Abstract
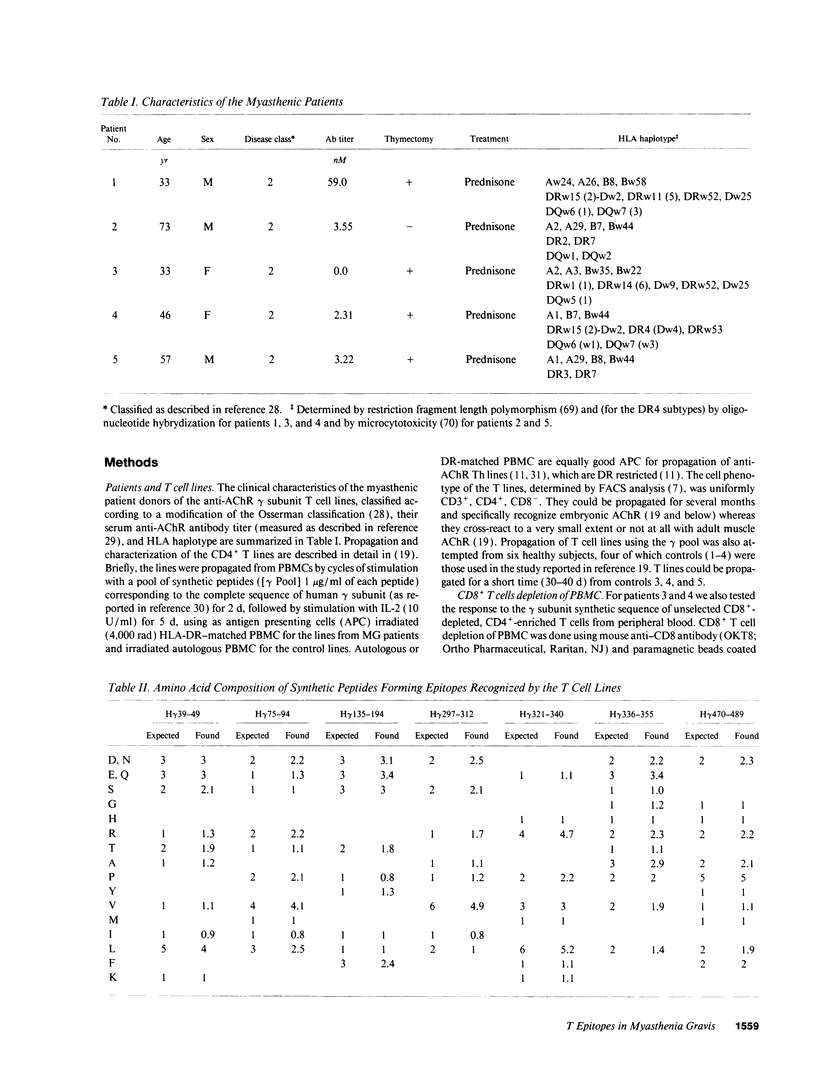
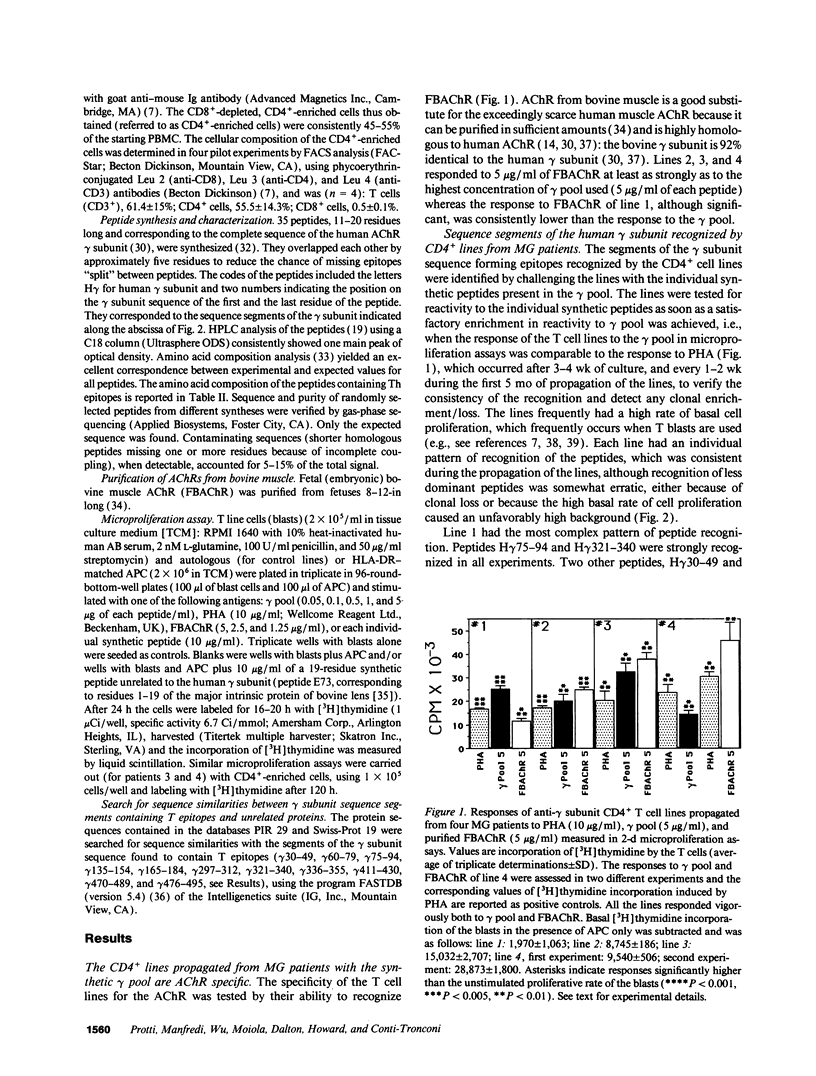
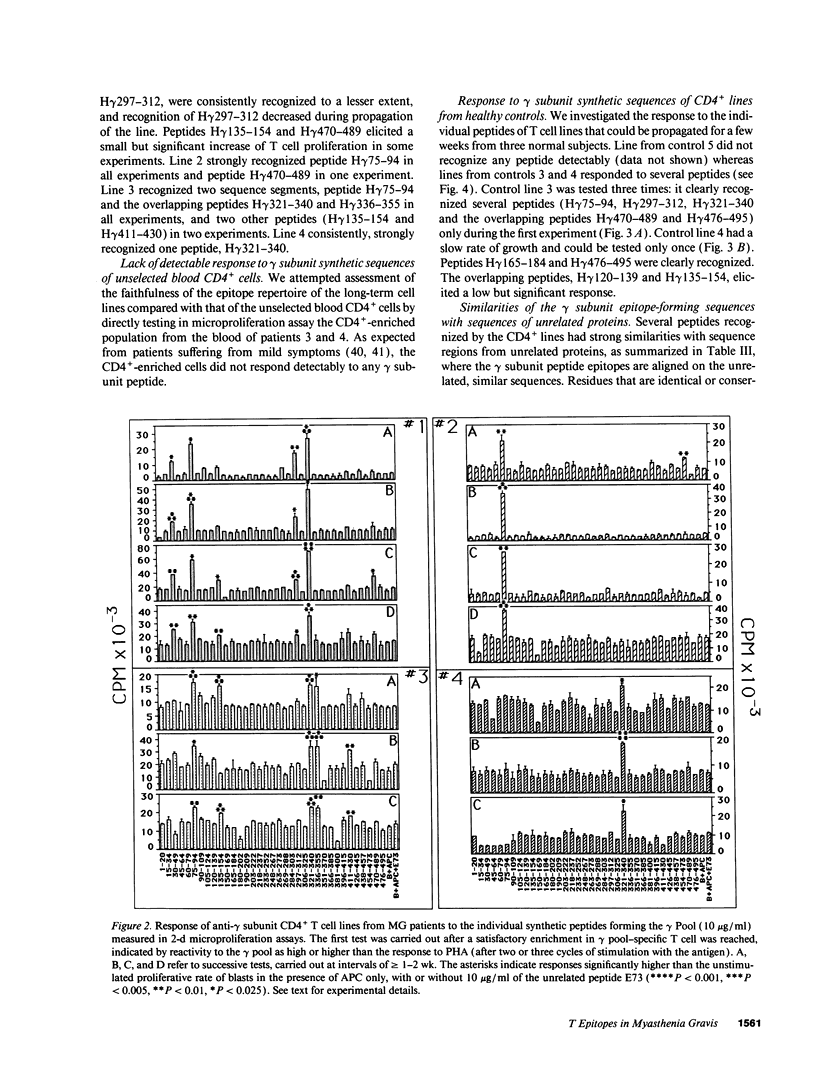
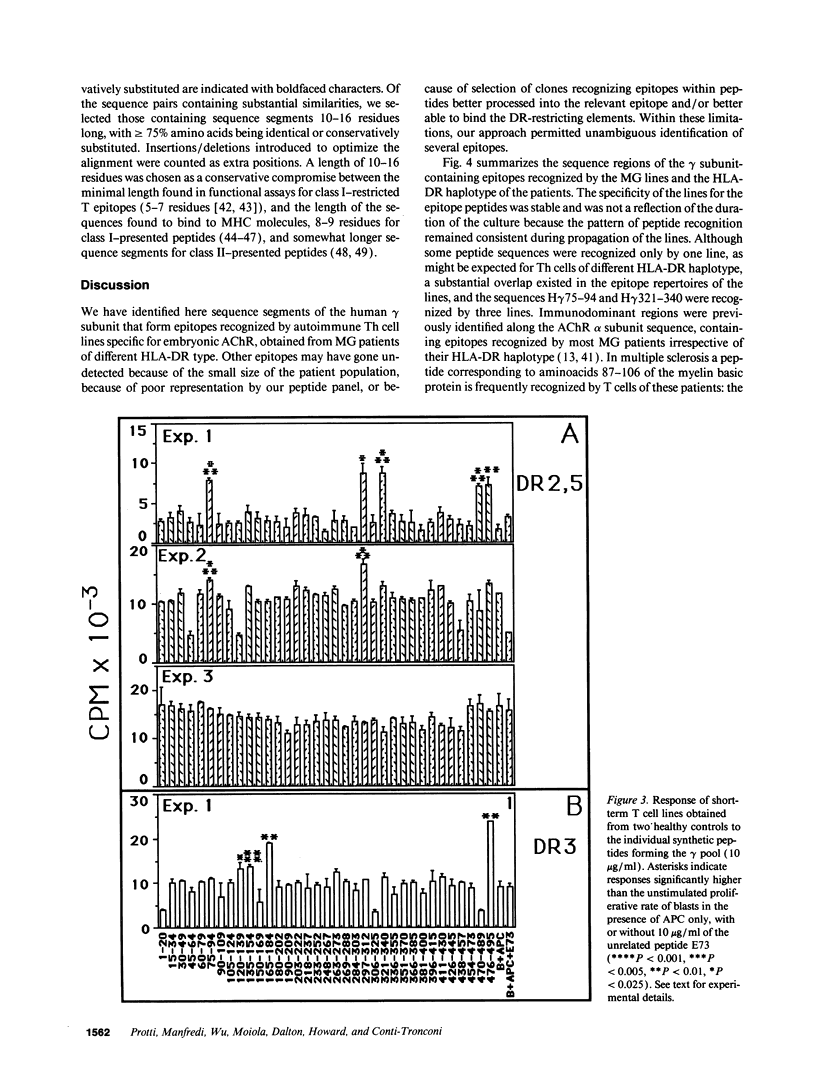
In myasthenia gravis (MG) an autoimmune response against muscle acetylcholine receptor (AChR) occurs. Embryonic muscle AChR contains a gamma subunit, substituted in adult muscle by a homologous epsilon subunit. Antibodies and CD4+ cells specific for embryonic AChR have been demonstrated in MG patients. We identified sequence segments of the human gamma subunit forming epitopes recognized by four embryonic AChR-specific CD4+ T cell lines, propagated from MG patients' blood by stimulation with synthetic peptides corresponding to the human gamma subunit sequence. Each line had an individual epitope repertoire, but two 20-residue sequence regions were recognized by three lines of different HLA haplotype. Most T epitope sequences were highly diverged between the gamma and the other AChR subunits, confirming the specificity of the T cells for embryonic AChR. These T cells may have been sensitized against AChR expressed by a tissue other than innervated skeletal muscle, possibly the thymus, which expresses an embryonic muscle AChR-like protein, containing a gamma subunit. Several sequence segments forming T epitopes are similar to regions of microbial and/or mammalian proteins unrelated to the AChR. These findings are consistent with the possibility that T cell cross-reactivity between unrelated proteins ("molecular mimicry"), proposed as a cause of autoimmune responses, is not a rare event.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert L. I., Papatestas A., Kark A., Osserman R. S., Osserman K. A histologic reappraisal of the thymus in myasthenia gravis. A correlative study of thymic pathology and response to thymectomy. Arch Pathol. 1971 Jan;91(1):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellone M., Ostlie N., Lei S., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Experimental myasthenia gravis in congenic mice. Sequence mapping and H-2 restriction of T helper epitopes on the alpha subunits of Torpedo californica and murine acetylcholine receptors. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2303–2310. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett S. J., Cease K. B., Ouyang C. S., Berzofsky J. A. Fine specificity of T cell recognition of the same peptide in association with different I-A molecules. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):771–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Dautricourt J. P., Maulik S., Relph J. Improved sensitivity of biological sequence database searches. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jul;6(3):237–245. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Stocks N. I., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Bernstein D. C., Mann D. L., Shearer G. M., Berzofsky J. A. Interleukin-2 production used to detect antigenic peptide recognition by T-helper lymphocytes from asymptomatic HIV-seropositive individuals. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):383–385. doi: 10.1038/339383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Val M., Schlicht H. J., Ruppert T., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Efficient processing of an antigenic sequence for presentation by MHC class I molecules depends on its neighboring residues in the protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1145–1153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90037-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demotz S., Grey H. M., Appella E., Sette A. Characterization of a naturally processed MHC class II-restricted T-cell determinant of hen egg lysozyme. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):682–684. doi: 10.1038/342682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerman K. E., Powers J. M., Brostoff S. W. A suppressor T-lymphocyte cell line for autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):265–267. doi: 10.1038/331265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Myasthenia gravis and myasthenic syndromes. Ann Neurol. 1984 Nov;16(5):519–534. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Deres K., Metzger J., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Identification of naturally processed viral nonapeptides allows their quantification in infected cells and suggests an allele-specific T cell epitope forecast. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):425–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon G., Sercarz E. Does the presence of self-reactive T cells indicate the breakdown of tolerance? Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Sep;56(3):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90150-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon G., Sercarz E. How some T cells escape tolerance induction. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):183–185. doi: 10.1038/342183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam A. M., Glynn P. Competition between foreign and self proteins in antigen presentation. Ovalbumin can inhibit activation of myelin basic protein-specific T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1177–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Yancey S. B., Cline J., Revel J. P., Horwitz J. The major intrinsic protein (MIP) of the bovine lens fiber membrane: characterization and structure based on cDNA cloning. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotti C., Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. Mammalian muscle acetylcholine receptor purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3148–3154. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granato D. A., Fulpius B. W., Moody J. F. Experimental myasthenia in Balb/c mice immunized with rat acetylcholine receptor from rat denervated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2872–2876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Hall Z. W. Immunological evidence for a change in subunits of the acetylcholine receptor in developing and denervated rat muscle. Neuron. 1988 Apr;1(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harcourt G. C., Sommer N., Rothbard J., Willcox H. N., Newsom-Davis J. A juxta-membrane epitope on the human acetylcholine receptor recognized by T cells in myasthenia gravis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1295–1300. doi: 10.1172/JCI113729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Conti-Tronconi B., Kalies I., Bertrams J., Toyka K. V. Genetic restriction of autoreactive acetylcholine receptor-specific T lymphocytes in myasthenia gravis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2393–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Kalies I., Kohleisen B., Heininger K., Conti-Tronconi B., Toyka K. V. Myasthenia gravis: stimulation of antireceptor autoantibodies by autoreactive T cell lines. Neurology. 1986 May;36(5):618–621. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.5.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Michels M., Tesch H., Fahsbender A., Heininger K., Conti-Tronconi B. M., Toyka K. V. Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells can present acetylcholine receptor to autologous autoreactive T cells. Immunol Lett. 1986 Mar;12(2-3):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Toyka K. V., Heininger K., Grosse-Wilde H., Kalies I. Autoimmune human T lymphocytes specific for acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):244–246. doi: 10.1038/310244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Toyka K. V., Tzartos S. J., Carson W., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Human T-helper lymphocytes in myasthenia gravis recognize the nicotinic receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5379–5383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Lane W. S., Robinson R. A., Madden D. R., Wiley D. C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):326–329. doi: 10.1038/353326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert L. E., Unanue E. R. Analysis of the interaction of peptide hen egg white lysozyme (34-45) with the I-Ak molecule. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. An assay for antibodies to human acetylcholine receptor in serum from patients with myasthenia gravis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Jan;7(1):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Shelton D., Fujii Y. Myasthenia gravis. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:233–284. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60847-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Levinson A. I., Zweiman B., Kornstein M. J. Antibodies to acetylcholine receptor and tetanus toxoid: in vitro synthesis by thymic lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1221–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone A. M., Fathman C. G. The structure of T-cell epitopes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:477–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The structure of HLA-B27 reveals nonamer self-peptides bound in an extended conformation. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):321–325. doi: 10.1038/353321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi A. A., Protti M. P., Wu X. D., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. CD4+ T-epitope repertoire on the human acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit in severe myasthenia gravis: a study with synthetic peptides. Neurology. 1992 May;42(5):1092–1100. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.5.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Howell M. D., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Brostoff S., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. A myelin basic protein peptide is recognized by cytotoxic T cells in the context of four HLA-DR types associated with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):19–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M. P., Earnest J. P., Young E. F., Choe S., Stroud R. M. The molecular neurobiology of the acetylcholine receptor. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:383–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Takai T., Imoto K., Noda M., Takahashi T., Numa S., Methfessel C., Sakmann B. Molecular distinction between fetal and adult forms of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):406–411. doi: 10.1038/321406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Adult thymus expresses an embryonic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-like protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Sep-Oct;29(1-3):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90150-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J. A., Levely M. E., Mitchell M. A., Smith C. W. A 16-amino acid peptide of respiratory syncytial virus 1A protein contains two overlapping T cell-stimulating sites distinguishable by class II MHC restriction elements. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2790–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noreen H. J., Davidson M. L., McCullough J., Bach F. H., Segall M. HLA class II typing by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) in unrelated bone marrow transplant patients. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 3):2968–2970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S. Many peptide fragments of alien antigens are homologous with host proteins, thus canalizing T-cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3065–3068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olanow C. W., Wechsler A. S., Sirotkin-Roses M., Stajich J., Roses A. D. Thymectomy as primary therapy in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;505:595–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb51328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panina-Bordignon P., Tan A., Termijtelen A., Demotz S., Corradin G., Lanzavecchia A. Universally immunogenic T cell epitopes: promiscuous binding to human MHC class II and promiscuous recognition by T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2237–2242. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette M., Fujita K., Kitze B., Whitaker J. N., Albert E., Kappos L., Wekerle H. Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocyte lines from MS patients and healthy individuals. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1770–1776. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protti M. P., Manfredi A. A., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. T cells in myasthenia gravis specific for embryonic acetylcholine receptor. Neurology. 1991 Nov;41(11):1809–1814. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.11.1809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protti M. P., Manfredi A. A., Straub C., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. CD4+ T cell response to the human acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit in myasthenia gravis. A study with synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1276–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protti M. P., Manfredi A. A., Straub C., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. Immunodominant regions for T helper-cell sensitization on the human nicotinic receptor alpha subunit in myasthenia gravis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7792–7796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protti M. P., Manfredi A. A., Straub C., Wu X. D., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. Use of synthetic peptides to establish anti-human acetylcholine receptor CD4+ cell lines from myasthenia gravis patients. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1711–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protti M. P., Manfredi A. A., Wu X. D., Moiola L., Howard J. F., Jr, Conti-Tronconi B. M. Myasthenia gravis. T epitopes on the delta subunit of human muscle acetylcholine receptor. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2253–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Rothbard J. B., Koszinowski U. H. A pentapeptide as minimal antigenic determinant for MHC class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):651–653. doi: 10.1038/337651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., Hong S. C., Barlow A., Janeway C. A., Jr Sequence analysis of peptides bound to MHC class II molecules. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):622–627. doi: 10.1038/353622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Sinha A. A., Mitchell D. J., Zamvil S. S., Rothbard J. B., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Involvement of distinct murine T-cell receptors in the autoimmune encephalitogenic response to nested epitopes of myelin basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8608–8612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Hodgkinson S., Rothbard J. B., Steinman L. Prevention of experimental encephalomyelitis with peptides that block interaction of T cells with major histocompatibility complex proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9470–9474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze S. M., Vicini S., Hall Z. W. Myasthenic serum selectively blocks acetylcholine receptors with long channel open times at developing rat endplates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2533–2537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönbeck S., Chrestel S., Hohlfeld R. Myasthenia gravis: prototype of the antireceptor autoimmune diseases. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1990;32:175–200. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60583-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Buus S., Colon S., Miles C., Grey H. M. Structural analysis of peptides capable of binding to more than one Ia antigen. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Kubo T., Perski H. J., Takahashi H., Noda M., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of human genomic DNA encoding gamma subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinigaglia F., Guttinger M., Kilgus J., Doran D. M., Matile H., Etlinger H., Trzeciak A., Gillessen D., Pink J. R. A malaria T-cell epitope recognized in association with most mouse and human MHC class II molecules. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):778–780. doi: 10.1038/336778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai T., Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Notake M., Shimizu S., Kayano T., Tanabe T., Tanaka K., Hirose T. Primary structure of gamma subunit precursor of calf-muscle acetylcholine receptor deduced from the cDNA sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. Isolation of an endogenously processed immunodominant viral peptide from the class I H-2Kb molecule. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):213–216. doi: 10.1038/348213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Whiting P. J., Schluep M., Heidenreich F., Lang B., Roberts A., Willcox N., Newsom-Davis J. Antibody heterogeneity and specificity in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;505:106–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb51286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg C. B., Hall Z. W. Antibodies from patients with myasthenia gravis recognize determinants unique to extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Hohlfeld R., Ketelsen U. P., Kalden J. R., Kalies I. Thymic myogenesis, T-lymphocytes and the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;377:455–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb33753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzemann V., Barg B., Nishikawa Y., Sakmann B., Numa S. Differential regulation of muscle acetylcholine receptor gamma- and epsilon-subunit mRNAs. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Mitchell D. J., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Schluep M., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Jeannet M., Steck A., Barkas T. Immunological heterogeneity of autoreactive T lymphocytes against the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in myasthenic patients. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2577–2583. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



