Abstract
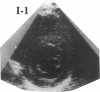
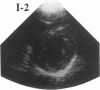
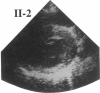
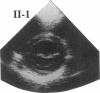
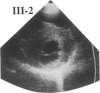
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy occurs as an autosomal dominant familial disorder or as a sporadic disease without familial involvement. While missense mutations in the beta cardiac myosin heavy chain (MHC) gene account for approximately half of all cases of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the molecular causes of sporadic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are unknown. To determine whether beta cardiac MHC mutations are also associated with sporadic disease, we screened this gene in seven individuals with sporadic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Mutations in the beta cardiac MHC genes were identified in two probands with sporadic disease. In that their parents were neither clinically nor genetically affected, we conclude that mutations in each proband arose de novo. Transmission of the mutation and disease to an offspring occurred in one pedigree, predicting that these are germline mutations. The demonstration of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy arising within a pedigree coincident with the appearance of a de novo mutation provides compelling genetic evidence that beta cardiac MHC mutations cause this disease. We suggest that de novo mutations account for some instances of sporadic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and that these mutations can be transmitted to children. The clinical benefits of defining mutations responsible for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy should also be available to some patients with sporadic disease.
Full text
PDF
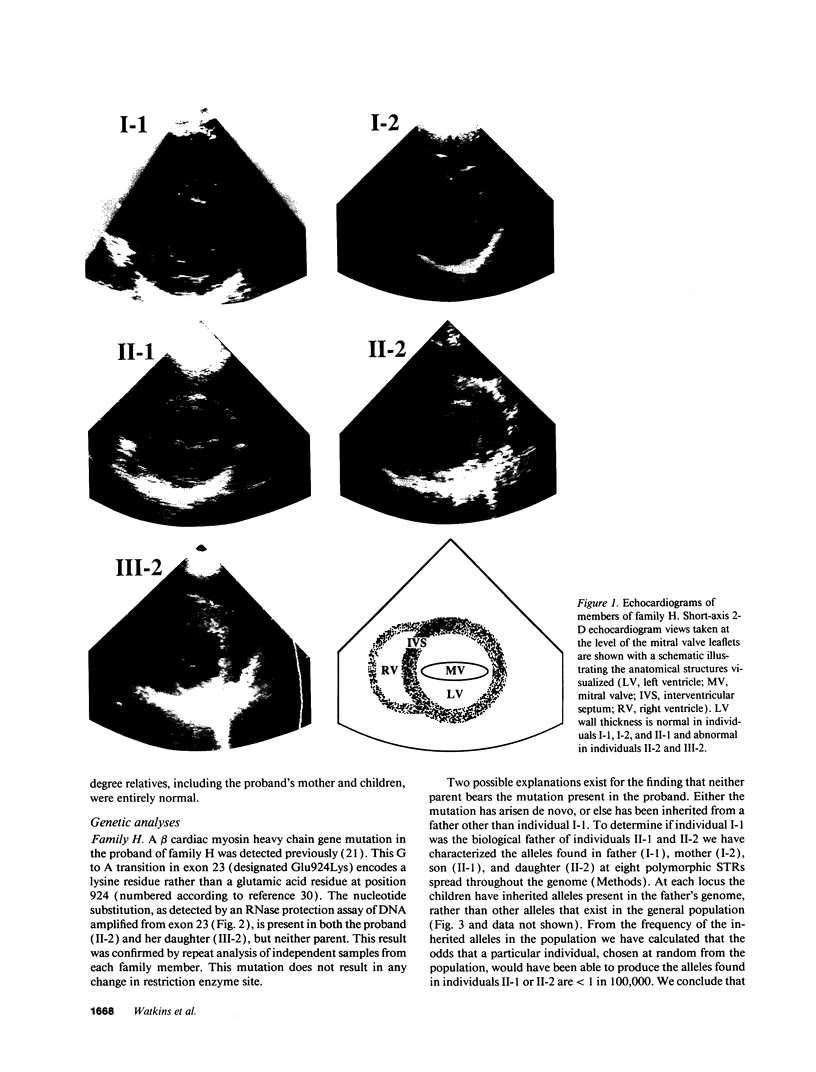
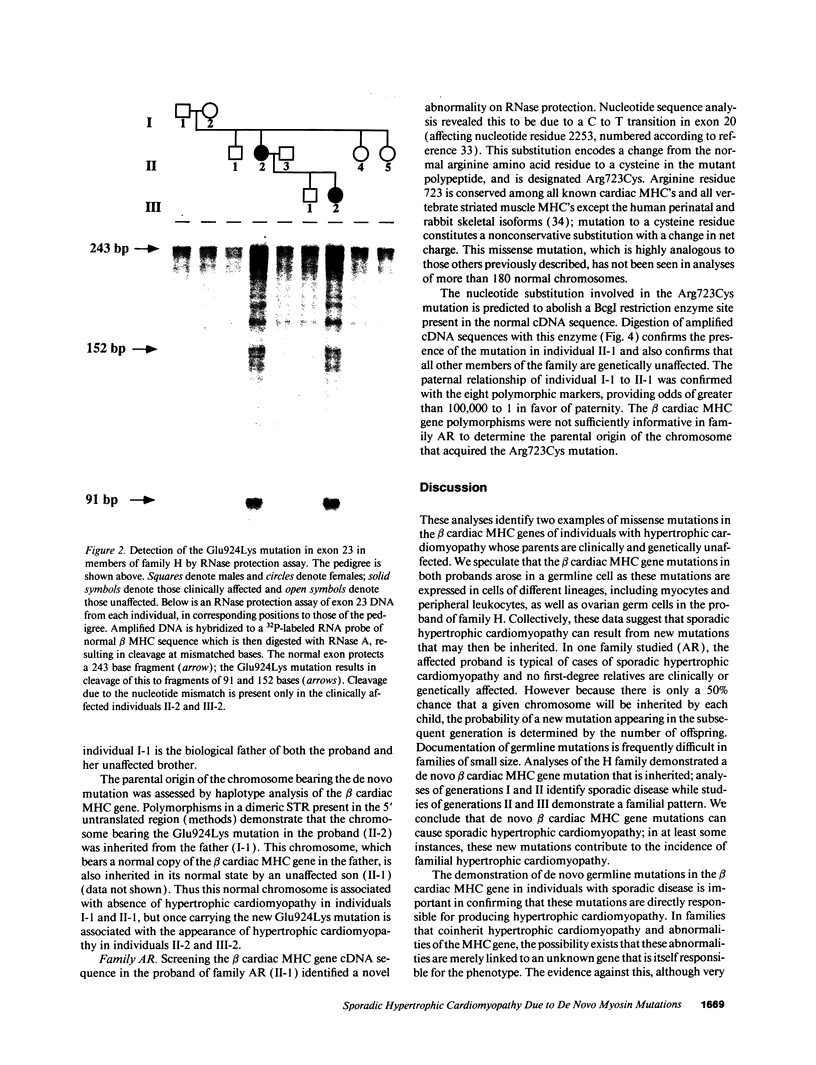


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark C. E., Henry W. L., Epstein S. E. Familial prevalence and genetic transmission of idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 4;289(14):709–714. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310042891402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J. The current status of myocardial disarray in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Br Heart J. 1984 Apr;51(4):361–363. doi: 10.1136/hrt.51.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N. D., Fananapazir L., Lin H. J., Mulvihill J., White R., Lalouel J. M., Lifton R. P., Nienhuis A. W., Leppert M. Evidence of genetic heterogeneity in five kindreds with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1992 Feb;85(2):635–647. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.2.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Morrow A. G., Roberts W. C. Myocardial ultrastructure in idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. A study of operatively excised left ventricular outflow tract muscle in 14 patients. Circulation. 1972 Apr;45(4):769–792. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.45.4.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Braunwald E. Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. Clinical analysis of 126 patients with emphasis on the natural history. Circulation. 1968 May;37(5):759–788. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.37.5.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Kass S., Tanigawa G., Vosberg H. P., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a beta cardiac myosin heavy chain gene missense mutation. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90274-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves S. C., Roche A. H., Neutze J. M., Whitlock R. M., Veale A. M. Inheritance of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a cross sectional and M mode echocardiographic study of 50 families. Br Heart J. 1987 Sep;58(3):259–266. doi: 10.1136/hrt.58.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLMAN A., GOODWIN J. F., TEARE D., RENWICK J. W. A family with obstructive cardiomyopathy (asymmetrical hypertrophy). Br Heart J. 1960 Sep;22:449–456. doi: 10.1136/hrt.22.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland H., Ohm O. J., Boman H., Thorsby E. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in three generations of a large Norwegian family. A clinical, echocardiographic, and genetic study. Br Heart J. 1986 Feb;55(2):168–175. doi: 10.1136/hrt.55.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry W. L., Clark C. E., Epstein S. E. Asymmetric septal hypertrophy. Echocardiographic identification of the pathognomonic anatomic abnormality of IHSS. Circulation. 1973 Feb;47(2):225–233. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.47.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick L., Petkovich N. J., Bolton C. F. Idiopathic hypertrophic subvalvular stenosis. A study of a family involving four generations. Clinical, hemodynamic and pathologic observations. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Mar;17(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke T., Diederich K. W., Haas W., Schleich J., Lichter P., Pfordt M., Bach A., Vosberg H. P. The complete sequence of the human beta-myosin heavy chain gene and a comparative analysis of its product. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):194–206. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90272-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarcho J. A., McKenna W., Pare J. A., Solomon S. D., Holcombe R. F., Dickie S., Levi T., Donis-Keller H., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Mapping a gene for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to chromosome 14q1. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1372–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Epstein S. E. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a discussion of nomenclature. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Jun;43(6):1242–1244. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90160-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Gottdiener J. S., Epstein S. E. Patterns and significance of distribution of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A wide angle, two dimensional echocardiographic study of 125 patients. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Sep;48(3):418–428. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Nichols P. F., 3rd, Pickle L. W., Wesley Y. E., Mulvihill J. J. Patterns of inheritance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: assessment by M-mode and two-dimensional echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Apr 1;53(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Tajik A. J., Ruttenberg H. D., Graham T. P., Atwood G. F., Victorica B. E., Lie J. T., Roberts W. C. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in infants: clinical features and natural history. Circulation. 1982 Jan;65(1):7–17. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. J., Kleinebenne A., Nihoyannopoulos P., Foale R. Echocardiographic measurement of right ventricular wall thickness in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: relation to clinical and prognostic features. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Feb;11(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARE J. A., FRASER R. G., PIROZYNSKI W. J., SHANKS J. A., STUBINGTON D. Hereditary cardiovascular dysplasia. A form of familial cardiomyopathy. Am J Med. 1961 Jul;31:37–62. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Rath D. S., Xiao H., Merril C. R. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human preproglucagon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):688–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Rath D. S., Xiao H., Merril C. R. Trinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human pancreatic phospholipase A-2 gene (PLA2). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7468–7468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Rath D. S., Merril C. R. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human cardiac beta-myosin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4019–4019. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Rath D. S., Merril C. R. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the int-2 proto-oncogene locus (INT2). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7468–7468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig A., Watkins H., Hwang D. S., Miri M., McKenna W., Traill T. A., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Preclinical diagnosis of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by genetic analysis of blood lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 19;325(25):1753–1760. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112193252501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. M., McKenna W. J. Distribution of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a two-dimensional echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Sep;2(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma V., Allen L., Magenis R. E., Litt M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D21S172 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1169–1169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. D., Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Vosberg H. P., Hiller G., Jarcho J. A., Morton C. C., McBride W. O., Mitchell A. L., Bale A. E., McKenna W. J. A locus for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is closely linked to the cardiac myosin heavy chain genes, CRI-L436, and CRI-L329 on chromosome 14 at q11-q12. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;47(3):389–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Jarcho J. A., Kass S., Solomon S. D., Vosberg H. P., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an alpha/beta cardiac myosin heavy chain hybrid gene. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90273-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins H., Rosenzweig A., Hwang D. S., Levi T., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. Characteristics and prognostic implications of myosin missense mutations in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1108–1114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D1S103 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2199–2199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuille M. A., Hampson R. M., Harris R. M., Affara N. A., Yates J. R., Ferguson-Smith M. A. CA repeat polymorphism at the ASS locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7472–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]