Abstract
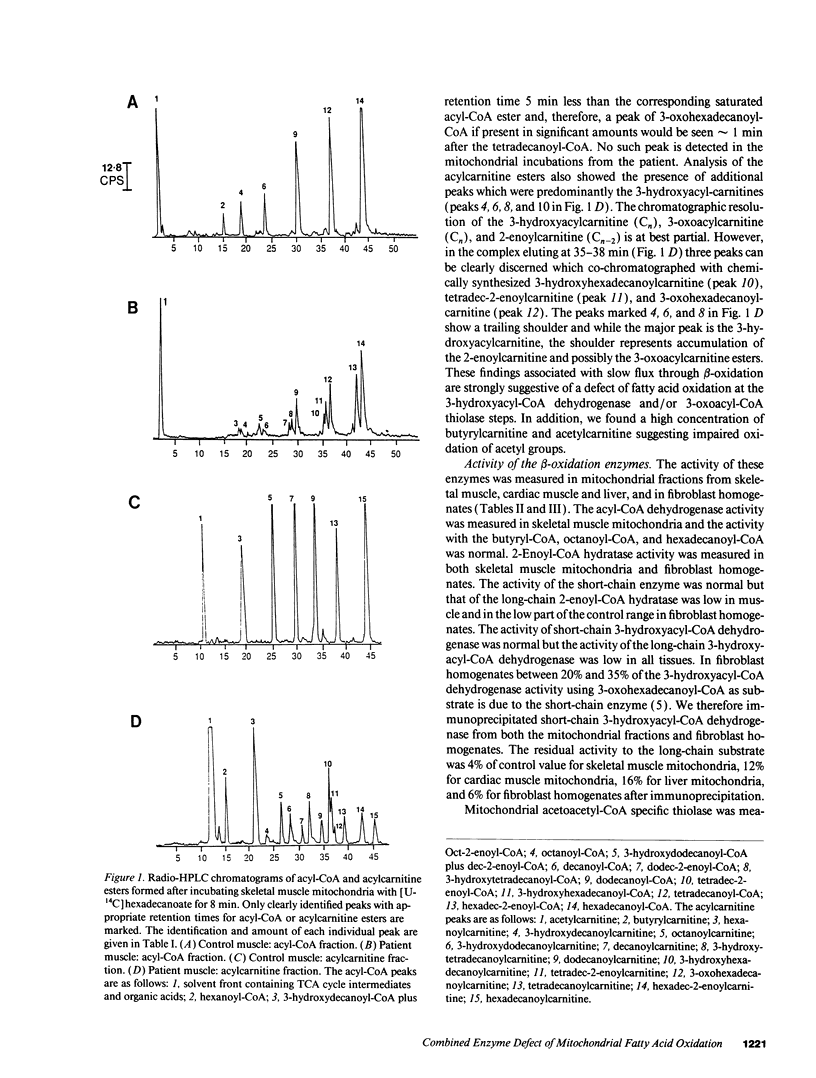
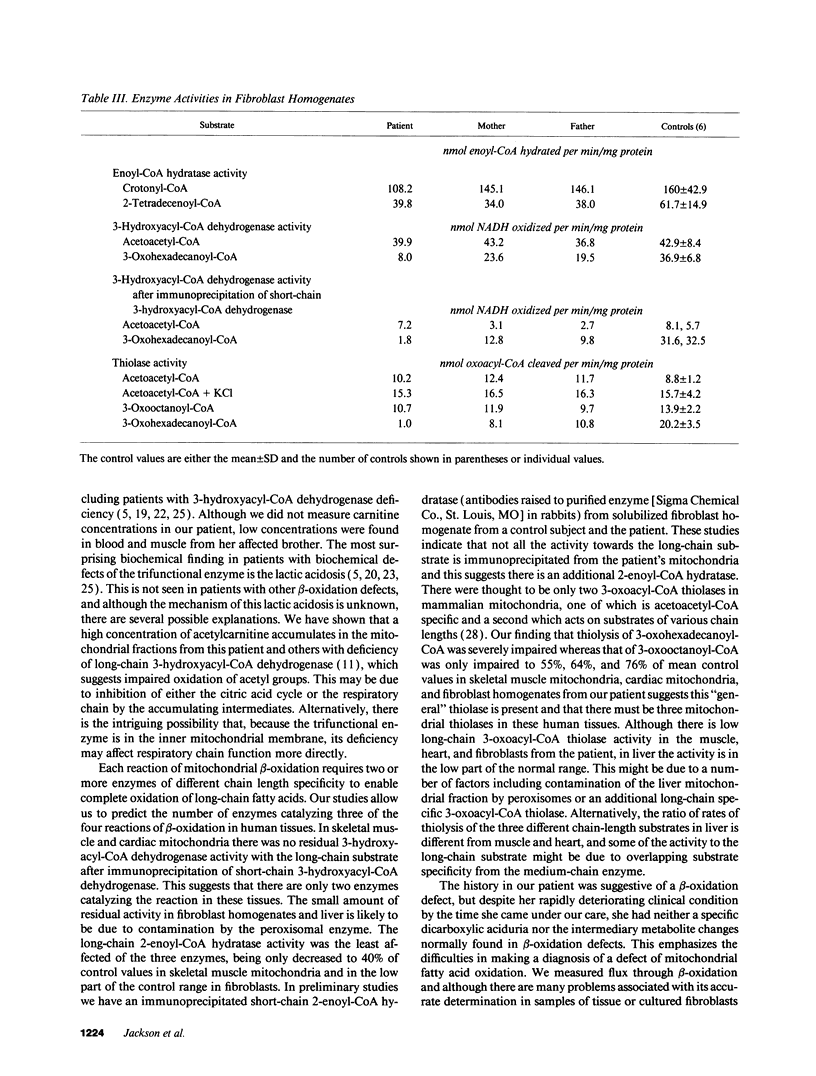
A young girl presented with recurrent episodes of muscle weakness culminating in a severe attack of generalized muscle weakness. In the muscle mitochondria from the patient there was an abnormal pattern of intermediates of beta-oxidation with an accumulation of 3-hydroxyacyl- and 2-enoyl-CoA and carnitine esters, and 3-oxoacylcarnitines. There was low activity of long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase in mitochondria from all tissues. The activity of long-chain 2-enoyl-CoA hydratase was low in muscle mitochondria and 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase activity measured with 3-oxohexadecanoyl-CoA as substrate was low in fibroblast, muscle, and cardiac mitochondria but only partial deficiency was present when the activity was measured with 3-oxooctanoyl-CoA. The activity of the long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase and long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase in fibroblasts from the patient's parents was intermediate between those of controls and the patient. The patient has a combined defect of the long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase, and long-chain 2-enoyl-CoA hydratase which appears to be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This suggests there is a multifunctional enzyme catalyzing these activities in human mitochondria and that this enzyme is deficient in our patient.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuiyan A. K., Jackson S., Turnbull D. M., Aynsley-Green A., Leonard J. V., Bartlett K. The measurement of carnitine and acyl-carnitines: application to the investigation of patients with suspected inherited disorders of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Clin Chim Acta. 1992 May 15;207(3):185–204. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(92)90118-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch-Machin M. A., Shepherd I. M., Watmough N. J., Sherratt H. S., Bartlett K., Darley-Usmar V. M., Milligan D. W., Welch R. J., Aynsley-Green A., Turnbull D. M. Fatal lactic acidosis in infancy with a defect of complex III of the respiratory chain. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):553–559. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter K., Pollitt R. J., Middleton B. Human liver long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase is a multifunctional membrane-bound beta-oxidation enzyme of mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90501-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionisi Vici C., Burlina A. B., Bertini E., Bachmann C., Mazziotta M. R., Zacchello F., Sabetta G., Hale D. E. Progressive neuropathy and recurrent myoglobinuria in a child with long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1991 May;118(5):744–746. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duran M., Wanders R. J., de Jager J. P., Dorland L., Bruinvis L., Ketting D., Ijlst L., van Sprang F. J. 3-Hydroxydicarboxylic aciduria due to long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency associated with sudden neonatal death: protective effect of medium-chain triglyceride treatment. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Jan;150(3):190–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01963564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., Goodman S. I. Deficiency of electron transfer flavoprotein or electron transfer flavoprotein:ubiquinone oxidoreductase in glutaric acidemia type II fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4517–4520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow A. M., Engel A. G., Bier D. M., Perry L. W., Dickie M., Todaro J., Brown B. I., Utter M. F. Hypoglycemia, hepatic dysfunction, muscle weakness, cardiomyopathy, free carnitine deficiency and long-chain acylcarnitine excess responsive to medium chain triglyceride diet. Pediatr Res. 1983 May;17(5):319–326. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198305000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S., Bartlett K., Land J., Moxon E. R., Pollitt R. J., Leonard J. V., Turnbull D. M. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Pediatr Res. 1991 Apr;29(4 Pt 1):406–411. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199104000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Whelan A. J., Ogden M. L., Alpers R., Zhang Z. F., Bellus G., Gregersen N., Dorland L., Strauss A. W. Molecular characterization of inherited medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9236–9240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kler R. S., Jackson S., Bartlett K., Bindoff L. A., Eaton S., Pourfarzam M., Frerman F. E., Goodman S. I., Watmough N. J., Turnbull D. M. Quantitation of acyl-CoA and acylcarnitine esters accumulated during abnormal mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22932–22938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehr J. P., Goodman S. I., Frerman F. E. Glutaric acidemia type II: heterogeneity of clinical and biochemical phenotypes. Pediatr Res. 1990 Mar;27(3):311–315. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199003000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt R. J. Clinical and biochemical presentations in 20 cases of hydroxydicarboxylic aciduria. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;321:495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchiccioli F., Wanders R. J., Aubourg P., Vianey-Liaud C., Ijlst L., Fabre M., Cartier N., Bougneres P. F. Deficiency of long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase: a cause of lethal myopathy and cardiomyopathy in early childhood. Pediatr Res. 1990 Dec;28(6):657–662. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199012000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherratt H. S., Watmough N. J., Johnson M. A., Turnbull D. M. Methods for study of normal and abnormal skeletal muscle mitochondria. Methods Biochem Anal. 1988;33:243–335. doi: 10.1002/9780470110546.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staack H., Binstock J. F., Schulz H. Purification and properties of a pig heart thiolase with broad chain length specificity and comparison of thiolases from pig heart and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1827–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull D. M., Bartlett K., Stevens D. L., Alberti K. G., Gibson G. J., Johnson M. A., McCulloch A. J., Sherratt H. S. Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency associated with a lipid-storage myopathy and secondary carnitine deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 8;311(19):1232–1236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411083111906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Izai K., Orii T., Hashimoto T. Novel fatty acid beta-oxidation enzymes in rat liver mitochondria. II. Purification and properties of enoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase trifunctional protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1034–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerkamp J. H., van Moerkerk T. B., Glatz J. F., Zuurveld J. G., Jacobs A. E., Wagenmakers A. J. 14CO2 production is no adequate measure of [14C]fatty acid oxidation. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1986 Jun;35(3):248–259. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(86)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanders R. J., Duran M., Ijlst L., de Jager J. P., van Gennip A. H., Jakobs C., Dorland L., van Sprang F. J. Sudden infant death and long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):52–53. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanders R. J., IJlst L., van Gennip A. H., Jakobs C., de Jager J. P., Dorland L., van Sprang F. J., Duran M. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: identification of a new inborn error of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1990;13(3):311–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01799383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watmough N. J., Bhuiyan A. K., Bartlett K., Sherratt H. S., Turnbull D. M. Skeletal muscle mitochondrial beta-oxidation. A study of the products of oxidation of [U-14C]hexadecanoate by h.p.l.c. using continuous on-line radiochemical detection. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):541–547. doi: 10.1042/bj2530541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watmough N. J., Turnbull D. M., Sherratt H. S., Bartlett K. Measurement of the acyl-CoA intermediates of beta-oxidation by h.p.l.c. with on-line radiochemical and photodiode-array detection. Application to the study of [U-14C]hexadecanoate oxidation by intact rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):261–269. doi: 10.1042/bj2620261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota I., Indo Y., Coates P. M., Tanaka K. Molecular basis of medium chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. An A to G transition at position 985 that causes a lysine-304 to glutamate substitution in the mature protein is the single prevalent mutation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):1000–1003. doi: 10.1172/JCI114761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



