Abstract
Recent experimental data have revealed that activins and inhibins exert pivotal effects on development. As part of our studies on growth and differentiation of the human fetal adrenal gland, we examined the subunit localization, as well as the mitogenic and steroidogenic actions of activin and inhibin in human fetal and adult adrenals. All three activin and inhibin subunit proteins (alpha, beta A, and beta B) were detected in the fetal and adult adrenal cortex. Immunoreactive activin-A dimer was demonstrated in midgestation fetal and neonatal adrenals. ACTH1-24-stimulated fetal adrenal cell expression of alpha and beta A subunit messenger RNA. In addition, ACTH elicited a rise in levels of immunoreactive alpha subunit secreted by fetal and adult adrenal cells. Human recombinant activin-A inhibited mitogenesis and enhanced ACTH-stimulated cortisol secretion by cultured fetal zone cells, but not definitive zone or adult adrenal cells. Recombinant inhibin-A had no apparent mitogenic or steroidogenic effects. Thus, activin selectively suppressed fetal zone proliferation and enhanced the ACTH-induced shift in the cortisol/dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate ratio of fetal zone steroid production. These data indicate that activin-A may be an autocrine or paracrine factor regulated by ACTH, involved in modulating growth and differentiated function of the human fetal adrenal gland.
Full text
PDF

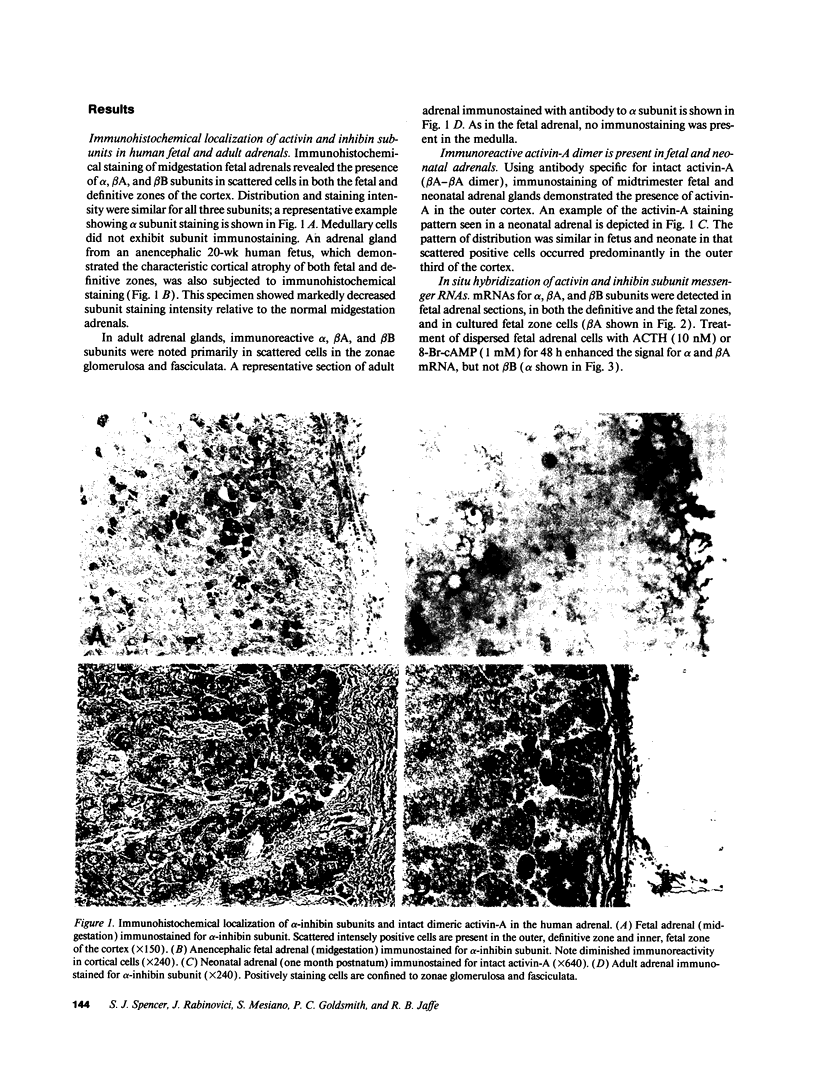
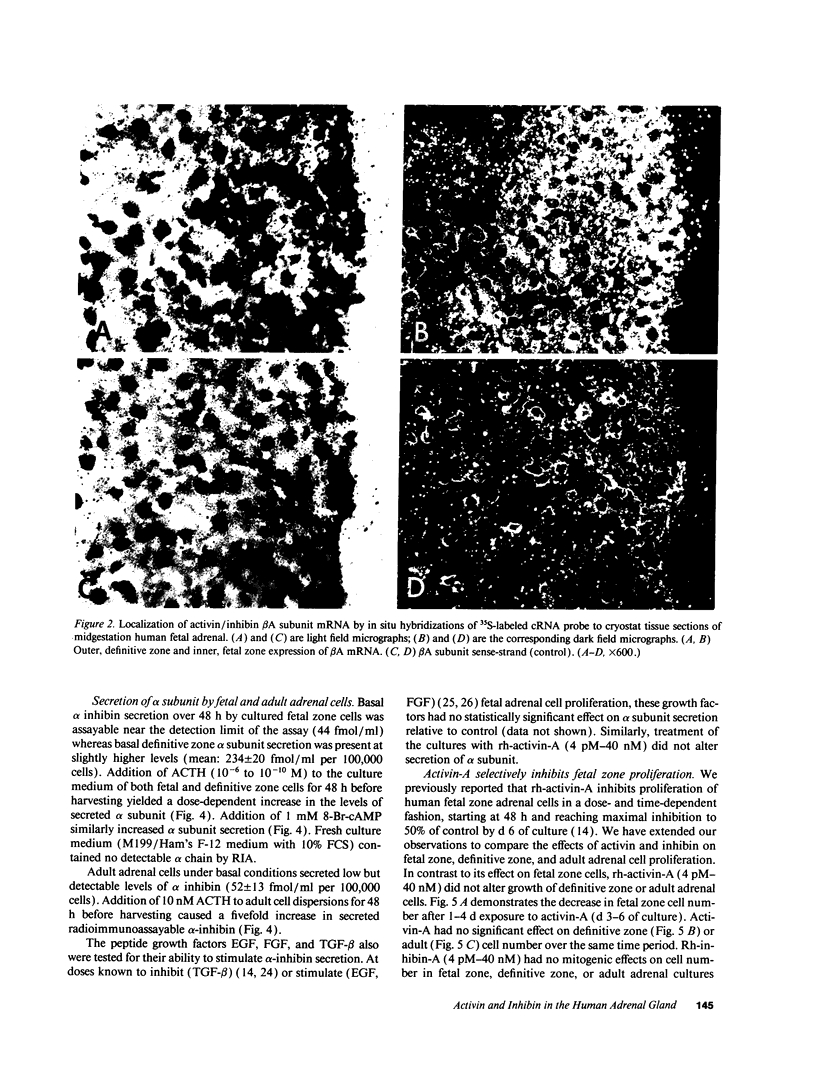




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilezikjian L. M., Corrigan A. Z., Vale W. Activin-A modulates growth hormone secretion from cultures of rat anterior pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5):2369–2376. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-5-2369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Lu L., Cooper S., Schwall R. H., Mason A. J., Nikolics K. Selective and indirect modulation of human multipotential and erythroid hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation by recombinant human activin and inhibin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9052–9056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. J., Hammond V. E., Evans B. A., Coghlan J. P., Haralambidis J., Hudson B., Penschow J. D., Richards R. I., Tregear G. W. Alpha-inhibin gene expression occurs in the ovine adrenal cortex, and is regulated by adrenocorticotropin. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Oct;1(10):699–706. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-10-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crickard K., Ill C. R., Jaffe R. B. Control of proliferation of human fetal adrenal cells in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Oct;53(4):790–796. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-4-790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Z. M., Li Y. P., Chen C. L. Analysis of the 5'-flanking regions of rat inhibin alpha- and beta-B-subunit genes suggests two different regulatory mechanisms. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1914–1925. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-1914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. K., Sai X., Shukovski L. Role of inhibin-related peptides as intragonadal regulators. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1990;2(3):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh A. J., Dahl K. D., Vaughan J., Tucker E., Rivier J., Bardin C. W., Vale W. Heterodimers and homodimers of inhibin subunits have different paracrine action in the modulation of luteinizing hormone-stimulated androgen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5082–5086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koritnik D. R., Laherty R. F., Rotten D., Jaffe R. B. A radioimmunoassay for dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in the circulation of rhesus monkeys. Steroids. 1983 Dec;42(6):653–667. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(83)90129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPolt P. S., Soto D., Su J. G., Campen C. A., Vaughan J., Vale W., Hsueh A. J. Activin stimulation of inhibin secretion and messenger RNA levels in cultured granulosa cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1666–1673. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Ying S. Y., Ueno N., Shimasaki S., Esch F., Hotta M., Guillemin R. A homodimer of the beta-subunits of inhibin A stimulates the secretion of pituitary follicle stimulating hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1129–1137. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C., Bald L. N., Fendly B. M., Mora-Worms M., Figari I. S., Patzer E. J., Palladino M. A. The autocrine production of transforming growth factor-beta 1 during lymphocyte activation. A study with a monoclonal antibody-based ELISA. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan R. I., Robertson D. M., de Kretser D., Burger H. G. Inhibin--a non-steroidal regulator of pituitary follicle stimulating hormone. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Feb;1(1):89–112. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(87)80054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty W. P., Novy M. J., Walsh S. W. Fetal and postnatal development of the adrenal glands in Macaca mulatta. Biol Reprod. 1981 Dec;25(5):1079–1089. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.5.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesiano S., Mellon S. H., Gospodarowicz D., Di Blasio A. M., Jaffe R. B. Basic fibroblast growth factor expression is regulated by corticotropin in the human fetal adrenal: a model for adrenal growth regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5428–5432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier H., Cajander S. B., Roberts V. J., Rivier C., Sawchenko P. E., Hsueh A. J., Vale W. Rapid changes in the expression of inhibin alpha-, beta A-, and beta B-subunits in ovarian cell types during the rat estrous cycle. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1352–1363. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier H., Rivier C., Evans R. M., Vale W. Gonadal and extragonadal expression of inhibin alpha, beta A, and beta B subunits in various tissues predicts diverse functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell B. F., Serón-Ferré M., Jaffe R. B. Cortisol-cortisone interrelationship in the late gestation rhesus monkey fetus in utero. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1837–1842. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsick R. A. Human fetal extremity lengths in the interval from 9 to 21 menstrual weeks of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Aug 15;149(8):883–887. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(84)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petraglia F., Vaughan J., Vale W. Inhibin and activin modulate the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin, and progesterone from cultured human placental cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5114–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riopel L., Branchaud C. L., Goodyer C. G., Adkar V., Lefebvre Y. Growth-inhibitory effect of TGF-B on human fetal adrenal cells in primary monolayer culture. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):233–238. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Flanders K. C., Kondaiah P., Thompson N. L., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Wakefield L., Rossi P., de Crombrugghe B., Heine U., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta: biochemistry and roles in embryogenesis, tissue repair and remodeling, and carcinogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1988;44:157–197. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571144-9.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts V., Meunier H., Sawchenko P. E., Vale W. Differential production and regulation of inhibin subunits in rat testicular cell types. Endocrinology. 1989 Nov;125(5):2350–2359. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-5-2350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts V., Meunier H., Vaughan J., Rivier J., Rivier C., Vale W., Sawchenko P. Production and regulation of inhibin subunits in pituitary gonadotropes. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):552–554. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. M., Giacometti M., Foulds L. M., Lahnstein J., Goss N. H., Hearn M. T., de Kretser D. M. Isolation of inhibin alpha-subunit precursor proteins from bovine follicular fluid. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2141–2149. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneyer A. L., Mason A. J., Burton L. E., Ziegner J. R., Crowley W. F., Jr Immunoreactive inhibin alpha-subunit in human serum: implications for radioimmunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Apr;70(4):1208–1212. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-4-1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwall R. H., Nikolics K., Szonyi E., Gorman C., Mason A. J. Recombinant expression and characterization of human activin A. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1237–1242. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwall R., Schmelzer C. H., Matsuyama E., Mason A. J. Multiple actions of recombinant activin-A in vivo. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1420–1423. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serón-Ferré M., Lawrence C. C., Siiteri P. K., Jaffe R. B. Steroid production by definitive and fetal zones of the human fetal adrenal gland. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Sep;47(3):603–609. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-3-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. J., Rabinovici J., Jaffe R. B. Human recombinant activin-A inhibits proliferation of human fetal adrenal cells in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Dec;71(6):1678–1680. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-6-1678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucheston M. E., Cannon M. S. Development of zonular patterns in the human adrenal gland. J Morphol. 1968 Dec;126(4):477–491. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051260408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino K., Nakamura T., Takio K., Titani K., Miyamoto K., Hasegawa Y., Igarashi M., Sugino H. Inhibin alpha-subunit monomer is present in bovine follicular fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1323–1329. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen G., Woolf T., Whitman M., Sokol S., Vaughan J., Vale W., Melton D. A. Activins are expressed early in Xenopus embryogenesis and can induce axial mesoderm and anterior structures. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90445-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. M., Rivier J., Corrigan A. Z., McClintock R., Campen C. A., Jolley D., Voglmayr J. K., Bardin C. W., Rivier C., Vale W. Detection and purification of inhibin using antisera generated against synthetic peptide fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1989;168:588–617. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)68044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S. Y. Inhibins, activins, and follistatins: gonadal proteins modulating the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocr Rev. 1988 May;9(2):267–293. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Shao L. E., Lemas V., Yu A. L., Vaughan J., Rivier J., Vale W. Importance of FSH-releasing protein and inhibin in erythrodifferentiation. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):765–767. doi: 10.1038/330765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]