Abstract
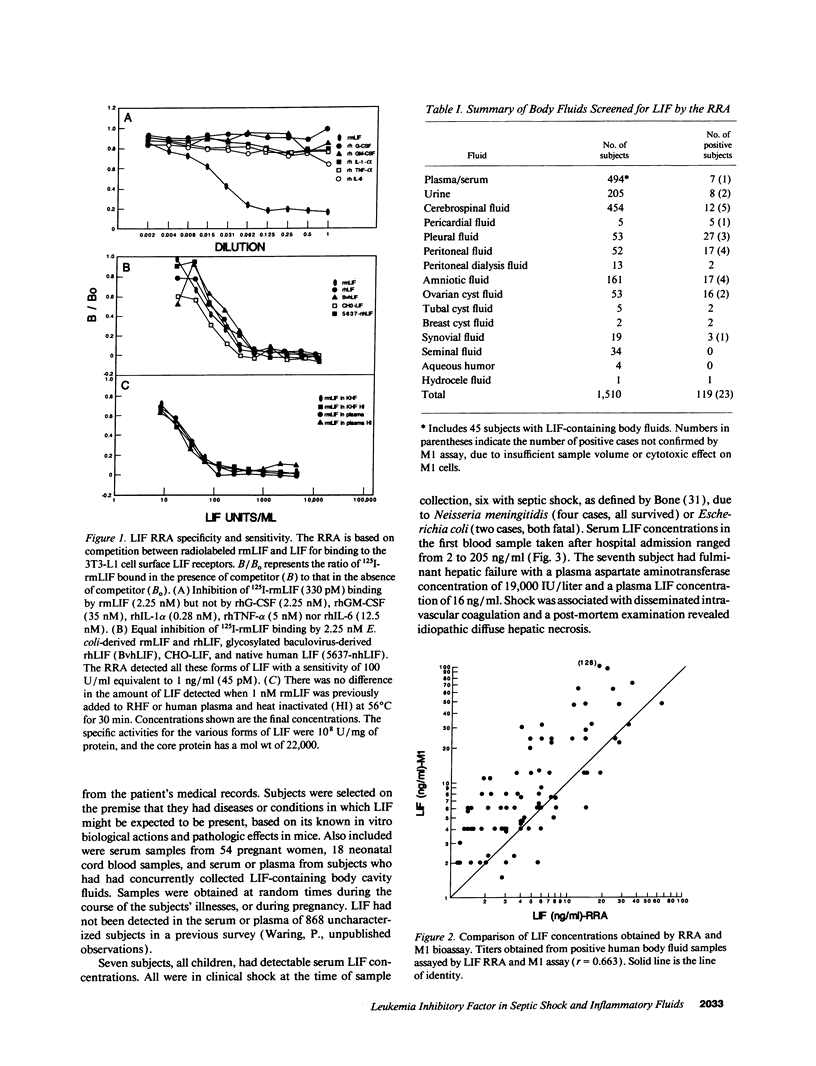
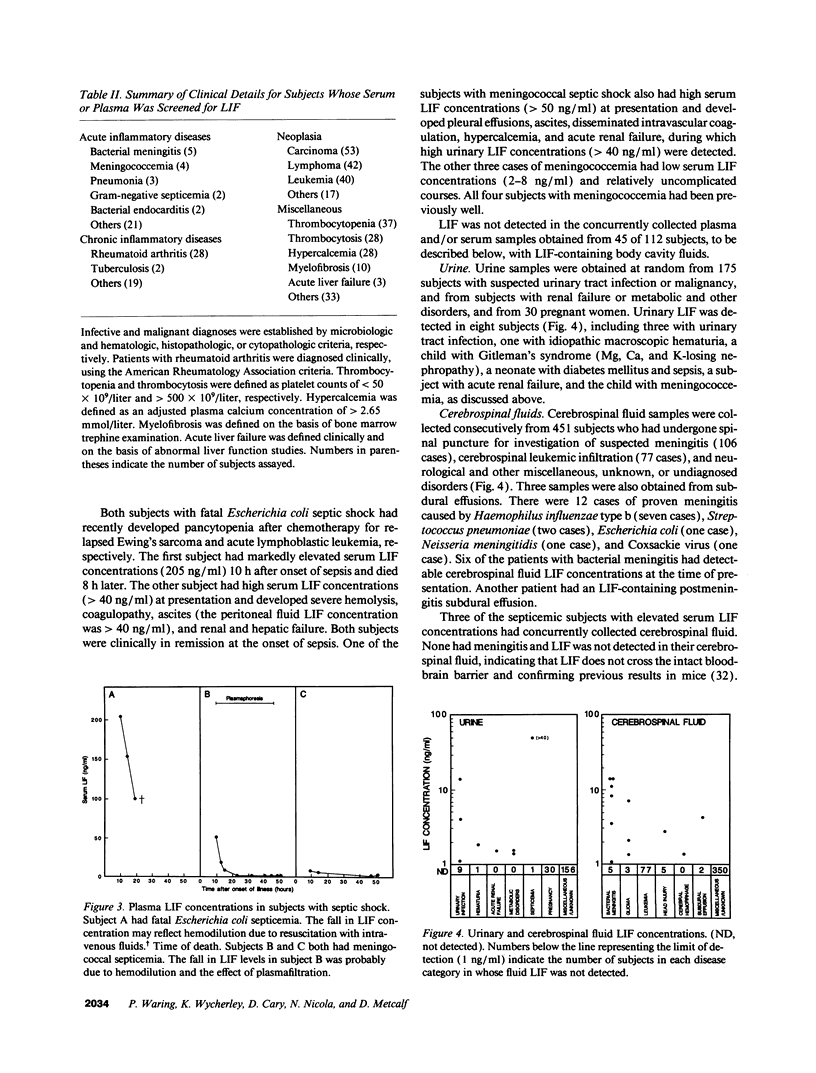
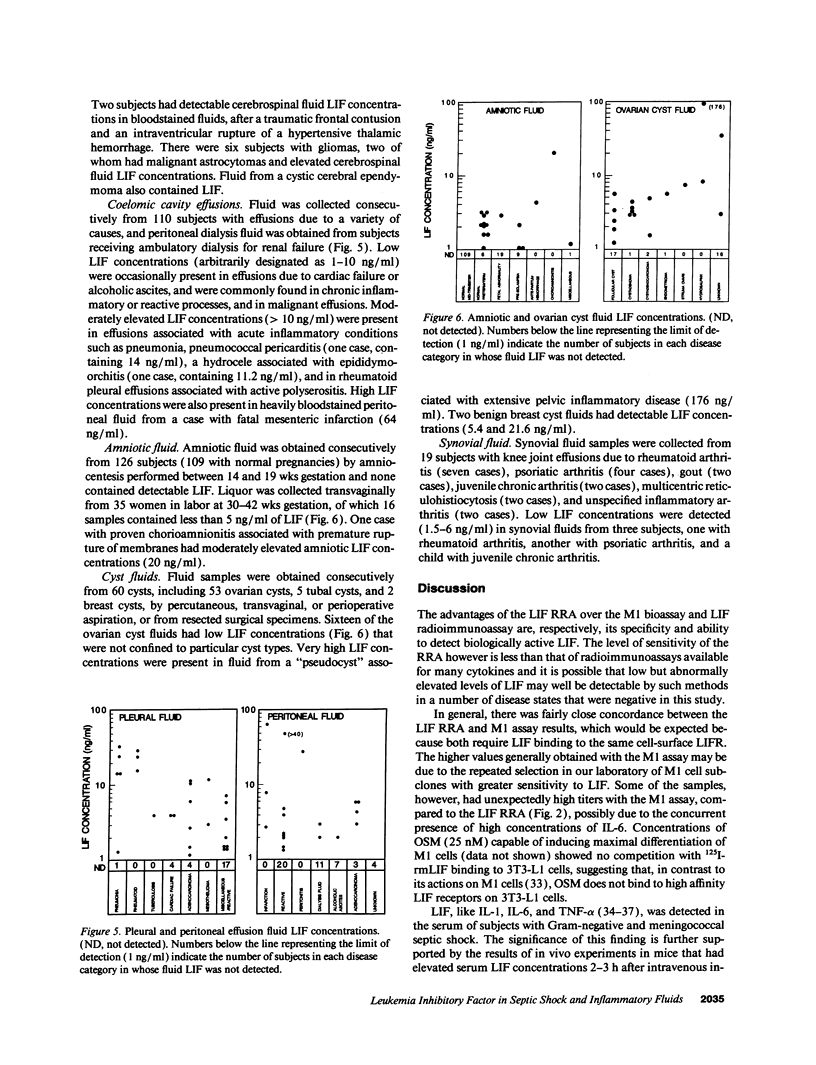
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) has many biological actions which parallel those of IL-1, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, but its role in the pathogenesis of human disease is unknown. A specific radioreceptor competition assay capable of detecting LIF at concentrations above 1 ng/ml (45 pM) was developed. To identify disease states in which LIF might be involved, a cross-sectional survey of serum and body fluids from approximately 1,500 subjects with a variety of diseases was performed using the LIF radioreceptor competition assay. Serum LIF concentrations were transiently elevated (2-200 ng/ml) in six subjects with meningococcal or Gram-negative septic shock, and in a subject with idiopathic fulminant hepatic failure. Moderately elevated LIF concentrations (> 10 ng/ml) were detected in cerebrospinal fluid from subjects with bacterial meningitis, in effusions associated with pneumonia and peritonitis, and in amniotic fluid from a woman with chorioamnionitis. Low LIF concentrations (1-10 ng/ml) were present in synovial fluid from subjects with inflammatory arthritis, amniotic fluid from women in labor, and some reactive, chronic inflammatory and malignant effusions and cyst fluids, but rarely in transudates. These initial findings suggest that LIF might be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammation and septic shock.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe E., Tanaka H., Ishimi Y., Miyaura C., Hayashi T., Nagasawa H., Tomida M., Yamaguchi Y., Hozumi M., Suda T. Differentiation-inducing factor purified from conditioned medium of mitogen-treated spleen cell cultures stimulates bone resorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5958–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Dayer J. M. Cytokines and cytokine inhibitors or antagonists in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Mar;33(3):305–315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Wong G. G. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor III shares structural and functional identity with leukemia-inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1163–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt H., Brunet L. J., Stewart C. L. Uterine expression of leukemia inhibitory factor coincides with the onset of blastocyst implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11408–11412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Sepsis, the sepsis syndrome, multi-organ failure: a plea for comparable definitions. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 15;114(4):332–333. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-4-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Gerain J., Heumann D., Baumgartner J. D., Glauser M. P. High circulating levels of interleukin-6 in patients with septic shock: evolution during sepsis, prognostic value, and interplay with other cytokines. The Swiss-Dutch J5 Immunoglobulin Study Group. Am J Med. 1991 Jul;91(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90069-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascan H., Anegón I., Praloran V., Naulet J., Godard A., Soulillou J. P., Jacques Y. Constitutive production of human interleukin for DA cells/leukemia inhibitory factor by human tumor cell lines derived from various tissues. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2592–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Bruce A. G. Oncostatin M binds the high-affinity leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. New Biol. 1992 Jan;4(1):61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Thut C. J., VandeBos T., Gimpel S. D., Delaney P. B., King J., Price V., Cosman D., Beckmann M. P. Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor is structurally related to the IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2839–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godard A., Heymann D., Raher S., Anegon I., Peyrat M. A., Le Mauff B., Mouray E., Gregoire M., Virdee K., Soulillou J. P. High and low affinity receptors for human interleukin for DA cells/leukemia inhibitory factor on human cells. Molecular characterization and cellular distribution. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3214–3222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A. Kinetic analyses of the binding of leukemia inhibitory factor to receptor on cells and membranes and in detergent solution. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10238–10247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Distribution and comparison of receptors for leukemia inhibitory factor on murine hemopoietic and hepatic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Feb;146(2):207–215. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Specific binding of murine leukemia inhibitory factor to normal and leukemic monocytic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5971–5975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Waring P. M., Metcalf D. Clearance and fate of leukemia-inhibitory factor (LIF) after injection into mice. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Sep;148(3):430–439. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Bukasa K., Sindic C. J., Van Damme J., Van Snick J. Elevated levels of the 26K human hybridoma growth factor (interleukin 6) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute infection of the central nervous system. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):320–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Miyaura C., Jin C. H., Akatsu T., Abe E., Nakamura Y., Yamaguchi A., Yoshiki S., Matsuda T., Hirano T. IL-6 is produced by osteoblasts and induces bone resorption. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3297–3303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Frei K., Kam-Hansen S., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in cerebrospinal fluid during bacterial, but not viral, meningitis. Evaluation in murine model infections and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert M., Mantovani L., Lindemann A., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Expression of leukemia inhibitory factor is regulated in human mesenchymal cells. Leukemia. 1991 May;5(5):361–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Toksoz D., Nishikawa S., Nishikawa S., Williams D., Zsebo K., Hogan B. L. Effect of Steel factor and leukaemia inhibitory factor on murine primordial germ cells in culture. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):750–752. doi: 10.1038/353750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Gearing D. P. A myelosclerotic syndrome in mice engrafted with cells producing high levels of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Leukemia. 1989 Dec;3(12):847–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Gearing D. P. Fatal syndrome in mice engrafted with cells producing high levels of the leukemia inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5948–5952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A. Clonal analysis of the actions of the murine leukemia inhibitory factor on leukemic and normal murine hemopoietic cells. Leukemia. 1988 Apr;2(4):216–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Hilton D., Nicola N. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor can potentiate murine megakaryocyte production in vitro. Blood. 1991 May 15;77(10):2150–2153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Gearing D. P. Effects of injected leukemia inhibitory factor on hematopoietic and other tissues in mice. Blood. 1990 Jul 1;76(1):50–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Int J Cell Cloning. 1991 Mar;9(2):95–108. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530090201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaura C., Onozaki K., Akiyama Y., Taniyama T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Suda T. Recombinant human interleukin 6 (B-cell stimulatory factor 2) is a potent inducer of differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells (M1). FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Yamaguchi K., Abe K. Purification of a lipoprotein lipase-inhibiting protein produced by a melanoma cell line associated with cancer cachexia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1085–1092. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Yamaguchi K., Honda S., Nagasaki K., Ueda M., Abe O., Abe K. Cancer cachexia syndrome developed in nude mice bearing melanoma cells producing leukemia-inhibitory factor. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6656–6659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R., Lee F., Chiu C. P. The genes for leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 are expressed in mouse blastocysts prior to the onset of hemopoiesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4953–4956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero R., Avila C., Santhanam U., Sehgal P. B. Amniotic fluid interleukin 6 in preterm labor. Association with infection. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1392–1400. doi: 10.1172/JCI114583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero R., Brody D. T., Oyarzun E., Mazor M., Wu Y. K., Hobbins J. C., Durum S. K. Infection and labor. III. Interleukin-1: a signal for the onset of parturition. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 May;160(5 Pt 1):1117–1123. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero R., Manogue K. R., Mitchell M. D., Wu Y. K., Oyarzun E., Hobbins J. C., Cerami A. Infection and labor. IV. Cachectin-tumor necrosis factor in the amniotic fluid of women with intraamniotic infection and preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Aug;161(2):336–341. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose T. M., Bruce A. G. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8641–8645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda K., Okamura S., Omori F., Mizuno Y., Hara T., Aoki T., Ueda K., Niho Y. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with meningitis. Blood. 1991 May 15;77(10):2214–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taupin J. L., Morel D., Moreau J. F., Gualde N., Potaux L., Bezian J. H. HILDA/LIF urinary excretion during acute kidney rejection. Transplantation. 1992 Mar;53(3):655–658. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199203000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomida M., Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y., Hozumi M., Okabe T., Takaku F. Induction by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor of differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemic M1 cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 27;207(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomida M., Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y., Hozumi M. Purification of a factor inducing differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemic M1 cells from conditioned medium of mouse fibroblast L929 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10978–10982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. L., Hilton D. J., Pease S., Willson T. A., Stewart C. L., Gearing D. P., Wagner E. F., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Gough N. M. Myeloid leukaemia inhibitory factor maintains the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):684–687. doi: 10.1038/336684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Fukada K., Aebersold R., Korsching S., Fann M. J., Patterson P. H. The cholinergic neuronal differentiation factor from heart cells is identical to leukemia inhibitory factor. Science. 1989 Dec 15;246(4936):1412–1416. doi: 10.1126/science.2512641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



