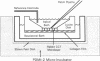
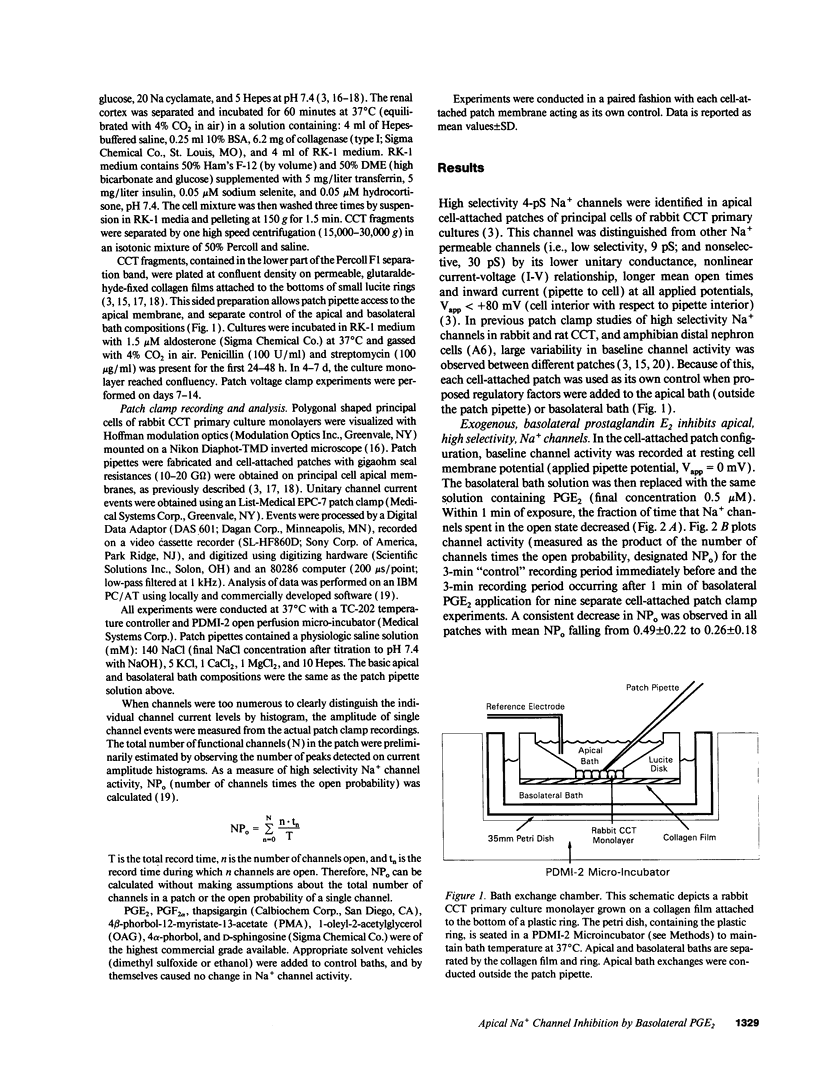
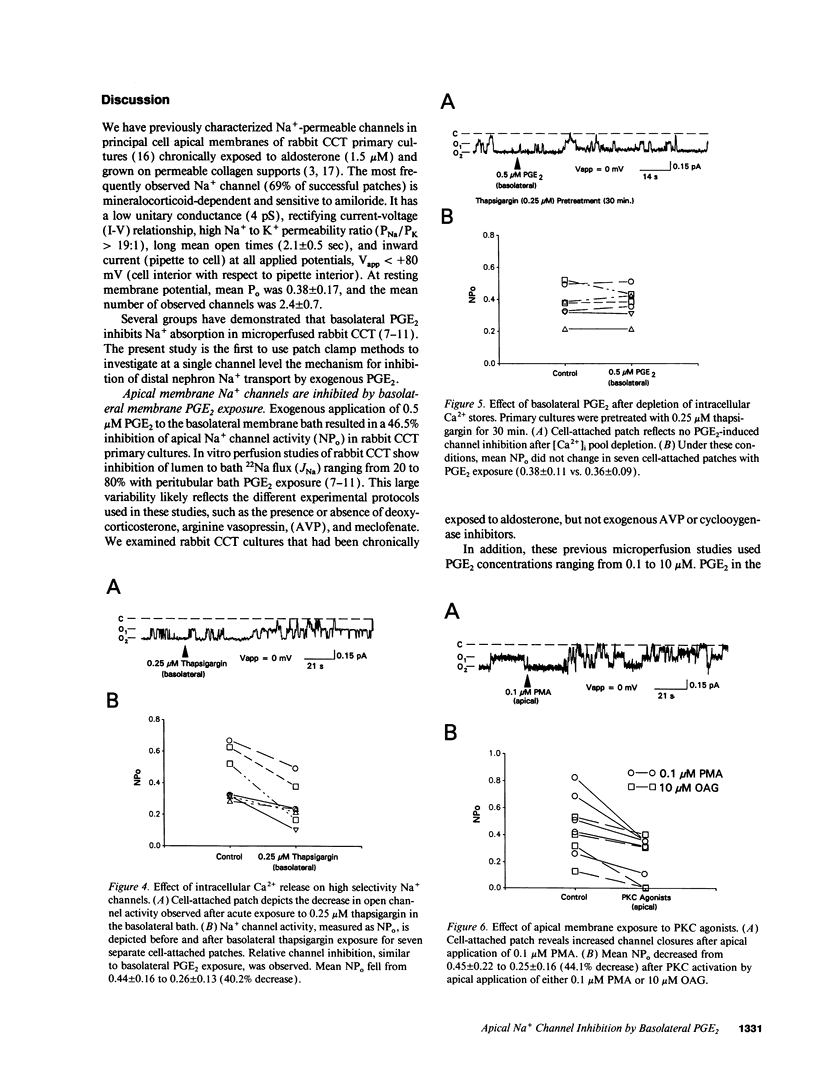
Abstract
We used the cell-attached patch clamp technique to investigate the interaction of exogenous prostaglandins (PG), intracellular [Ca2+]i, and protein kinase C (PKC) on the high selectivity, 4 pS Na+ channel found in the principal cell apical membrane of rabbit cortical collecting tubule (CCT) cultures grown on collagen supports with 1.5 microM aldosterone. Application of 0.5 microM PGE2 to the basolateral membrane decreased mean NP0 (number of channels times the open probability) for apical Na+ channels by 46.5% (n = 9). There was no consistent change in NP0 after apical 0.5 microM PGE2 (n = 12) or after apical or basolateral 0.5 microM PGF2 alpha (n = 8). Release of [Ca2+]i stores with 0.25 microM thapsigargin (n = 7), or activation of apical membrane PKC with apical 0.1 microM 4 beta-phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (n = 5) or 10 microM 1-oleyl-2-acetylglycerol (n = 4) also decreased NP0. Depletion of [Ca2+]i stores (0.25 microM thapsigargin pretreatment) (n = 7) or inhibition of apical PKC (100 microM D-sphingosine pretreatment) (n = 8) abolished the inhibitory effects of basolateral PGE2. Conclusions: (a) apical Na+ transport in rabbit CCT principal cells is modulated by basolateral PGE2; (b) the mechanism involves release of IP3-sensitive, [Ca2+]i stores; and (c) Ca(2+)-dependent activation of apical membrane PKC, which then inhibits apical Na+ channels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bello-Reuss E., Weber M. R. Electrophysiological studies of primary cultures of rabbit distal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 2):F899–F909. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.5.F899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. Renal tubular arachidonic acid metabolism. Kidney Int. 1991 Mar;39(3):438–449. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Reif M. C., Schafer J. A. Clonidine and PGE2 have different effects on Na+ and water transport in rat and rabbit CCD. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 2):F126–F136. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.1.F126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Wesolek J., McCullen J., Rys-Sikora K., Pandol S., Rood R. P., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Carbachol- and elevated Ca(2+)-induced translocation of functionally active protein kinase C to the brush border of rabbit ileal Na+ absorbing cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):855–863. doi: 10.1172/JCI115387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon B. S., Breckon R., Burke C., Anderson R. J. Phorbol esters inhibit adenylate cyclase activity in cultured collecting tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C183–C191. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Hamilton K. L. The amiloride-blockable sodium channel of epithelial tissue. Ion Channels. 1988;1:251–282. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7302-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Windhager E. E. Ca2(+)-dependent inhibition of sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F568–F582. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. R., Baum M., Kokko J. P. Effects of protein kinase C activation on sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2 transport in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1561–1570. doi: 10.1172/JCI113242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt W. F., Lechene C. ADH-PGE2 interactions in cortical collecting tubule. I. Depression of sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F452–F460. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert R. L., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct by increasing intracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1992–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI115227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Imai M. Effects of prostaglandins on Na transport in isolated collecting tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Feb 22;373(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00584850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Effect of prostaglandins on renal epithelial electrolyte transport. Kidney Int. 1981 Jun;19(6):791–796. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Hinton C. F., Eaton D. C. Potassium permeable channels in primary cultures of rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):441–452. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Kemendy A. E., Kokko K. E., Hinton C. F., Marunaka Y., Eaton D. C. Regulation of the amiloride-blockable sodium channel from epithelial tissue. Mol Cell Biochem. 1990 Dec 20;99(2):141–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00230344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Webster C. L., Eaton D. C. Eicosanoids modulate apical Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels in cultured rabbit principal cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):F116–F126. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.1.F116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Eaton D. C. Effects of vasopressin and cAMP on single amiloride-blockable Na channels. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):C1071–C1084. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.5.C1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G. Aldosterone regulation of sodium and potassium transport in the cortical collecting duct. Semin Nephrol. 1990 Jul;10(4):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Effects of cell Ca and pH on Na channels from rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F333–F339. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P. Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1172/JCI108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Patterns of K+ permeation following inhibition of Na+ transport in rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):F120–F126. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.1.F120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnheim K. Intrinsic regulation of apical sodium entry in epithelia. Physiol Rev. 1991 Apr;71(2):429–445. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase M., Handler J. S. Activators of protein kinase C inhibit sodium transport in A6 epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C517–C522. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]