Abstract
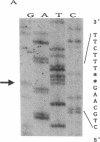
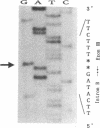
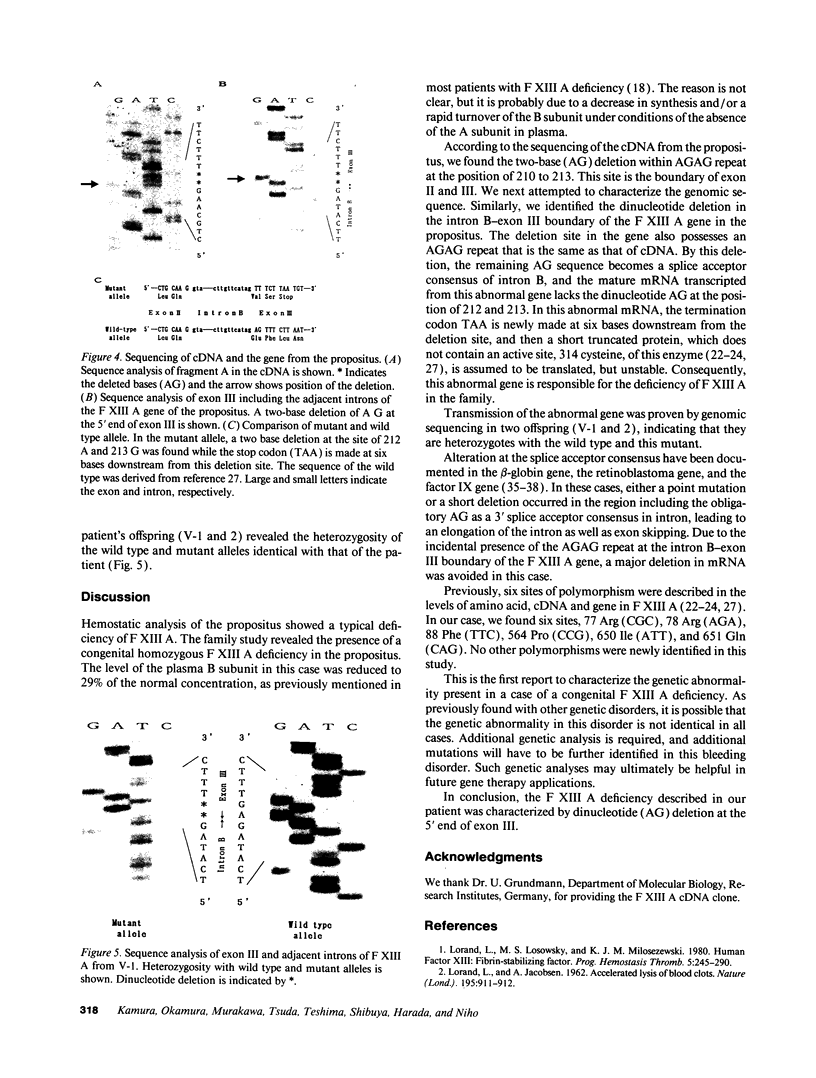
A congenital deficiency of the coagulation Factor XIII A subunit (F XIII A) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that is characterized by a life-long bleeding tendency complicated by a difficulty in healing. Thus far, no molecular genetic analysis of this disorder has been reported. In this study, we demonstrate the molecular abnormalities in a family with this disorder. We performed Northern blot analysis of peripheral blood monocytes obtained from the propositus and found a 4-kb single band of F XIII A mRNA whose size was identical with that of normal subjects. Exons II-XV, which encode all the amino acids, were individually amplified by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). All PCR products from the propositus had lengths indistinguishable from those of the wild type on agarose gel, suggesting that this defect results from either a point mutation or a short deletion/insertion. The sequencing of F XIII A cDNA from the propositus revealed a deletion of the dinucleotide AG within the AGAG repeat at the position of 210 to 213. Concerning the genomic sequence, a deletion of dinucleotide AG was also demonstrated in the intron B-exon III boundary. This deletion appeared to cause a frameshift mutation making a new stop codon shortly thereafter, and leading to a deficiency of plasma F XIII A. The heterozygosity of the F XIII A deficiency in the patient's offspring was documented by the nucleotide sequences of their exon III.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird M., Driscoll C., Schreiner H., Sciarratta G. V., Sansone G., Niazi G., Ramirez F., Bank A. A nucleotide change at a splice junction in the human beta-globin gene is associated with beta 0-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4218–4221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Board P. G., Webb G. C., McKee J., Ichinose A. Localization of the coagulation factor XIII A subunit gene (F13A) to chromosome bands 6p24----p25. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(1):25–27. doi: 10.1159/000132580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn H. Comparative studies on the fibrin-stabilizing factors from human plasma, platelets and placentas. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:256–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Scully P., Lee W. H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.2300823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I. Comparative studies on tissue transglutaminase and factor XIII. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:240–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Lewis M. S., Folk J. E. Relationships of the catalytic properties of human plasma and platelet transglutaminases (activated blood coagulation factor XIII) to their subunit structures. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):940–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUCKERT F., JUNG E., SHMERLING D. H. A hitherto undescribed congenital haemorrhagic diathesis probably due to fibrin stabilizing factor deficiency. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Dec 15;5:179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Whitaker A. N. Fibrin crosslinks and lysis rates. Thromb Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Green P. M., High K. A., Sommer S., Lillicrap D. P., Ludwig M., Olek K., Reitsma P. H., Goossens M., Yoshioka A. Haemophilia B: database of point mutations and short additions and deletions--second edition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2193–2219. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolami A., Burul A., Fabris F., Cappellato G., Betterle C. Studies on factor XIII antigen in congenital factor XIII deficiency. A tentative classification of the disease in two groups. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1978;105(1):131–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann U., Amann E., Zettlmeissl G., Küpper H. A. Characterization of cDNA coding for human factor XIIIa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson P., Becker S., Lynch G., McDonagh J. Identification of intracellular factor XIII in human monocytes and macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):528–534. doi: 10.1172/JCI112002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Davie E. W. Characterization of the gene for the a subunit of human factor XIII (plasma transglutaminase), a blood coagulation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5829–5833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Hendrickson L. E., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Amino acid sequence of the a subunit of human factor XIII. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6900–6906. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiesselbach T. H., Wagner R. H. Demonstration of factor XIII in human megakaryocytes by a fluorescent antibody technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:318–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopaciuk S., Lovette K. M., McDonagh J., Chuang H. Y., McDonagh Subcellular distribution of fibrinogen and factor XIII in human blood platelets. Thromb Res. 1976 Apr;8(4):453–465. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90223-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Losowsky M. S., Miloszewski K. J. Human factor XIII: fibrin-stabilizing factor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:245–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D. Immunologic studies of proteins associated with subcellular fractions of normal human platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):651–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida Y., Ikematsu S., Fukutake K., Fujimaki M., Fukutake K., Kakishita E. A new rapid and simple assay for factor XIII activity using dansylcadaverine incorporation and gel filtration. Thromb Res. 1984 Oct 15;36(2):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon M. C., Russell J. A., Low S., Sinclair G. D., Jones A. R., Blahey W., Ruether B. A., Hoar D. I. Hemopoietic origin of factor XIII A subunits in platelets, monocytes, and plasma. Evidence from bone marrow transplantation studies. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):787–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. W., Lorand L., Mockros L. F. Viscoelastic properties of fibrin clots. Biorheology. 1973 Mar;10(1):29–42. doi: 10.3233/bir-1973-10105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Asakura H., Yoshida T., Ito K., Okafuji K., Yoshida T., Matsuda T. A familial factor XIII subunit B deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1990 Mar;74(3):290–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Lorand L. Contribution of fibrin stabilization to clot strength. Supplementation of factor XIII-deficient plasma with the purified zymogen. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1336–1341. doi: 10.1172/JCI110885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of blood coagulation factor XIIIa (fibrinoligase, transglutaminase) from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8019–8023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg L. J., Shiu D. T., Conkling P. R., Shuman M. A. Identification of normal human peripheral blood monocytes and liver as sites of synthesis of coagulation factor XIII a-chain. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):579–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg L. J., Shiu D. T., Greenberg C. S., Kan Y. W., Shuman M. A. Localization of the gene for coagulation factor XIII a-chain to chromosome 6 and identification of sites of synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):649–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI112862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölpl A., Lattke H., Board P. G., Arnold R., Schmeiser T., Kubanek B., Robin-Winn M., Pichelmayr R., Goldmann S. F. Coagulation factor XIII A and B subunits in bone marrow and liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1987 Jan;43(1):151–153. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198701000-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]