Abstract
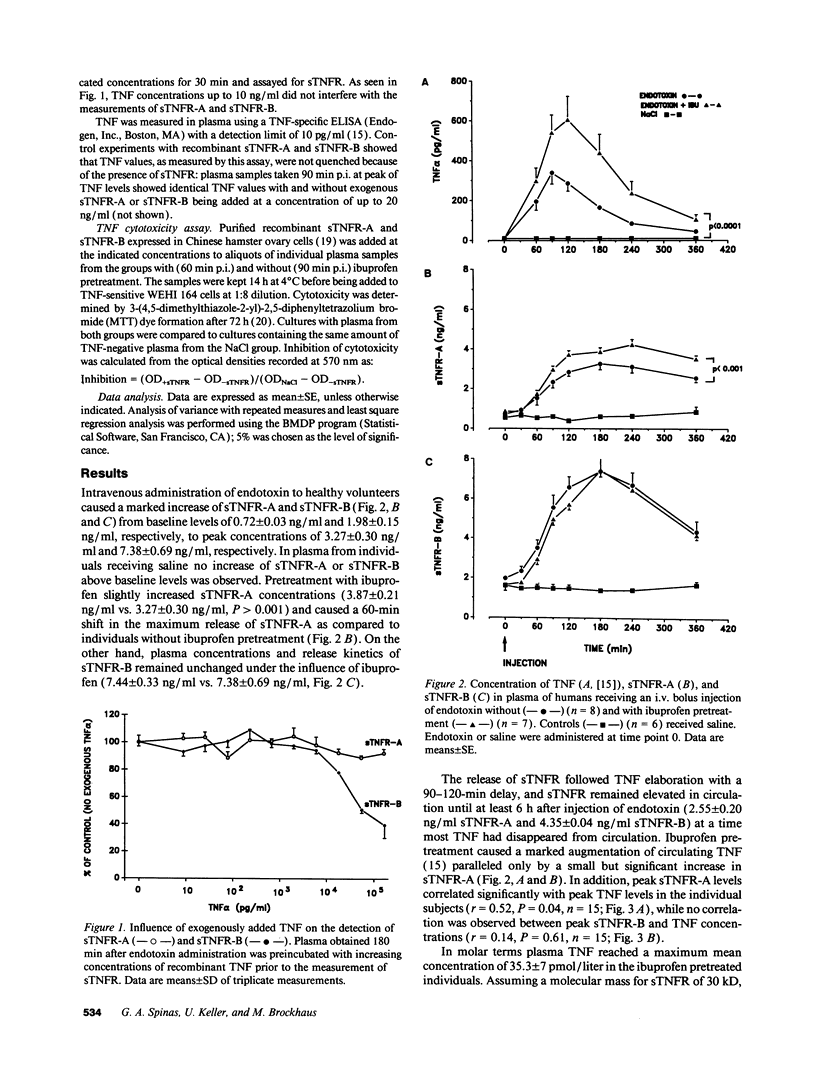
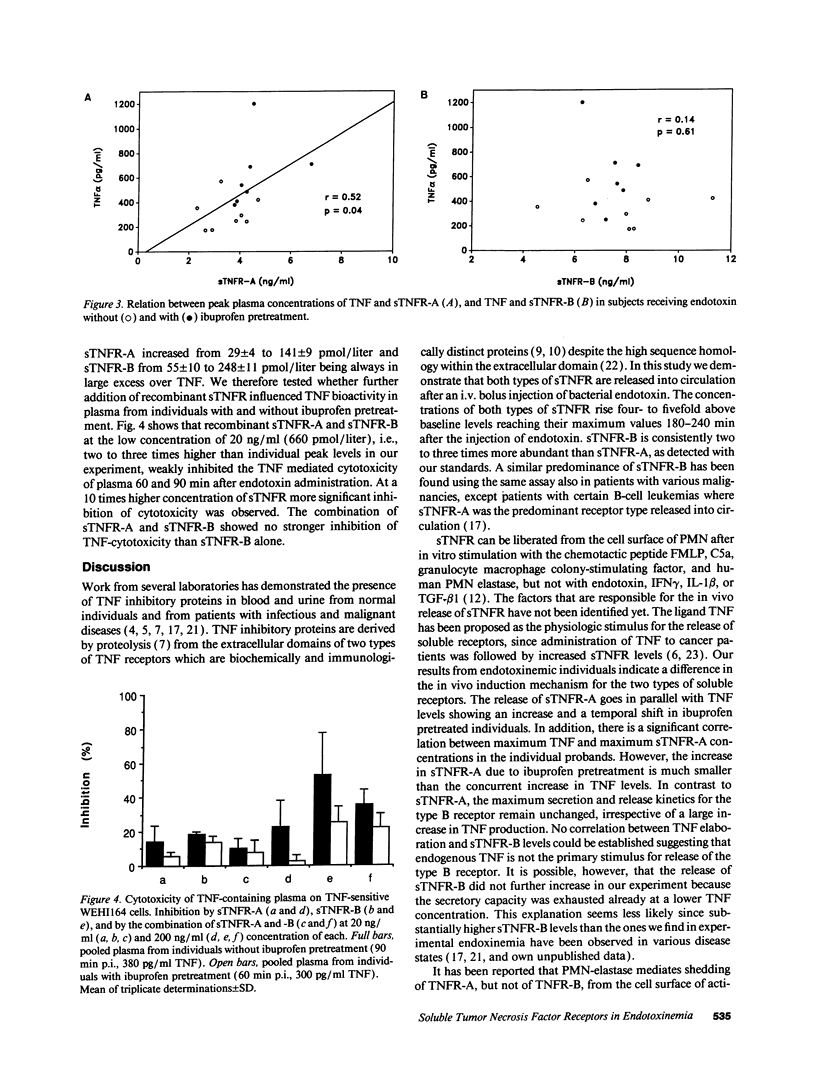
Serial plasma samples from human volunteers obtained after intravenous administration of Escherichia coli endotoxin were analyzed for the presence of circulating soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors (sTNFR). A four- to fivefold increase of type A (p75) and type B (p55) sTNFR was observed 3 h after endotoxin challenge. Pretreatment of the volunteers with ibuprofen before the injection of endotoxin resulted in a slight increase (3.87 +/- 0.2 vs. 3.27 +/- 0.3 ng/ml) and temporal shift of sTNFR-A release concurrent to a marked augmentation of TNF levels (603 +/- 118 vs. 338 +/- 56 pg/ml) as compared to the group without ibuprofen pretreatment. There was a significant correlation between peak sTNFR-A levels and peak TNF levels in the individual probands (r = 0.52, P = 0.04). On the contrary, release kinetics and plasma concentrations of sTNFR-B were identical in both groups (7.38 +/- 0.69 vs. 7.44 +/- 0.33 ng/ml) and no correlation with individual TNF levels was observed. The amount of sTNFR liberated upon endotoxin challenge was not sufficient to block TNF-mediated cytotoxic effects. Our data indicate that the release in vivo of type A and type B sTNFR upon a short exposure to endotoxin is regulated differently.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Englemann H., Hornik V., Skornick Y., Levo Y., Wallach D., Kushtai G. Increased serum levels of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 15;51(20):5602–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembic Z., Loetscher H., Gubler U., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Lesslauer W. Two human TNF receptors have similar extracellular, but distinct intracellular, domain sequences. Cytokine. 1990 Jul;2(4):231–237. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90022-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digel W., Porzsolt F., Schmid M., Herrmann F., Lesslauer W., Brockhaus M. High levels of circulating soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor in hairy cell leukemia and type B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1690–1693. doi: 10.1172/JCI115769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberts I., Stephens S., Francot G. J., van der Linden C. J., Buurman W. A. Evidence for different effects of soluble TNF-receptors on various TNF measurements in human biological fluids. Lancet. 1991 Aug 24;338(8765):515–516. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90591-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Novick D., Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Brockhaus M., Baeuerle P. A., Remy R., Kolbeck R., van Loon A. P. Expression of the types A and B tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors is independently regulated, and both receptors mediate activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B. TNF alpha is not needed for induction of a biological effect via TNF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22409–22417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Brockhaus M., van Loon A. P. Two different cell types have different major receptors for human tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14927–14934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Brewer M. T., Baker S. L., Schwartz P. E., King M. W., Hale K. K., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Vannice J. L. A second tumor necrosis factor receptor gene product can shed a naturally occurring tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8331–8335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C., DeFay K., Albert I., Lu S. D. A novel form of TNF/cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Malik S., Slevin M. L., Olsson I. Infusion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) causes an increase in circulating TNF-binding protein in humans. Cytokine. 1990 Nov;2(6):402–406. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Gentz R., Zulauf M., Lustig A., Tabuchi H., Schlaeger E. J., Brockhaus M., Gallati H., Manneberg M., Lesslauer W. Recombinant 55-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor. Stoichiometry of binding to TNF alpha and TNF beta and inhibition of TNF activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18324–18329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martich G. D., Danner R. L., Ceska M., Suffredini A. F. Detection of interleukin 8 and tumor necrosis factor in normal humans after intravenous endotoxin: the effect of antiinflammatory agents. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1021–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck R., Brockhaus M., Frey J. R. Cell surface tumor necrosis factor (TNF) accounts for monocyte- and lymphocyte-mediated killing of TNF-resistant target cells. Cell Immunol. 1989 Aug;122(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Olsson I. A tumor necrosis factor binding protein is present in human biological fluids. Eur J Haematol. 1988 Nov;41(5):414–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1988.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Brockhaus M., Wallach D., Engelmann H., Nathan C. F. Human neutrophil elastase releases a ligand-binding fragment from the 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor. Comparison with the proteolytic activity responsible for shedding of TNF receptors from stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18846–18853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Nathan C. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptors by activated human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel B., Brockhaus M., Dürmüller U., Gudat F. Tumor necrosis factor receptors in lymphoid tissues and lymphomas. Source and site of action of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):7–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. A human inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1511–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Bloesch D., Kaufmann M. T., Keller U., Dayer J. M. Induction of plasma inhibitors of interleukin 1 and TNF-alpha activity by endotoxin administration to normal humans. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):R993–R997. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.5.R993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Bloesch D., Keller U., Zimmerli W., Cammisuli S. Pretreatment with ibuprofen augments circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and elastase during acute endotoxinemia. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):89–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



