Abstract
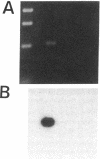
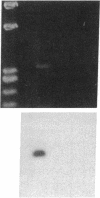
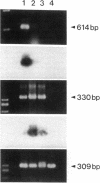
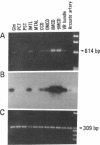
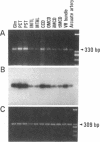
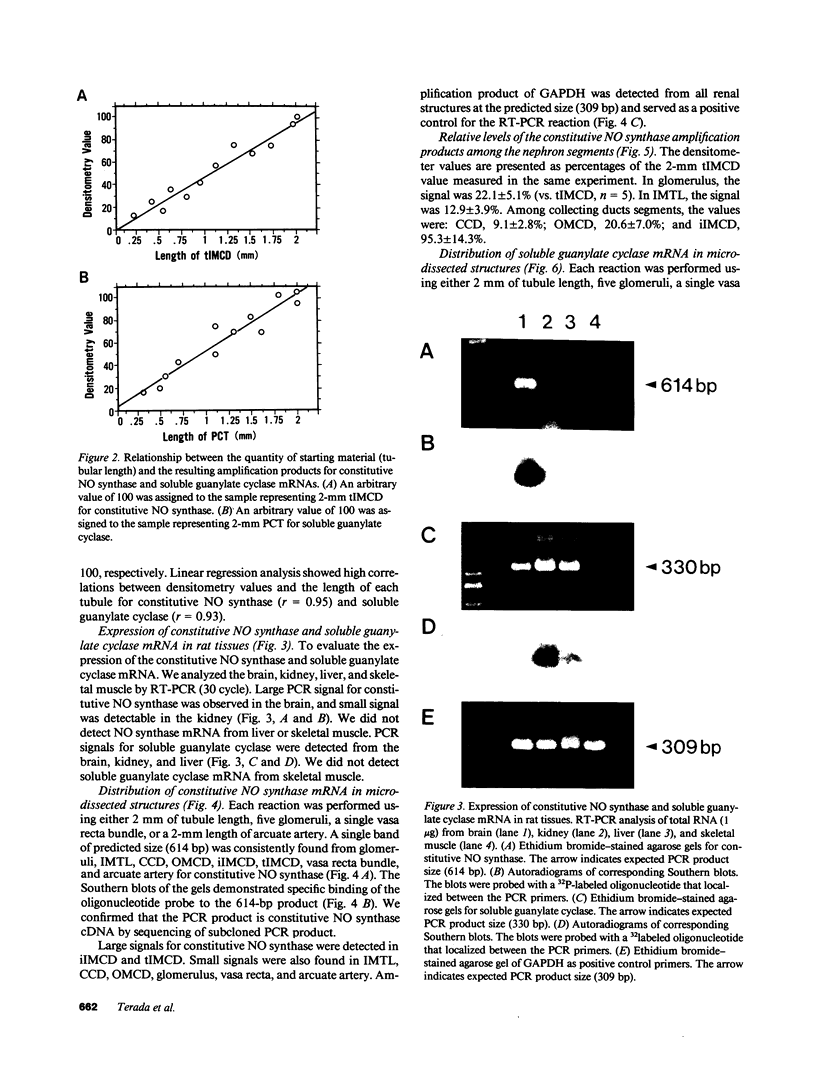
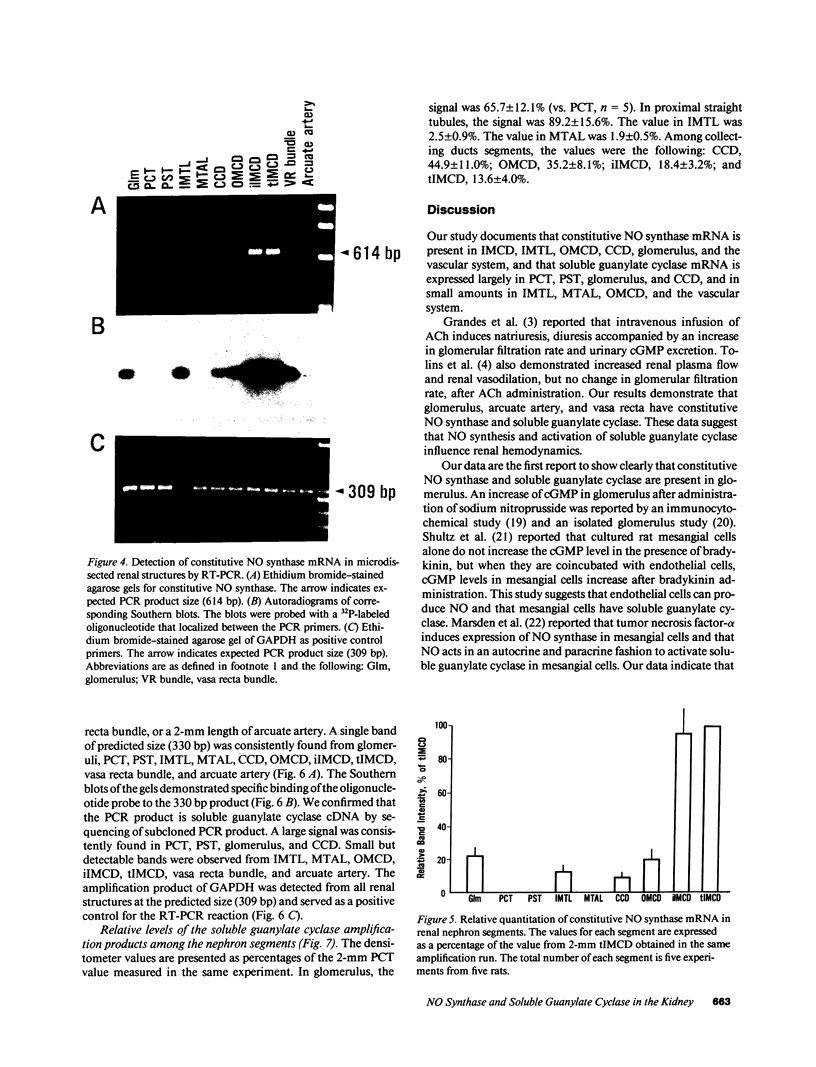
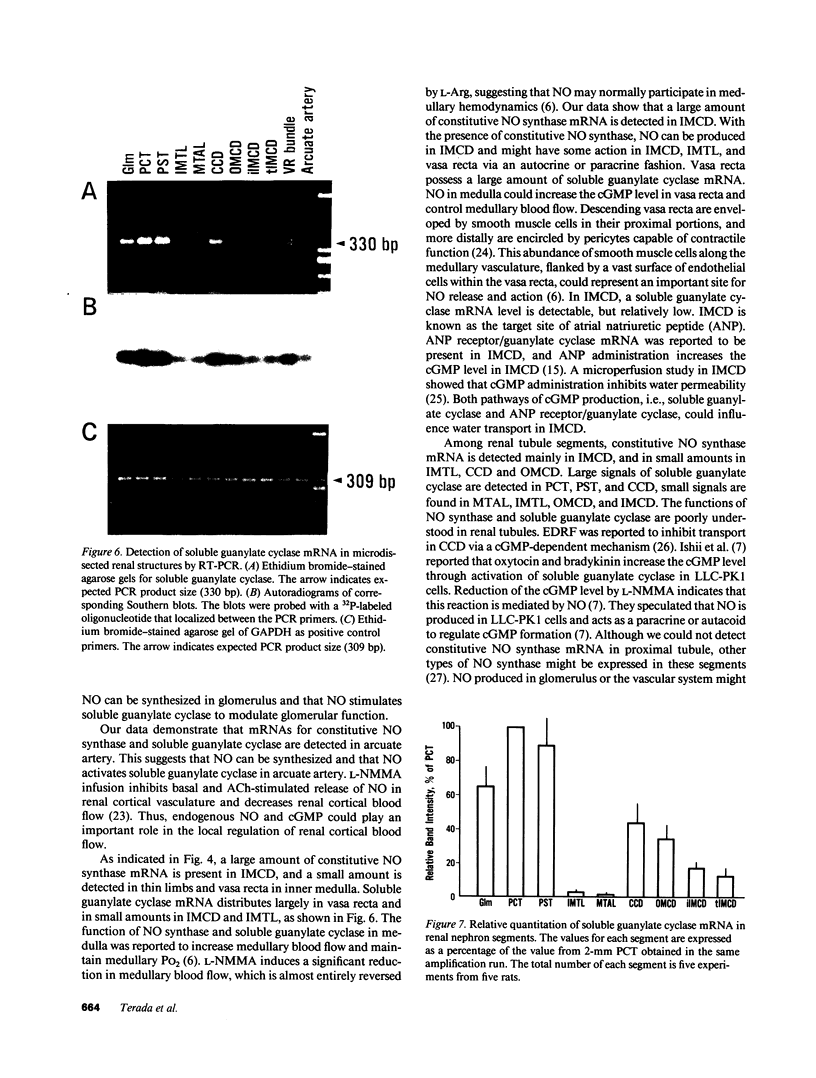
Stimulation of the release of nitric oxide (NO) in the kidney has been shown to result in renal hemodynamic changes and natriuresis. NO is a potent stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase, leading to an increase of cyclic GMP. The precise localization of NO synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase in the renal structure is not known. In this study, the microlocalization of mRNAs coding for constitutive NO synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase was carried out in the rat kidney, using an assay of reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction in individual microdissected renal tubule segments along the nephron, glomeruli, vasa recta bundle, and arcuate arteries. A large signal for constitutive NO synthase was detected in inner medullary collecting duct. Small signals were detected in inner medullary thin limb, cortical collecting duct, outer medullary collecting duct, glomerulus, vasa recta, and arcuate artery. Soluble guanylate cyclase mRNA is expressed largely in glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, proximal straight tubule, and cortical collecting duct, and in small amounts in medullary thick ascending limb, inner medullary thin limb, outer medullary collecting duct, inner medullary collecting duct, and the vascular system. Our data demonstrate that NO can be produced locally in the kidney, and that soluble guanylate cyclase is widely distributed in glomerulus, renal tubules, and the vascular system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K. Absolute mRNA quantification using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A novel approach by a PCR aided transcript titration assay (PATTY). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9437–9446. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkelmans H. S., Schipper J., Hudson L., Steinbusch H. W., de Vente J. cGMP immunocytochemistry in aorta, kidney, retina and brain tissues of the rat after perfusion with nitroprusside. Histochemistry. 1989;93(2):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00315967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biondi M. L., Dousa T., Vanhoutte P., Romero J. C. Evidences for the existence of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the renal medulla. Am J Hypertens. 1990 Nov;3(11):876–878. doi: 10.1093/ajh/3.11.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Ballermann B. J. Endothelium-dependent vascular responses. Mediators and mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1373–1378. doi: 10.1172/JCI114309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezis M., Heyman S. N., Dinour D., Epstein F. H., Rosen S. Role of nitric oxide in renal medullary oxygenation. Studies in isolated and intact rat kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):390–395. doi: 10.1172/JCI115316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. Y., Porush J. G., Faubert P. F. Renal medullary circulation: hormonal control. Kidney Int. 1990 Jan;37(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Schmidt H. H., Pollock J. S., Sheng H., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Nakane M., Murad F. Isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from different cell types. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 24;42(10):1849–1857. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90581-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin J. L. Inhibition of Jv by ANF in rat proximal straight tubules requires angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F907–F911. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland G., Perrin S., Blanchard K., Bunn H. F. Analysis of cytokine mRNA and DNA: detection and quantitation by competitive polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Warner T. D., Sheng H., Murad F. Endothelin increases cyclic GMP levels in LLC-PK1 porcine kidney epithelial cells via formation of an endothelium-derived relaxing factor-like substance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):1102–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Ballermann B. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates soluble guanylate cyclase in bovine glomerular mesangial cells via an L-arginine-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1843–1852. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A. Endogenous nitric oxide: physiology, pathology and clinical relevance. Eur J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;21(4):361–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1991.tb01383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Murphy H. R., Martin B. M., Garcia-Perez A. Detection of specific mRNAs in single nephron segments by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1470–F1474. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane M., Arai K., Saheki S., Kuno T., Buechler W., Murad F. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs coding for soluble guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16841–16845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Sands J. M., Knepper M. A. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits vasopressin-stimulated osmotic water permeability in rat inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1172/JCI113742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz P. J., Schorer A. E., Raij L. Effects of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and nitric oxide on rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):F162–F167. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.1.F162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Moriyama T., Martin B. M., Knepper M. A., Garcia-Perez A. RT-PCR microlocalization of mRNA for guanylyl cyclase-coupled ANF receptor in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F1080–F1087. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Yoshiyama N., Shiigai T., Marumo F. Leukotriene D4 inhibits atrial natriuretic factor-dependent cGMP production in rat glomerulus. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F95–F99. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolins J. P., Palmer R. M., Moncada S., Raij L. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in regulation of renal hemodynamic responses. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H655–H662. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder C. E., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. The involvement of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the regulation of renal cortical blood flow in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):967–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. S., Potter L. R., Garbers D. L. A new form of guanylyl cyclase is preferentially expressed in rat kidney. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 11;29(49):10872–10878. doi: 10.1021/bi00501a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]