Abstract
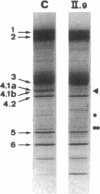
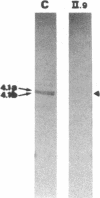
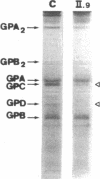
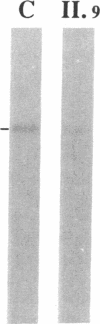
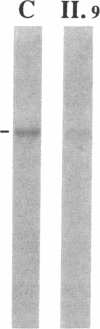
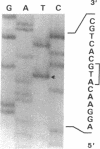
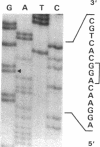
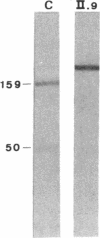
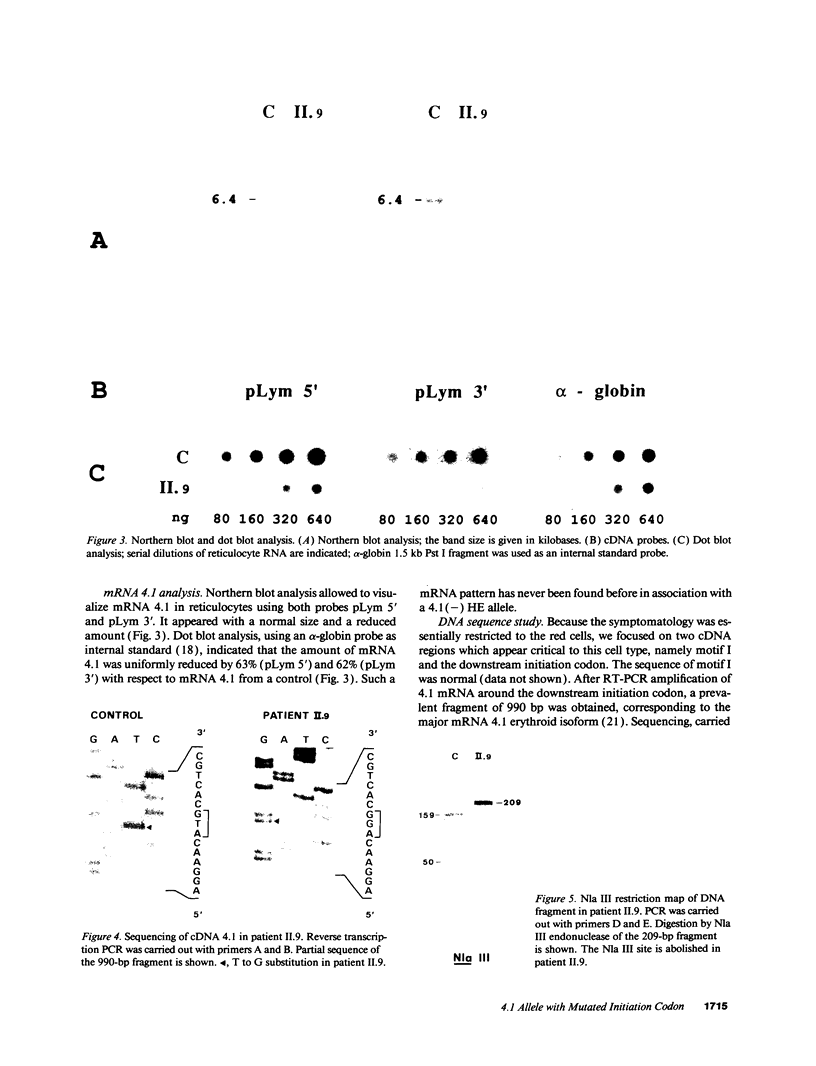
We studied a 43 yr-old Spanish patient with homozygous 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis. Any form of protein 4.1 was missing in the red cells. Spectrin and actin were slightly, yet significantly, diminished. Alterations appeared at the level of proteins 4.5 and 4.9. Glycophorin C was sharply reduced. The abnormal allele was associated with the -++-- haplotype (Pvu II, Bgl II, Bgl II, Pvu II, Pvu II). mRNA 4.1(-) had an apparently normal size but was diminished by about two-thirds. Because the abnormal phenotype pertained to the red cell, we sequenced the 4.1 cDNA regions that appear critical to this cell type. The ultimate change turned out to be a point mutation of the downstream translation initiation codon (AUG-->AGG). No disorders in other cell types could be related with certainty to the present 4.1(-) HE allele.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloisio N., Morlé L., Bachir D., Guetarni D., Colonna P., Delaunay J. Red cell membrane sialoglycoprotein beta in homozygous and heterozygous 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 11;816(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alloisio N., Morlé L., Dorléac E., Gentilhomme O., Bachir D., Guetarni D., Colonna P., Bost M., Zouaoui Z., Roda L. The heterozygous form of 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis [the 4.1(-) trait]. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alloisio N., Morlé L., Maréchal J., Roux A. F., Ducluzeau M. T., Guetarni D., Pothier B., Baklouti F., Ghanem A., Kastally R. Sp alpha V/41: a common spectrin polymorphism at the alpha IV-alpha V domain junction. Relevance to the expression level of hereditary elliptocytosis due to alpha-spectrin variants located in trans. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2169–2177. doi: 10.1172/JCI115250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Marchesi V. T. Regulation of the association of membrane skeletal protein 4.1 with glycophorin by a polyphosphoinositide. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):295–298. doi: 10.1038/318295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baklouti F., Maréchal J., Wilmotte R., Alloisio N., Morlé L., Ducluzeau M. T., Denoroy L., Mrad A., Ben Aribia M. H., Kastally R. Elliptocytogenic alpha I/36 spectrin Sfax lacks nine amino acids in helix 3 of repeat 4. Evidence for the activation of a cryptic 5'-splice site in exon 8 of spectrin alpha-gene. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2464–2470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Benz E. J., Jr Nonsense mutations in the human beta-globin gene affect mRNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The spectrin-actin junction of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Foley S. F. Phorbol ester- and Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of human red cell membrane skeletal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7701–7709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J. G., Chan J. Y., Chasis J. A., Kan Y. W., Mohandas N. Tissue- and development-specific alternative RNA splicing regulates expression of multiple isoforms of erythroid membrane protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8273–8280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J. G., Shitamoto R., Parra M., Winardi R., Kabra A., Smith J., Mohandas N. Hereditary elliptocytosis due to both qualitative and quantitative defects in membrane skeletal protein 4.1. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2438–2443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J., Kan Y. W., Shohet S. B., Mohandas N. Molecular cloning of protein 4.1, a major structural element of the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9512–9516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J., Marchesi S., Kim R., Agre P., Kan Y. W., Mohandas N. Molecular analysis of insertion/deletion mutations in protein 4.1 in elliptocytosis. II. Determination of molecular genetic origins of rearrangements. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):524–530. doi: 10.1172/JCI114739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J., Mohandas N., Tchernia G., Kan Y. W. Molecular basis of hereditary elliptocytosis due to protein 4.1 deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 11;315(11):680–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609113151105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilov Y. N., Fennell R., Ling E., Cohen C. M. Selective modulation of band 4.1 binding to erythrocyte membranes by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2556–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay J., Alloisio N., Morlé L., Pothier B. The red cell skeleton and its genetic disorders. Mol Aspects Med. 1990;11(3):161–241. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(90)90001-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feddal S., Brunet G., Roda L., Chabanis S., Alloisio N., Morlé L., Ducluzeau M. T., Maréchal J., Robert J. M., Benz E. J., Jr Molecular analysis of hereditary elliptocytosis with reduced protein 4.1 in the French Northern Alps. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):2113–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feo C. J., Fischer S., Piau J. P., Grange M. J., Tchernia G. Première observation de l'absence d'une protéine de la membrane érythrocytaire (bande 4(1)) dans un cas d'anémie elliptocytaire familiale. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1980;22(4):315–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt G. D., Haltiwanger R. S., Torres C. R., Hart G. W. Erythrocytes contain cytoplasmic glycoproteins. O-linked GlcNAc on Band 4.1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14847–14850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Leto T. L., Marchesi V. T. Differential phosphorylation of multiple sites in protein 4.1 and protein 4.9 by phorbol ester-activated and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9073–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba M., Maede Y. O-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine moiety on discrete peptide of multiple protein 4.1 isoforms regulated by alternative pathways. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18149–18155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert S., Zail S. Partial deficiency of protein 4.1 in hereditary elliptocytosis. Am J Hematol. 1987 Nov;26(3):263–272. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830260308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto T. L., Marchesi V. T. A structural model of human erythrocyte protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4603–4608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Derick L. H., Palek J. Visualization of the hexagonal lattice in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):527–536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire M., Smith B. L., Agre P. Distinct variants of erythrocyte protein 4.1 inherited in linkage with elliptocytosis and Rh type in three white families. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moi P., Cash F. E., Liebhaber S. A., Cao A., Pirastu M. An initiation codon mutation (AUG----GUG) of the human alpha 1-globin gene. Structural characterization and evidence for a mild thalassemic phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1416–1421. doi: 10.1172/JCI113220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morlé F., Lopez B., Henni T., Godet J. alpha-Thalassaemia associated with the deletion of two nucleotides at position -2 and -3 preceding the AUG codon. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1245–1250. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03767.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack G. R., Anderson R. A., Leto T. L., Marchesi V. T. Interactions between protein 4.1 and band 3. An alternative binding site for an element of the membrane skeleton. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3676–3683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirastu M., Saglio G., Chang J. C., Cao A., Kan Y. W. Initiation codon mutation as a cause of alpha thalassemia. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12315–12317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothier B., Morlé L., Alloisio N., Ducluzeau M. T., Caldani C., Féo C., Garbarz M., Chaveroche I., Dhermy D., Lecomte M. C. Spectrin Nice (beta 220/216): a shortened beta-chain variant associated with an increase of the alpha I/74 fragment in a case of elliptocytosis. Blood. 1987 Jun;69(6):1759–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M. E., Takakuwa Y., Conboy J., Tchernia G., Mohandas N. Glycophorin C content of human erythrocyte membrane is regulated by protein 4.1. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2229–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondag D., Alloisio N., Blanchard D., Ducluzeau M. T., Colonna P., Bachir D., Bloy C., Cartron J. P., Delaunay J. Gerbich reactivity in 4.1 (-) hereditary elliptocytosis and protein 4.1 level in blood group Gerbich deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1987 Jan;65(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb06133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam G., Bertics P. J., Anderson R. A. Phosphorylation of protein 4.1 on tyrosine-418 modulates its function in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5222–5226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. J., Tang T. K. Rapid localization of membrane skeletal protein 4.1 (EL1) to human chromosome 1p33----p34.2 by nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;57(2-3):119–119. doi: 10.1159/000133128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. K., Leto T. L., Correas I., Alonso M. A., Marchesi V. T., Benz E. J., Jr Selective expression of an erythroid-specific isoform of protein 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3713–3717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. K., Qin Z., Leto T., Marchesi V. T., Benz E. J., Jr Heterogeneity of mRNA and protein products arising from the protein 4.1 gene in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):617–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. K., Tam K. B., Chien S. Two RFLPs in the human protein 4.1 gene (EL1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):6057–6057. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchernia G., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Deficiency of skeletal membrane protein band 4.1 in homozygous hereditary elliptocytosis. Implications for erythrocyte membrane stability. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):454–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI110275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]