Abstract
Fusion of ligands such as growth factors to other proteins often dramatically reduces the affinity of the ligand for its receptor. With recombinant DNA techniques, the attachment point between the two proteins has until now been restricted to either the amino or the carboxyl terminus of the ligand. However, binding may be greatly compromised if both ends are close to the site at which the ligand binds to its receptor. To construct a single-chain growth factor fusion protein with the connection at a new site on the growth factor, we constructed a DNA fragment encoding circularly permuted interleukin 4 (IL4), termed IL4(38-37). This was accomplished by placing a start codon before position 38, connecting codons 1 and 129 with a sequence encoding a peptide linker, and placing a stop codon after codon 37 of IL4. IL4(38-37) was fused via its new carboxyl terminus, Lys37, to a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin. The purified circularly permuted IL4-toxin bound to the IL4 receptor with 10-fold higher affinity than an IL4-toxin in which the toxin was fused to the carboxyl terminus of IL4. Circular permuteins of growth factors can improve the effectiveness of recombinant fusion proteins, because the junction can be moved to a site on the growth factor which allows it to bind with higher affinity.
Full text
PDF


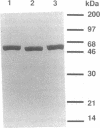
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allured V. S., Collier R. J., Carroll S. F., McKay D. B. Structure of exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.0-Angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1320–1324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Buchner J., Pastan I. Independent domain folding of Pseudomonas exotoxin and single-chain immunotoxins: influence of interdomain connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Lee B. K., Pastan I. Recombinant immunotoxins containing the VH or VL domain of monoclonal antibody B3 fused to Pseudomonas exotoxin. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):2774–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwalder A., Szadkowski H., Kirschner K. A fully active variant of dihydrofolate reductase with a circularly permuted sequence. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1621–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C., Aykent S., Kimack N. M., Levine A. D. Disulfide assignments in recombinant mouse and human interleukin 4. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1515–1523. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Gallo M. G., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. A recombinant single-chain immunotoxin composed of anti-Tac variable regions and a truncated diphtheria toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9491–9494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Williams D. E., Broxmeyer H. E., Dunn J., Farrah T., Jeffery E., Clevenger W., deRoos P., Martin U., Friend D. Enhanced hematopoietic activity of a human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-interleukin 3 fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5809–5813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debinski W., Puri R. K., Kreitman R. J., Pastan I. A wide range of human cancers express interleukin 4 (IL4) receptors that can be targeted with chimeric toxin composed of IL4 and Pseudomonas exotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14065–14070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Wu P., Varshavsky A. Heat-inducible degron: a method for constructing temperature-sensitive mutants. Science. 1994 Mar 4;263(5151):1273–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.8122109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchêne A. M., Patte J., Gutierrez C., Chandler M. A simple and efficient system for the construction of phoA gene fusions in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1992 May 1;114(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90714-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G. M., DeFeo-Jones D., Tai J. Y., Vuocolo G. A., Patrick D. R., Heimbrook D. C., Oliff A. Epidermal growth factor receptor binding is affected by structural determinants in the toxin domain of transforming growth factor-alpha-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2860–2867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell H. P., Gayle M. A., Grosmaire L., Ledbetter J. A. Genetic construction and characterization of a fusion protein consisting of a chimeric F(ab') with specificity for carcinomas and human IL-2. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2446–2452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. P., Creighton T. E. Circular and circularly permuted forms of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshorn S. C., Svensson H. P., Kerr D. E., Somerville J. E., Senter P. D., Fell H. P. Genetic construction, expression, and characterization of a single chain anti-carcinoma antibody fused to beta-lactamase. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2123–2127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. P., Osslund T. D., Eisenberg D. The structure of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor and its relationship to other growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5167–5171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., George H. J., Cooke G. M., Tritch R. J., Newton R. C., Dwivedi A., Lischwe M., Salemme F. R., Weber P. C., Horuk R. Permuteins of interleukin 1 beta--a simplified approach for the construction of permutated proteins having new termini. Protein Eng. 1992 Jul;5(5):427–431. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.5.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito W., Kurosawa Y. Development of an artificial antibody system with multiple valency using an Fv fragment fused to a fragment of protein A. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20668–20675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean L. F., Murphy J. R. Diphtheria toxin receptor-binding domain substitution with interleukin 6: genetic construction and interleukin 6 receptor-specific action of a diphtheria toxin-related interleukin 6 fusion protein. Protein Eng. 1991 Dec;4(8):989–994. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.8.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Karplus P. A. Hematopoietic growth factors: understanding functional diversity in structural terms. Blood. 1993 Dec 1;82(11):3229–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman R. J., Bailon P., Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Recombinant immunotoxins containing anti-Tac(Fv) and derivatives of Pseudomonas exotoxin produce complete regression in mice of an interleukin-2 receptor-expressing human carcinoma. Blood. 1994 Jan 15;83(2):426–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman R. J., Batra J. K., Seetharam S., Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Single-chain immunotoxin fusions between anti-Tac and Pseudomonas exotoxin: relative importance of the two toxin disulfide bonds. Bioconjug Chem. 1993 Mar-Apr;4(2):112–120. doi: 10.1021/bc00020a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le H. V., Seelig G. F., Syto R., Ramanathan L., Windsor W. T., Borkowski D., Trotta P. P. Selective proteolytic cleavage of recombinant human interleukin 4. Evidence for a critical role of the C-terminus. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9576–9582. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis J. M., McDonald R. A., Nashed N. T., Wondrak E. M., Jerina D. M., Oroszlan S., Mora P. T. Autoprocessing of the HIV-1 protease using purified wild-type and mutated fusion proteins expressed at high levels in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger K., Hommel U., Herold M., Hofsteenge J., Kirschner K. Correct folding of circularly permuted variants of a beta alpha barrel enzyme in vivo. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):206–210. doi: 10.1126/science.2643160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger K., Szadkowski H., Kirschner K. An 8-fold beta alpha barrel protein with redundant folding possibilities. Protein Eng. 1990 Mar;3(4):249–258. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.4.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Bishai W., Borowski M., Miyanohara A., Boyd J., Nagle S. Genetic construction, expression, and melanoma-selective cytotoxicity of a diphtheria toxin-related alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8258–8262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. Circularly permuted DNA, RNA and proteins--a review. Gene. 1993 Mar 30;125(2):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90317-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Chaudhary V., FitzGerald D. J. Recombinant toxins as novel therapeutic agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:331–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R., Garrett D. S., March C. J., Frieden E. A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. The high-resolution, three-dimensional solution structure of human interleukin-4 determined by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 6;32(26):6744–6762. doi: 10.1021/bi00077a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R., Garrett D. S., March C. J., Frieden E. A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Three-dimensional solution structure of human interleukin-4 by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1673–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior T. I., Helman L. J., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Cytotoxic activity of a recombinant fusion protein between insulin-like growth factor I and Pseudomonas exotoxin. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan L., Ingram R., Sullivan L., Greenberg R., Reim R., Trotta P. P., Le H. V. Immunochemical mapping of domains in human interleukin 4 recognized by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3549–3556. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern C. P., Wilson K. E. Ligand binding properties of human cellular retinoic acid binding protein II expressed in E. coli as a glutathione-S-transferase fusion protein. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 26;321(2-3):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock F., Everett M., Klein M. Overexpression and structure--function analysis of a bioengineered IL-2/IL-6 chimeric lymphokine. Protein Eng. 1992 Sep;5(6):583–591. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.6.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. M., Sibanda B. L. Amino and carboxy-terminal regions in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):443–460. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. R., Cook W. J., Zhao B. G., Cameron R. P., Jr, Ealick S. E., Walter R. L., Jr, Reichert P., Nagabhushan T. L., Trotta P. P., Bugg C. E. Crystal structure of recombinant human interleukin-4. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20371–20376. doi: 10.2210/pdb2int/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. P., Snider C. E., Strom T. B., Murphy J. R. Structure/function analysis of interleukin-2-toxin (DAB486-IL-2). Fragment B sequences required for the delivery of fragment A to the cytosol of target cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11885–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Pavlovsky A., Gustchina A. Hematopoietic cytokines: similarities and differences in the structures, with implications for receptor binding. Protein Sci. 1993 Sep;2(9):1373–1382. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. R., Schachman H. K. Aspartate transcarbamoylase containing circularly permuted catalytic polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11980–11984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang T., Bertelsen E., Benvegnu D., Alber T. Circular permutation of T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12311–12318. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]