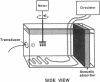
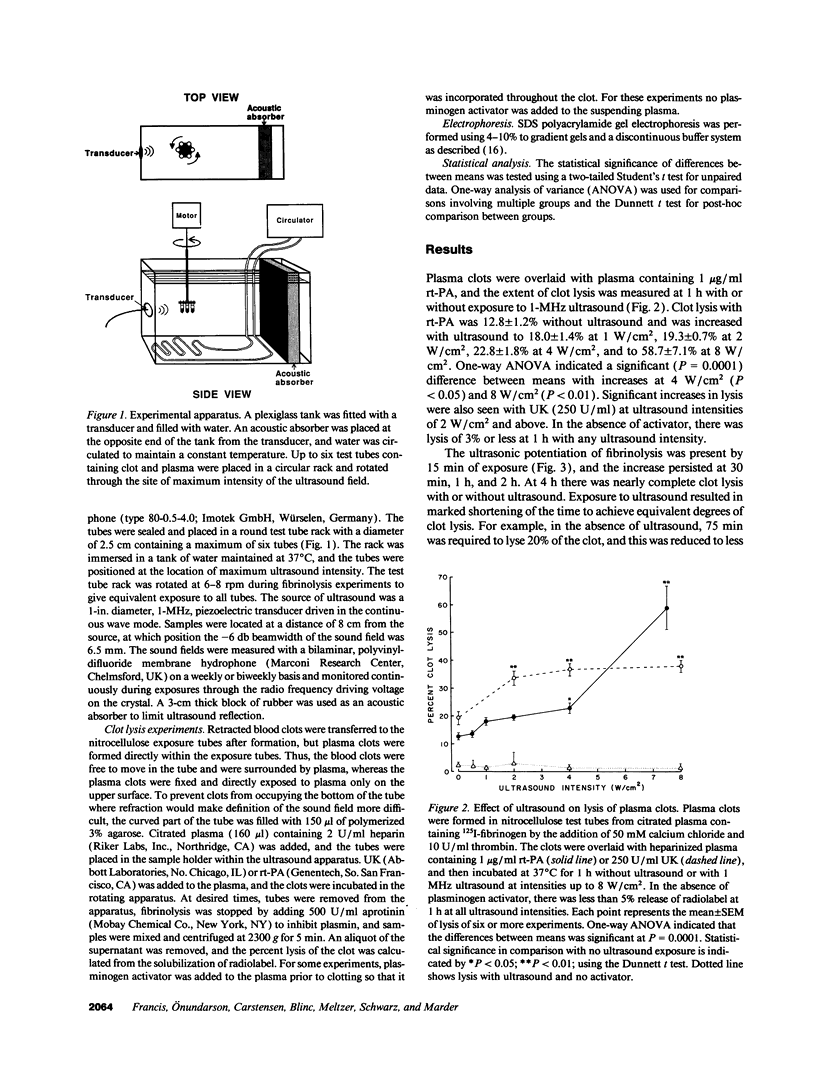
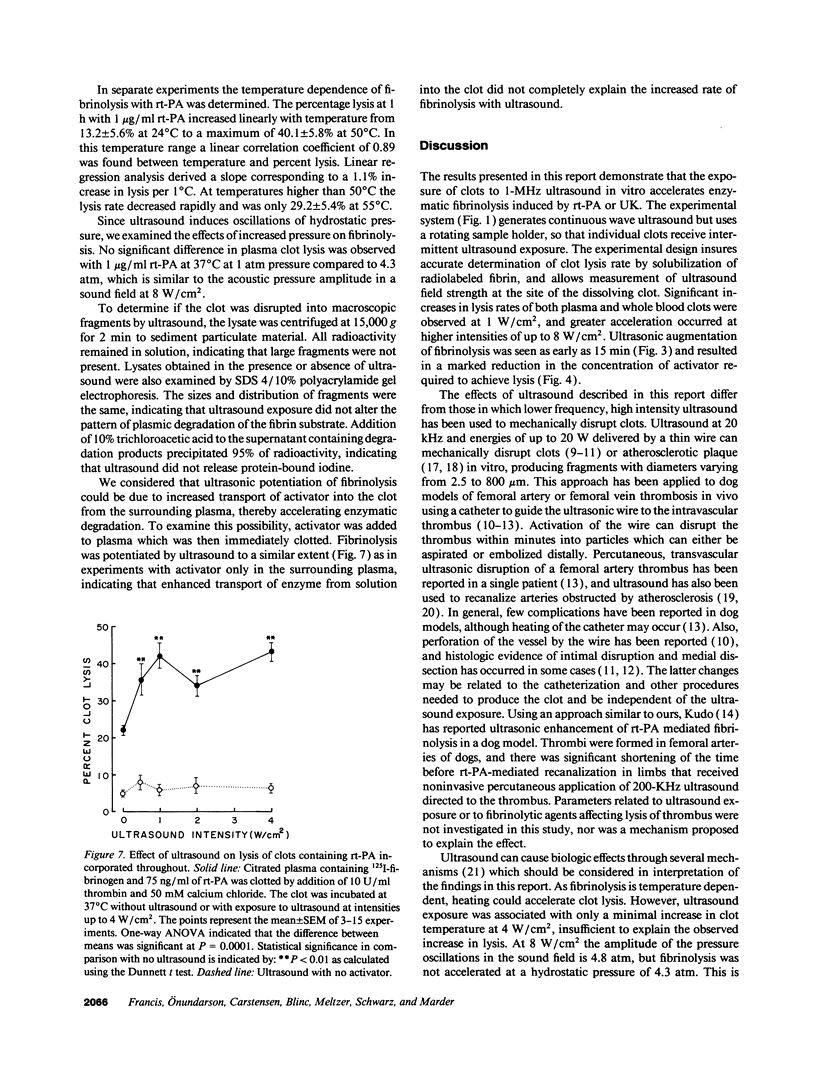
Abstract
The effect of ultrasound on the rate of fibrinolysis has been investigated using an in vitro system. Plasma or blood clots containing a trace label of 125I fibrin were suspended in plasma containing plasminogen activator and intermittently exposed to continuous wave 1-MHz ultrasound at intensities up to 8 W/cm2. Plasma clot lysis at 1 h with 1 microgram/ml recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) was 12.8 +/- 1.2% without ultrasound and was significantly (P = 0.0001) increased by exposure to ultrasound with greater lysis at 1 W/cm2 (18.0 +/- 1.4%), 2 W/cm2 (19.3 +/- 0.7%), 4 W/cm2 (22.8 +/- 1.8%), and 8 W/cm2 (58.7 +/- 7.1%). Significant increases in lysis were also seen with urokinase at ultrasound intensities of 2 W/cm2 and above. Exposure of clots to ultrasound in the absence of plasminogen activator did not increase lysis. Ultrasound exposure resulted in a marked reduction in the rt-PA concentration required to achieve an equivalent degree of lysis to that seen without ultrasound. For example, 15% lysis occurred in 1 h at 1 microgram/ml rt-PA without ultrasound or with 0.2 microgram/ml with ultrasound, a five-fold reduction in concentration. Ultrasound at 1 W/cm2 and above also potentiated lysis of retracted whole blood clots mediated by rt-PA or urokinase. The maximum temperature increase of plasma clots exposed to 4 W/cm2 ultrasound was only 1.7 degrees C, which could not explain the enhancement of fibrinolysis. Ultrasound exposure did not cause mechanical fragmentation of the clot into sedimentable fragments, nor did it alter the sizes of plasmic derivatives as demonstrated by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. We conclude that ultrasound at 1 MHz potentiates enzymatic fibrinolysis by a nonthermal mechanism at energies that can potentially be applied and tolerated in vivo to accelerate therapeutic fibrinolysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apfel R. E., Holland C. K. Gauging the likelihood of cavitation from short-pulse, low-duty cycle diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1991;17(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(91)90125-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariani M., Fishbein M. C., Chae J. S., Sadeghi H., Michael A. D., Dubin S. B., Siegel R. J. Dissolution of peripheral arterial thrombi by ultrasound. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1680–1688. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinc A., Planinsic G., Keber D., Jarh O., Lahajnar G., Zidansek A., Demsar F. Dependence of blood clot lysis on the mode of transport of urokinase into the clot--a magnetic resonance imaging study in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1991 May 6;65(5):549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Jr, Hardin C. L. Fibrin has larger pores when formed in the presence of erythrocytes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):H1069–H1073. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.5.H1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater B. V., Williams A. R. Platelet aggregation induced in vitro by therapeutic ultrasound. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Oct 31;38(3):640–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro J. H., Knatterud G., Roberts R., Borer J., Cohen L. S., Dalen J., Dodge H. T., Francis C. K., Hillis D., Ludbrook P. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Trial, Phase I: A comparison between intravenous tissue plasminogen activator and intravenous streptokinase. Clinical findings through hospital discharge. Circulation. 1987 Jul;76(1):142–154. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst A., Schenk E. A., Gracewski S. M., Woodlock T. J., Murant F. G., Alliger H., Meltzer R. S. Ability of high-intensity ultrasound to ablate human atherosclerotic plaques and minimize debris size. Am J Cardiol. 1991 Jul 15;68(2):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90751-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischell T. A., Abbas M. A., Grant G. W., Siegel R. J. Ultrasonic energy. Effects on vascular function and integrity. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1783–1795. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Martin S. E. Plasmic degradation of crosslinked fibrin. I. Structural analysis of the particulate clot and identification of new macromolecular-soluble complexes. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell L. A., Miller D. L., Nyborg W. L. Ultrasonically induced intravascular streaming and thrombus formation adjacent to a micropipette. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1986 Mar;12(3):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(86)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore J. M., Sloan M., Price T. R., Randall A. M., Bovill E., Collen D., Forman S., Knatterud G. L., Sopko G., Terrin M. L. Intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, and subdural hematoma after acute myocardial infarction and thrombolytic therapy in the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction Study. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction, Phase II, pilot and clinical trial. Circulation. 1991 Feb;83(2):448–459. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.2.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H., Ingrisch H., Mietaschk A., Rath H. Local low-dose thrombolytic therapy of peripheral arterial occlusions. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 23;307(26):1627–1630. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212233072606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong A. S., Chae J. S., Dubin S. B., Lee S., Fishbein M. C., Siegel R. J. Ultrasonic clot disruption: an in vitro study. Am Heart J. 1990 Aug;120(2):418–422. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(90)90088-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandarpa K., Drinker P. A., Singer S. J., Caramore D. Forceful pulsatile local infusion of enzyme accelerates thrombolysis: in vivo evaluation of a new delivery system. Radiology. 1988 Sep;168(3):739–744. doi: 10.1148/radiology.168.3.3406403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr C. L., Gregory D. W., Chan K. K., Watmough D. J., Wheatley D. N. Ultrasound-induced damage of veins in pig ears, as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1989;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(89)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Sherry S. Thrombolytic therapy: current status (1). N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1512–1520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Nyborg W. L., Whitcomb C. C. Platelet aggregation induced by ultrasound under specialized conditions in vitro. Science. 1979 Aug 3;205(4405):505–507. doi: 10.1126/science.451616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair C. H., Dhall D. P. Studies on fibrin network structure: the effect of some plasma proteins. Thromb Res. 1991 Feb 1;61(3):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90109-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popma J. J., Topol E. J. Adjuncts to thrombolysis for myocardial reperfusion. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Jul 1;115(1):34–44. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-1-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenschein U., Bernstein J. J., DiSegni E., Kaplinsky E., Bernheim J., Rozenzsajn L. A. Experimental ultrasonic angioplasty: disruption of atherosclerotic plaques and thrombi in vitro and arterial recanalization in vivo. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Mar 1;15(3):711–717. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90651-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenschein U., Rozenszajn L. A., Kraus L., Marboe C. C., Watkins J. F., Rose E. A., David D., Cannon P. J., Weinstein J. S. Ultrasonic angioplasty in totally occluded peripheral arteries. Initial clinical, histological, and angiographic results. Circulation. 1991 Jun;83(6):1976–1986. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.6.1976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. J., Cumberland D. C., Myler R. K., DonMichael T. A. Percutaneous ultrasonic angioplasty:initial clinical experience. Lancet. 1989 Sep 30;2(8666):772–774. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. J., Fishbein M. C., Forrester J., Moore K., DeCastro E., Daykhovsky L., DonMichael T. A. Ultrasonic plaque ablation. A new method for recanalization of partially or totally occluded arteries. Circulation. 1988 Dec;78(6):1443–1448. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.78.6.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. J., Goldhaber S. Z., Yusuf S., Peto R., Hennekens C. H. Effect of intravenous streptokinase on acute myocardial infarction: pooled results from randomized trials. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 4;307(19):1180–1182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211043071904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stump D. C., Califf R. M., Topol E. J., Sigmon K., Thornton D., Masek R., Anderson L., Collen D. Pharmacodynamics of thrombolysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. Correlation with characteristics of and clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction. The TAMI Study Group. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1222–1230. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trübestein G., Engel C., Etzel F., Sobbe A., Cremer H., Stumpff U. Thrombolysis by ultrasound. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:697s–698s. doi: 10.1042/cs051697s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley A. D., Laird W. R., Williams A. R. Intra-vascular thrombosis associated with dental ultrasound. J Oral Pathol. 1987 May;16(5):256–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1987.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. R., Chater B. V., Allen K. A., Sherwood M. R., Sanderson J. H. Release of beta-thromboglobulin from human platelets by therapeutic intensities of ultrasound. Br J Haematol. 1978 Sep;40(1):133–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf S., Collins R., Peto R., Furberg C., Stampfer M. J., Goldhaber S. Z., Hennekens C. H. Intravenous and intracoronary fibrinolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction: overview of results on mortality, reinfarction and side-effects from 33 randomized controlled trials. Eur Heart J. 1985 Jul;6(7):556–585. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]