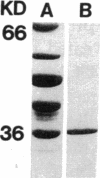
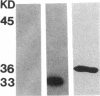
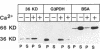
Abstract
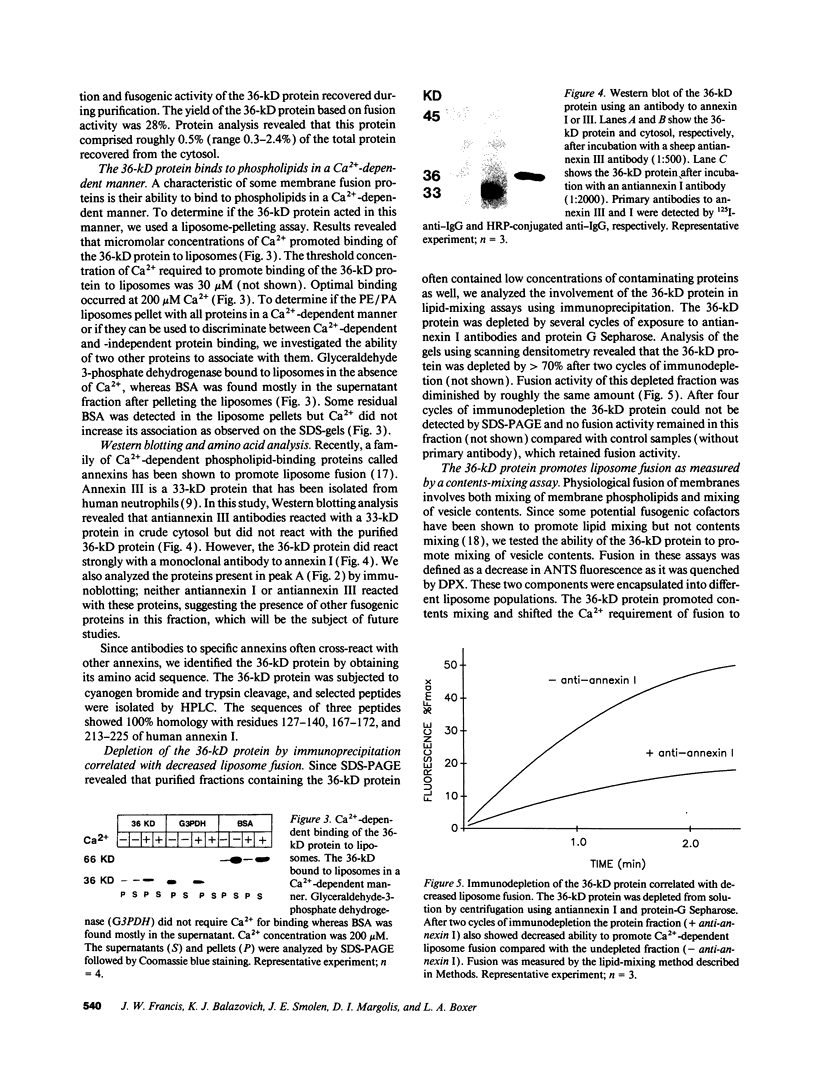
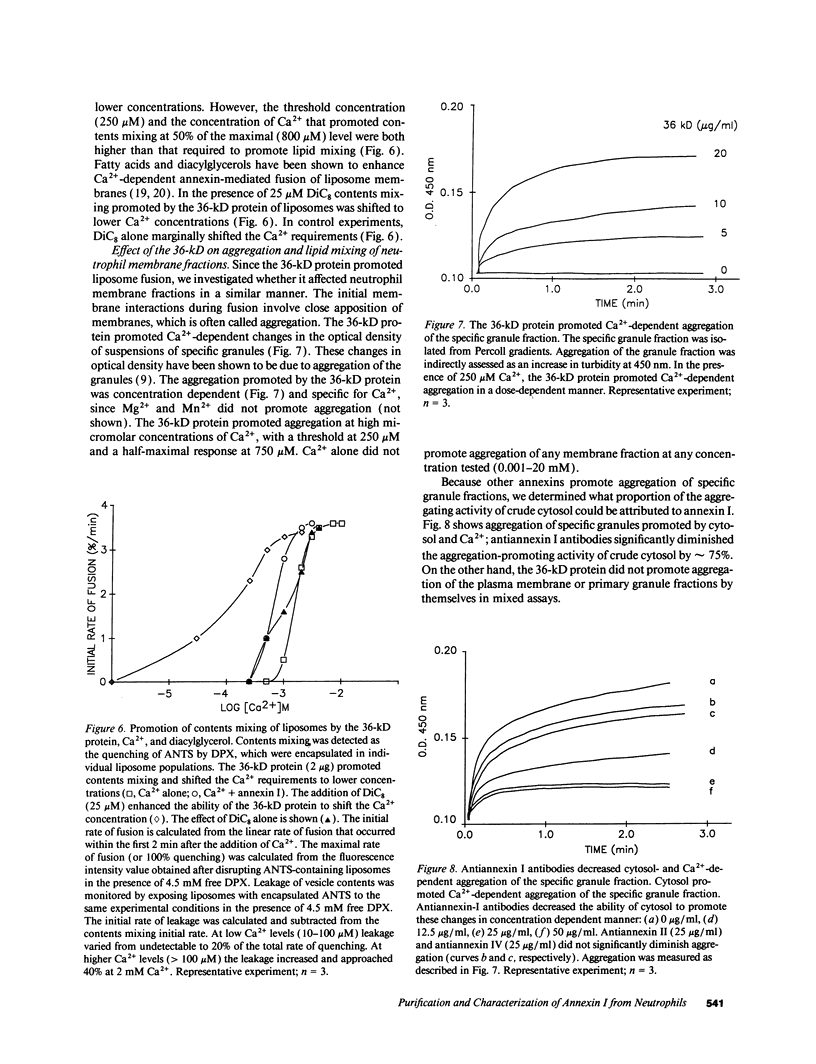
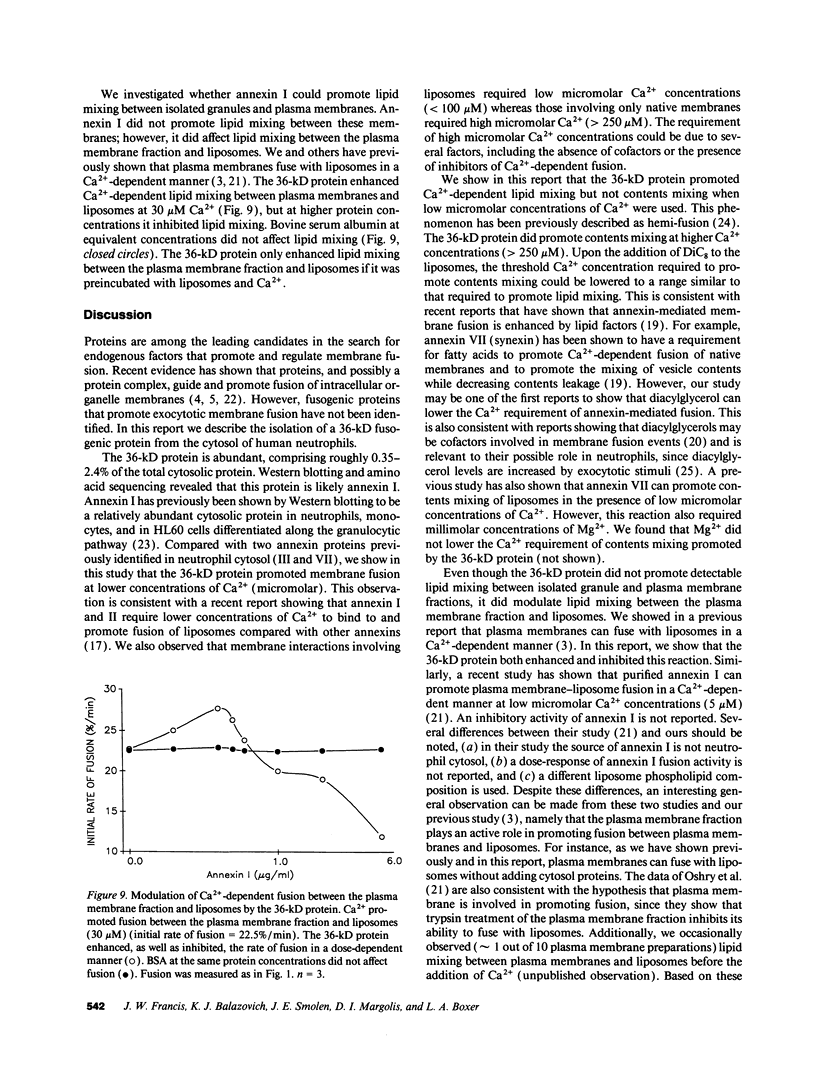
The mechanism and cofactor requirements of exocytotic membrane fusion in neutrophils are unknown. Cytosolic proteins have been implicated in membrane fusion events. We assessed neutrophil cytosol for the presence of fusogenic proteins using a liposome fusion assay (lipid mixing). A fusogenic 36-kD protein containing amino acid sequence homology with human annexin I was purified from the cytosol of human neutrophils. This protein also shared functional characteristics with annexin I: it associated with and promoted lipid mixing of liposomes in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner at micromolar Ca2+ concentrations. The 36-kD protein required diacylglycerol to promote true fusion (contents mixing) at the same Ca2+ concentrations used for lipid mixing. The 36-kD protein exhibited a biphasic dose-response curve, by both promoting and inhibiting Ca(2+)-dependent lipid-mixing between liposomes and a plasma membrane fraction. The 36-kD protein also promoted Ca(2+)-dependent increases in aggregation of a specific granule fraction, as measured by a turbidity increase. Antiannexin I antibodies depleted the 36-kD protein from the cytosol by greater than 70% and diminished its ability to promote lipid mixing. Antiannexin I antibodies also decreased by greater than 75% the ability of neutrophil cytosol to promote Ca(2+)-dependent aggregation of the specific granules. These data suggest that annexin I may be involved in aggregation and fusion events in neutrophils.
Full text
PDF

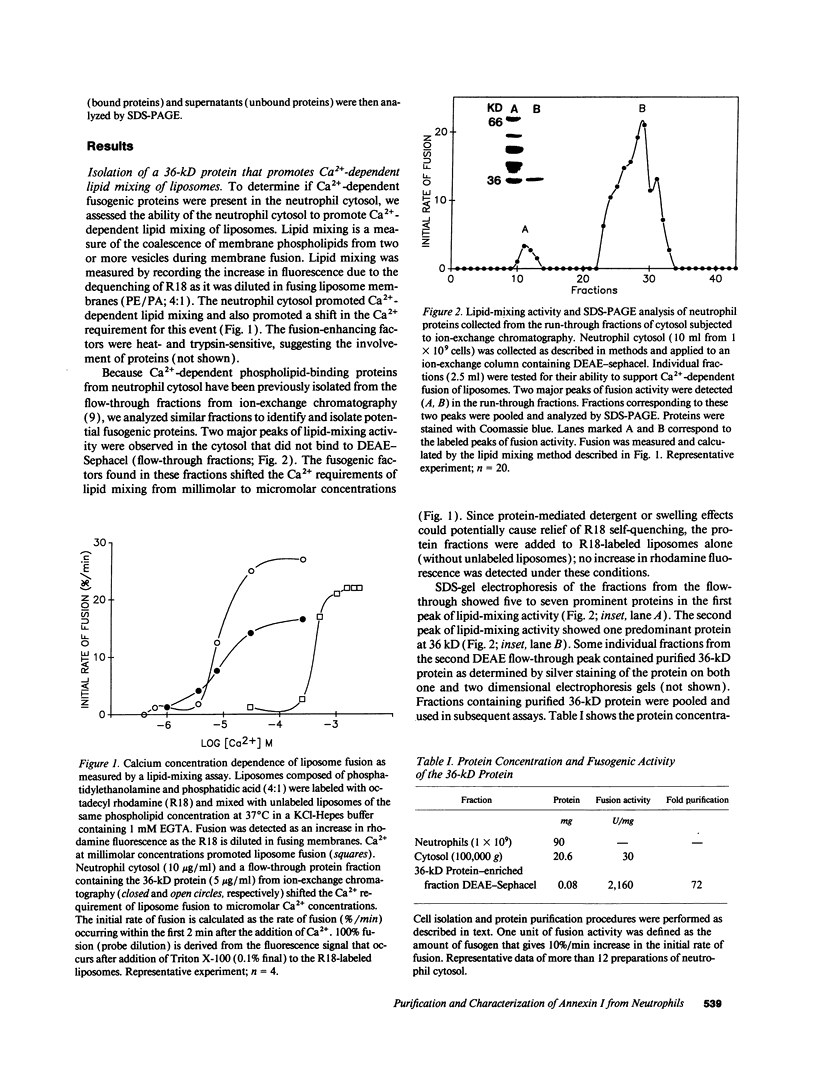


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agwu D. E., McPhail L. C., Chabot M. C., Daniel L. W., Wykle R. L., McCall C. E. Choline-linked phosphoglycerides. A source of phosphatidic acid and diglycerides in stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1405–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. A simple method for the accurate determination of free [Ca] in Ca-EGTA solutions. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C404–C408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood R. A., Ernst J. D. Characterization of Ca2(+)-dependent phospholipid binding, vesicle aggregation and membrane fusion by annexins. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj2660195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess S. W., Massenburg D., Yates J., Lentz B. R. Poly(ethylene glycol)-induced lipid mixing but not fusion between synthetic phosphatidylcholine large unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4193–4200. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. D. Annexin III translocates to the periphagosomal region when neutrophils ingest opsonized yeast. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3110–3114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. D., Hoye E., Blackwood R. A., Jaye D. Purification and characterization of an abundant cytosolic protein from human neutrophils that promotes Ca2(+)-dependent aggregation of isolated specific granules. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1065–1071. doi: 10.1172/JCI114537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis J. W., Smolen J. E., Balazovich K. J., Sandborg R. R., Boxer L. A. Calcium-dependent fusion of the plasma membrane fraction from human neutrophils with liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 11;1025(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90183-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaconi M. E., Lew D. P., Carpentier J. L., Magnusson K. E., Sjögren M., Stendahl O. Cytosolic free calcium elevation mediates the phagosome-lysosome fusion during phagocytosis in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1555–1564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Naemura J. R., Painter R. G., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G. Intracellular localization of N-formyl chemotactic receptor and Mg2+ dependent ATPase in human granulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 17;719(3):556–568. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers P., Bentz J., Alford D., Nir S., Papahadjopoulos D., Hong K. Synexin enhances the aggregation rate but not the fusion rate of liposomes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4430–4439. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers P., Ernst J. D., Düzgünes N., Hong K. L., Fedor J., Goldstein I. M., Papahadjopoulos D. Synexin-like proteins from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Identification and characterization of granule-aggregating and membrane-fusing activities. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7850–7858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers P., Hong K., Papahadjopoulos D. Free fatty acid enhancement of cation-induced fusion of liposomes: synergism with synexin and other promoters of vesicle aggregation. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6784–6794. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshry L., Meers P., Mealy T., Tauber A. I. Annexin-mediated membrane fusion of human neutrophil plasma membranes and phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1066(2):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90192-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner H. Regulation of membrane fusion during exocytosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1989;119:197–286. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60652-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Movement of proteins through the Golgi stack: a molecular dissection of vesicular transport. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1460–1468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer D. W., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L. Intracellular free calcium localization in neutrophils during phagocytosis. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):663–666. doi: 10.1126/science.4048951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Characterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding and phosphorylation of lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6931–6937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. P., Banschbach J., Alford D., Ellens H., Lis L. J., Quinn P. J., Yeagle P. L., Bentz J. Physiological levels of diacylglycerols in phospholipid membranes induce membrane fusion and stabilize inverted phases. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3703–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song L. Y., Ahkong Q. F., Georgescauld D., Lucy J. A. Membrane fusion without cytoplasmic fusion (hemi-fusion) in erythrocytes that are subjected to electrical breakdown. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 31;1065(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg B. W., Balch W. E., Rothman J. E. A novel prefusion complex formed during protein transport between Golgi cisternae in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg B. W., Rothman J. E. Multiple cytosolic components promote intra-Golgi protein transport. Resolution of a protein acting at a late stage, prior to membrane fusion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2208–2213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- William F., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S., Kraft A. S. Differentiation of HL-60 cells is associated with an increase in the 35-kDa protein lipocortin I. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Dec;137(3):402–410. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]