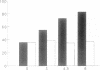Abstract
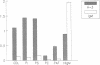
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APLS) is characterized by thrombocytopenia, thromboembolic phenomena, and recurrent fetal loss, associated with anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA) and/or lupus anticoagulant. The syndrome may be primary or may be associated with other conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus. We have previously shown the ability to induce APLS in naive mice following passive transfer of serum and monoclonal ACAs. Similarly we generated the secondary APLS in BALB/c mice following immunization with a pathogenic anti-DNA antibody. In the current study we report on the induction of primary APLS following immunization of BALB/c mice with a human monoclonal ACA (H-3). The mice developed high persistent titers of ACA. The APLS was characterized by prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time, low fecundity rate (21% vs. 48% of control immunized mice), high resorption index of fetuses (25% vs. 3%), and low weights of embryos and placentae. Our study points to the ability of inducing primary APLS in naive mice. The induction of various presentations of APLS by different ACA may explain the diversity of clinical manifestations seen in patients with APLS.
Full text
PDF
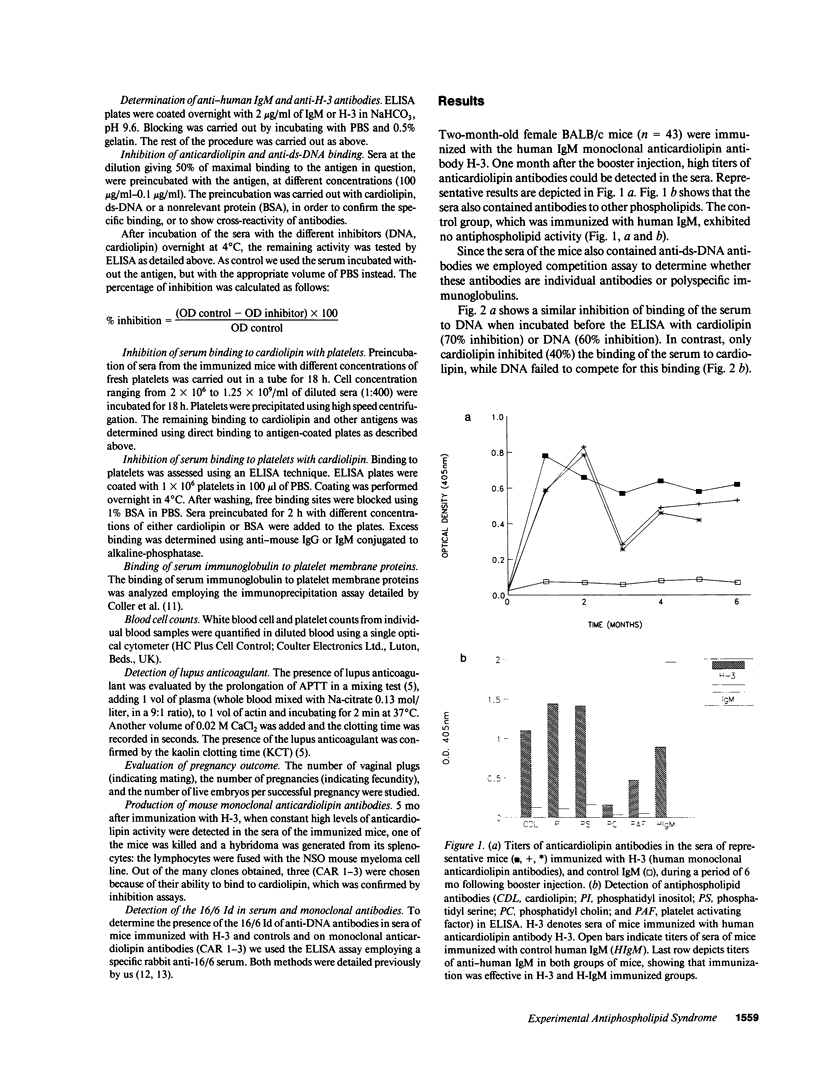
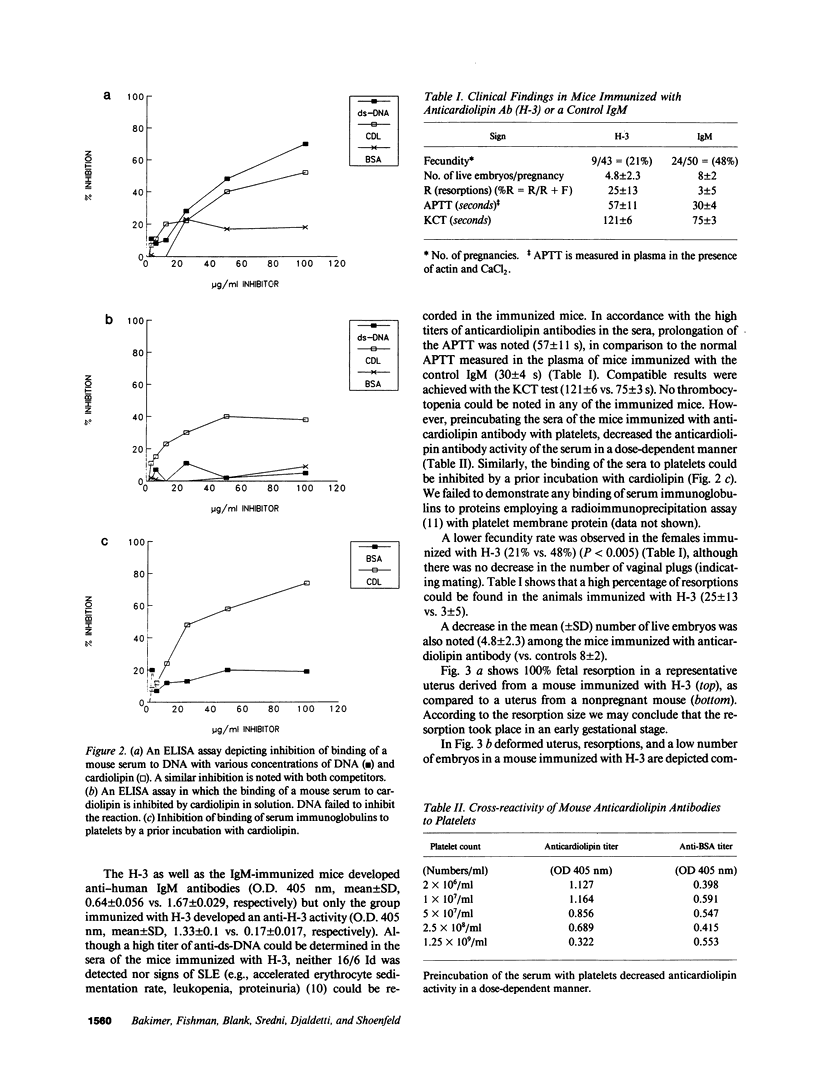
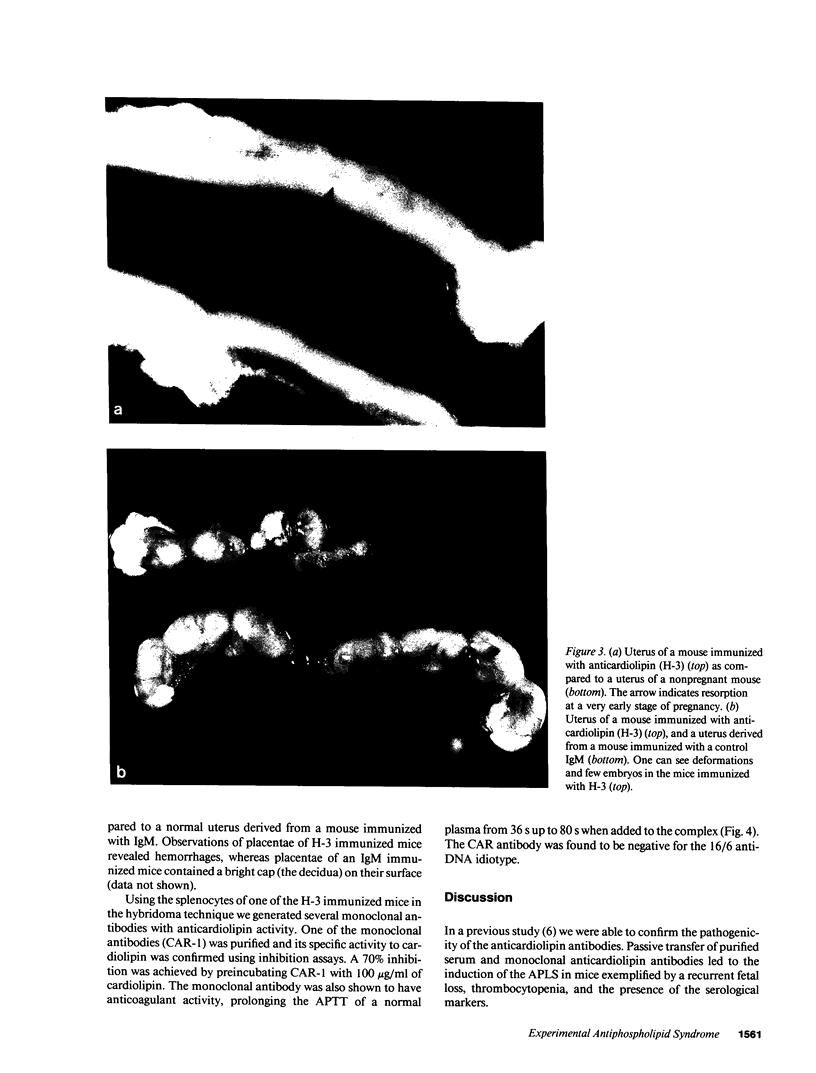


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Sanchez-Guerrero J. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1989 Apr;16(4):482–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson R. A., Khamashta M. A., Ordi-Ros J., Derksen R. H., Machin S. J., Barquinero J., Outt H. H., Harris E. N., Vilardell-Torres M., Hughes G. R. The "primary" antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Nov;68(6):366–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Cohen J., Toder V., Shoenfeld Y. Induction of anti-phospholipid syndrome in naive mice with mouse lupus monoclonal and human polyclonal anti-cardiolipin antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3069–3073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Krup M., Mendlovic S., Fricke H., Mozes E., Talal N., Coates A. R., Shoenfeld Y. The importance of the pathogenic 16/6 idiotype in the induction of SLE in naive mice. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Jan;31(1):45–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Dudley D. J., Mitchell M. D., Creighton K. A., Abbott T. M., Hammond E. H., Daynes R. A. Immunoglobulin G fractions from patients with antiphospholipid antibodies cause fetal death in BALB/c mice: a model for autoimmune fetal loss. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Jul;163(1 Pt 1):210–216. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(11)90700-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa K., Shimada K., Nawata Y., Ishii T., Tomioka H., Yoshida S., Koike T. Monoclonal hybridoma anti-cardiolipin antibodies from SLE mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Oct;74(1):110–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Madaio M. P., Rauch J., Reichlin M., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Anti-DNA antibody idiotypes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1984 Aug 25;2(8400):417–422. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92904-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Schwartz R. S. Multiple serologic reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):132–138. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. Antiphospholipid antibodies: more than just a disease marker? Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90020-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlovic S., Brocke S., Shoenfeld Y., Ben-Bassat M., Meshorer A., Bakimer R., Mozes E. Induction of a systemic lupus erythematosus-like disease in mice by a common human anti-DNA idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2260–2264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossent J. C., Huysen V., Smeenk R. J., Swaak A. J. Low avidity antibodies to double stranded DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal study of their clinical significance. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Aug;48(8):677–682. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.8.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammaritano L. R., Gharavi A. E., Lockshin M. D. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: immunologic and clinical aspects. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Oct;20(2):81–96. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(90)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Hsu-Lin S. C., Gabriels J. E., Silberstein L. E., Furie B. C., Furie B., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Production of autoantibodies by human-human hybridomas. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):205–208. doi: 10.1172/JCI110595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A., Rauch J., Madaio M. P., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Idiotypic cross-reactions of monoclonal human lupus autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):718–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Rauch J., Massicotte H., Datta S. K., André-Schwartz J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Polyspecificity of monoclonal lupus autoantibodies produced by human-human hybridomas. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):414–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Teplizki H. A., Mendlovic S., Blank M., Mozes E., Isenberg D. A. The role of the human anti-DNA idiotype 16/6 in autoimmunity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jun;51(3):313–325. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R. J., Lucassen W. A., Swaak T. J. Is anticardiolipin activity a cross-reaction of anti-DNA or a separate entity? Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jun;30(6):607–617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]