Abstract
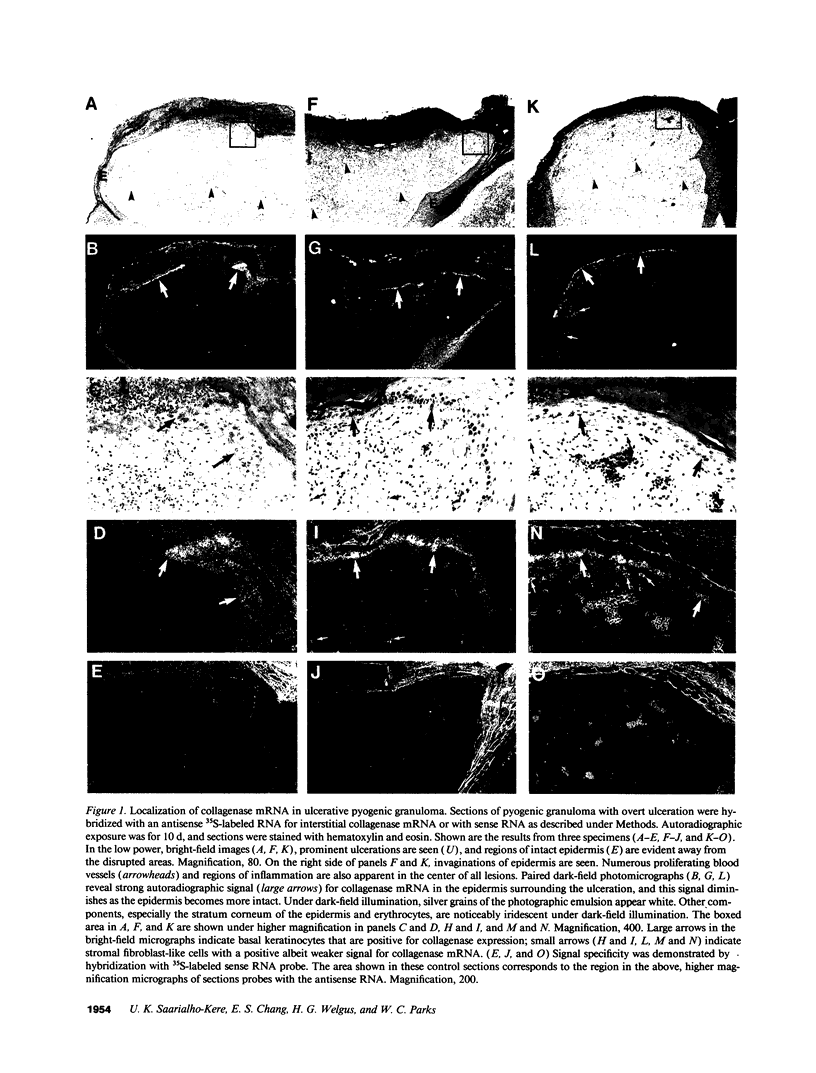
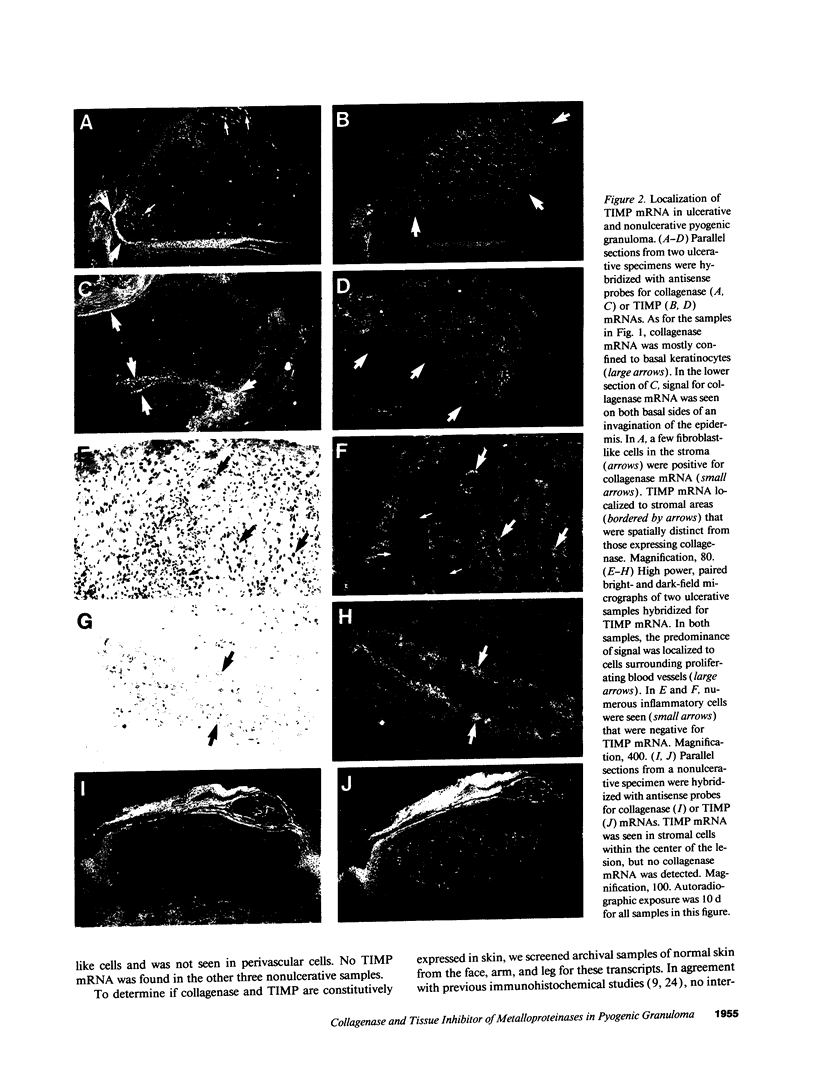
To examine the role of metalloproteinases in tissue remodeling associated with wound healing, we used in situ hybridization to localize the expression of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in samples of pyogenic granuloma. Strong hybridization for collagenase mRNA was detected in basal keratinocytes near the advancing edge of all ulcerative lesions, but no collagenase mRNA was seen in samples without ulceration. Distinct from the sites of collagenase expression, TIMP mRNA was detected in stromal cells and in cells surrounding proliferating vessels. No collagenase mRNA was found in the epidermis of healthy skin, although occasional stromal cells contained collagenase or TIMP mRNAs, and TIMP mRNA was detected in hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Our results suggest that basal keratinocytes adjacent to wounded epidermis are critically involved in matrix remodeling, much more so than adjacent or underlying dermal fibroblasts. Furthermore, as several reports have suggested, TIMP may play a role in angiogenesis. Finally, in contrast to findings from other models which indicate that collagenase and TIMP proteins are secreted by the same cells, our data also demonstrate that these proteins can be produced in vivo independently of each other.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertaux B., Hornebeck W., Eisen A. Z., Dubertret L. Growth stimulation of human keratinocytes by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):679–685. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12483956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Sommer A., Thompson R. C., Anderson D. C., Smith C. G., Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers J. W., Hernandez A. D., Kim J. H., Stricklin G. P. Immunolocalization of collagenase inhibitor in normal skin and basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Dec;17(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowcat N. L., Savage F. J., Hembry R. M., Boulos P. B. Role of collagenase in colonic anastomoses: a reappraisal. Br J Surg. 1988 Apr;75(4):330–334. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C. C., Chua B. H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mRNA for collagenase and TIMP in human skin fibroblasts. Connect Tissue Res. 1990;25(2):161–170. doi: 10.3109/03008209009006990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. D., Kobayashi D. K., Welgus H. G. Regulation of the expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and collagenase by retinoids and glucocorticoids in human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1280–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI113203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Whitham S. E., Docherty A. J., Angel P., Heath J. K. Transforming growth factor beta modulates the expression of collagenase and metalloproteinase inhibitor. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1899–1904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Paine M. M., Littman B. H. Gene expression (collagenase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases, complement, and HLA-DR) in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovium. Quantitative analysis and effect of intraarticular corticosteroids. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1094–1105. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Wilhelm S. M., Kronberger A., Bauer E. A., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z. Human fibroblast collagenase. Complete primary structure and homology to an oncogene transformation-induced rat protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hembry R. M., Ehrlich H. P. Immunolocalization of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in hypertrophic scar tissue. Br J Dermatol. 1986 Oct;115(4):409–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb06235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T. T., Rea T. J., Flenniken A. M., Williams B. R., Groppi V. E., Buhl A. E. Localization of TIMP in cycling mouse hair. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):877–879. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupper T. S. The activated keratinocyte: a model for inducible cytokine production by non-bone marrow-derived cells in cutaneous inflammatory and immune responses. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6 Suppl):146S–150S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCachren S. S. Expression of metalloproteinases and metalloproteinase inhibitor in human arthritic synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1085–1093. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Docherty A. J., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J. Metalloproteinases and tissue damage. Br J Rheumatol. 1991;30 (Suppl 1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Werb Z. Biosynthesis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases by human fibroblasts in culture. Stimulation by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate and interleukin 1 in parallel with collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3079–3083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nappi O., Wick M. R. Disseminated lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma). A clinicopathologic study of two cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986 Oct;8(5):379–385. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198610000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. J., Woodley D. T., Stricklin G. P., O'Keefe E. J. Enhanced synthesis of collagenase by human keratinocytes cultured on type I or type IV collagen. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Mar;94(3):341–346. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser I. W., Stenmark K. R., Suthar M., Crouch E. C., Mecham R. P., Parks W. C. Regional heterogeneity of elastin and collagen gene expression in intralobar arteries in response to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension as demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1073–1088. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rømer J., Lund L. R., Eriksen J., Ralfkiaer E., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., Danø K., Kristensen P. Differential expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type-1 inhibitor during healing of mouse skin wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Nov;97(5):803–811. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12486833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Fliszar C. J., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Human 92- and 72-kilodalton type IV collagenases are elastases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. D., Campbell E. J., Kobayashi D. K., Welgus H. G. Immune modulation of metalloproteinase production in human macrophages. Selective pretranslational suppression of interstitial collagenase and stromelysin biosynthesis by interferon-gamma. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1204–1210. doi: 10.1172/JCI114826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Streuli C. H., Martins-Green M., Bissell M. J. Designer microenvironments for the analysis of cell and tissue function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;2(5):864–874. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90085-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudbeck B. D., Jeffrey J. J., Welgus H. G., Mecham R. P., McCourt D., Parks W. C. Purification and characterization of bovine interstitial collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Mar;293(2):370–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90408-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takigawa M., Nishida Y., Suzuki F., Kishi J., Yamashita K., Hayakawa T. Induction of angiogenesis in chick yolk-sac membrane by polyamines and its inhibition by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP and TIMP-2). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1264–1271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90822-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Bauer E. A., Stricklin G. P. Elevated levels of human collagenase inhibitor in blister fluids of diverse etiology. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Nov;87(5):592–596. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12455837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Campbell E. J., Cury J. D., Eisen A. Z., Senior R. M., Wilhelm S. M., Goldberg G. I. Neutral metalloproteinases produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. Enzyme profile, regulation, and expression during cellular development. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1496–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI114867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Fliszar C. J., Seltzer J. L., Schmid T. M., Jeffrey J. J. Differential susceptibility of type X collagen to cleavage by two mammalian interstitial collagenases and 72-kDa type IV collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13521–13527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. The collagen substrate specificity of human skin fibroblast collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9511–9515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Human skin fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Comparative studies in human connective tissues, serum, and amniotic fluid. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12259–12264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Mainardi C. L., Vater C. A., Harris E. D., Jr Endogenous activiation of latent collagenase by rheumatoid synovial cells. Evidence for a role of plasminogen activator. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 5;296(18):1017–1023. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705052961801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. K., Cawston T. E., Hazleman B. L. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates the production of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) by human synovial and skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 3;1094(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90010-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh H., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Indik Z., Sheppard P., Anderson N., Rosenbloom J. C., Cicila G., Yoon K., Rosenbloom J. Sequence variation of bovine elastin mRNA due to alternative splicing. Coll Relat Res. 1987 Sep;7(4):235–247. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(87)80030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]