Abstract
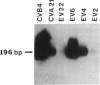
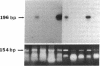
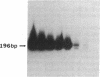
Enteroviruses have been considered to be a possible cause of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. We used a polymerase chain reaction methodology for the identification of enteroviral RNA in an attempt to provide evidence of a role for enteroviruses in the pathogenesis of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. The methodology was shown to identify a wide variety of enteroviruses with a sensitivity up to 0.1-1 plaque-forming units/gram of tissue. 5 of 11 cases (45%) of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy, as well as 9 of 24 cases (38%) of a wide variety of other cardiac conditions (including normal heart), were positive for enteroviral nucleic acid sequences; all eight control cases of breast carcinoma tested were negative. These results suggest that both the normal and abnormal heart may represent a site of latent or low-grade persistent enteroviral infection, and that the mere presence of enteroviral nucleic acid sequences is not specifically associated with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelmann W. H. Viral myocarditis and its sequelae. Annu Rev Med. 1973;24:145–152. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.24.020173.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aretz H. T., Billingham M. E., Edwards W. D., Factor S. M., Fallon J. T., Fenoglio J. J., Jr, Olsen E. G., Schoen F. J. Myocarditis. A histopathologic definition and classification. Am J Cardiovasc Pathol. 1987 Jan;1(1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ezra J., Johnson D. A., Rossi J., Cook N., Wu A. Effect of fixation on the amplification of nucleic acids from paraffin-embedded material by the polymerase chain reaction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):351–354. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1704393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge G., MacArthur C. G., Waterson A. P., Goodwin J. F., Oakley C. M. Antibodies to Coxsackie B viruses in congestive cardiomyopathy. Br Heart J. 1979 Jun;41(6):692–696. doi: 10.1136/hrt.41.6.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Tracy S., Gauntt C. J., Fortmueller U. Molecular detection and identification of enteroviruses using enzymatic amplification and nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.843-850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J., Gomez P. T., Duffey P. S., Grant J. A., Trent D. W., Witherspoon S. M., Paque R. E. Characterization and myocarditic capabilities of coxsackievirus B3 variants in selected mouse strains. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):598–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.598-605.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin O., Sole M. J., Butany J. W., Chia W. K., McLaughlin P. R., Liu P., Liew C. C. Detection of enterovirus RNA in myocardial biopsies from patients with myocarditis and cardiomyopathy using gene amplification by polymerase chain reaction. Circulation. 1990 Jul;82(1):8–16. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler S., Galili N., Sklar J. L., Donlon T. A., Blume K. G., Cleary M. L. Expression of bcr-abl fusion transcripts following bone marrow transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Leukemia. 1990 Aug;4(8):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngan B. Y., Nourse J., Cleary M. L. Detection of chromosomal translocation t(14;18) within the minor cluster region of bcl-2 by polymerase chain reaction and direct genomic sequencing of the enzymatically amplified DNA in follicular lymphomas. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1759–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. C., Ferrans V. J. Pathologic anatomy of the cardiomyopathies. Idiopathic dilated and hypertrophic types, infiltrative types, and endomyocardial disease with and without eosinophilia. Hum Pathol. 1975 May;6(3):287–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose N. R., Herskowitz A., Neumann D. A., Neu N. Autoimmune myocarditis: a paradigm of post-infection autoimmune disease. Immunol Today. 1988 Apr;9(4):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A., Eastman P. S., Ruth J. L., Hirata K. K., Levin M. J. Nonisotopic oligomeric probes for the human enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2669–2671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2669-2671.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Billingham M. E. Leukocytic infiltrates in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. A source of confusion with active myocarditis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Jun;10(6):405–412. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198606000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A., Billingham M. E., Cleary M. L. Detection of Coxsackievirus B3 RNA in myocardial tissues by the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):497–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]