Abstract
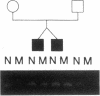
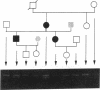
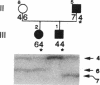
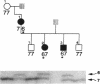
Generalized resistance to thyroid hormone (GRTH) is a syndrome of variable reduction of tissue responsiveness to thyroid hormone. 28 different point mutations in the human thyroid hormone receptor beta (TR beta) gene have been associated with GRTH. These mutations are clustered in two regions of the T3 binding domain of the TR beta (codons 310-347 and 417-453). We now report point mutations in the TR beta gene of six additional families with GRTH and show that three mutations occurred each in three families with GRTH, and that three other mutations were each present in two families. In 11 of these 15 families, lack of a common ancestor could be confirmed by genetic analysis. 28 of the 38 point mutations so far identified, including all those occurring in more than one family, are located in cytosine-guanine-rich areas of the TR beta gene. Differences in clinical and laboratory findings in unrelated families harboring the same TR beta mutation suggest that genetic variability of other factors modulate the expression of thyroid hormone action.
Full text
PDF
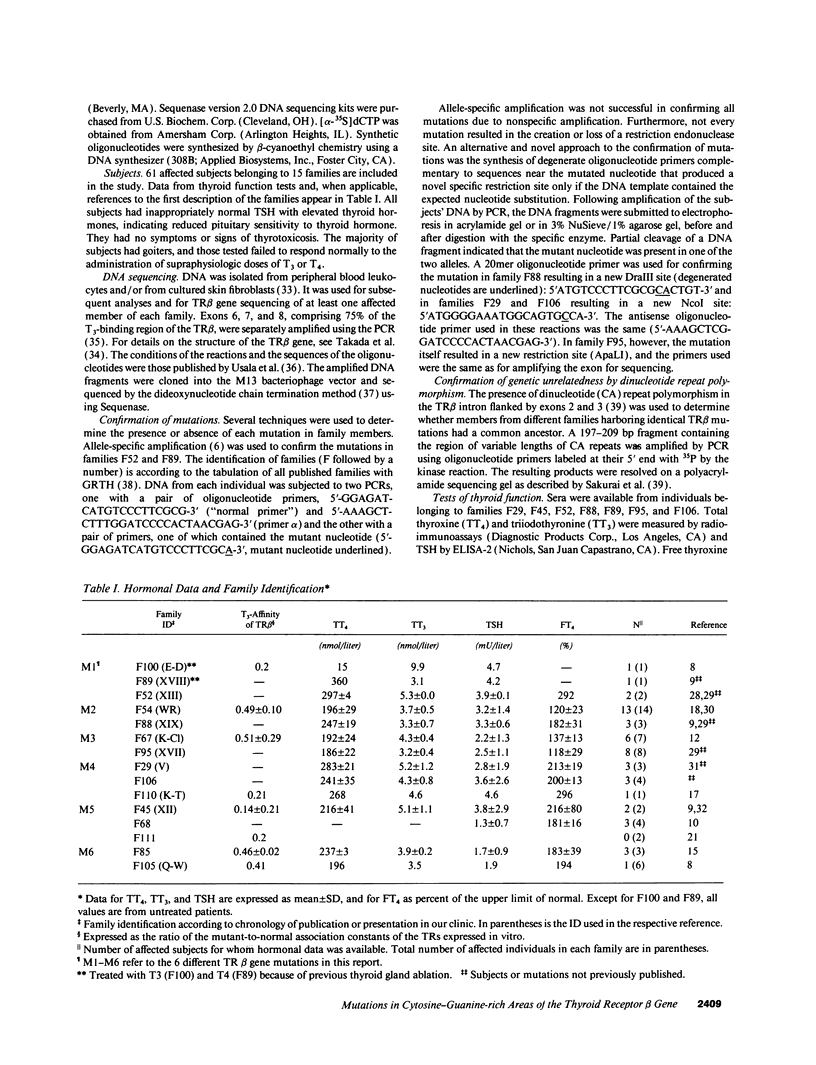



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M., Nagaya T., Tone Y., Jameson J. L., Chatterjee V. K. Functional properties of a novel mutant thyroid hormone receptor in a family with generalized thyroid hormone resistance syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1992 Mar;36(3):281–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1992.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behr M., Loos U. A point mutation (Ala229 to Thr) in the hinge domain of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor gene in a family with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1119–1126. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1324420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd C. V., Teh B. T., Hayward N. K., Hickman P. E., Ward G. J., Cameron D. P. Single base mutation in the hormone binding domain of the thyroid hormone receptor beta gene in generalised thyroid hormone resistance demonstrated by single stranded conformation polymorphism analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):606–612. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90151-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. R., Lubahn D. B., Wilson E. M., French F. S., Migeon C. J., Corden J. L. Functional characterization of naturally occurring mutant androgen receptors from subjects with complete androgen insensitivity. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1759–1772. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman K. D., Djuh Y. Y., Nicholson D., Rhooms P., Wartofsky L., Fein H. G., Usala S. J., Hao E. H., Bradley W. E., Berard J. Generalized thyroid hormone resistance: identification of an arginine to cystine mutation in codon 315 of the c-erb A beta thyroid hormone receptor. J Endocrinol Invest. 1992 Sep;15(8):573–579. doi: 10.1007/BF03344927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli P., Refetoff S., Murata Y. Resistance to thyroid hormone diagnosed by the reduced response of fibroblasts to the triiodothyronine-induced suppression of fibronectin synthesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Aug;65(2):242–246. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-2-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee V. K., Nagaya T., Madison L. D., Datta S., Rentoumis A., Jameson J. L. Thyroid hormone resistance syndrome. Inhibition of normal receptor function by mutant thyroid hormone receptors. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1977–1984. doi: 10.1172/JCI115225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Krawczak M. The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions causing human genetic disease: patterns and predictions. Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;85(1):55–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00276326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cugini C. D., Jr, Leidy J. W., Jr, Chertow B. S., Bérard J., Bradley W. E., Menke J. B., Hao E. H., Usala S. J. An arginine to histidine mutation in codon 315 of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor in a kindred with generalized resistance to thyroid hormones results in a receptor with significant 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine binding activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 May;74(5):1164–1170. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.5.1314846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling D. S., Beebe J. S., Burnside J., Winslow E. R., Chin W. W. 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) receptor-auxiliary protein (TRAP) binds DNA and forms heterodimers with the T3 receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):73–84. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bellis A., Quigley C. A., Cariello N. F., el-Awady M. K., Sar M., Lane M. V., Wilson E. M., French F. S. Single base mutations in the human androgen receptor gene causing complete androgen insensitivity: rapid detection by a modified denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis technique. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;6(11):1909–1920. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.11.1480178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Yang C. R., Au M., Casanova J., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. A domain containing leucine-zipper-like motifs mediate novel in vivo interactions between the thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1610–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Janssen O. E., Weiss R. E., Murata Y., Seo H., Refetoff S. The relative expression of mutant and normal thyroid hormone receptor genes in patients with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone determined by estimation of their specific messenger ribonucleic acid products. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jan;76(1):64–69. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.1.8421105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes I. A., Ichikawa K., Degroot L. J., John R., Jones M. K., Hall R., Scanlon M. F. Non-adenomatous inappropriate TSH hypersecretion and euthyroidism requires no treatment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1987 Oct;27(4):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1987.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inappropriate secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):339–351. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz P. B., D'Ercole A. J., Utiger R. D. Peripheral resistance to thyroid hormone in an infant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Nov;53(5):958–963. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-5-958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeberl D. D., Bottema C. D., Buerstedde J. M., Sommer S. S. Functionally important regions of the factor IX gene have a low rate of polymorphism and a high rate of mutation in the dinucleotide CpG. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):448–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Triiodothyronine: review of recent studies of its physiology and pathophysiology in man. Metabolism. 1972 Nov;21(11):1073–1092. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich J., Utiger R. D. Triiodothyronine radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):157–166. doi: 10.1172/JCI106786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul M. J., Marcelli M., Zoppi S., Wilson C. M., Griffin J. E., Wilson J. D. Mutations in the ligand-binding domain of the androgen receptor gene cluster in two regions of the gene. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2097–2101. doi: 10.1172/JCI116093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier C. A., Dickstein B. M., Ashizawa K., McClaskey J. H., Muchmore P., Ransom S. C., Menke J. B., Hao E. H., Usala S. J., Bercu B. B. Variable transcriptional activity and ligand binding of mutant beta 1 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptors from four families with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):248–258. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mixson A. J., Parrilla R., Ransom S. C., Wiggs E. A., McClaskey J. H., Hauser P., Weintraub B. D. Correlations of language abnormalities with localization of mutations in the beta-thyroid hormone receptor in 13 kindreds with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone: identification of four new mutations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Oct;75(4):1039–1045. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.4.1400869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
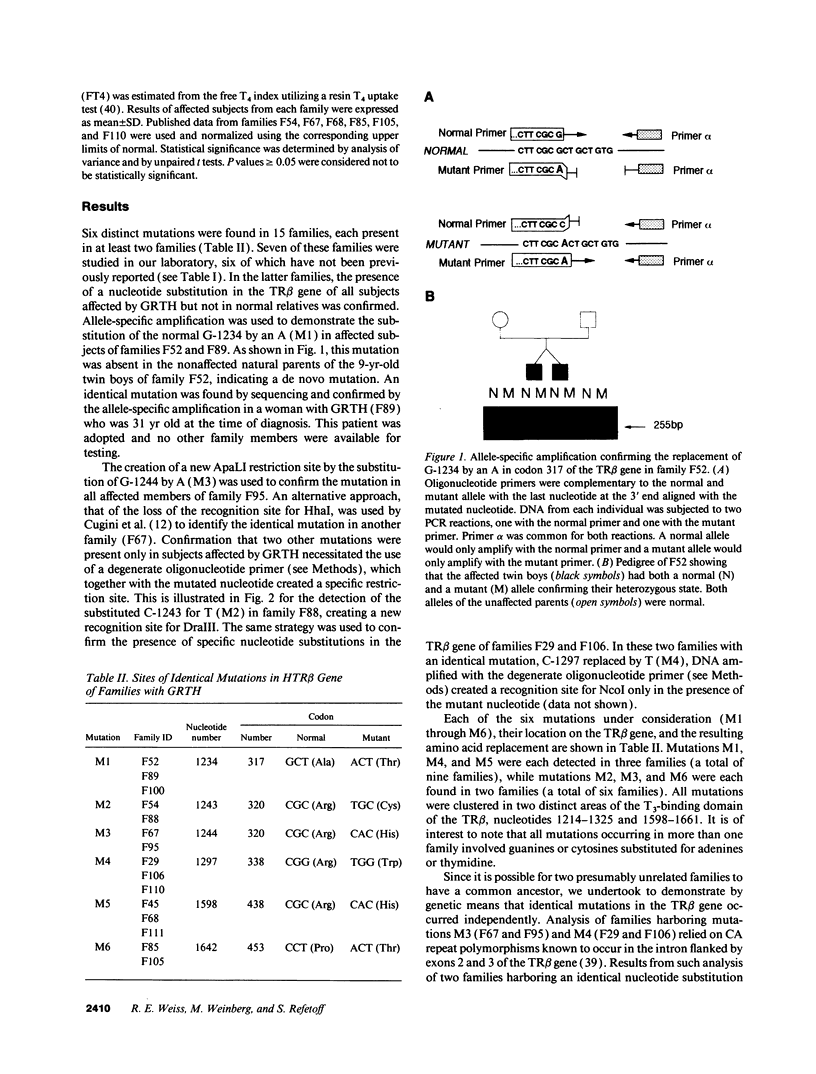
- Murata Y., Refetoff S., Horwitz A. L., Smith T. J. Hormonal regulation of glycosaminoglycan accumulation in fibroblasts from patients with resistance to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1233–1239. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya T., Madison L. D., Jameson J. L. Thyroid hormone receptor mutants that cause resistance to thyroid hormone. Evidence for receptor competition for DNA sequences in target genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13014–13019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya T., Madison L. D., Jameson J. L. Thyroid hormone receptor mutants that cause resistance to thyroid hormone. Evidence for receptor competition for DNA sequences in target genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13014–13019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao R., Haji M., Yanase T., Ogo A., Takayanagi R., Katsube T., Fukumaki Y., Nawata H. A single amino acid substitution (Met786----Val) in the steroid-binding domain of human androgen receptor leads to complete androgen insensitivity syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 May;74(5):1152–1157. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.5.1569163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara A. S., Caplan R. H., Gundersen C. B., Wickus G. G., Elston A. C., 3rd Peripheral resistance to thyroid hormone in a family: heterogeneity of clinical presentation. J Pediatr. 1983 Aug;103(2):228–232. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla R., Mixson A. J., McPherson J. A., McClaskey J. H., Weintraub B. D. Characterization of seven novel mutations of the c-erbA beta gene in unrelated kindreds with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Evidence for two "hot spot" regions of the ligand binding domain. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1172/JCI115542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S. Syndromes of thyroid hormone resistance. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):E88–E98. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.2.E88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ris-Stalpers C., Trifiro M. A., Kuiper G. G., Jenster G., Romalo G., Sai T., van Rooij H. C., Kaufman M., Rosenfield R. L., Liao S. Substitution of aspartic acid-686 by histidine or asparagine in the human androgen receptor leads to a functionally inactive protein with altered hormone-binding characteristics. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1562–1569. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin N. I., Hagen S. R., Collaço F., Refetoff S., Selenkow H. A. Serum tests for measurement of thyroid function. Hormones. 1971;2(5):266–279. doi: 10.1159/000178240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai A., Nakai A., DeGroot L. J. Structural analysis of human thyroid hormone receptor beta gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jun 18;71(2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai A., Takeda K., Ain K., Ceccarelli P., Nakai A., Seino S., Bell G. I., Refetoff S., DeGroot L. J. Generalized resistance to thyroid hormone associated with a mutation in the ligand-binding domain of the human thyroid hormone receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8977–8981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Forman B. M., Horowitz Z. D., Ye Z. S. Regulation of gene expression by thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):957–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI113449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarne D. H., Refetoff S., Rosenfield R. L., Farriaux J. P. Sex hormone-binding globulin in the diagnosis of peripheral tissue resistance to thyroid hormone: the value of changes after short term triiodothyronine administration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Apr;66(4):740–746. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-4-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Nakamura H., Tagami T., Miyoshi Y., Tanaka K., Imura H. A point mutation of the T3 receptor beta 1 gene in a kindred of generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;84(3):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuto Y., Wakabayashi I., Amuro N., Minami S., Okazaki T. A point mutation in the 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine-binding domain of thyroid hormone receptor-beta associated with a family with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):213–217. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallridge R. C., Parker R. A., Wiggs E. A., Rajagopal K. R., Fein H. G. Thyroid hormone resistance in a large kindred: physiologic, biochemical, pharmacologic, and neuropsychologic studies. Am J Med. 1989 Mar;86(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanjaard R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. Ligand-binding and heterodimerization activities of a conserved region in the ligand-binding domain of the thyroid hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8587–8591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Balzano S., Sakurai A., DeGroot L. J., Refetoff S. Screening of nineteen unrelated families with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone for known point mutations in the thyroid hormone receptor beta gene and the detection of a new mutation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):496–502. doi: 10.1172/JCI115023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Sakurai A., DeGroot L. J., Refetoff S. Recessive inheritance of thyroid hormone resistance caused by complete deletion of the protein-coding region of the thyroid hormone receptor-beta gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jan;74(1):49–55. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.1.1727829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Weiss R. E., Refetoff S. Rapid localization of mutations in the thyroid hormone receptor-beta gene by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in 18 families with thyroid hormone resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Apr;74(4):712–719. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.4.1548332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Bale A. E., Gesundheit N., Weinberger C., Lash R. W., Wondisford F. E., McBride O. W., Weintraub B. D. Tight linkage between the syndrome of generalized thyroid hormone resistance and the human c-erbA beta gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1217–1220. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Menke J. B., Watson T. L., Bérard W. E., Bradley C., Bale A. E., Lash R. W., Weintraub B. D. A new point mutation in the 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine-binding domain of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor is tightly linked to generalized thyroid hormone resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jan;72(1):32–38. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Menke J. B., Watson T. L., Wondisford F. E., Weintraub B. D., Bérard J., Bradley W. E., Ono S., Mueller O. T., Bercu B. B. A homozygous deletion in the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor gene in a patient with generalized thyroid hormone resistance: isolation and characterization of the mutant receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):327–335. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Tennyson G. E., Bale A. E., Lash R. W., Gesundheit N., Wondisford F. E., Accili D., Hauser P., Weintraub B. D. A base mutation of the C-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor in a kindred with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Molecular heterogeneity in two other kindreds. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):93–100. doi: 10.1172/JCI114438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. E., Refetoff S. Thyroid hormone resistance. Annu Rev Med. 1992;43:363–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.43.020192.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Sugawara A., Refetoff S., Chin W. W. New insights on the mechanism(s) of the dominant negative effect of mutant thyroid hormone receptor in generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1825–1831. doi: 10.1172/JCI116058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]