Abstract
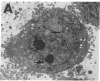
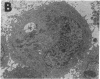
Cytokines have been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of brain diseases in which neurological dysfunction has been attributed to a change in amino acid neurotransmitter metabolism. In the present in vitro study, we investigated the effects of cytokines on astrocyte glutamine synthetase (GS) activity and subsequently on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Proinflammatory cytokines IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 at a concentration of 20 ng/ml did not affect GS activity; however, tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibited this activity by 20% in mixed neuronal/astrocyte cultures. Treatment for 24 h with transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 1 or -beta 2 inhibited up to 60% GS activity. TGF-beta 2 also inhibited GS in enriched astrocyte cultures with an ED50 of 10 pg/ml. Antibodies specific to TGF-beta 2 blocked this effect. Treatment of astrocytes with TGF-beta 2 (250 pg/ml) resulted in markedly dilated rough endoplasmic reticulum. Since astrocyte GS may play a protective role in NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity, we treated mixed neuronal/astrocyte cultures with TGF-beta 2 (250 pg/ml) and found a threefold potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. These data suggest that TGF-beta impairs astrocyte GS function and enhances neurotoxicity, thus providing insight into understanding one mechanism of cytokine-mediated central nervous system disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonelli-Orlidge A., Saunders K. B., Smith S. R., D'Amore P. A. An activated form of transforming growth factor beta is produced by cocultures of endothelial cells and pericytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Alzheimer's disease and dementia. Med Sect Proc. 1988:129–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Methods for antagonizing glutamate neurotoxicity. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1990 Summer;2(2):105–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Lynch G. S. The neurobiology of learning and memory. Cognition. 1989 Nov;33(1-2):201–241. doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(89)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R. A. Oxidative damage to behavior during aging. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1597–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.1684251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Smale G., Pencev D. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human peripheral blood monocytes and neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):396–402. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. Cytokines: molecular and biological characteristics. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;76:189–201. doi: 10.3109/03009748809102969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz L. Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes I. Turnover and metabolism of putative amino acid transmitters. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(3):277–323. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Baemayr J., Weil M., Merrill J. E. Lymphokines and immunoregulatory molecules in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Mar;58(3):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen O. S., Brooksbank B. W., Balázs R. Neuronal plasticity and astrocytic reaction in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Aug;98(1):63–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90182-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekow J., Wachsman W., McCutchan J. A., Cronin M., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Transforming growth factor beta and noncytopathic mechanisms of immunodeficiency in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8321–8325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Choi D. W. Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J Neurosci Methods. 1987 May;20(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(87)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maimone D., Gregory S., Arnason B. G., Reder A. T. Cytokine levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Apr;32(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90073-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapstone T., McMichael M., Goldthwait D. Expression of platelet-derived growth factors, transforming growth factors, and the ros gene in a variety of primary human brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 1991 Feb;28(2):216–222. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199102000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A., Bell K. P., Norenberg M. D. Glutamine synthetase: glial localization in brain. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.14400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Chen I. S. HIV-1, macrophages, glial cells, and cytokines in AIDS nervous system disease. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2391–2397. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.2065887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Bridges R. J., Cotman C. W. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:365–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 2;161(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver C. N., Starke-Reed P. E., Stadtman E. R., Liu G. J., Carney J. M., Floyd R. A. Oxidative damage to brain proteins, loss of glutamine synthetase activity, and production of free radicals during ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury to gerbil brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5144–5147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino M. A., Morris R. E., Starnes H. F., Levinson A. D. The transforming growth factor-betas. A new family of immunoregulatory molecules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;593:181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Chao C. C., Hu S., Thielen K., Shaskan E. G. Glioblastoma, transforming growth factor-beta, and Candida meningitis: a potential link. Am J Med. 1992 Mar;92(3):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90075-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Gekker G., Chao C. C., Schut R., Molitor T. W., Balfour H. H., Jr Cocaine potentiates HIV-1 replication in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cocultures. Involvement of transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarello V. J., Wispelwey B., Long W. J., Jr, Scheld W. M. Recombinant human interleukin-1 induces meningitis and blood-brain barrier injury in the rat. Characterization and comparison with tumor necrosis factor. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1360–1366. doi: 10.1172/JCI115140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramilo O., Sáez-Llorens X., Mertsola J., Jafari H., Olsen K. D., Hansen E. J., Yoshinaga M., Ohkawara S., Nariuchi H., McCracken G. H., Jr Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin and interleukin 1 beta initiate meningeal inflammation. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):497–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. L., Markovac J., Datta S. C., Goldstein G. W. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates phosphoinositol metabolism and translocation of protein kinase C in cultured astrocytes. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Oct 31;93(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Aizenman E. Hundred-fold increase in neuronal vulnerability to glutamate toxicity in astrocyte-poor cultures of rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Aug 28;103(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Amin S., Leitner M. Glutamate uptake disguises neurotoxic potency of glutamate agonists in cerebral cortex in dissociated cell culture. J Neurosci. 1992 Jan;12(1):56–61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-01-00056.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluesener H. J. Transforming growth factors type beta 1 and beta 2 suppress rat astrocyte autoantigen presentation and antagonize hyperinduction of class II major histocompatibility complex antigen expression by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Apr;27(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K., Raine C. S., Cannella B., Brosnan C. F. Identification of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):949–954. doi: 10.1172/JCI115102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher P. K., Hu S. X. Increased glutamate uptake and glutamine synthetase activity in neuronal cell cultures surviving chronic hypoxia. Glia. 1990;3(5):350–357. doi: 10.1002/glia.440030506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotrel A., Paskevich P. A., Kiely D. K., Bird E. D., Williams R. S., Myers R. H. Morphometric analysis of the prefrontal cortex in Huntington's disease. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):1117–1123. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.7.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. The transforming growth factor-betas: past, present, and future. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;593:1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama K., Brunori A., Mayer M. L. Glial uptake of excitatory amino acids influences neuronal survival in cultures of mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):779–791. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talwar D., Sher P. K. Benzodiazepine receptor development in murine glial cultures. Dev Neurosci. 1987;9(3):183–189. doi: 10.1159/000111621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toru-Delbauffe D., Baghdassarian-Chalaye D., Gavaret J. M., Courtin F., Pomerance M., Pierre M. Effects of transforming growth factor beta 1 on astroglial cells in culture. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):1056–1061. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunkel A. R., Wispelwey B., Scheld W. M. Bacterial meningitis: recent advances in pathophysiology and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Apr 15;112(8):610–623. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-8-610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Allen J. B., McCartney-Francis N., Morganti-Kossmann M. C., Kossmann T., Ellingsworth L., Mai U. E., Mergenhagen S. E., Orenstein J. M. Macrophage- and astrocyte-derived transforming growth factor beta as a mediator of central nervous system dysfunction in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):981–991. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., McCartney-Francis N., Mergenhagen S. E. Inflammatory and immunomodulatory roles of TGF-beta. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Kuppner M. C., De Tribolet N. Transforming growth factor-beta 2 down-regulates HLA-DR antigen expression on human malignant glioma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1623–1626. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martin R., Haendler B., Hofer-Warbinek R., Gaugitsch H., Wrann M., Schlüsener H., Seifert J. M., Bodmer S., Fontana A., Hofer E. Complementary DNA for human glioblastoma-derived T cell suppressor factor, a novel member of the transforming growth factor-beta gene family. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3673–3677. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]