. Calmodulin dissociation regulates brush border myosin I (110-kD-calmodulin) mechanochemical activity in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1137–1147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J., Hall A., Bresnick A., Warren V., Hock R., Bennett H., Ogihara S. Actin polymerization and pseudopod extension during amoeboid chemotaxis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;10(1-2):77–90. doi: 10.1002/cm.970100113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Disruption of the Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain gene by homologous recombination. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1086–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.3576222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Madara J. L. Established intestinal cell lines as model systems for electrolyte transport studies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:354–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92082-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Tisdale L. D., Masui H. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G204–G208. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudouet B., Robine S., Huet C., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Blair L., Coudrier E., Louvard D. Changes in villin synthesis and subcellular distribution during intestinal differentiation of HT29-18 clones. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):359–369. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil W., Wenzl E., Vattay P., Starlinger M., Sogukoglu T., Schiessel R. Repair of rabbit duodenal mucosa after acid injury in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1973–1986. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Huet C., Arpin M., Louvard D. Villin induces microvilli growth and actin redistribution in transfected fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Lynch T. J., Brzeska H., Korn E. D. Myosin I is located at the leading edges of locomoting Dictyostelium amoebae. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):328–331. doi: 10.1038/341328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Fodrin is the general spectrin-like protein found in most cells whereas spectrin and the TW protein have a restricted distribution. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. S., Green L. A., Ainger K. J., Morrow J. S. Mechanism of cytoskeletal regulation (I): functional differences correlate with antigenic dissimilarity in human brain and erythrocyte spectrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 8;830(2):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J., Holifield B. Cell locomotion. Actin alone in lamellipodia. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):107–108. doi: 10.1038/352107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht G., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Madara J. L. Clostridium difficile toxin A perturbs cytoskeletal structure and tight junction permeability of cultured human intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI113760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hergott G. J., Sandig M., Kalnins V. I. Cytoskeletal organization of migrating retinal pigment epithelial cells during wound healing in organ culture. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;13(2):83–93. doi: 10.1002/cm.970130203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Geiger B., Schlessinger J. Mobility of microinjected rhodamine actin within living chicken gizzard cells determined by fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):835–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90445-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Barenberg D., Carlson S. Effects of cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J., Dharmsathaphorn K., Carlson S. Structural analysis of a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1133–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Cytoskeletal dynamics and nerve growth. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):761–772. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Carlson S., Madara J. L. Rapid barrier restitution in an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial injury. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):237–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Carlson S., Madara J. L. Villus contraction aids repair of intestinal epithelium after injury. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):G274–G283. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.2.G274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S. Organization, chemistry, and assembly of the cytoskeletal apparatus of the intestinal brush border. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:209–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Allen R. A., Bokoch G. M., Painter R. G., Traynor A. E., Sklar L. A. Signal transduction and cytoskeletal activation in the neutrophil. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jan;67(1):285–322. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinnerthaler G., Geiger B., Small J. V. Contact formation during fibroblast locomotion: involvement of membrane ruffles and microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):747–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinard J. H., Pollard T. D. Microinjection into Acanthamoeba castellanii of monoclonal antibodies to myosin-II slows but does not stop cell locomotion. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(1):42–52. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Kupfer A. The directed migration of eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. E., Preston A. S., Johnson J. P., Handler J. S. Porous-bottom dishes for culture of polarized cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):C136–C139. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.1.C136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. Actin microfilament dynamics in locomoting cells. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):126–131. doi: 10.1038/352126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. L. Exchange of actin subunits at the leading edge of living fibroblasts: possible role of treadmilling. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):597–602. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]