Abstract
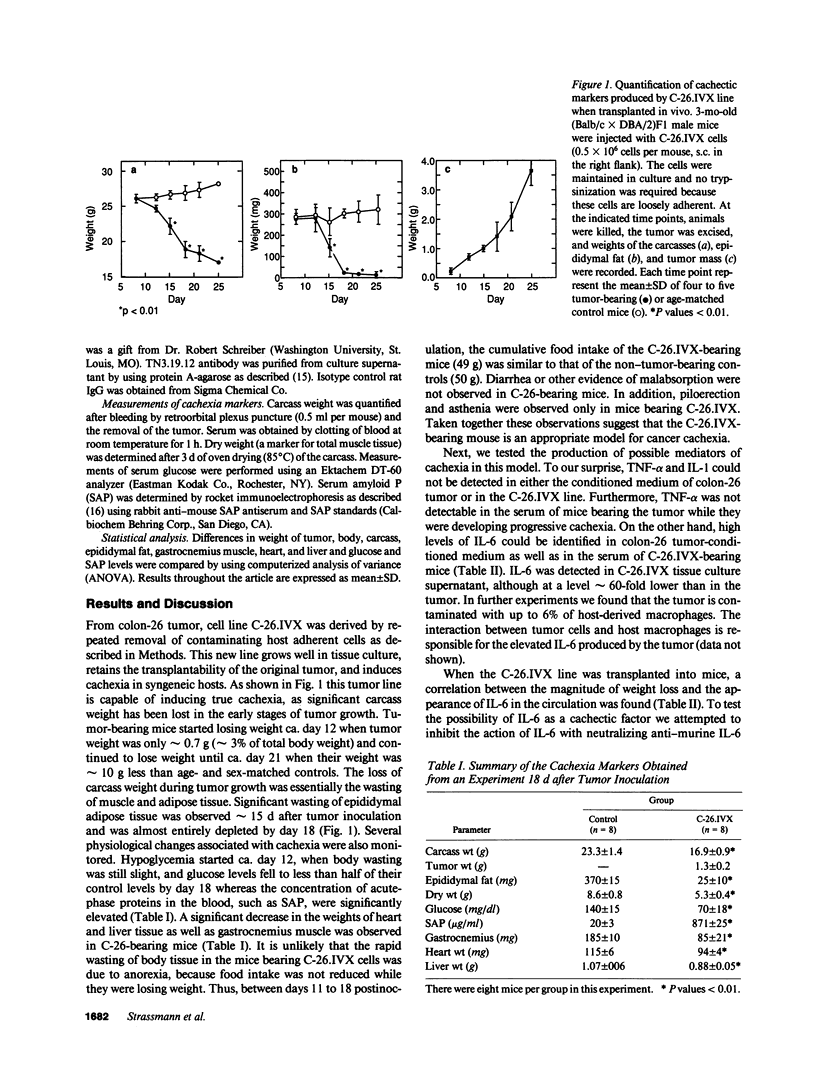
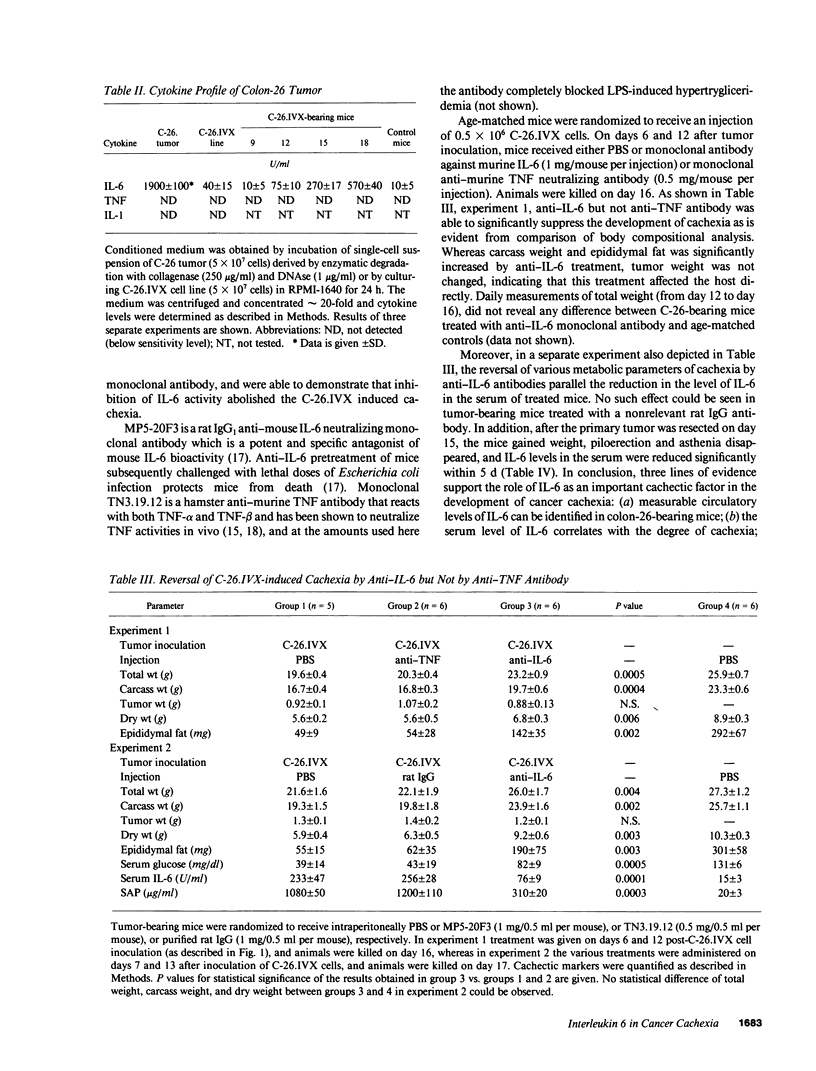
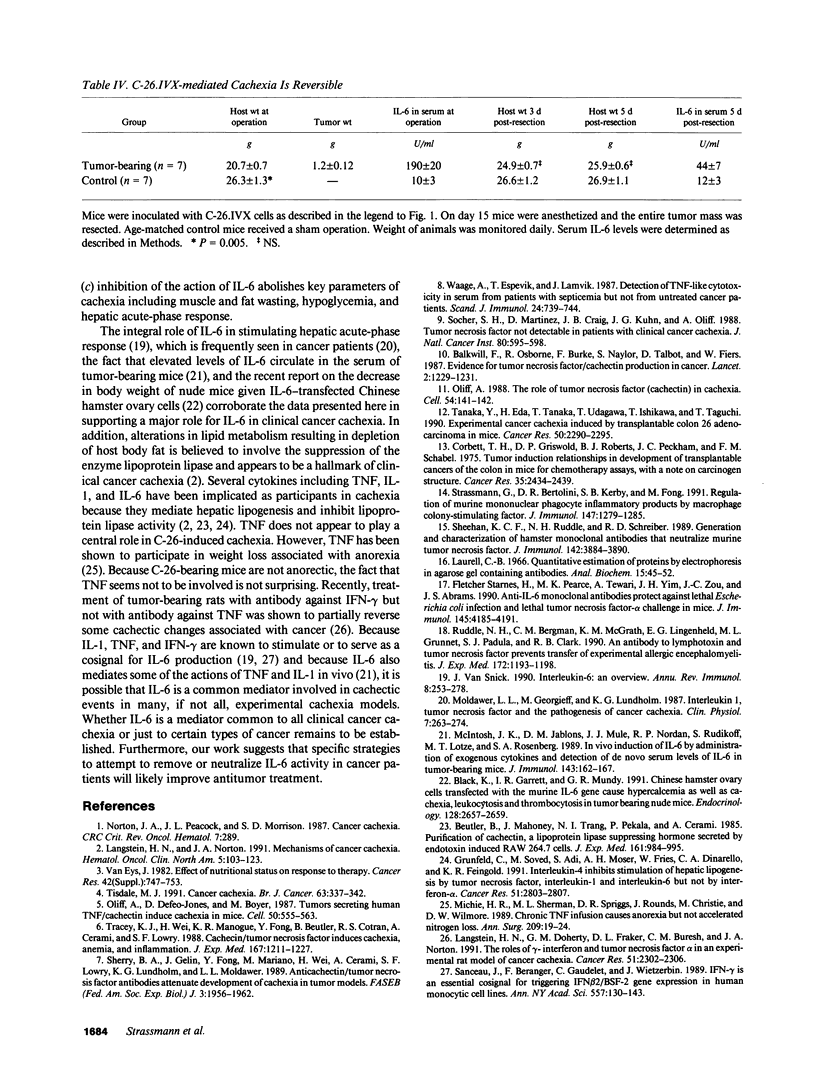
In this report we describe an experimental model of cachexia that fulfills the criteria of an early effect with a small tumor mass not related to the growth rate of the tumor, and progressive wasting of muscle and fat without a detectable loss of appetite. C-26.IVX is a cell line derived from murine colon-26 adenocarcinoma which retains the transplantability of the original tumor and induces true cachexia in syngeneic hosts. Evidence is presented to support a role for interleukin (IL-6) as a cachectic factor in the development of cancer cachexia in this model system. Thus, increasing levels of IL-6 in C-26.IVX-bearing mice correlate with the development of cachexia. If the primary tumors were resected, mice gained weight and the levels of IL-6 in the serum were reduced significantly. Moreover, monoclonal antibody to murine IL-6 (but not anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody) was able to significantly suppress the development of key parameters of cachexia in tumor bearing mice.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill F., Osborne R., Burke F., Naylor S., Talbot D., Durbin H., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Evidence for tumour necrosis factor/cachectin production in cancer. Lancet. 1987 Nov 28;2(8570):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black K., Garrett I. R., Mundy G. R. Chinese hamster ovarian cells transfected with the murine interleukin-6 gene cause hypercalcemia as well as cachexia, leukocytosis and thrombocytosis in tumor-bearing nude mice. Endocrinology. 1991 May;128(5):2657–2659. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-5-2657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett T. H., Griswold D. P., Jr, Roberts B. J., Peckham J. C., Schabel F. M., Jr Tumor induction relationships in development of transplantable cancers of the colon in mice for chemotherapy assays, with a note on carcinogen structure. Cancer Res. 1975 Sep;35(9):2434–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Soued M., Adi S., Moser A. H., Fiers W., Dinarello C. A., Feingold K. R. Interleukin 4 inhibits stimulation of hepatic lipogenesis by tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 1, and interleukin 6 but not by interferon-alpha. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):2803–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langstein H. N., Doherty G. M., Fraker D. L., Buresh C. M., Norton J. A. The roles of gamma-interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha in an experimental rat model of cancer cachexia. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2302–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langstein H. N., Norton J. A. Mechanisms of cancer cachexia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Feb;5(1):103–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. K., Jablons D. M., Mulé J. J., Nordan R. P., Rudikoff S., Lotze M. T., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo induction of IL-6 by administration of exogenous cytokines and detection of de novo serum levels of IL-6 in tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Sherman M. L., Spriggs D. R., Rounds J., Christie M., Wilmore D. W. Chronic TNF infusion causes anorexia but not accelerated nitrogen loss. Ann Surg. 1989 Jan;209(1):19–24. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198901000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., Georgieff M., Lundholm K. Interleukin 1, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (cachectin) and the pathogenesis of cancer cachexia. Clin Physiol. 1987 Aug;7(4):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1987.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J. A., Peacock J. L., Morrison S. D. Cancer cachexia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1987;7(4):289–327. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(87)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Defeo-Jones D., Boyer M., Martinez D., Kiefer D., Vuocolo G., Wolfe A., Socher S. H. Tumors secreting human TNF/cachectin induce cachexia in mice. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. The role of tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) in cachexia. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90543-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Bergman C. M., McGrath K. M., Lingenheld E. G., Grunnet M. L., Padula S. J., Clark R. B. An antibody to lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor prevents transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1193–1200. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanceau J., Beranger F., Gaudelet C., Wietzerbin J. IFN-gamma is an essential cosignal for triggering IFN-beta 2/BSF-2/IL-6 gene expression in human monocytic cell lines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:130-41, discussion 141-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B. A., Gelin J., Fong Y., Marano M., Wei H., Cerami A., Lowry S. F., Lundholm K. G., Moldawer L. L. Anticachectin/tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibodies attenuate development of cachexia in tumor models. FASEB J. 1989 Jun;3(8):1956–1962. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.8.2721856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socher S. H., Martinez D., Craig J. B., Kuhn J. G., Oliff A. Tumor necrosis factor not detectable in patients with clinical cancer cachexia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Jun 15;80(8):595–598. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.8.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Pearce M. K., Tewari A., Yim J. H., Zou J. C., Abrams J. S. Anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies protect against lethal Escherichia coli infection and lethal tumor necrosis factor-alpha challenge in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassmann G., Bertolini D. R., Kerby S. B., Fong M. Regulation of murine mononuclear phagocyte inflammatory products by macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Lack of IL-1 and prostaglandin E2 production and generation of a specific IL-1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Eda H., Tanaka T., Udagawa T., Ishikawa T., Horii I., Ishitsuka H., Kataoka T., Taguchi T. Experimental cancer cachexia induced by transplantable colon 26 adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 15;50(8):2290–2295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M. J. Cancer cachexia. Br J Cancer. 1991 Mar;63(3):337–342. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Espevik T., Lamvik J. Detection of tumour necrosis factor-like cytotoxicity in serum from patients with septicaemia but not from untreated cancer patients. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Dec;24(6):739–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



