Abstract
X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis is associated with kidney stones and renal tubular dysfunction in childhood progressing to renal failure in adulthood. The primary defect causing this renal tubular disorder is unknown and determining the chromosomal location of the mutant gene would represent an important step toward defining the biochemical basis. We have performed linkage studies in 102 members (10 affected males, 47 unaffected males, 15 obligate heterozygote females, and 30 unaffected females) from five generations of one family. As genetic markers we used 10 cloned human X chromosome fragments identifying restriction fragment length polymorphisms and seven pairs of oligonucleotide primers identifying microsatellite polymorphisms. Linkage with the locus DXS255 was established with a peak LOD score = 5.91 at 3.6% recombination, thereby localizing the X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis gene to the pericentromeric region of the short arm of the X chromosome (Xp11.22). Multilocus analysis indicated that the mutant gene was distal to DXS255 but proximal to the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on Xp. Thus, the gene that causes X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis maps to the pericentromeric region of the short arm of the X chromosome (Xp11.22), and further characterization of this gene will help to elucidate the factors controlling renal tubular function and mineral homeostasis.
Full text
PDF

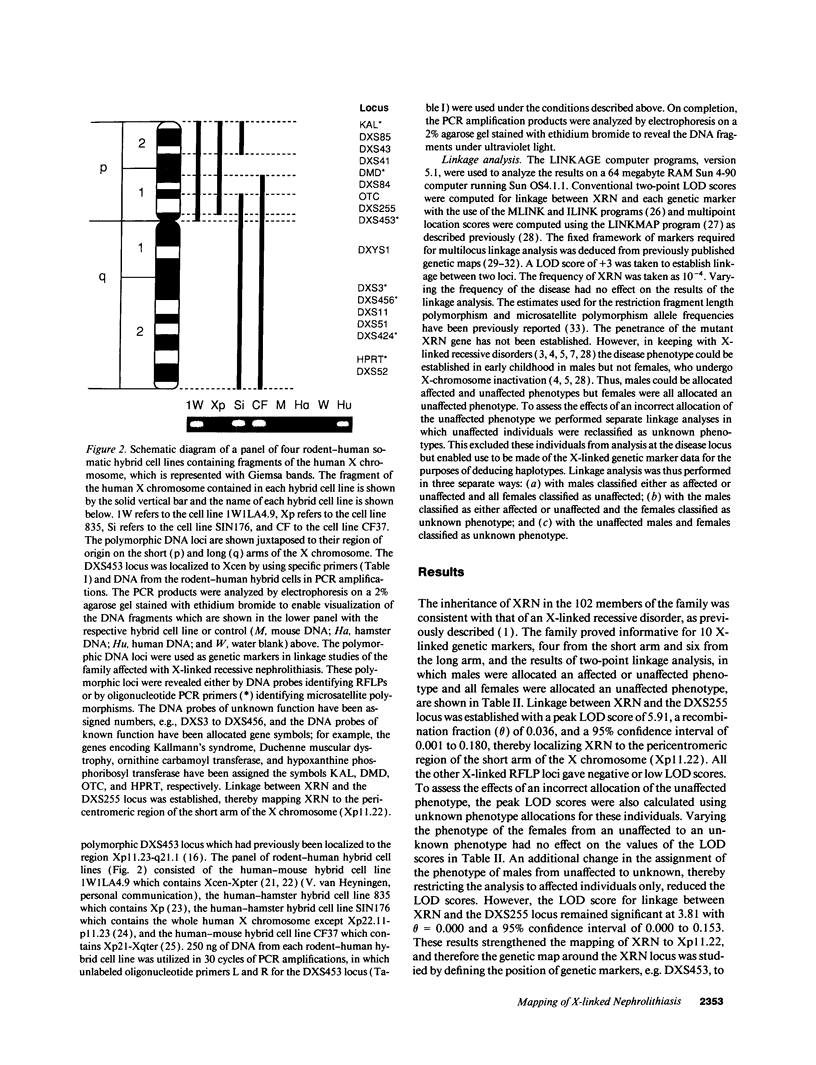




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkin C. L., Hasstedt S. J., Menlove L., Cannon L., Kirschner N., Schwartz C., Nguyen K., Skolnick M. Mapping of Alport syndrome to the long arm of the X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):249–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attree O., Olivos I. M., Okabe I., Bailey L. C., Nelson D. L., Lewis R. A., McInnes R. R., Nussbaum R. L. The Lowe's oculocerebrorenal syndrome gene encodes a protein highly homologous to inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):239–242. doi: 10.1038/358239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. F., Hostikka S. L., Zhou J., Chow L. T., Oliphant A. R., Gerken S. C., Gregory M. C., Skolnick M. H., Atkin C. L., Tryggvason K. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1224–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.2349482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouloux P. M., Hardelin J. P., Munroe P., Kirk J. M., Legouis R., Levilliers J., Hazan J., Weissenbach J., Petit C. A dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the Kallmann locus (Xp22.3). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5453–5453. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens P. R., Fenwick R. G., Chamberlain J. S., Gibbs R. A., de Andrade M., Chakraborty R., Caskey C. T. Carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy families, using dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):951–960. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. J., Boyd Y., Brownlee G. G., Craig I. W. Multi-allelic RFLP for M27 beta, an anonymous single copy genomic clone at Xp11.3-Xcen [HGM9 provisional no. DXS255]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9616–9616. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frymoyer P. A., Scheinman S. J., Dunham P. B., Jones D. B., Hueber P., Schroeder E. T. X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis with renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 5;325(10):681–686. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109053251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne C. M., Todd J. A. Tetranucleotide repeat polymorphism at the HPRT locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5450–5450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle C., Williamson R., de la Chapelle A., Herva R. R., Haapala K., Bates G., Willard H. F., Pearson P., Davies K. E. Mapping DNA sequences in a human X-chromosome deletion which extends across the region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):451–462. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner C. U., Trofatter J. A., Mahtani M. M., Willard H. F., DeGennaro L. J. A highly polymorphic dinucleotide repeat on the proximal short arm of the human X chromosome: linkage mapping of the synapsin I/A-raf-1 genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):184–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE C. U., TERREY M., MacLACHLAN E. A. Organic-aciduria, decreased renal ammonia production, hydrophthalmos, and mental retardation; a clinical entity. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1952 Feb;83(2):164–184. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1952.02040060030004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Thiselton D. L., Bateman J. B., Ngo J. T., Sparkes R. S., Coleman M., Davies K. E., Bhattacharya S. S. Localisation of the gene for Norrie disease to between DXS7 and DXS426 on Xp. Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;88(3):349–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00197273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):397–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luty J. A., Guo Z., Willard H. F., Ledbetter D. H., Ledbetter S., Litt M. Five polymorphic microsatellite VNTRs on the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):776–783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H., Shapiro L. J. Expression of an X-linked gene from an inactive human X chromosome in mouse-human hybrid cells: further evidence for the noninactivation of the steroid sulfatase locus in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6759–6763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabholz M., Miggiano V., Bodmer W. Genetic analysis with human--mouse somatic cell hybrids. Nature. 1969 Jul 26;223(5204):358–363. doi: 10.1038/223358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteous D. J., Morten J. E., Cranston G., Fletcher J. M., Mitchell A., van Heyningen V., Fantes J. A., Boyd P. A., Hastie N. D. Molecular and physical arrangements of human DNA in HRAS1-selected, chromosome-mediated transfectants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2223–2232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver D. N., Lewis R. A., Nussbaum R. L. Mapping the Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome to Xq24-q26 by use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):282–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI112795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier P., Newton R., Forbes S. A., Ivens A., Moore G. E. Polymorphic dinucleotide repeat at the DXS3 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4793–4793. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Bouloux P., Wooding C., Chotai K., Broad P. M., Spurr N. K., Besser G. M., O'Riordan J. L. Association of parathyroid tumors in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 with loss of alleles on chromosome 11. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 27;321(4):218–224. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907273210403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Davies K. E., Whyte M. P., Wooding C., O'Riordan J. L. Mapping the gene causing X-linked recessive idiopathic hypoparathyroidism to Xq26-Xq27 by linkage studies. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):40–45. doi: 10.1172/JCI114712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., O'Riordan J. L. Inherited forms of rickets and osteomalacia. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Feb;2(1):157–191. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(88)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Ledbetter S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the DXS453, DXS454 and DXS458 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4037–4037. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




