Abstract
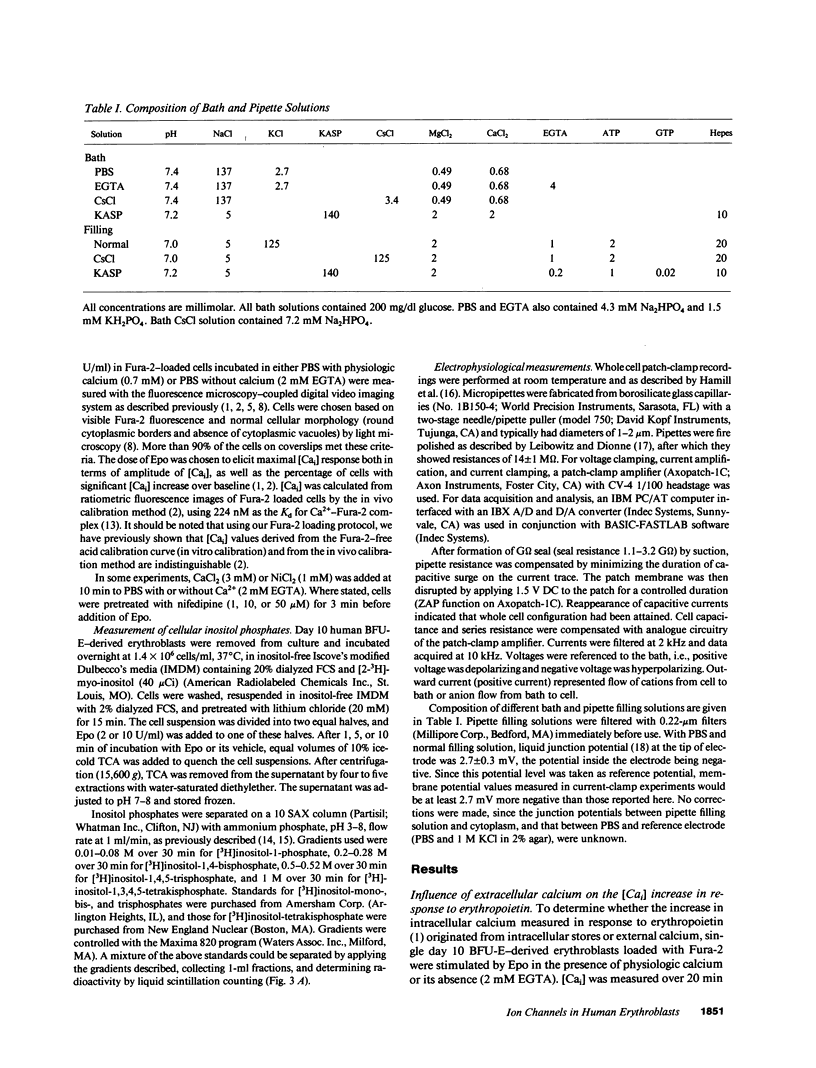
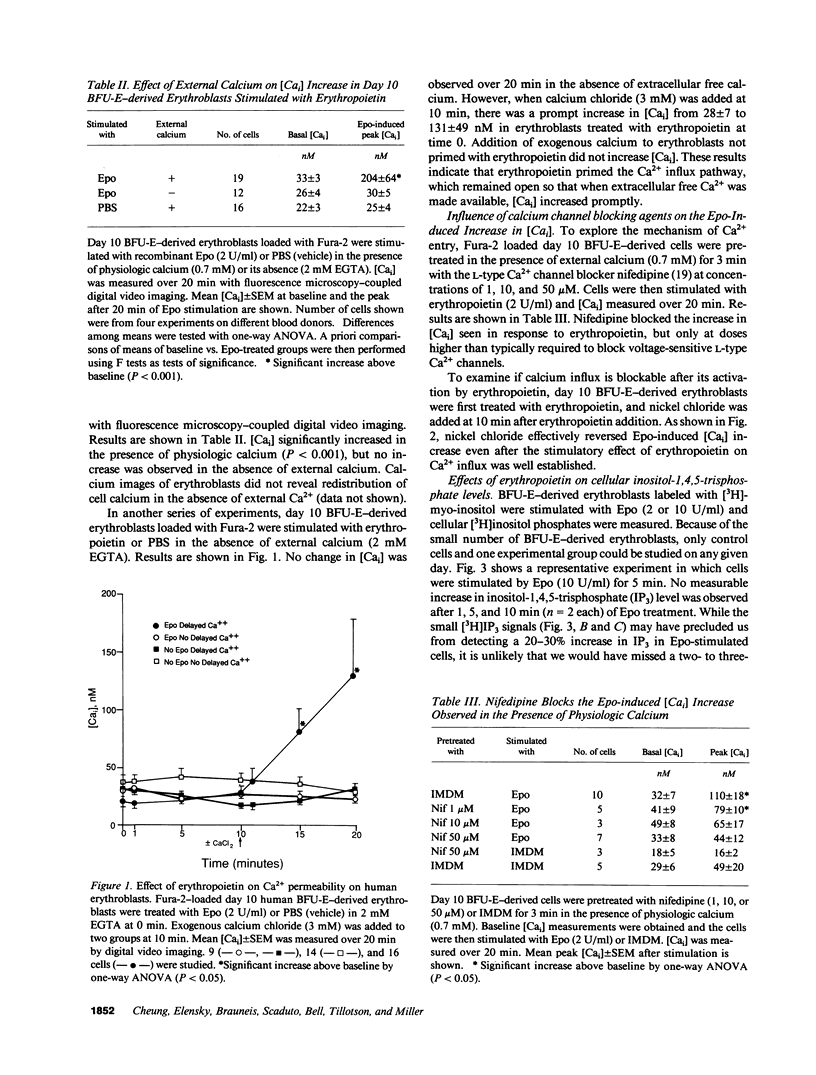
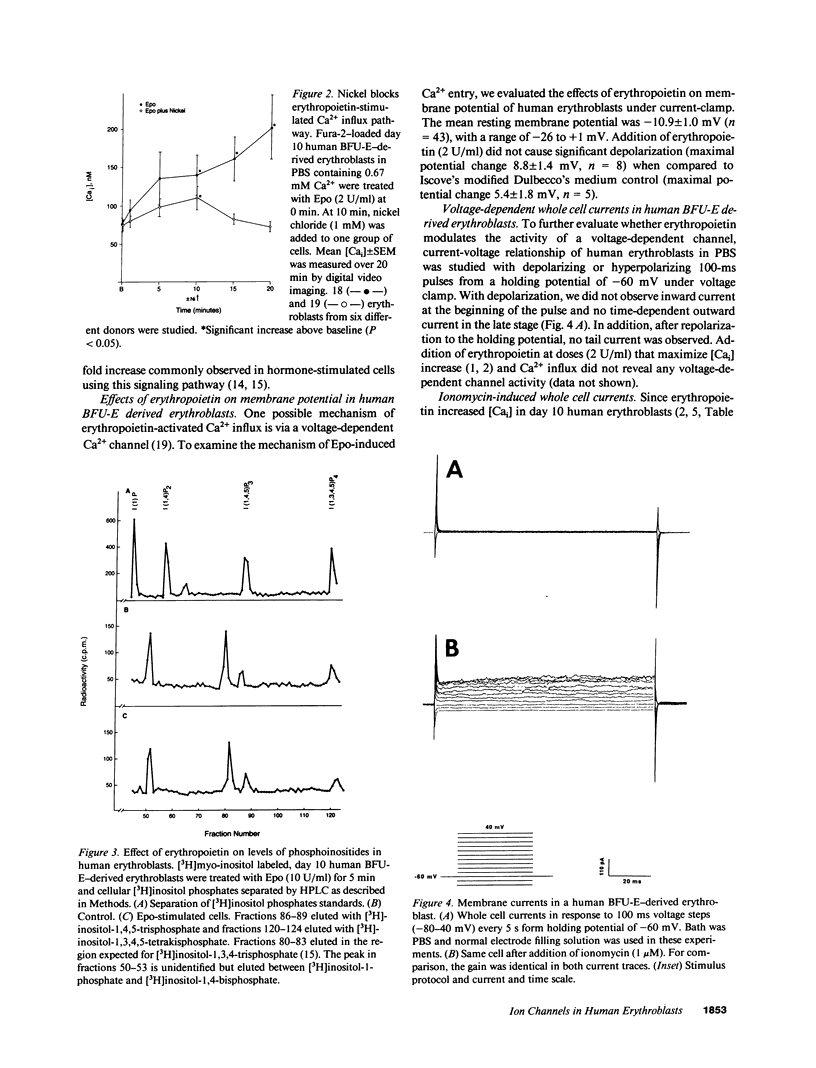
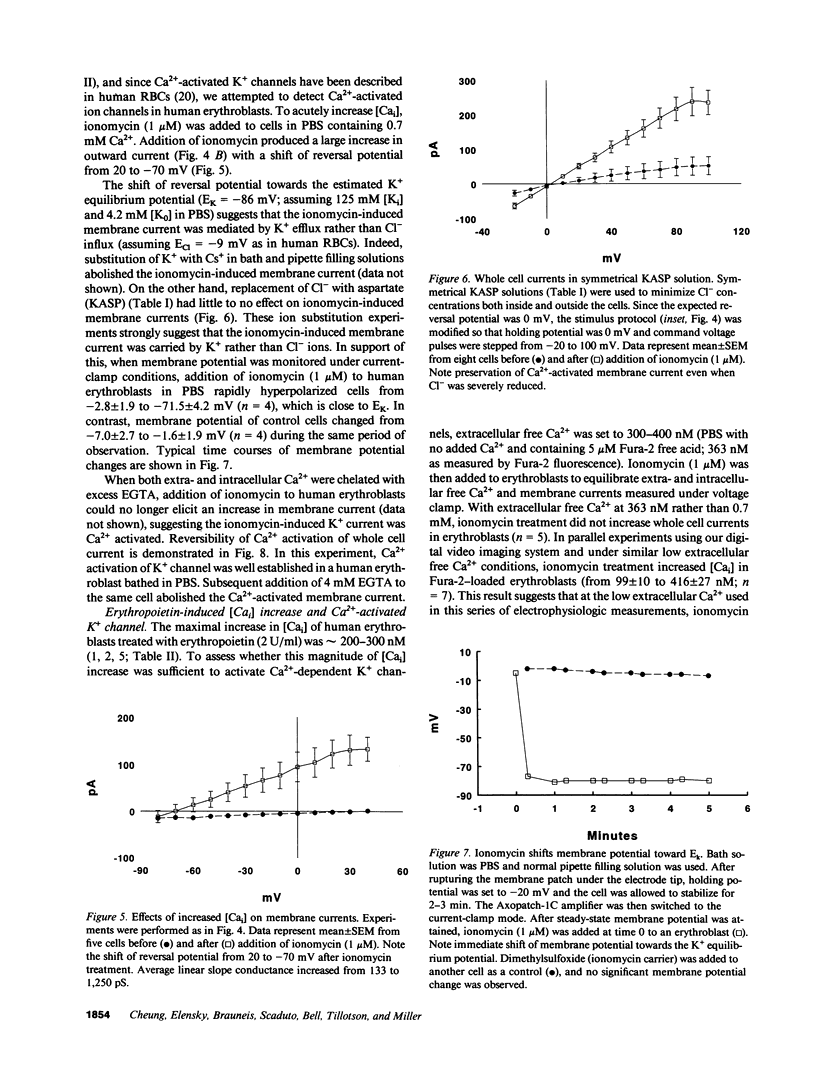
To investigate the mechanism of intracellular Ca2+ ([Cai]) increase in human burst-forming unit-erythroid-derived erythroblasts by erythropoietin, we measured [Cai] with digital video imaging, cellular phosphoinositides with high performance liquid chromatography, and plasma membrane potential and currents with whole cell patch clamp. Chelation of extracellular free Ca2+ abolished [Cai] increase induced by erythropoietin. In addition, the levels of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate did not increase in erythropoietin-treated erythroblasts. These results indicate that in erythropoietin-stimulated cells, Ca2+ influx rather than intracellular Ca2+ mobilization was responsible for [Cai] rise. Both Ni2+ and moderately high doses of nifedipine blocked [Cai] increase, suggesting involvement of ion channels. Resting membrane potential in human erythroblasts was -10.9 +/- 1.0 mV and was not affected by erythropoietin, suggesting erythropoietin modulated a voltage-independent ion channel permeable to Ca2+. No voltage-dependent ion channel but a Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel was detected in human erythroblasts. The magnitude of erythropoietin-induced [Cai] increase, however, was insufficient to open Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. Our data suggest erythropoietin modulated a voltage-independent ion channel permeable to Ca2+, resulting in sustained increases in [Cai].
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. The Croonian lecture, 1988. Inositol lipids and calcium signalling. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Sep 22;234(1277):359–378. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. S., Rossier M. F., Hughes A. R., Shears S. B., Armstrong D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of Ca2+ entry into acinar cells by a non-phosphorylatable inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):162–165. doi: 10.1038/352162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanou-Tzedaki S. A., Setchenska M. S., Arnstein H. R. Stimulation of the adenylate cyclase activity of rabbit bone marrow immature erythroblasts by erythropoietin and haemin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 3;155(2):363–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct G protein gating of ion channels. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):H401–H410. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.3.H401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caubet J. F., Mitjavila M. T., Dubart A., Roten D., Weil S. C., Vainchenker W. Expression of the c-fos protooncogene by human and murine erythroblasts. Blood. 1989 Aug 15;74(3):947–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. S., Wojchowski D. M., Sytkowski A. J. Erythropoietin rapidly alters phosphorylation of pp43, an erythroid membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2933–2936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean N. M., Moyer J. D. Separation of multiple isomers of inositol phosphates formed in GH3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):361–366. doi: 10.1042/bj2420361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDOS G. The function of calcium in the potassium permeability of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Dec;30(3):653–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grygorczyk R., Schwarz W., Passow H. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in human red cells. Comparison of single-channel currents with ion fluxes. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):693–698. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84211-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of calcium channels in rat clonal pituitary cells with patch electrode voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:231–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Welsh M. J. Voltage-dependent and Ca2(+)-activated ion channels in human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):491–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI114464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Oberhauser A., Labarca P., Alvarez O. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:385–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. D., Dionne V. E. A polisher for patch pipets. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Oct;410(3):338–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00580286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Muallem S., Seymour C. A. Properties of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in one-step inside-out vesicles from human red cell membranes. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):742–744. doi: 10.1038/296742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. Ion channels and signal transduction in lymphocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:415–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Clapham D. E. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates an endothelial Ca(2+)-permeable channel. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):356–358. doi: 10.1038/355356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason-Garcia M., Weill C. L., Beckman B. S. Rapid activation by erythropoietin of protein kinase C in nuclei of erythroid progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):490–497. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. A., Cheung J. Y., Tillotson D. L., Hope S. M., Scaduto R. C., Jr Erythropoietin stimulates a rise in intracellular-free calcium concentration in single BFU-E derived erythroblasts at specific stages of differentiation. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. A., Foster K., Robishaw J. D., Whitfield C. F., Bell L., Cheung J. Y. Role of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanosine triphosphate-binding proteins in the response of erythroblasts to erythropoietin. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. A., Scaduto R. C., Jr, Tillotson D. L., Botti J. J., Cheung J. Y. Erythropoietin stimulates a rise in intracellular free calcium concentration in single early human erythroid precursors. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):309–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI113588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mladenovic J., Kay N. E. Erythropoietin induces rapid increases in intracellular free calcium in human bone marrow cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Jul;112(1):23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Smith M. J., Snyder K., Emeagwali D. Amplified expression of three jun family members inhibits erythroleukemia differentiation. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1830–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawanobori T., Takanashi H., Hiraoka M., Iida Y., Kamisaka K., Maezawa H. Electrophysiological properties of isolated rat liver cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):580–585. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todokoro K., Watson R. J., Higo H., Amanuma H., Kuramochi S., Yanagisawa H., Ikawa Y. Down-regulation of c-myb gene expression is a prerequisite for erythropoietin-induced erythroid differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8900–8904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A., Hille B. GnRH-induced Ca2+ oscillations and rhythmic hyperpolarizations of pituitary gonadotropes. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.1734523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D., Cecchi X., Spalvins A., Canessa M. Charybdotoxin blocks with high affinity the Ca-activated K+ channel of Hb A and Hb S red cells: individual differences in the number of channels. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(3):243–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01872162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelamarty R. V., Miller B. A., Scaduto R. C., Jr, Yu F. T., Tillotson D. L., Cheung J. Y. Three-dimensional intracellular calcium gradients in single human burst-forming units-erythroid-derived erythroblasts induced by erythropoietin. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1799–1809. doi: 10.1172/JCI114638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



