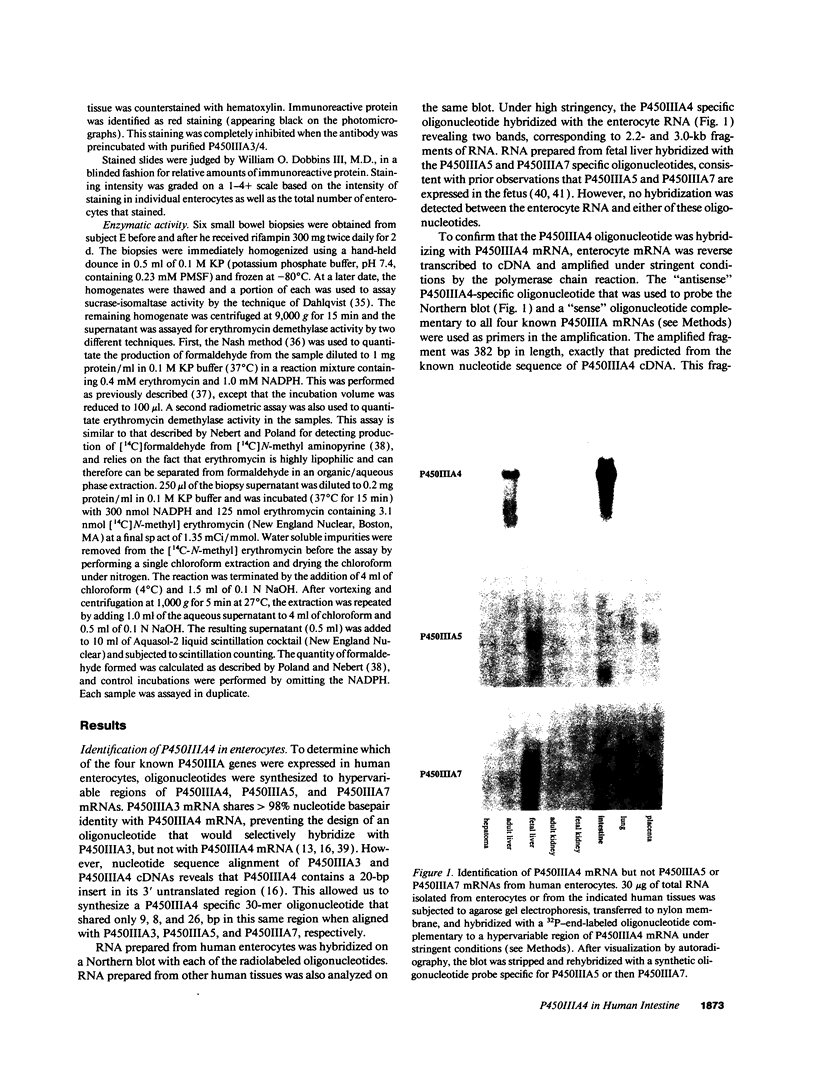
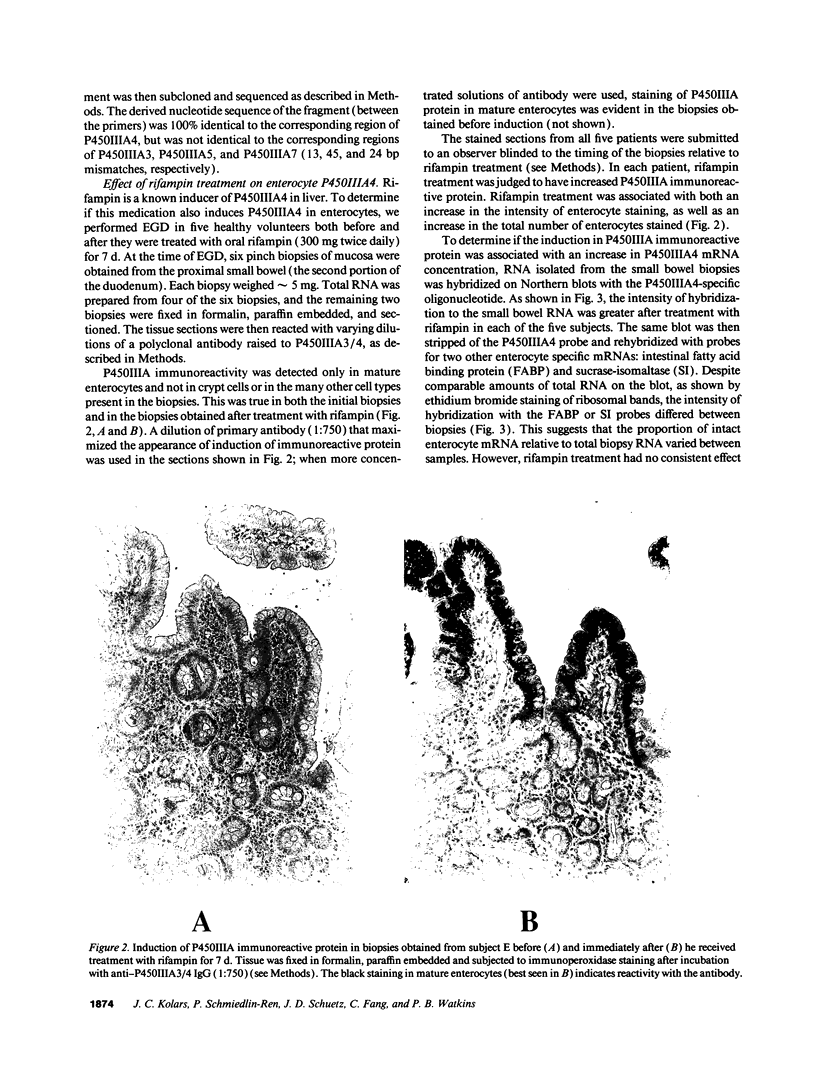
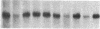Abstract
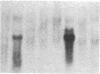
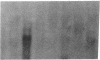
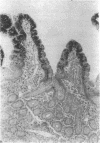
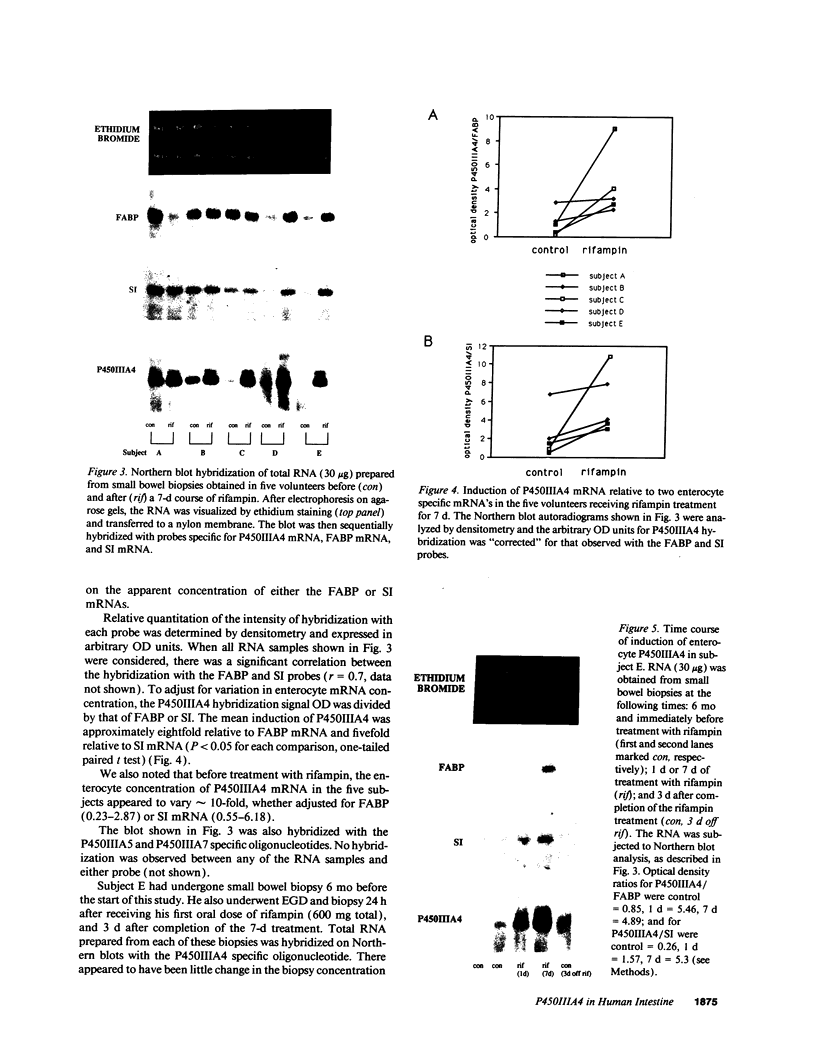
Enzymes within the P450IIIA (CYP3A) subfamily appear to account for significant "first pass" metabolism of some drugs in the intestine. To identify which of the known P450IIIA genes are expressed in intestine, enterocyte RNA was hybridized on Northern blots with synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to hypervariable regions of hepatic P450IIIA4, P450IIIA5, and P450IIIA7 cDNAs. Hybridization was detected only with the P450IIIA4-specific oligonucleotide. The identity of the hybridizing mRNA was confirmed to be P450IIIA4 by direct sequencing of a DNA fragment amplified from enterocyte cDNA by the polymerase chain reaction. To determine if enterocyte P450IIIA4 is inducible, biopsies of small bowel mucosa were obtained from five volunteers before and after they received 7d of treatment with rifampin, a known inducer of P450IIIA4 in liver. Rifampin treatment resulted in a five- or eightfold mean increase (P < 0.05) in the biopsy concentration of P450IIIA4 mRNA when normalized for content of sucrase isomaltase or intestinal fatty acid binding protein mRNAs, respectively. Rifampin also induced P450IIIA immunoreactive protein in enterocytes in each of the subjects, as judged by immunohistochemistry, and resulted in a 10-fold increase in P450IIIA4-specific catalytic activity (erythromycin N-demethylation) in the one patient studied. Our identification of inducible P450IIIA4 in enterocytes may in part account for drug interactions characteristic of P450IIIA4 substrates and suggests a strategy for controlling entry into the body of a major class of xenobiotics.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama T., Yamano S., Waxman D. J., Lapenson D. P., Meyer U. A., Fischer V., Tyndale R., Inaba T., Kalow W., Gelboin H. V. Cytochrome P-450 hPCN3, a novel cytochrome P-450 IIIA gene product that is differentially expressed in adult human liver. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence and distinct specificities of cDNA-expressed hPCN1 and hPCN3 for the metabolism of steroid hormones and cyclosporine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10388–10395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargetzi M. J., Aoyama T., Gonzalez F. J., Meyer U. A. Lidocaine metabolism in human liver microsomes by cytochrome P450IIIA4. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Nov;46(5):521–527. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaune P. H., Umbenhauer D. R., Bork R. W., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Isolation and sequence determination of a cDNA clone related to human cytochrome P-450 nifedipine oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8064–8068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork R. W., Muto T., Beaune P. H., Srivastava P. K., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Characterization of mRNA species related to human liver cytochrome P-450 nifedipine oxidase and the regulation of catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):910–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combalbert J., Fabre I., Fabre G., Dalet I., Derancourt J., Cano J. P., Maurel P. Metabolism of cyclosporin A. IV. Purification and identification of the rifampicin-inducible human liver cytochrome P-450 (cyclosporin A oxidase) as a product of P450IIIA gene subfamily. Drug Metab Dispos. 1989 Mar-Apr;17(2):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1984 Apr;44(2):169–172. doi: 10.3109/00365518409161400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels N. J., Dover J. S., Schachter R. K. Interaction between cyclosporin and rifampicin. Lancet. 1984 Sep 15;2(8403):639–639. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90629-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First M. R., Schroeder T. J., Weiskittel P., Myre S. A., Alexander J. W., Pesce A. J. Concomitant administration of cyclosporin and ketoconazole in renal transplant recipients. Lancet. 1989 Nov 18;2(8673):1198–1201. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91802-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ged C., Rouillon J. M., Pichard L., Combalbert J., Bressot N., Bories P., Michel H., Beaune P., Maurel P. The increase in urinary excretion of 6 beta-hydroxycortisol as a marker of human hepatic cytochrome P450IIIA induction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;28(4):373–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Schmid B. J., Umeno M., Mcbride O. W., Hardwick J. P., Meyer U. A., Gelboin H. V., Idle J. R. Human P450PCN1: sequence, chromosome localization, and direct evidence through cDNA expression that P450PCN1 is nifedipine oxidase. DNA. 1988 Mar;7(2):79–86. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Characterization of human microsomal cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:241–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Martin M. V., Beaune P. H., Kremers P., Wolff T., Waxman D. J. Characterization of rat and human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 forms involved in nifedipine oxidation, a prototype for genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5051–5060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Müller-Enoch D., Blair I. A. Oxidation of quinidine by human liver cytochrome P-450. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;30(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Bakran A., Johnson R. W., Rowland M. Cyclosporin-erythromycin interaction in renal transplant patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;27(4):475–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacolot F., Simon I., Dreano Y., Beaune P., Riche C., Berthou F. Identification of the cytochrome P450 IIIA family as the enzymes involved in the N-demethylation of tamoxifen in human liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 15;41(12):1911–1919. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90131-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolars J. C., Awni W. M., Merion R. M., Watkins P. B. First-pass metabolism of cyclosporin by the gut. Lancet. 1991 Dec 14;338(8781):1488–1490. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92302-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolars J. C., Schmiedlin-Ren P., Dobbins W. O., 3rd, Schuetz J., Wrighton S. A., Watkins P. B. Heterogeneity of cytochrome P450IIIA expression in rat gut epithelia. Gastroenterology. 1992 Apr;102(4 Pt 1):1186–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolars J. C., Stetson P. L., Rush B. D., Ruwart M. J., Schmiedlin-Ren P., Duell E. A., Voorhees J. J., Watkins P. B. Cyclosporine metabolism by P450IIIA in rat enterocytes--another determinant of oral bioavailability? Transplantation. 1992 Mar;53(3):596–602. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199203000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori M., Nishio K., Kitada M., Shiramatsu K., Muroya K., Soma M., Nagashima K., Kamataki T. Fetus-specific expression of a form of cytochrome P-450 in human livers. Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4430–4433. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori M., Nishio K., Ohi H., Kitada M., Kamataki T. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA containing the entire coding region for human fetal liver cytochrome P-450. J Biochem. 1989 Feb;105(2):161–163. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronbach T., Fischer V., Meyer U. A. Cyclosporine metabolism in human liver: identification of a cytochrome P-450III gene family as the major cyclosporine-metabolizing enzyme explains interactions of cyclosporine with other drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Jun;43(6):630–635. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronbach T., Mathys D., Umeno M., Gonzalez F. J., Meyer U. A. Oxidation of midazolam and triazolam by human liver cytochrome P450IIIA4. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey M. R., Kolars J. C., Merion R. M., Campbell D. A., Aldrich M., Watkins P. B. Cyclosporin toxicity at therapeutic blood levels and cytochrome P-450 IIIA. Lancet. 1990 Jan 6;335(8680):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90137-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molowa D. T., Schuetz E. G., Wrighton S. A., Watkins P. B., Kremers P., Mendez-Picon G., Parker G. A., Guzelian P. S. Complete cDNA sequence of a cytochrome P-450 inducible by glucocorticoids in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5311–5315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray G. I., Barnes T. S., Sewell H. F., Ewen S. W., Melvin W. T., Burke M. D. The immunocytochemical localisation and distribution of cytochrome P-450 in normal human hepatic and extrahepatic tissues with a monoclonal antibody to human cytochrome P-450. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;25(4):465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichard L., Fabre I., Fabre G., Domergue J., Saint Aubert B., Mourad G., Maurel P. Cyclosporin A drug interactions. Screening for inducers and inhibitors of cytochrome P-450 (cyclosporin A oxidase) in primary cultures of human hepatocytes and in liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1990 Sep-Oct;18(5):595–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A. P., Nebert D. W. A sensitive radiometric assay of aminopyrine N-demethylation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jan;184(1):269–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptachcinski R. J., Venkataramanan R., Burckart G. J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of cyclosporin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986 Mar-Apr;11(2):107–132. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198611020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz J. D., Molowa D. T., Guzelian P. S. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a new member of the glucocorticoid-responsive cytochromes P450 in human liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 1;274(2):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Guengerich F. P. Evidence for cytochrome P-450NF, the nifedipine oxidase, being the principal enzyme involved in the bioactivation of aflatoxins in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):462–465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Klisak I. J., Zollman S., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. The human and rodent intestinal fatty acid binding protein genes. A comparative analysis of their structure, expression, and linkage relationships. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16060–16071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber P. G., Yu L., Wu G. D., Judge T. A. Sucrase-isomaltase gene expression along crypt-villus axis of human small intestine is regulated at level of mRNA abundance. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):G123–G130. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.1.G123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. W., Kari P. H., Lu A. Y., Thomas P. E., Guengerich F. P., Vyas K. P. Biotransformation of lovastatin. IV. Identification of cytochrome P450 3A proteins as the major enzymes responsible for the oxidative metabolism of lovastatin in rat and human liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 1;290(2):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90551-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Hamilton T. A., Annesley T. M., Ellis C. N., Kolars J. C., Voorhees J. J. The erythromycin breath test as a predictor of cyclosporine blood levels. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Aug;48(2):120–129. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1990.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Murray S. A., Winkelman L. G., Heuman D. M., Wrighton S. A., Guzelian P. S. Erythromycin breath test as an assay of glucocorticoid-inducible liver cytochromes P-450. Studies in rats and patients. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):688–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI113933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B. Role of cytochromes P450 in drug metabolism and hepatotoxicity. Semin Liver Dis. 1990 Nov;10(4):235–250. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Wrighton S. A., Maurel P., Schuetz E. G., Mendez-Picon G., Parker G. A., Guzelian P. S. Identification of an inducible form of cytochrome P-450 in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6310–6314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Wrighton S. A., Schuetz E. G., Molowa D. T., Guzelian P. S. Identification of glucocorticoid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of rats and man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1029–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI113156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Brian W. R., Sari M. A., Iwasaki M., Guengerich F. P., Raucy J. L., Molowa D. T., Vandenbranden M. Studies on the expression and metabolic capabilities of human liver cytochrome P450IIIA5 (HLp3). Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;38(2):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Maurel P., Schuetz E. G., Watkins P. B., Young B., Guzelian P. S. Identification of the cytochrome P-450 induced by macrolide antibiotics in rat liver as the glucocorticoid responsive cytochrome P-450p. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2171–2178. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Ring B. J., Watkins P. B., VandenBranden M. Identification of a polymorphically expressed member of the human cytochrome P-450III family. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]