Abstract
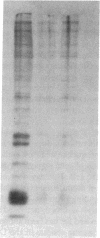
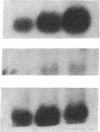
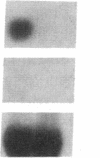
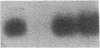
The alveolar surface of the lung is a major target for oxidant injury. After injury, repair of the alveolar epithelium is dependent on the ability of epithelial type 2 (T2) cells to proliferate. The regulation of T2 cell proliferation and the effect of reactive oxygen (O2) species on this lung cell proliferation have not been well defined. To investigate this process we focused on the regulation of two late cell cycle genes, histone and thymidine kinase, in T2 cells and fibroblasts exposed in vitro to varying periods of hyperoxia (95% O2). Hyperoxia for 24 to 48 h arrested cell proliferation in a SV40T-immortalized T2 cell line we have developed and in primary and SV40T-immortalized lung fibroblasts. Despite the cessation of proliferation, histone and TK mRNA continued to be expressed at high levels; mRNA half-lives were markedly prolonged but neither protein was translated. Thus proliferation arrest induced by hyperoxia was associated with posttranscriptional control of at least two late cell cycle-related genes. This form of proliferation arrest is also seen when primary and SV40T-T2 cells but not fibroblasts are serum deprived, suggesting that T2 cells in vitro may be uniquely sensitive to alterations in their redox state and that these alterations in turn affect translational control of a subset of proliferation-related genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti P. A. Oxidant stress and carcinogenesis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;21(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1991.tb01350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ng J. L., Shoemaker D. L., Schimmel P., Holmes E. W. Reversal of creatine kinase translational repression by 3' untranslated sequences. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1003–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.2343304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement A., Campisi J., Farmer S. R., Brody J. S. Constitutive expression of growth-related mRNAs in proliferating and nonproliferating lung epithelial cells in primary culture: evidence for growth-dependent translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement A., Steele M. P., Brody J. S., Riedel N. SV40T-immortalized lung alveolar epithelial cells display post-transcriptional regulation of proliferation-related genes. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Oct;196(2):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90251-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D. Morphologic changes in pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:721–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T., Edwards D. R., Parfett C. L. Gene expression during the mammalian cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 28;865(2):83–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman H. J., Fisher A. B. Antioxidant enzymes of rat granular pneumocytes. Constitutive levels and effect of hyperoxia. Lab Invest. 1981 Jul;45(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Alamo I., Jr, Hollander M. C. DNA damage-inducible transcripts in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8800–8804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Nebert D. W., Hollander M. C., Luethy J. D., Papathanasiou M., Fargnoli J., Holbrook N. J. Mammalian genes coordinately regulated by growth arrest signals and DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4196–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Knight G. B., Pardee A. B. Nuclear posttranscriptional processing of thymidine kinase mRNA at the onset of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Chang L. Y., Crapo J. D. Rat lung alveolar type I epithelial cell injury and response to hyperoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Feb;4(2):115–125. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Oxidation-reduction and the molecular mechanism of a regulatory RNA-protein interaction. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.2711187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. M. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Chest. 1985 Dec;88(6):900–905. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.6.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H. Genetic toxicology of oxygen. Mutat Res. 1989 Jul;219(4):193–208. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(89)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Weibel E. R., Kaplan H. P., Robinson F. R. Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and morphometric studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):101–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman M. G., Kelly T. J. Cell cycle regulation of thymidine kinase: residues near the carboxyl terminus are essential for the specific degradation of the enzyme at mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2538–2546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. cis-trans models for post-transcriptional gene regulation. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):870–872. doi: 10.1126/science.2683086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D. M., Horowitz J. A., Casey J. L., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Translation and the stability of mRNAs encoding the transferrin receptor and c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7778–7782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupitza G., Cerutti P. Poly(ADP-ribosylation) of histones in intact human keratinocytes. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):4054–4060. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruys V., Wathelet M., Poupart P., Contreras R., Fiers W., Content J., Huez G. The 3' untranslated region of the human interferon-beta mRNA has an inhibitory effect on translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon Y. K., Hecht N. B. Cytoplasmic protein binding to highly conserved sequences in the 3' untranslated region of mouse protamine 2 mRNA, a translationally regulated transcript of male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Anderson M. E. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. P., Lawrence D. A. Cell cycle progression of glutathione-depleted human peripheral blood mononuclear cells is inhibited at S phase. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1974–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. E., Hook G. E. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of alveolar type II cells in response to silica and other pulmonary toxicants. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Apr;85:15–23. doi: 10.1289/ehp.85-1568321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A. The regulation of histone synthesis in the cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:827–861. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.004143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou M. A., Kerr N. C., Robbins J. H., McBride O. W., Alamo I., Jr, Barrett S. F., Hickson I. D., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction by ionizing radiation of the gadd45 gene in cultured human cells: lack of mediation by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Hentze M. W., Haile D. J., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. The iron-responsive element binding protein: a method for the affinity purification of a regulatory RNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5768–5772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherley J. L., Kelly T. J. Regulation of human thymidine kinase during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8350–8358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thet L. A., Parra S. C., Shelburne J. D. Sequential changes in lung morphology during the repair of acute oxygen-induced lung injury in adult rats. Exp Lung Res. 1986;11(3):209–228. doi: 10.3109/01902148609064297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Hayaishi O. ADP-ribosylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:73–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent F., Brun H., Clain E., Ronot X., Adolphe M. Effects of oxygen-free radicals on proliferation kinetics of cultured rabbit articular chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Nov;141(2):262–266. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent F., Corral M., Defer N., Adolphe M. Effects of oxygen free radicals on articular chondrocytes in culture: c-myc and c-Ha-ras messenger RNAs and proliferation kinetics. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Feb;192(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90049-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuillaume M. Reduced oxygen species, mutation, induction and cancer initiation. Mutat Res. 1987 Jul;186(1):43–72. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(87)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagoe S., Kohda T., Oishi M. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors suppress UV-induced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3522–3527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]