Abstract
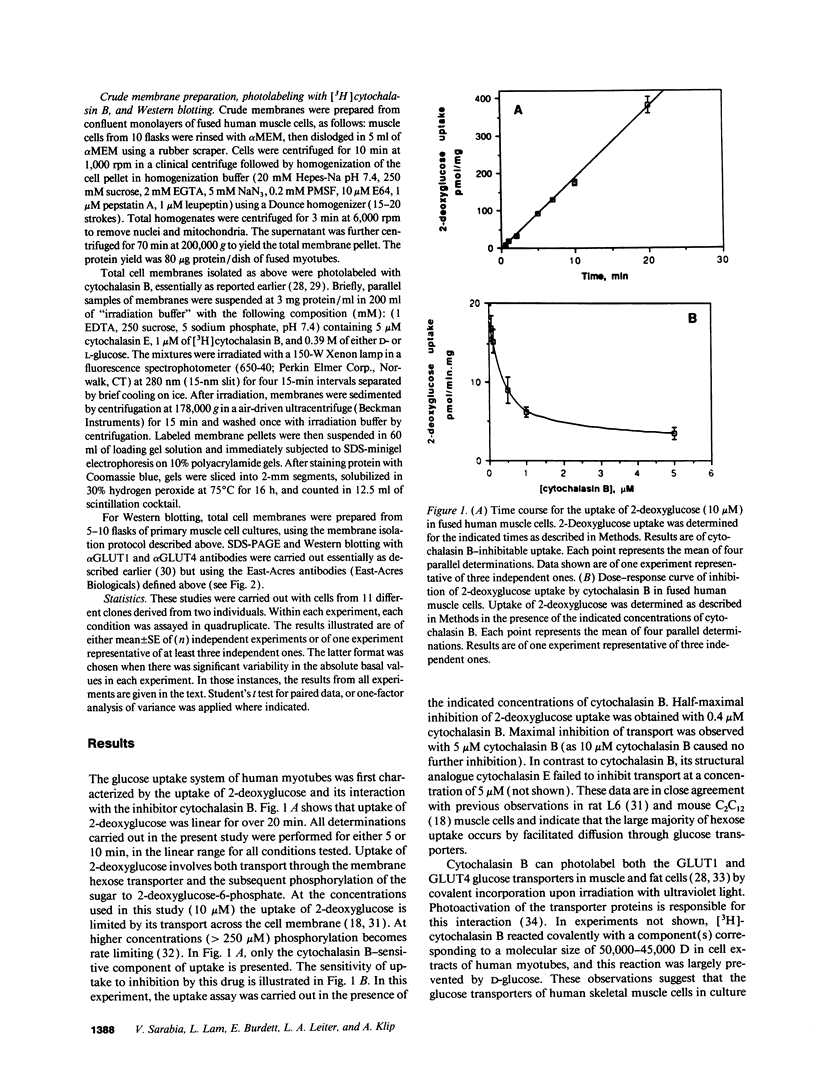
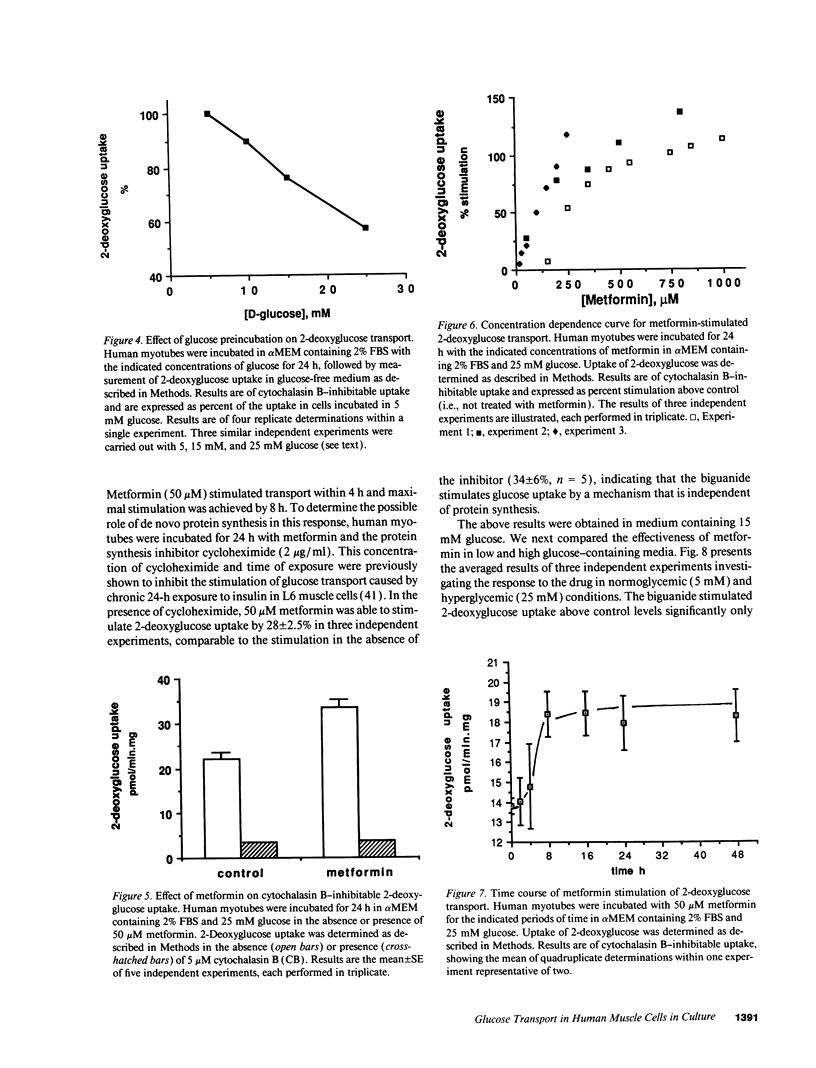
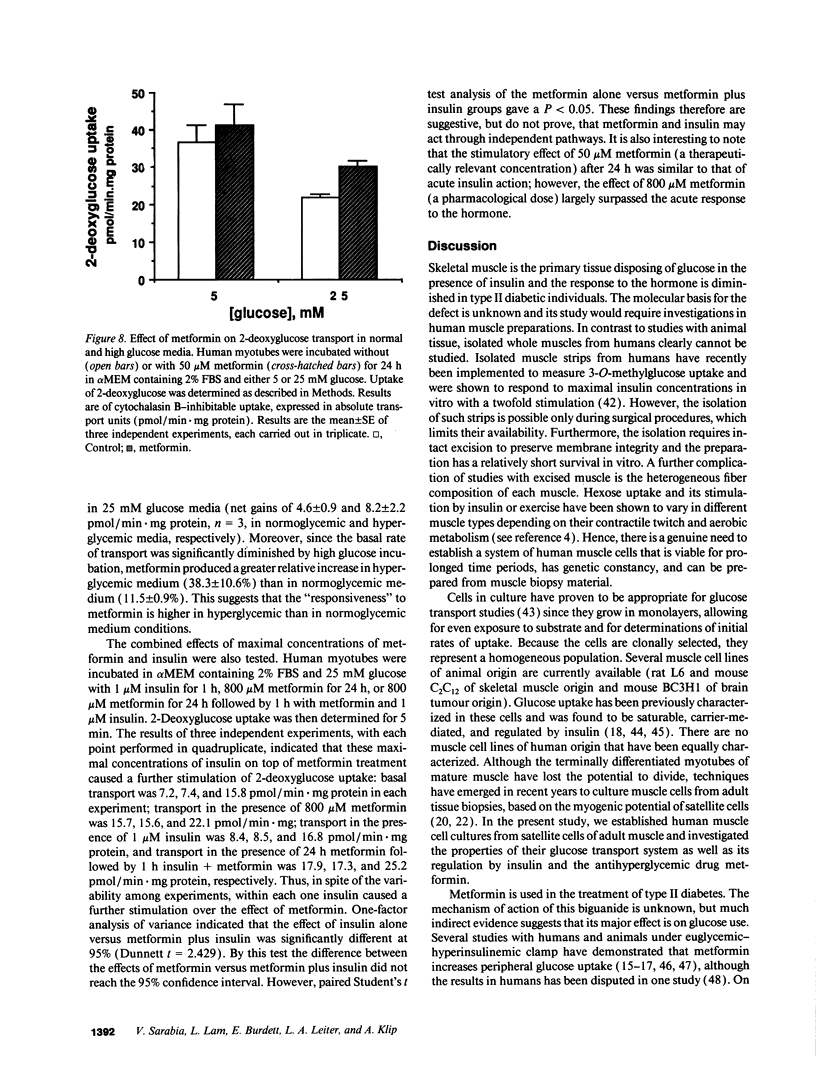
Primary human muscle cell cultures were established and the regulation of glucose transport was investigated. Primary cultures were allowed to proceed to the stage of myotubes through fusion of myoblasts or were used for clonal selection based on fusion potential. In clonally selected cultures, hexose (2-deoxy-glucose) uptake into myotubes was linear within the time of study and inhibitable by cytochalasin B (IC50 = 400 nM). Cytochalasin B photolabeled a protein(s) of 45,000-50,000 D in a D-glucose-protectable manner, suggesting identity with the glucose transporters. In the myotube stage, the cells expressed both the GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transporter protein isoforms at an average molar ratio of 7:1. Preincubation in media of increasing glucose concentrations (range 5-25 mM) progressively decreased the rate of 2-deoxyglucose uptake. Insulin elevated 2-deoxyglucose uptake in a dose-dependent manner, with half maximal stimulation achieved at 3.5 nM. Insulin also stimulated the transport of the nonmetabolizable hexose 3-O-methylglucose, as well as the activity of glycogen synthase, responsible for nonoxidative glucose metabolism. The oral antihyperglycemic drug metformin stimulated the cytochalasin B-sensitive component of both 2-deoxyglucose and 3-O-methylglucose uptake. Maximal stimulation was observed at 8 h of exposure to 50 microM metformin, and this effect was not prevented by incubation with the protein-synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. The relative effect of metformin was higher in cells incubated in 25 mM glucose than in 5 mM glucose, consistent with its selective action in hyperglycemic conditions in vivo. Metformin (50 microM for 24 h) was more effective than insulin (1 microM for 1 h) in stimulating hexose uptake and the hormone was effective on top of the stimulation caused by the biguanide, suggesting independent mechanisms of action.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey C. J. Metformin revisited: its actions and indications for use. Diabet Med. 1988 May-Jun;5(4):315–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1988.tb00996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. J., Puah J. A. Effect of metformin on glucose metabolism in mouse soleus muscle. Diabete Metab. 1986 Aug;12(4):212–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A. D., Brechtel G., Wallace P., Edelman S. V. Rates and tissue sites of non-insulin- and insulin-mediated glucose uptake in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):E769–E774. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.6.E769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilan P. J., Klip A. Glycation of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter in vitro and its functional consequences. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):661–667. doi: 10.1042/bj2680661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Webster C. Isolation and characterization of human muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourey R. E., Koranyi L., James D. E., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A. Effects of altered glucose homeostasis on glucose transporter expression in skeletal muscle of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):542–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI114742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Kitagawa K., Lienhard G. E., Gould G. W. Translocation of the brain-type glucose transporter largely accounts for insulin stimulation of glucose transport in BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):597–601. doi: 10.1042/bj2690597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G., Scarlett J. A., Kao M., Olefsky J. M. Role of glucose transport in the postreceptor defect of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):1016–1022. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Jun;37(6):667–687. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deziel M., Pegg W., Mack E., Rothstein A., Klip A. Labelling of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter with 3H-labelled cytochalasin B occurs via protein photoactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 30;772(3):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohm G. L., Tapscott E. B., Pories W. J., Dabbs D. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Fushiki T., Atkinson S. M., Elton C. W., Caro J. F. An in vitro human muscle preparation suitable for metabolic studies. Decreased insulin stimulation of glucose transport in muscle from morbidly obese and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):486–494. doi: 10.1172/JCI113622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Vranic M., Holloszy J. O., Klip A. Exercise induces recruitment of the "insulin-responsive glucose transporter". Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13427–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrink J., Bihler I. Membrane transport: its relation to cellular metabolic rates. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1177–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.1096301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantus I. G., Brosseau R. Mechanism of action of metformin: insulin receptor and postreceptor effects in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Oct;63(4):898–905. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-4-898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayn K. N., Adnitt P. I. Effects of metformin on glucose uptake by isolated diaphragm from normal and diabetic rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Dec 1;21(23):3153–3162. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayn K. N., Adnitt P. I., Turner P. The use of human skeletal muscle in vitro for biochemical and pharmacological studies of glucose uptake. Clin Sci. 1973 Jan;44(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/cs0440055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Birnbaum M. J. Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2662408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Bell G. I. Facilitative glucose transporters: an expanding family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jan;15(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90125-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinovart J. J., Salavert A., Massagué J., Ciudad C. J., Salsas E., Itarte E. Glycogen synthase: a new activity ratio assay expressing a high sensitivity to the phosphorylation state. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80515-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hother-Nielsen O., Schmitz O., Andersen P. H., Beck-Nielsen H., Pedersen O. Metformin improves peripheral but not hepatic insulin action in obese patients with type II diabetes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Mar;120(3):257–265. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1200257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Hawa M. I., Jaspan J. B., Sim B. M., Disilvio L., Featherbe D., Kurtz A. B. Mechanism of metformin action in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1987 May;36(5):632–640. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.5.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. E., Oosterhof A., Veerkamp J. H. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose uptake in cultured human muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 9;1051(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90127-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Rossetti L., Lodish H. F., Charron M. J. Decreased in vivo glucose uptake but normal expression of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2197–2206. doi: 10.1172/JCI115254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
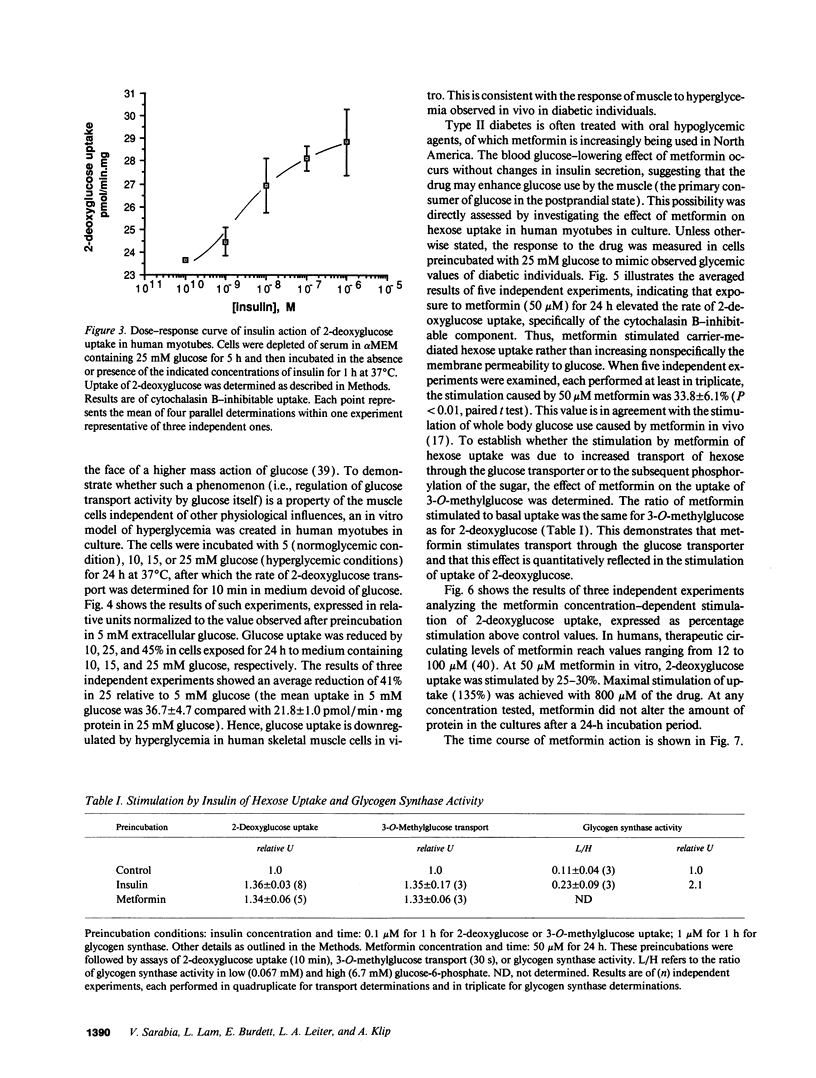
- Kelley D. E., Mandarino L. J. Hyperglycemia normalizes insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose oxidation and storage in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1999–2007. doi: 10.1172/JCI114935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Deziel M., Walkert D. Chemical identity of the glucose transporter with the [3H]cytochalasin B-photolabelled component of human erythrocyte membranes. Equal sensitivity to trypsin and endoglycosidase F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Gumà A., Ramlal T., Bilan P. J., Lam L., Leiter L. A. Stimulation of hexose transport by metformin in L6 muscle cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1992 May;130(5):2535–2544. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.5.1572281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Leiter L. A. Cellular mechanism of action of metformin. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):696–704. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Li G., Logan W. J. Induction of sugar uptake response to insulin by serum depletion in fusing L6 myoblasts. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):E291–E296. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.3.E291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Logan W. J., Li G. Hexose transport in L6 muscle cells. Kinetic properties and the number of [3H]cytochalasin B binding sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 7;687(2):265–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Pâquet M. R. Glucose transport and glucose transporters in muscle and their metabolic regulation. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):228–243. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Gulve E. A., Holloszy J. O. Recruitment of GLUT-4 glucose transporters by insulin in diabetic rat skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 30;172(2):728–736. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90735-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T. Protein kinase C is not required for insulin stimulation of hexose uptake in muscle cells in culture. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):131–136. doi: 10.1042/bj2420131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Young D. A., Holloszy J. O. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscles. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Walker D., Ransome K. J., Schroer D. W., Lienhard G. E. Identification of the glucose transporter in rat skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebovitz H. E., Pasmantier R. Combination insulin-sulfonylurea therapy. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):667–675. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L. J., Wright K. S., Verity L. S., Nichols J., Bell J. M., Kolterman O. G., Beck-Nielsen H. Effects of insulin infusion on human skeletal muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase, phosphofructokinase, and glycogen synthase. Evidence for their role in oxidative and nonoxidative glucose metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):655–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI113118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthaei S., Hamann A., Klein H. H., Benecke H., Kreymann G., Flier J. S., Greten H. Association of Metformin's effect to increase insulin-stimulated glucose transport with potentiation of insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from intracellular pool to plasma membrane in rat adipocytes. Diabetes. 1991 Jul;40(7):850–857. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.7.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesmer O. T., Lo T. C. Hexose transport in human myoblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):15–24. doi: 10.1042/bj2620015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsumoto Y., Burdett E., Grant A., Klip A. Differential expression of the GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transporters during differentiation of L6 muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):652–659. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91615-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Wilson L. Inhibition of the transport of several hexoses in mammalian cells by cytochalasin B. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4102–4105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Bak J. F., Andersen P. H., Lund S., Moller D. E., Flier J. S., Kahn B. B. Evidence against altered expression of GLUT1 or GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of patients with obesity or NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Jul;39(7):865–870. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.7.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentikäinen P. J., Neuvonen P. J., Penttilä A. Pharmacokinetics of metformin after intravenous and oral administration to man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(3):195–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00562061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager R., Schernthaner G., Graf H. Effect of metformin on peripheral insulin sensitivity in non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabete Metab. 1986 Dec;12(6):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramlal T., Sarabia V., Bilan P. J., Klip A. Insulin-mediated translocation of glucose transporters from intracellular membranes to plasma membranes: sole mechanism of stimulation of glucose transport in L6 muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarabia V., Klip A. Regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ in clonal human muscle cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1130–1137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92720-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarabia V., Ramlal T., Klip A. Glucose uptake in human and animal muscle cells in culture. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;68(2):536–542. doi: 10.1139/o90-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert M. L., Schimmel S. D., Pollet R. J. The development of insulin receptors and responses in the differentiating nonfusing muscle cell line BC3H-1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2337–2345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Schlender K. K., Larner J. A rapid filter paper assay for UDPglucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase, including an improved biosynthesis of UDP-14C-glucose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn A. W., Gumbiner B., Bulacan F., Brechtel G., Henry R. R. Multiple defects in muscle glycogen synthase activity contribute to reduced glycogen synthesis in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):489–495. doi: 10.1172/JCI115022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Ramlal T., Donovan J. A., Doering T. P., Sandra A., Klip A., Pessin J. E. Insulin and glucose-dependent regulation of the glucose transport system in the rat L6 skeletal muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6587–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Ramlal T., Sarabia V., Koivisto U. M., Bilan P. J., Pessin J. E., Klip A. Glucose transport activity in L6 muscle cells is regulated by the coordinate control of subcellular glucose transporter distribution, biosynthesis, and mRNA transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1516–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallberg-Henriksson H., Holloszy J. O. Activation of glucose transport in diabetic muscle: responses to contraction and insulin. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C233–C237. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. S., Johnston P., Sheu W. H., Hollenbeck C. B., Jeng C. Y., Goldfine I. D., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Effect of metformin on carbohydrate and lipoprotein metabolism in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasin R., Van Beers G., Nurse K. C., Al-Ani S., Landon D. N., Thompson E. J. A quantitative technique for growing human adult skeletal muscle in culture starting from mononucleated cells. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Jul;32(3):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]