Abstract
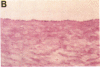
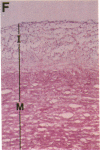
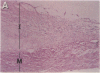
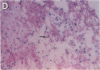
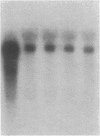
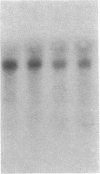
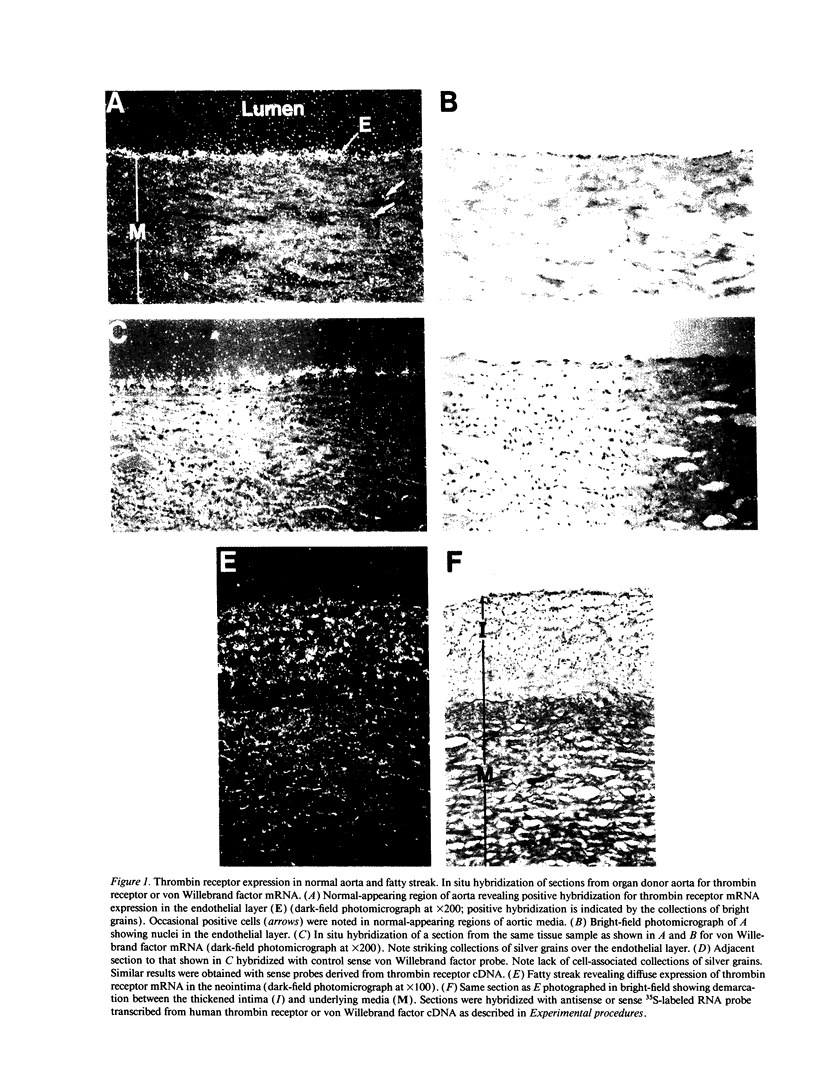
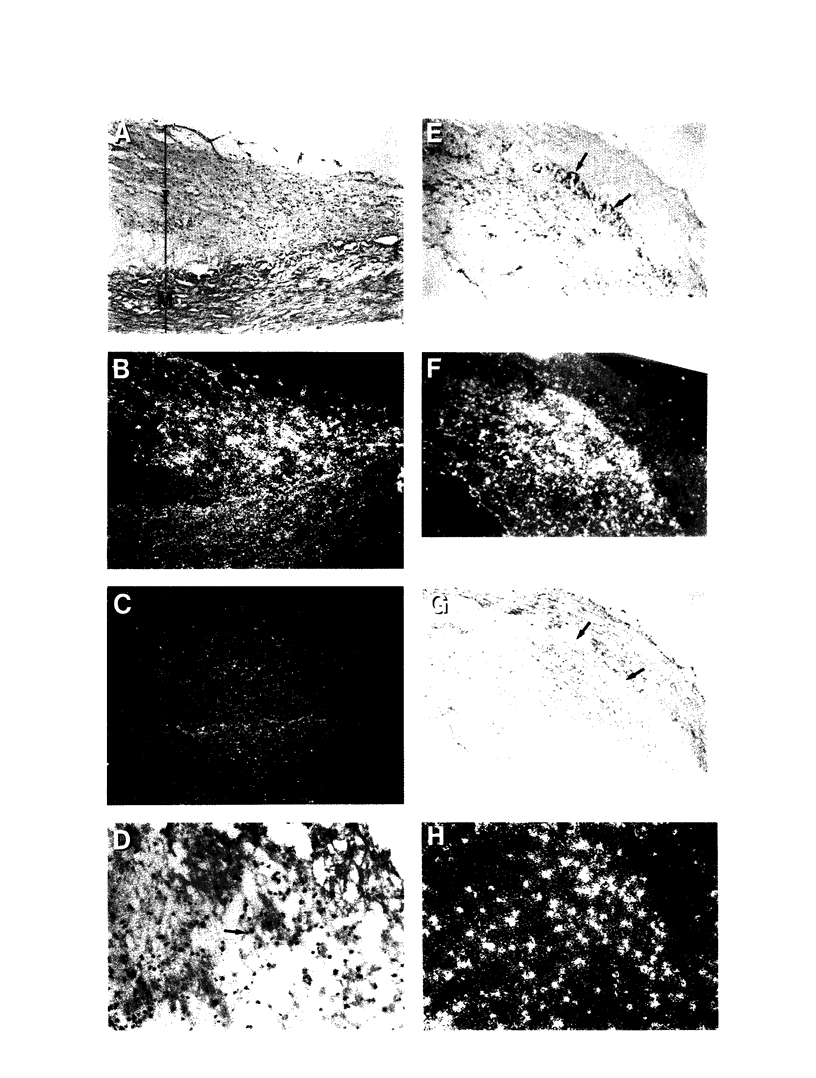
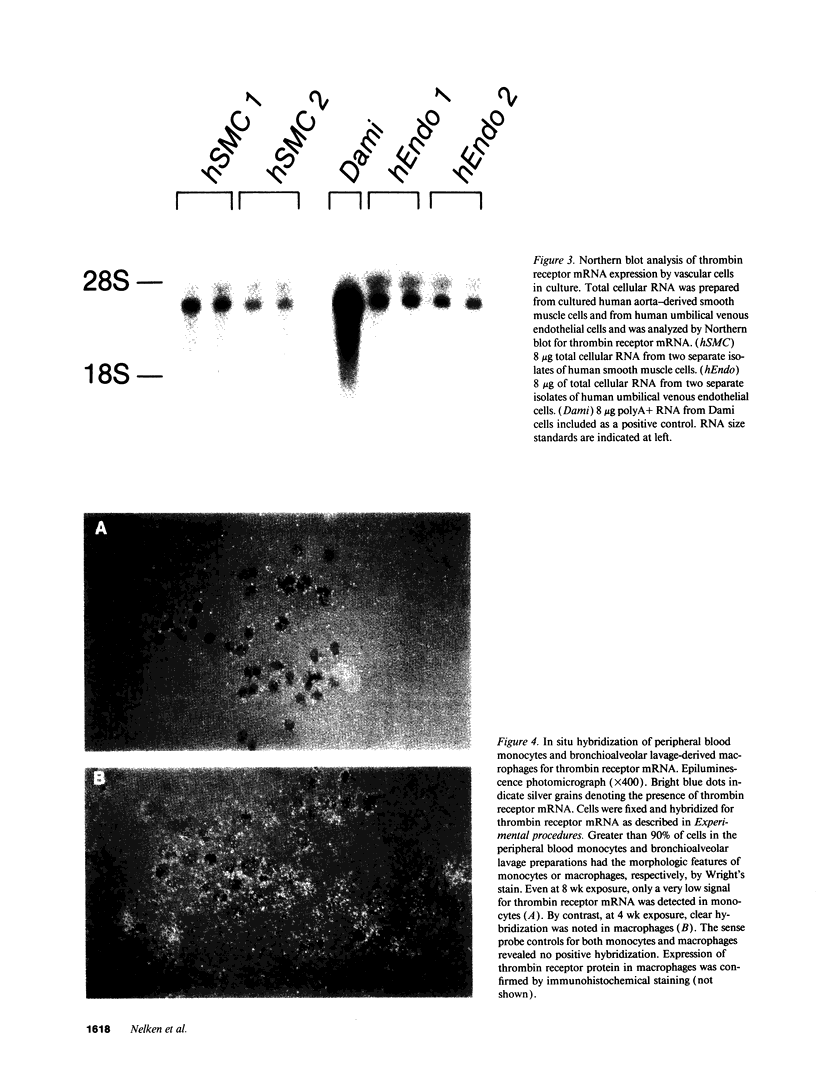
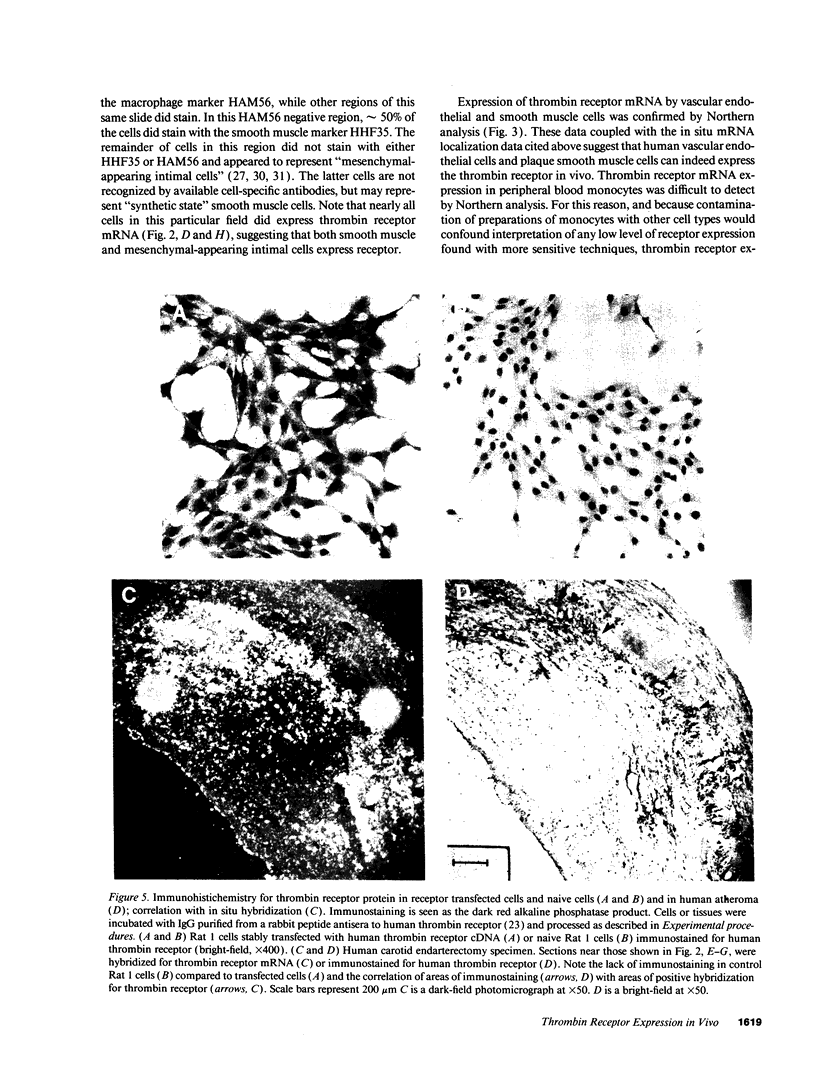
Thrombin is a multifunctional serine protease generated at sites of vascular injury. A host of thrombin actions on vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and macrophages has been defined in cell culture systems, but the in vivo significance of these activities is unknown. We have defined the expression of the recently identified receptor for thrombin in human arteries by both in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. In normal-appearing arteries, thrombin receptor was expressed almost exclusively in the endothelial layer. By contrast, in human atheroma, the receptor was widely expressed, both in regions rich in macrophages and in regions rich in vascular smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal-appearing intimal cells of unknown origin. Thrombin receptor was expressed by human vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in culture and by macrophages obtained by bronchioalveolar lavage, thus demonstrating that all three cell types are indeed capable of expressing the thrombin receptor. These results establish thrombin receptor activation as a candidate for contributing to sclerotic and inflammatory processes in the human vasculature, such as those that occur in atherosclerosis and restenosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Wilner G. D., Fenton J. W., 2nd Monocyte chemotaxis: stimulation by specific exosite region in thrombin. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6836310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenic activity of blood components. I. Thrombin and prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Teng N. N., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenicity of thrombin and surface alterations on mouse splenocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Aug;101(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I. Characterization of a functional thrombin receptor. Issues and opportunities. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):351–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI115592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. O., Gibbs V. C., Milfay D. F., Garovoy M. R., Williams L. T. Thrombin stimulates c-sis gene expression in microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9579–9582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. G., Lüscher E. F. Actions of thrombin and other coagulant and proteolytic enzymes on blood platelets. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):857–858. doi: 10.1038/216857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidt J. F., Allison P., Noble S., Ashton J., Golino P., McNatt J., Buja L. M., Willerson J. T. Thrombin is an important mediator of platelet aggregation in stenosed canine coronary arteries with endothelial injury. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):18–27. doi: 10.1172/JCI114138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald D. J., Fitzgerald G. A. Role of thrombin and thromboxane A2 in reocclusion following coronary thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7585–7589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster V., Badimon L., Badimon J. J., Chesebro J. H. The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes (1). N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 23;326(4):242–250. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201233260406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Sznycer-Laszuk R. Thrombin induction of plasminogen activator-inhibitor in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):165–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI112271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson S. R., Harker L. A. Interruption of acute platelet-dependent thrombosis by the synthetic antithrombin D-phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl chloromethyl ketone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3184–3188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori R., Hamilton K. K., Fugate R. D., McEver R. P., Sims P. J. Stimulated secretion of endothelial von Willebrand factor is accompanied by rapid redistribution to the cell surface of the intracellular granule membrane protein GMP-140. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7768–7771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heras M., Chesebro J. H., Penny W. J., Bailey K. R., Badimon L., Fuster V. Effects of thrombin inhibition on the development of acute platelet-thrombus deposition during angioplasty in pigs. Heparin versus recombinant hirudin, a specific thrombin inhibitor. Circulation. 1989 Mar;79(3):657–665. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.3.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. S., Sorisky A., Church W. R., Simons E. R., Rittenhouse S. E. "Thrombin" receptor-directed ligand accounts for activation by thrombin of platelet phospholipase C and accumulation of 3-phosphorylated phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18435–18438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. H., Nelken N. A., Coughlin S. R. Thrombin-induced events in non-platelet cells are mediated by the unique proteolytic mechanism established for the cloned platelet thrombin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):827–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Charo I. F., Nelken N. A., Esmon N., Esmon C. T., Coughlin S. R. "Mirror image" antagonists of thrombin-induced platelet activation based on thrombin receptor structure. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):444–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI115604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Ishii K., Coughlin S. R. Cloned platelet thrombin receptor is necessary for thrombin-induced platelet activation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1350–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang I. K., Gold H. K., Ziskind A. A., Leinbach R. C., Fallon J. T., Collen D. Prevention of platelet-rich arterial thrombosis by selective thrombin inhibition. Circulation. 1990 Jan;81(1):219–225. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelken N. A., Coughlin S. R., Gordon D., Wilcox J. N. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human atheromatous plaques. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1121–1127. doi: 10.1172/JCI115411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngaiza J. R., Jaffe E. A. A 14 amino acid peptide derived from the amino terminus of the cleaved thrombin receptor elevates intracellular calcium and stimulates prostacyclin production in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1656–1661. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Human endothelial cells in culture produce platelet-activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) when stimulated with thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3534–3538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarembock I. J., Gertz S. D., Gimple L. W., Owen R. M., Powers E. R., Roberts W. C. Effectiveness of recombinant desulphatohirudin in reducing restenosis after balloon angioplasty of atherosclerotic femoral arteries in rabbits. Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):232–243. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A. Thrombin-cellular interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;485:228–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vouret-Craviari V., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Rasmussen U. B., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Pouysségur J. Synthetic alpha-thrombin receptor peptides activate G protein-coupled signaling pathways but are unable to induce mitogenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):95–102. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Ley C. W., Jaffe E. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):923–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Williams L. T., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Platelet-derived growth factor mRNA detection in human atherosclerotic plaques by in situ hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1134–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI113671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]