Abstract
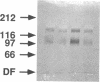
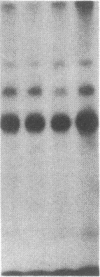
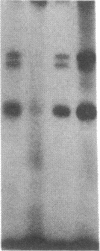
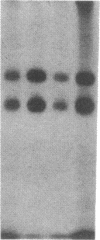
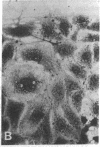
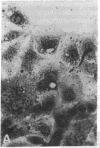
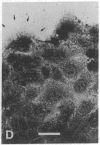
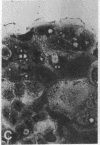
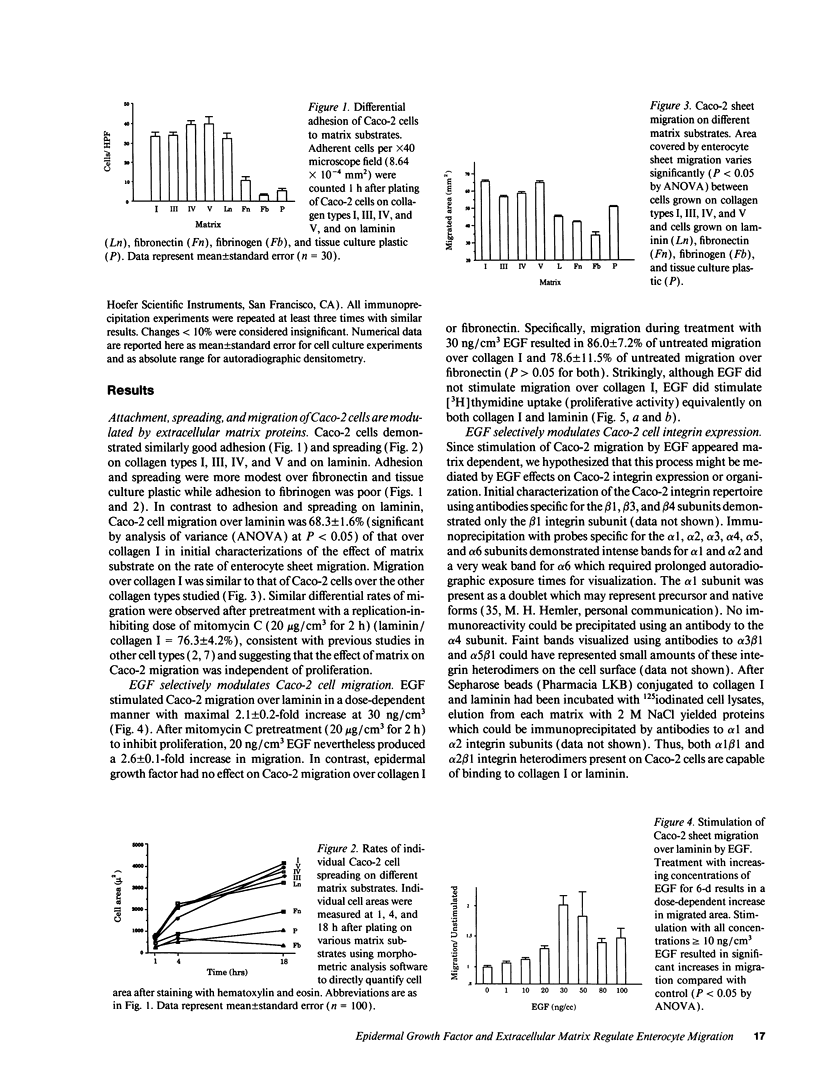
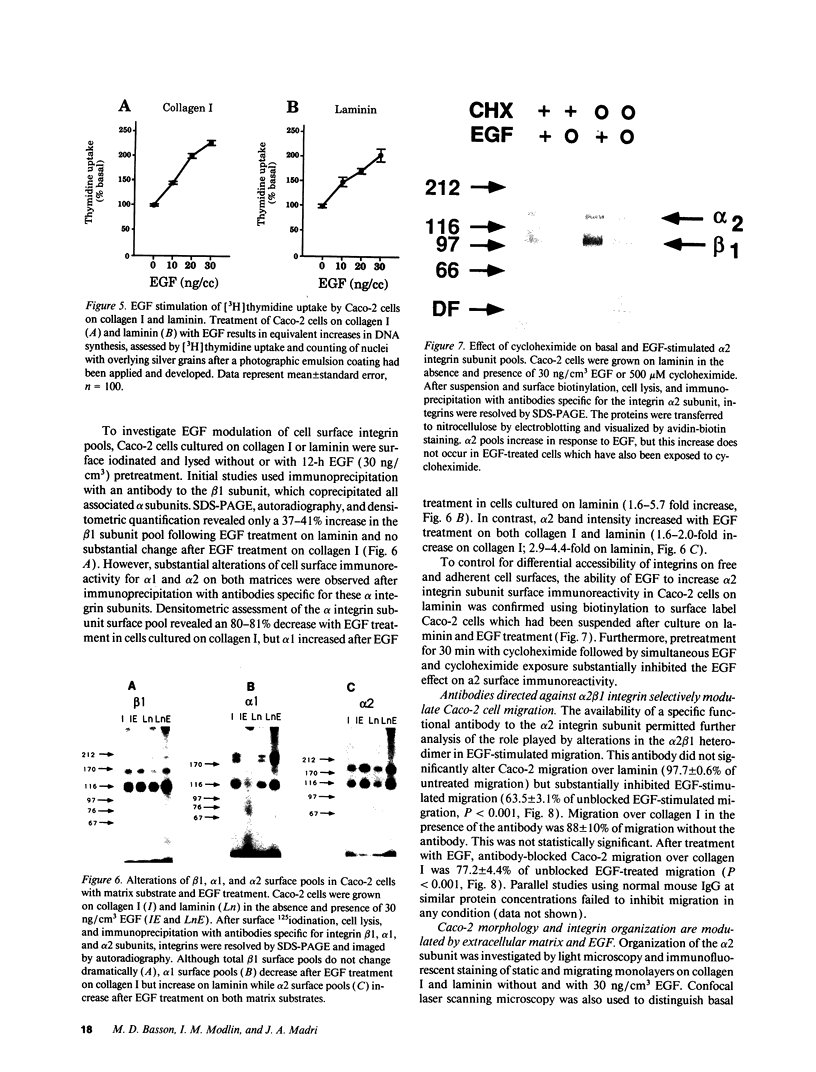
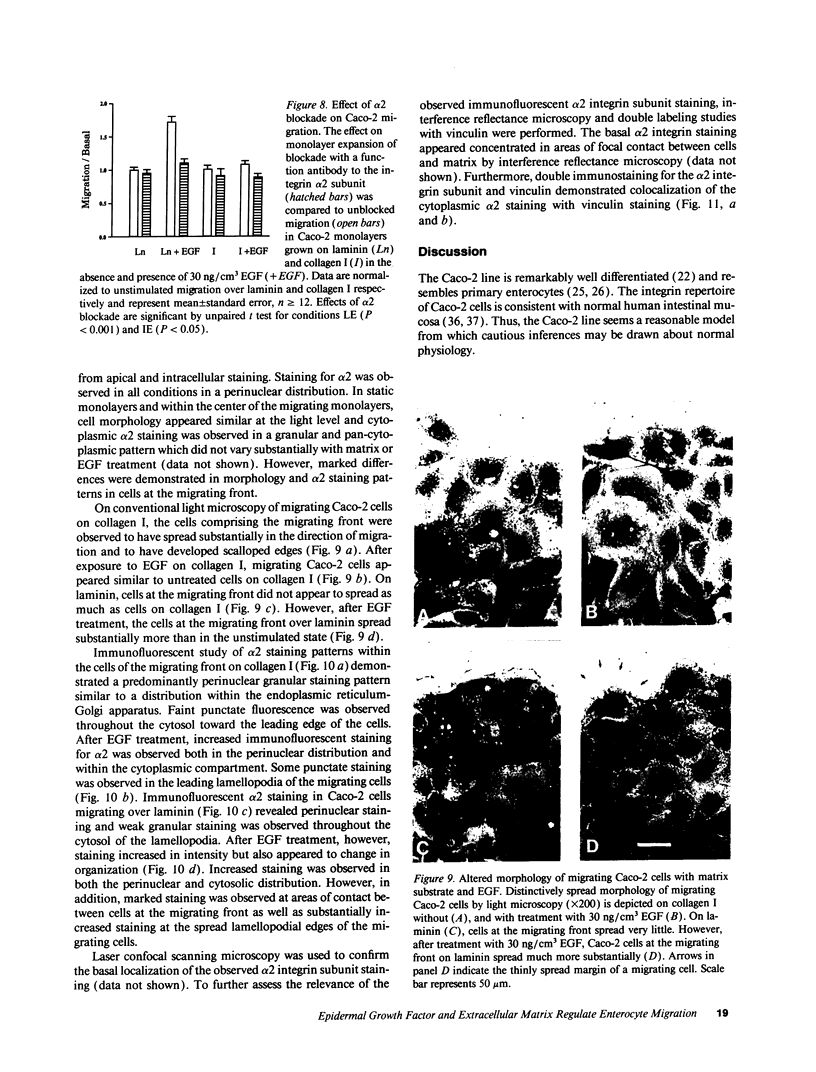
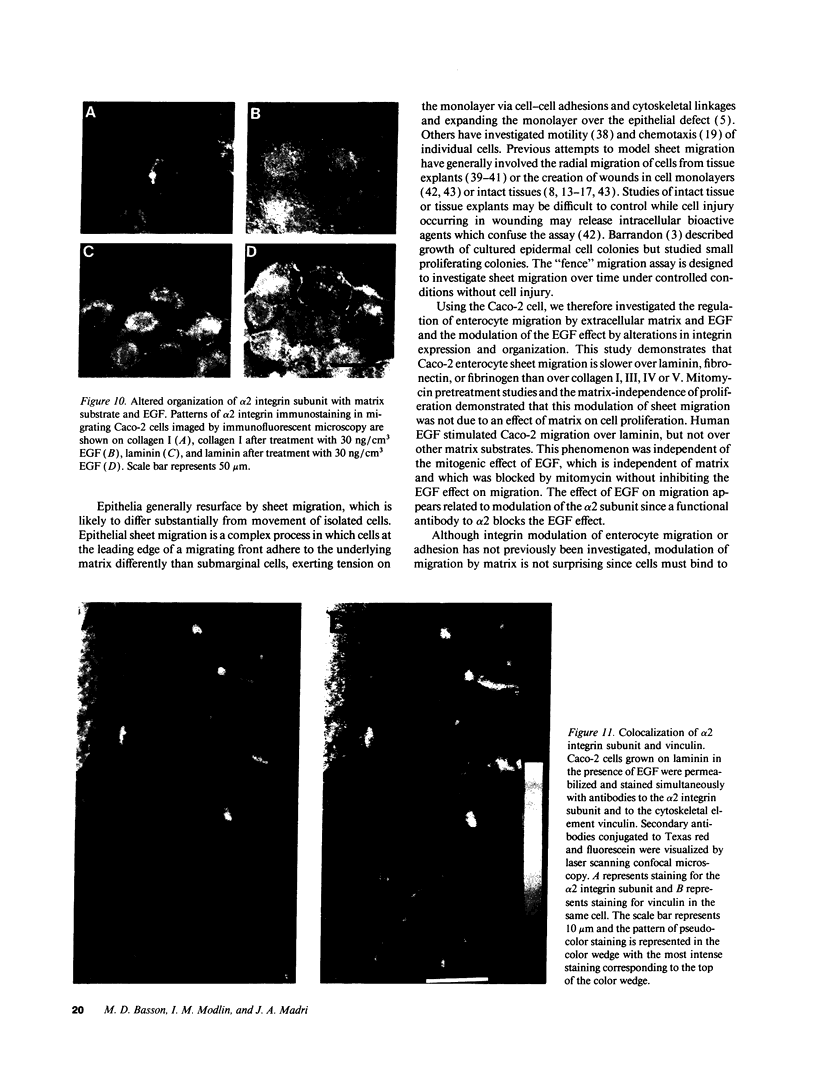
The modulation of enterocyte sheet migration was studied using Caco-2 cells, a well-differentiated human colonic cell line. Although Caco-2 cells attached and spread equivalently over collagen types I, III, IV, and V and laminin, migration over laminin was significantly slower than migration over the collagen types. Fibronectin was a poor substrate for attachment, spreading, and migration. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulated migration over laminin but did not alter Caco-2 migration over collagen or fibronectin. This effect was independent of cell proliferation, which was stimulated equivalently on both laminin and collagen I. Expression and organization of cell surface receptors for matrix (integrins) were studied using antibodies specific for beta and alpha integrin subunits. Integrin surface expression was assessed by immunoprecipitation of surface 125iodinated control and EGF-treated cells. Beta 1 surface pools did not change substantially in any condition studied. Alpha 1 subunit pools were decreased after EGF treatment on collagen I but alpha 1 pools increased after EGF treatment on laminin. Surface pools of alpha 2 subunits were increased following EGF treatment whether cells were cultured on laminin or collagen I. However, traditional immunofluorescent and laser confocal imaging demonstrated substantial differences in the character of alpha 2 subunit organization between collagen and laminin in the migrating cell front. Furthermore, a functional antibody to the alpha 2 subunit inhibited EGF stimulation of migration over laminin without substantial effects on basal migration over laminin or collagen I. Thus, EGF appears to exert a matrix-specific effect on enterocyte migration by modulation of integrin expression and organization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M. Analysis of fibronectin receptor function with monoclonal antibodies: roles in cell adhesion, migration, matrix assembly, and cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):863–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Daise M., Levine E. M., Buck C. A. Identification and characterization of cell-substratum adhesion receptors on cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1992–2002. doi: 10.1172/JCI114109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrandon Y., Green H. Cell migration is essential for sustained growth of keratinocyte colonies: the roles of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1131–1137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson C. T., Knowles W. J., Bell L., Albelda S. M., Castronovo V., Liotta L. A., Madri J. A. Spatiotemporal segregation of endothelial cell integrin and nonintegrin extracellular matrix-binding proteins during adhesion events. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):789–801. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp R. D., Barnard J. A., McCutchen C. M., Cherner J. A., Coffey R. J., Jr Localization of transforming growth factor alpha and its receptor in gastric mucosal cells. Implications for a regulatory role in acid secretion and mucosal renewal. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1172/JCI114223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L., Madri J. A. Effect of platelet factors on migration of cultured bovine aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1989 Oct;65(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.4.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellas R. E., Bendori R., Farmer S. R. Epidermal growth factor activation of vinculin and beta 1-integrin gene transcription in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Regulation through a protein kinase C-independent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12008–12014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Brown K. D. Epidermal growth factor promotes the chemotactic migration of cultured rat intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):107–112. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Valentine-Braun K. A., Northup J. K., Hollenberg M. D. Epidermal-growth-factor-stimulated phosphorylation of calpactin II in membrane vesicles shed from cultured A-431 cells. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):577–583. doi: 10.1042/bj2590577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Florent G., Chakrabarty S., Brattain D., Brattain M. G. Alterations of the biological characteristics of a colon carcinoma cell line by colon-derived substrata material. Cancer Res. 1988 May 15;48(10):2825–2831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Curtsinger L., 3rd, Brightwell J. R., Ackerman D. M., Tobin G. R., Polk H. C., Jr, George-Nascimento C., Valenzuela P., Schultz G. S. Enhancement of epidermal regeneration by biosynthetic epidermal growth factor. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1319–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Wayner E. A., Bouchard T. S., Kaur P. The role of integrins alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha 3 beta 1 in cell-cell and cell-substrate adhesion of human epidermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1387–1404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Barbat A., Dussaulx E., Brattain M. G., Zweibaum A. Epithelial polarity, villin expression, and enterocytic differentiation of cultured human colon carcinoma cells: a survey of twenty cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1936–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Trugnan G., Dussaulx E., Zweibaum A., Rousset M. Monensin inhibits the expression of sucrase-isomaltase in Caco-2 cells at the mRNA level. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Spiro R. C. Biosynthetic and functional properties of an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed receptor involved in human melanoma cell attachment to vitronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17703–17711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy M. Y., Richman P. I., Horton M. A., MacDonald T. T. Expression of the VLA family of integrins in human intestine. J Pathol. 1990 Jan;160(1):35–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1711600109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Goustin A. S., Soderquist A. M., Shipley G. D., Wolfshohl J., Carpenter G., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor alpha and beta expression in human colon cancer lines: implications for an autocrine model. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4590–4594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M., Timpl R. Expression of nidogen and laminin in basement membranes during mouse embryogenesis and in teratocarcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):372–382. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90491-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Morphoregulatory molecules. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3533–3543. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers U., Klumperman J., Hauri H. P. Nocodazole, a microtubule-active drug, interferes with apical protein delivery in cultured intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):13–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Urry L. A., Hemler M. E. Receptor functions for the integrin VLA-3: fibronectin, collagen, and laminin binding are differentially influenced by Arg-Gly-Asp peptide and by divalent cations. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):169–181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Hüttner I. Cytoplasmic filaments and gap junctions in epithelial cells and myofibroblasts during wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):561–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallis B., Edelman A. M., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chain from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13089–13093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodlad R. A., Wilson T. J., Lenton W., Gregory H., McCullagh K. G., Wright N. A. Intravenous but not intragastric urogastrone-EGF is trophic to the intestine of parenterally fed rats. Gut. 1987 May;28(5):573–582. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo M., Toda K., Grinnell F. Activation of human keratinocyte migration on type I collagen and fibronectin. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jun;96(Pt 2):197–205. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn U. Extracellular matrix proteins in small-intestinal cell cultures. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1988;151:70–78. doi: 10.3109/00365528809095916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn U., Stallmach A., Hahn E. G., Riecken E. O. Basement membrane components are potent promoters of rat intestinal epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):322–335. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90821-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebda P. A. Stimulatory effects of transforming growth factor-beta and epidermal growth factor on epidermal cell outgrowth from porcine skin explant cultures. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Nov;91(5):440–445. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12476480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heino J., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta switches the pattern of integrins expressed in MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells and causes a selective loss of cell adhesion to laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21806–21811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz P. U., Kasper M., van Noorden S., Polak J. M., Gregory H., Pearse A. G. Immunohistochemical localisation of urogastrone to human duodenal and submandibular glands. Gut. 1978 May;19(5):408–413. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.5.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Sanchez-Madrid F., Flotte T. J., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Bhan A. K., Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Glycoproteins of 210,000 and 130,000 m.w. on activated T cells: cell distribution and antigenic relation to components on resting cells and T cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3011–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda A., Noguchi N., Takehara H., Ohashi Y., Asuwa N., Mori Y. Cooperative enhancement of hyaluronic acid synthesis by combined use of IGF-I and EGF, and inhibition by tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein, in cultured mesothelial cells from rabbit pericardial cavity. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jan;98(Pt 1):91–98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Buck C., Beckerle M. C., Burridge K. Interaction of plasma membrane fibronectin receptor with talin--a transmembrane linkage. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):531–533. doi: 10.1038/320531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. K., La Van F. B. Enhancement of wound healing by growth factors. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 13;321(2):111–112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907133210209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh M., Joh T., Imai S., Miyamoto T., Matsusako K., Iwai A., Katsumi K., Endo K., Goto K., Takeuchi T. Experimental and clinical studies on epidermal growth factor for gastric mucosal protection and healing of gastric ulcers. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988;10 (Suppl 1):S7–12. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198812001-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. A novel effect of EGF on mRNA stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4957–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Foote L. J., Falcioni R., Sonnenberg A., Stringer C. D., Crouse C., Hemler M. E. Analysis of the tumor-associated antigen TSP-180. Identity with alpha 6-beta 4 in the integrin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15515–15521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhofer D., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Alpha 2 beta 1 integrins from different cell types show different binding specificities. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):615–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolega J. The movement of cell clusters in vitro: morphology and directionality. J Cell Sci. 1981 Jun;49:15–32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.49.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Dembinski A., Warzecha Z., Brzozowski T., Gregory H. Role of epidermal growth factor in healing of chronic gastroduodenal ulcers in rats. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretz K., Schlag P., Boumsell L., Möller P. Expression of VLA-alpha 2, VLA-alpha 6, and VLA-beta 1 chains in normal mucosa and adenomas of the colon, and in colon carcinomas and their liver metastases. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):741–750. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucik D. F., Kuo S. C., Elson E. L., Sheetz M. P. Preferential attachment of membrane glycoproteins to the cytoskeleton at the leading edge of lamella. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):1029–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E. R. Epithelial restitution in the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988;10 (Suppl 1):S72–S77. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198812001-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larjava H., Peltonen J., Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Gralnick H. R., Uitto J., Yamada K. M. Novel function for beta 1 integrins in keratinocyte cell-cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):803–815. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Quaroni A., Nichols B., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenetic pathways of plasma membrane proteins in Caco-2, a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K., Tanaka M., Shigeno C., Yamamoto I., Ohta S., Rikimaru K., Hatanaka M., Konishi J. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the anchorage-independent growth of human squamous cell carcinomas overexpressing its receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Johansen M., Bjerkvig R., Humphrey P. A., Bigner S. H., Bigner D. D., Laerum O. D. Effect of epidermal growth factor on glioma cell growth, migration, and invasion in vitro. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 15;50(18):6039–6044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Pratt B. M., Yannariello-Brown J. Matrix-driven cell size change modulates aortic endothelial cell proliferation and sheet migration. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):18–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks R., Nishikawa T. Active epidermal movement in human skin in vitro. Br J Dermatol. 1973 Mar;88(3):245–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1973.tb07542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Ito S. Gastrointestinal cell plasma membrane wounding and resealing in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1989 May;96(5 Pt 1):1238–1248. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(89)80010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Carlson S., Madara J. L. Rapid barrier restitution in an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial injury. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):237–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto A., Okamura K., Hamanaka R., Sato Y., Shima N., Higashio K., Kuwano M. Hepatocyte growth factor modulates migration and proliferation of human microvascular endothelial cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):1042–1049. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91924-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall M., Ryan G. B., O'Brien B. M. The effect of epidermal growth factor on wound healing in mice. J Surg Res. 1982 Aug;33(2):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(82)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royce L. S., Baum B. J. Physiologic levels of salivary epidermal growth factor stimulate migration of an oral epithelial cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):401–403. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov Olsen P. Role of epidermal growth factor in gastroduodenal mucosal protection. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988;10 (Suppl 1):S146–S151. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198812001-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Hogervorst F., Osterop A., Veltman F. E. Identification and characterization of a novel antigen complex on mouse mammary tumor cells using a monoclonal antibody against platelet glycoprotein Ic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14030–14038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Linders C. J., Modderman P. W., Damsky C. H., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Integrin recognition of different cell-binding fragments of laminin (P1, E3, E8) and evidence that alpha 6 beta 1 but not alpha 6 beta 4 functions as a major receptor for fragment E8. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenn K. S., Madri J. A., Roll F. J. Migrating epidermis produces AB2 collagen and requires continual collagen synthesis for movement. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):229–232. doi: 10.1038/277229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Matter K., Baur B., Bucher K., Höchli M., Hauri H. P. Dissection of the asynchronous transport of intestinal microvillar hydrolases to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1853–1861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Bragg L. E., Saxena S. K. The effect of intestinal resection and urogastrone on intestinal regeneration. Arch Surg. 1990 Dec;125(12):1617–1621. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410240099020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne H. J., Jose D. G., Zhang H. Y., Dempsey P. J., Whitehead R. H. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the synthesis of cell-attachment proteins in the human breast cancer cell line PMC42. Int J Cancer. 1987 Aug 15;40(2):207–212. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan C. W., McKnight M. K., Brattain D. E., Brattain M. G., Yeoman L. C. Different epidermal growth factor growth responses and receptor levels in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 1988 Dec 1;43(1-2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(88)90226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Pike C., Elia G. Induction of a novel epidermal growth factor-secreting cell lineage by mucosal ulceration in human gastrointestinal stem cells. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):82–85. doi: 10.1038/343082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannariello-Brown J., Wewer U., Liotta L., Madri J. A. Distribution of a 69-kD laminin-binding protein in aortic and microvascular endothelial cells: modulation during cell attachment, spreading, and migration. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1773–1786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Quaranta V., Tamura R. N., Reichardt L. F. Laminin receptors in the retina: sequence analysis of the chick integrin alpha 6 subunit. Evidence for transcriptional and posttranslational regulation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):405–416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]