Abstract
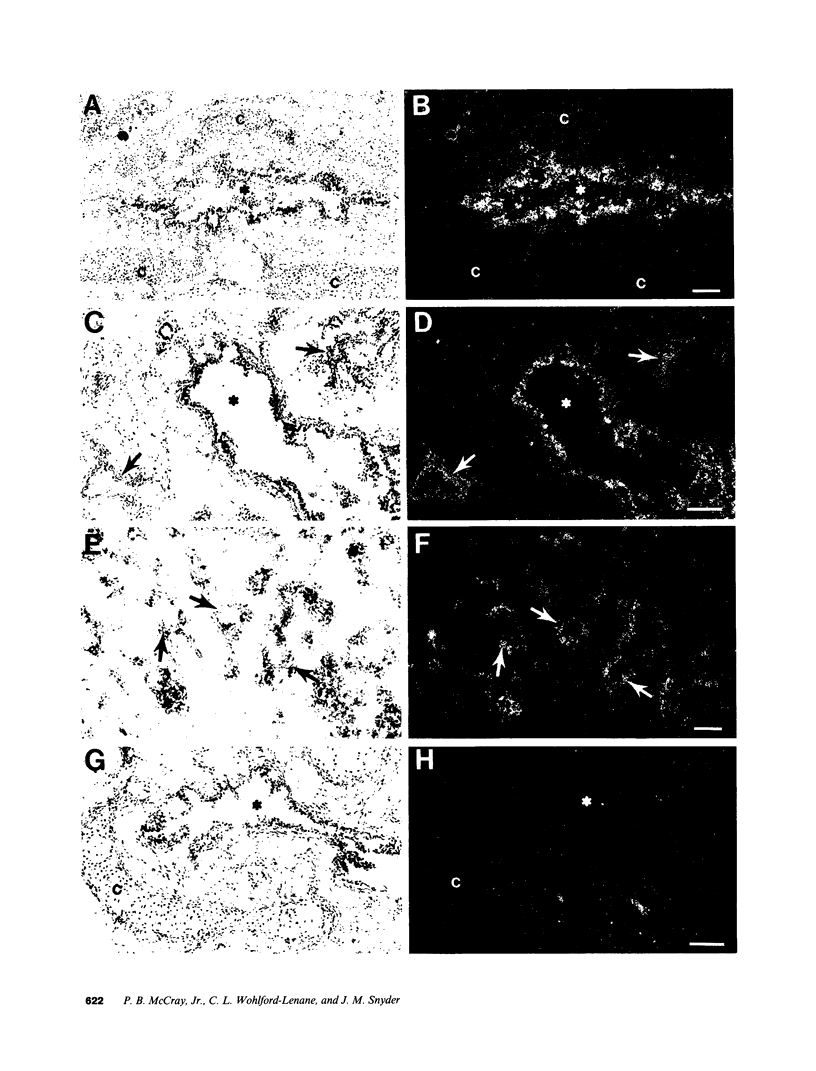
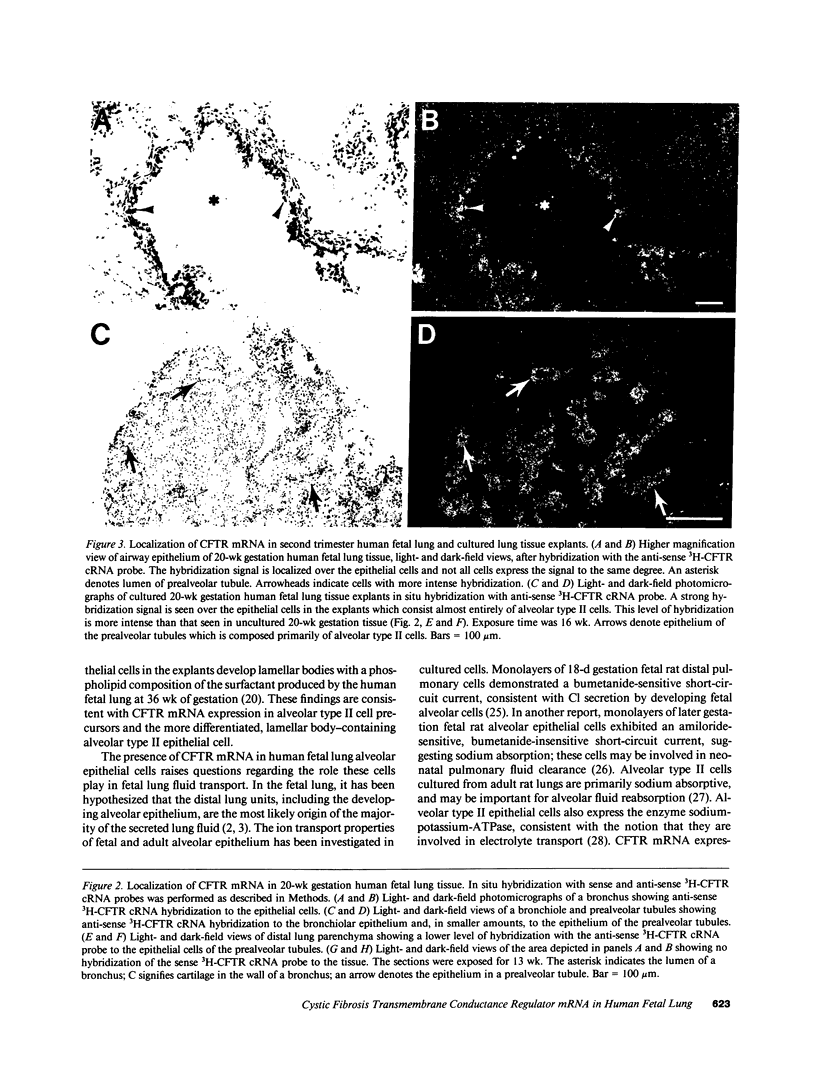
The fetal pulmonary epithelium secretes fluid. Cl transport is presumed to provide the driving force for net fluid secretion, although the cellular mechanisms have not been well identified in the fetus. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a cAMP- and nucleoside triphosphate-regulated Cl channel; mutations in CFTR cause cystic fibrosis. We hypothesized that if CFTR is involved in fetal lung fluid transport, the fetal pulmonary epithelium should express CFTR mRNA. We used the technique of in situ hybridization with 3H-anti-sense and, as a control, 3H-sense CFTR cRNA probes to localize CFTR mRNA in human fetal lung tissue and cultured lung explants and determine when in gestation it is expressed. Epithelial cells of both first and second trimester lung tissues expressed CFTR mRNA. A decreasing gradient of CFTR mRNA expression was present from the proximal to the distal pulmonary epithelium. Cultured second trimester lung tissue explants expressed more CFTR mRNA than the uncultured starting tissue, suggesting CFTR gene expression increased during the five days in culture. Furthermore, alveolar type II cells in cultured explants expressed CFTR mRNA, suggesting that these cells are Cl-secretory and may be involved in lung fluid transport. These data confirm that CFTR mRNA is expressed in the human fetal pulmonary epithelium, consistent with the Cl-secretory properties of the fetal lung.
Full text
PDF

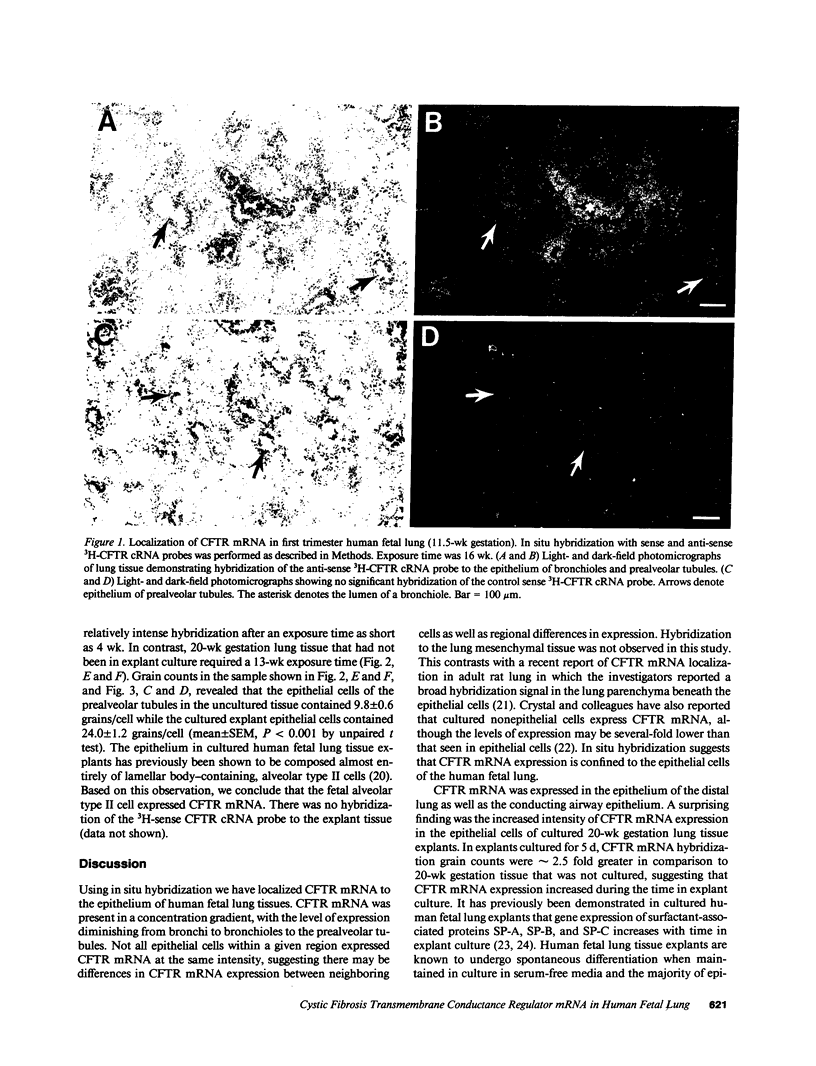


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcorn D., Adamson T. M., Lambert T. F., Maloney J. E., Ritchie B. C., Robinson P. M. Morphological effects of chronic tracheal ligation and drainage in the fetal lamb lung. J Anat. 1977 Jul;123(Pt 3):649–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. P., Berger H. A., Rich D. P., Gregory R. J., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Nucleoside triphosphates are required to open the CFTR chloride channel. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):775–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. P., Gregory R. J., Thompson S., Souza D. W., Paul S., Mulligan R. C., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Demonstration that CFTR is a chloride channel by alteration of its anion selectivity. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.1712984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Bookstein C., Vaandrager A., DeJonge H. R., Buse J., Musch M. W. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator mRNA expression relative to ion-nutrient transport in spontaneously differentiating human intestinal CaCo-2 epithelial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Oct;118(4):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow C. W., Landau L. I., Taussig L. M. Bronchial mucous glands in the newborn with cystic fibrosis. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Dec;139(4):240–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00442171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. A. Functions of the alveolar lining. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jun;115(6 Pt 2):67–71. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.S.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterly J. R., Oppenheimer E. H. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas: structural changes in peripheral airways. Thorax. 1968 Nov;23(6):670–675. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.6.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A., Chalkley G., Goodman S., Coleman L. Expression of the cystic fibrosis gene in human development. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):305–310. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., White R. T., Warr R. G., Benson B. J., Hawgood S., Ballard P. L. Regulation of messenger RNAs for the hydrophobic surfactant proteins in human lung. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1191–1197. doi: 10.1172/JCI114000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Widdicombe J. H., Sanders M. J., Misfeldt D. S., Berry L. C., Jr Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6033–6037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray P. B., Jr, Bettencourt J. D., Bastacky J. Developing bronchopulmonary epithelium of the human fetus secretes fluid. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):L270–L279. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.3.L270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray P. B., Jr, Reenstra W. W., Louie E., Johnson J., Bettencourt J. D., Bastacky J. Expression of CFTR and presence of cAMP-mediated fluid secretion in human fetal lung. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):L472–L481. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.4.L472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray P. B., Jr, Welsh M. J. Developing fetal alveolar epithelial cells secrete fluid in primary culture. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):L494–L500. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.6.L494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H., Rafii B., Post M. Bioelectric properties of fetal alveolar epithelial monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):L201–L206. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.4.L201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom M. J., Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate analogs and beta-adrenergic agonists induce the synthesis of the major surfactant apoprotein in human fetal lung in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1155–1163. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olver R. E., Strang L. B. Ion fluxes across the pulmonary epithelium and the secretion of lung liquid in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):327–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornoy A., Arnon J., Katznelson D., Granat M., Caspi B., Chemke J. Pathological confirmation of cystic fibrosis in the fetus following prenatal diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):935–947. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinton P. M. Cystic fibrosis: a disease in electrolyte transport. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2709–2717. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.2197151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. K., Cott G. R. Ontogeny of ion transport across fetal pulmonary epithelial cells in monolayer culture. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):L178–L187. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.261.2.L178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., McCarthy K. M. Cytochemical localization of Na+-K+-ATPase in rat type II pneumocytes. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 May;60(5):1584–1589. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.5.1584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Johnston J. M., Mendelson C. R. Differentiation of type II cells of human fetal lung in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(1):17–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00209962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R. Insulin inhibits the accumulation of the major lung surfactant apoprotein in human fetal lung explants maintained in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1250–1257. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strang L. B. Fetal lung liquid: secretion and reabsorption. Physiol Rev. 1991 Oct;71(4):991–1016. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.4.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeifert G. T., Szabó M., Papp Z. Morphology of cystic fibrosis at 17 weeks of gestation. Clin Genet. 1985 Dec;28(6):561–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAIDIS T. S., AREY J. B. THE INTESTINAL LESIONS IN CYSTIC FIBROSIS OF THE PANCREAS. J Pediatr. 1963 Sep;63:444–453. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trezise A. E., Buchwald M. In vivo cell-specific expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):434–437. doi: 10.1038/353434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valman H. B., France N. E. The vas deferens in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1969 Sep 13;2(7620):566–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90263-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Gil J. Electron microscopic demonstration of an extracellular duplex lining layer of alveoli. Respir Physiol. 1968 Jan;4(1):42–57. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(68)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlford-Lenane C. L., Durham P. L., Snyder J. M. Localization of surfactant-associated protein C (SP-C) mRNA in fetal rabbit lung tissue by in situ hybridization. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Feb;6(2):225–234. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/6.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Nakamura H., Trapnell B. C., Chu C. S., Dalemans W., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene in cells of non-epithelial origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5417–5423. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]