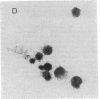
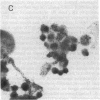
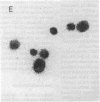
Abstract
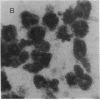
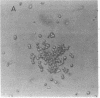
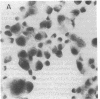
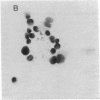
Human epidermal keratinocytes (EK) secrete factors able to sustain the proliferation of early myeloid cells and, in particular, the generation of basophils. This activity was previously attributed to IL-3, although no definitive in situ demonstration of this cytokine was provided. In regard to the possible physiological relevance of these data, we investigated herein the nature of EK-derived factors responsible for basophil promotion. Our data show that EK-derived supernatants (EK-sup) contain IL-3 as well as soluble CD23 (sCD23), both known for their colony stimulating activity. Messenger RNA for IL-3 and CD23 were also detected in EK. Blocking experiments using specific neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAb) further indicate that EK-derived basophil promoting activity is mainly due to the presence of IL-3 and sCD23 in EK-sup. Furthermore, by contrast to IL-3, sCD23 secretion by EK is cortisone sensitive and highly enhanced by IL-4, suggesting distinct regulatory mechanisms for their production.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Lyman S. D., Baird A., Wignall J. M., Eisenman J., Rauch C., March C. J., Boswell H. S., Gimpel S. D., Cosman D. Molecular cloning of mast cell growth factor, a hematopoietin that is active in both membrane bound and soluble forms. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90304-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avanzi G. C., Lista P., Giovinazzo B., Miniero R., Saglio G., Benetton G., Coda R., Cattoretti G., Pegoraro L. Selective growth response to IL-3 of a human leukaemic cell line with megakaryoblastic features. Br J Haematol. 1988 Jul;69(3):359–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertaux B., Morlière P., Moreno G., Courtalon A., Massé J. M., Dubertret L. Growth of melanocytes in a skin equivalent model in vitro. Br J Dermatol. 1988 Oct;119(4):503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1988.tb03254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertho J. M., Fourcade C., Dalloul A. H., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D. Synergistic effect of interleukin 1 and soluble CD23 on the growth of human CD4+ bone marrow-derived T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1073–1076. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieber T., Rieger A., Neuchrist C., Prinz J. C., Rieber E. P., Boltz-Nitulescu G., Scheiner O., Kraft D., Ring J., Stingl G. Induction of Fc epsilon R2/CD23 on human epidermal Langerhans cells by human recombinant interleukin 4 and gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):309–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billaud M., Busson P., Huang D., Mueller-Lantzch N., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Wakasugi H., Seigneurin J. M., Tursz T., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-containing nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells express the B-cell activation antigen blast2/CD23 and low levels of the EBV receptor CR2. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4121–4128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4121-4128.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., Hayday A. C., Bottomly K. Cytokines in T-cell development. Immunol Today. 1991 Jul;12(7):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90037-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalloul A. H., Arock M., Fourcade C., Hatzfeld A., Bertho J. M., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D. Human thymic epithelial cells produce interleukin-3. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalloul A. H., Fourcade C., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D. Thymic epithelial cell-derived supernatants sustain the maturation of human prothymocytes: involvement of interleukin 1 and CD23. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2633–2636. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner M., Luger T. A. Human keratinocytes and epidermoid carcinoma cell lines produce a cytokine with interleukin 3-like activity. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Apr;88(4):353–361. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Peleman R. Influence of recombinant IL-4, IFN-alpha, and IFN-gamma on the production of human IgE-binding factor (soluble CD23). J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Suter U., Mossalayi D., Bettler B., Sarfati M., Hofstetter H., Kilcherr E., Debre P., Dalloul A. Expression, structure, and function of the CD23 antigen. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:149–191. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Flores-Romo L., Cairns J. A., Millsum M. J., Lane P. J., Johnson G. D., MacLennan I. C. CD23: a multi-functional receptor/lymphokine? Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Weinstein Y. Immunological regulation of hematopoietic/lymphoid stem cell differentiation by interleukin 3. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanotte M., Arock M., Lacaze N., Guy-Grand D. Murine basophil-mast differentiation: toward optimal conditions for selective growth and maturation of basophil-mast or allied cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Nov;129(2):199–206. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Production of interleukin-8 by human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes in response to interleukin-1 or tumour necrosis factor. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Kock A., Kirnbauer R., Schwarz T., Ansel J. C. Keratinocyte-derived interleukin 3. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;548:253–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb18813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Stadler B. M., Katz S. I., Oppenheim J. J. Epidermal cell (keratinocyte)-derived thymocyte-activating factor (ETAF). J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1493–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdin C., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Levy C. A., Suter U., Alaimo D., Kilchherr E., Frost H., Delespesse G. Cloning and expression of the cDNA coding for a human lymphocyte IgE receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):109–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossalayi M. D., Arock M., Bertho J. M., Blanc C., Dalloul A. H., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Delespesse G., Debré P. Proliferation of early human myeloid precursors induced by interleukin-1 and recombinant soluble CD23. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):1924–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossalayi M. D., Lecron J. C., Dalloul A. H., Sarfati M., Bertho J. M., Hofstetter H., Delespesse G., Debre P. Soluble CD23 (Fc epsilon RII) and interleukin 1 synergistically induce early human thymocyte maturation. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):959–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudde G. C., Hansel T. T., von Reijsen F. C., Osterhoff B. F., Bruijnzeel-Koomen C. A. IgE: an immunoglobulin specialized in antigen capture? Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):440–443. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Kumar V., Bennett M. Acute rejection of murine bone marrow allografts by natural killer cells and T cells. Differences in kinetics and target antigens recognized. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1499–1509. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponec M., Weerheim A., Kempenaar J., Boonstra J. Proliferation and differentiation of human squamous carcinoma cell lines and normal keratinocytes: effects of epidermal growth factor, retinoids, and hydrocortisone. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Aug;24(8):764–770. doi: 10.1007/BF02623646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier K. J. The thymus according to Schambacher: medullary ducts and reticular epithelium of thymus and thymomas. Cancer. 1981 Sep 1;48(5):1183–1199. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810901)48:5<1183::aid-cncr2820480524>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Austen K. F. Recent advances in the cellular and molecular biology of mast cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Schmidt G., Besemer J., Mayer P., Zenke G., Liehl E., Hinterberger W., Lechner K., Maurer D., Bettelheim P. Interleukin-3 is a differentiation factor for human basophils. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1763–1769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Morrissey P. J., Mochizuki D. Y., de Vries P., Anderson D., Cosman D., Boswell H. S., Cooper S., Grabstein K. H., Broxmeyer H. E. T-cell growth factor P40 promotes the proliferation of myeloid cell lines and enhances erythroid burst formation by normal murine bone marrow cells in vitro. Blood. 1990 Sep 1;76(5):906–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaar M., Karassik R. L., Schnipper L. E., Gilchrest B. A. Effects of alpha and beta interferons on cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jul;85(1):70–74. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12275353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Hawley-Nelson P., Koehler B., Stanley J. R. A survey of transformation markers in differentiating epidermal cell lines in culture. Cancer Res. 1980 Dec;40(12):4694–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]