Abstract
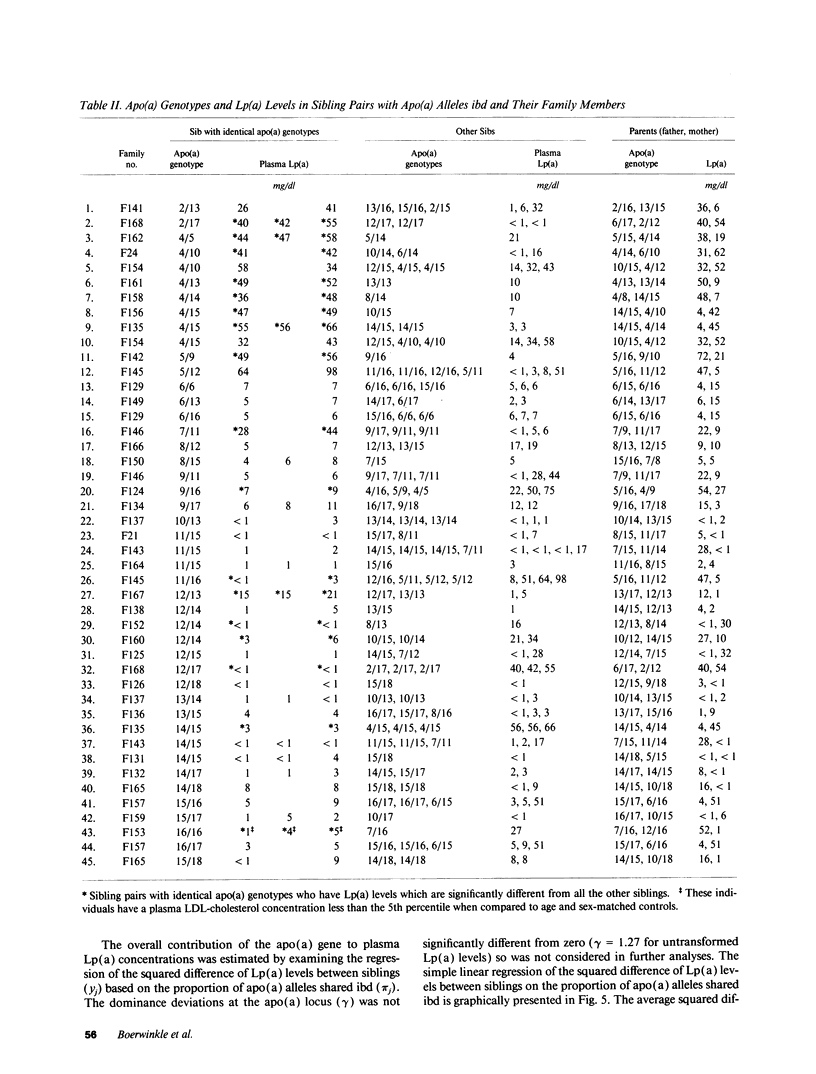
Plasma lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], a low density lipoprotein particle with an attached apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)], varies widely in concentration between individuals. These concentration differences are heritable and inversely related to the number of kringle 4 repeats in the apo(a) gene. To define the genetic determinants of plasma Lp(a) levels, plasma Lp(a) concentrations and apo(a) genotypes were examined in 48 nuclear Caucasian families. Apo(a) genotypes were determined using a newly developed pulsed-field gel electrophoresis method which distinguished 19 different genotypes at the apo(a) locus. The apo(a) gene itself was found to account for virtually all the genetic variability in plasma Lp(a) levels. This conclusion was reached by analyzing plasma Lp(a) levels in siblings who shared zero, one, or two apo(a) genes that were identical by descent (ibd). Siblings with both apo(a) alleles ibd (n = 72) have strikingly similar plasma Lp(a) levels (r = 0.95), whereas those who shared no apo(a) alleles (n = 52), had dissimilar concentrations (r = -0.23). The apo(a) gene was estimated to be responsible for 91% of the variance of plasma Lp(a) concentration. The number of kringle 4 repeats in the apo(a) gene accounted for 69% of the variation, and yet to be defined cis-acting sequences at the apo(a) locus accounted for the remaining 22% of the inter-individual variation in plasma Lp(a) levels. During the course of these studies we observed the de novo generation of a new apo(a) allele, an event that occurred once in 376 meioses.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Adolphson J. L., Hazzard W. R. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. J., Hazzard W. R. Immunochemical quantification of human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. Lipids. 1974 Jan;9(1):15–26. doi: 10.1007/BF02533209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. J., Wahl P., Hazzard W. R. Quantitative genetic studies of the human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. Biochem Genet. 1974 Jun;11(6):475–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00486079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos C. I., Elston R. C., Wilson A. F., Bailey-Wilson J. E. A more powerful robust sib-pair test of linkage for quantitative traits. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(3):435–449. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azen E., Lyons K. M., McGonigal T., Barrett N. L., Clements L. S., Maeda N., Vanin E. F., Carlson D. M., Smithies O. Clones from the human gene complex coding for salivary proline-rich proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5561–5565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrolan N., Gavish D., Breslow J. L. Plasma lipoprotein(a) concentration is controlled by apolipoprotein(a) (apo(a)) protein size and the abundance of hepatic apo(a) mRNA in a cynomolgus monkey model. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13866–13872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG K. A NEW SERUM TYPE SYSTEM IN MAN--THE LP SYSTEM. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG K., MOHR J. GENETICS OF THE LP SYSTEM. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1963;13:349–360. doi: 10.1159/000151818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. Unequal crossover generates variation in ubiquitin coding unit number at the human UbC polyubiquitin locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):534–542. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Chen S. H., Visvikis S., Hanis C. L., Siest G., Chan L. Signal peptide-length variation in human apolipoprotein B gene. Molecular characteristics and association with plasma glucose levels. Diabetes. 1991 Nov;40(11):1539–1544. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.11.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Sing C. F. The use of measured genotype information in the analysis of quantitative phenotypes in man. III. Simultaneous estimation of the frequencies and effects of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism and residual polygenetic effects on cholesterol, betalipoprotein and triglyceride levels. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;51(Pt 3):211–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb00874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Xiong W. J., Fourest E., Chan L. Rapid typing of tandemly repeated hypervariable loci by the polymerase chain reaction: application to the apolipoprotein B 3' hypervariable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):212–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen G. H., Guyton J. R., Attar M., Farmer J. A., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Association of levels of lipoprotein Lp(a), plasma lipids, and other lipoproteins with coronary artery disease documented by angiography. Circulation. 1986 Oct;74(4):758–765. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.4.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., Hegele R. A., Hass P. E., Emi M., Wu L. L., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M., Williams R. R., White R. L., Lalouel J. M. Genetic linkage between lipoprotein(a) phenotype and a DNA polymorphism in the plasminogen gene. Genomics. 1988 Oct;3(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Ghanem K. I., Guevara J., Jr, Nava M. L., Patsch W., Morrisett J. D. Polymorphic forms of human apolipoprotein[a]: inheritance and relationship of their molecular weights to plasma levels of lipoprotein[a]. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):603–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish D., Azrolan N., Breslow J. L. Plasma Ip(a) concentration is inversely correlated with the ratio of Kringle IV/Kringle V encoding domains in the apo(a) gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1172/JCI114395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H. C., Michel J. B., Blouquit Y., Chapman M. J. Lipoprotein(a) and apolipoprotein(a) in a New World monkey, the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Association of variable plasma lipoprotein(a) levels with a single apolipoprotein(a) isoform. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jul-Aug;11(4):1030–1041. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.4.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseman J. K., Elston R. C. The investigation of linkage between a quantitative trait and a marker locus. Behav Genet. 1972 Mar;2(1):3–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01066731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Williams R. R. Three alleles for quantitative Lp(a). Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Wilson D. E., Edwards C. Q., Cannon W. N., Carmelli D., Williams R. R. The genetics of quantitative plasma Lp(a): analysis of a large pedigree. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):179–188. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt D., Milner J., Breckenridge C., Maguire G. Heritability of "sinking" pre-beta lipoprotein level: a twin study. Clin Genet. 1977 Mar;11(3):224–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt D., Milner J., Owen A. R., Breckenridge W. C., Maguire G. F., Jones G. J., Little J. A. The inheritance of sinking-pre-beta lipoprotein and its relation to the Lp(a) antigen. Clin Genet. 1982 May;21(5):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Britten M. L., Manis G. S., Rainwater D. L. Apolipoprotein(a) (Apo(a)) glycoprotein isoforms result from size differences in Apo(a) mRNA in baboons. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6013–6016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu X. Y., Burghes A. H., Bulman D. E., Ray P. N., Worton R. G. Evidence for mutation by unequal sister chromatid exchange in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;44(6):855–863. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu X. Y., Ray P. N., Worton R. G. Mechanisms of tandem duplication in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene include both homologous and nonhomologous intrachromosomal recombination. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2471–2477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iselius L., Dahlén G., de Faire U., Lundman T. Complex segregation analysis of the Lp(a)/pre-beta 1-lipoprotein trait. Clin Genet. 1981 Aug;20(2):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Neumann R., Wilson V. Repeat unit sequence variation in minisatellites: a novel source of DNA polymorphism for studying variation and mutation by single molecule analysis. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):473–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koschinsky M. L., Beisiegel U., Henne-Bruns D., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M. Apolipoprotein(a) size heterogeneity is related to variable number of repeat sequences in its mRNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):640–644. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul M. J., Marcelli M., Tilley W. D., Griffin J. E., Isidro-Gutierrez R. F., Wilson J. D. Molecular basis of androgen resistance in a family with a qualitative abnormality of the androgen receptor and responsive to high-dose androgen therapy. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1413–1421. doi: 10.1172/JCI115147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Dieplinger H., Lackner C., Hoppichler F., Lloyd J. K., Muller D. R., Labeur C., Talmud P. J., Utermann G. Abetalipoproteinemia with an ApoB-100-lipoprotein(a) glycoprotein complex in plasma. Indication for an assembly defect. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Fless G. M., Levin E. G., Scanu A. M., Plow E. F. A potential basis for the thrombotic risks associated with lipoprotein(a). Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):301–303. doi: 10.1038/339301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Berg K., Dahlen G., Ferrell R. E., Rhoads G. G. Genetics of the Lp lipoprotein in Japanese-Americans. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano K., Swindle M. M., Spinale F., Ishihara K., Kanazawa S., Smith A., Biederman R. W., Clamp L., Hamada Y., Zile M. R. Depressed contractile function due to canine mitral regurgitation improves after correction of the volume overload. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2077–2086. doi: 10.1172/JCI115238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Rousseau F., Heitz D., Kretz C., Devys D., Hanauer A., Boué J., Bertheas M. F., Mandel J. L. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1097–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle A. D., Darmady J. M., Siggers D. C. Double pre-beta lipoprotein in ischaemic heart disease. Clin Genet. 1978 Feb;13(2):233–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1978.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholzer C., Hallman D. M., Saha N., Sigurdsson G., Lackner C., Császár A., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):607–614. doi: 10.1007/BF00201550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. S., Schreffler D. C., Sing C. F., Harvie N. R. The genetics of the Lp antigen. I. Its quantitation and distribution in a sample population. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;38(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed M., Hoppichler F., Reaveley D., McCarthy S., Thompson G. R., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Relation of serum lipoprotein(a) concentration and apolipoprotein(a) phenotype to coronary heart disease in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 24;322(21):1494–1499. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005243222104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Schultz J. S., Shreffler D. C. The genetics of the Lp antigen. II. A family study and proposed models of genetic control. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;38(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Gendler S., Griffiths B., Corney G., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Bramwell M. E. The human tumour-associated epithelial mucins are coded by an expressed hypervariable gene locus PUM. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):82–84. doi: 10.1038/328082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Duba C., Menzel H. J. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):47–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00291233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hopferwieser T., Seitz C. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of LP(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00291232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):904–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2530631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L. Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90195-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., Guttormsen S. A., Schultz J. S. Linkage between the loci for the Lp(a) lipoprotein (LP) and plasminogen (PLG). Hum Genet. 1988 May;79(1):80–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00291716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. K., Nakamura Y., White R. Molecular characterization of a spontaneously generated new allele at a VNTR locus: no exchange of flanking DNA sequence. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenker G., Költringer P., Boné G., Niederkorn K., Pfeiffer K., Jürgens G. Lipoprotein(a) as a strong indicator for cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 1986 Sep-Oct;17(5):942–945. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.5.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








