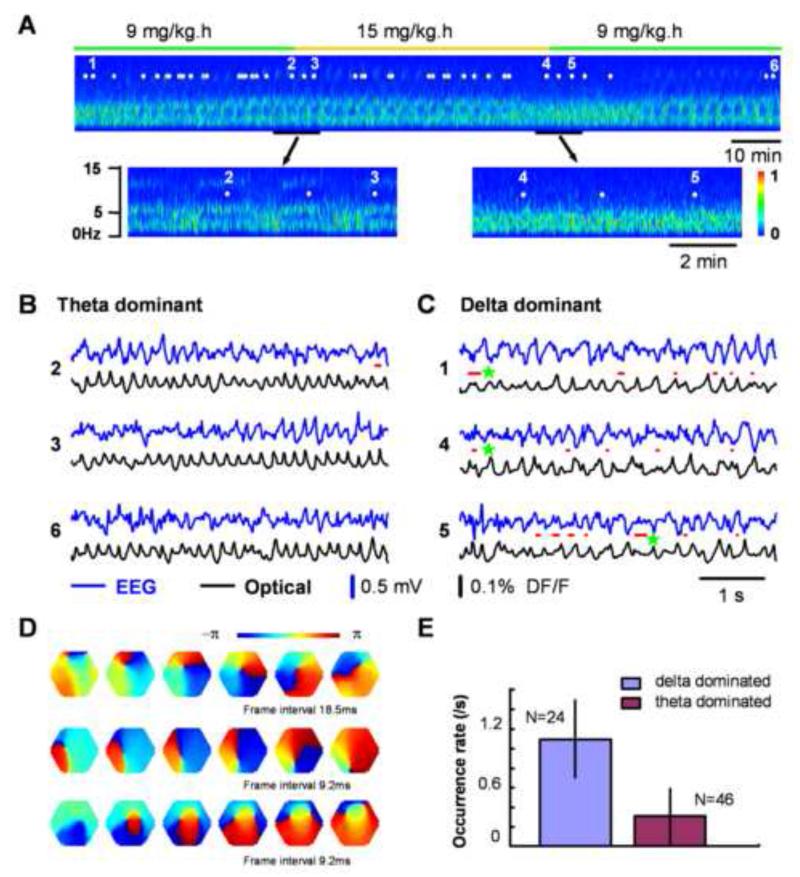
Figure 2. Spiral waves during sleep-like states.
A. EEG spectrum during sleep-like states. The EEG recording started about 4 hours after the initial injection of 50 mg/kg pentobarbital. A low level of anesthesia is maintained by continuous tail vein infusion of pentobarbital at 9 mg/kg-hour (green bar). The EEG was filtered between 1 - 40 Hz for clarity. Note that the power of the spectrum transitions periodically between theta (~ 6Hz) and delta (1-4 Hz) dominant states when pentobarbital infusion is maintained at a low constant rate. With higher infusion rate (15mg/kg-hour) of pentobarbital (marked with orange bar), the alternating patterns in the EEG shifted to the delta-dominant state. Note: there are approximately 20 min delays of drug effects because of the slow infusion of pentobarbital. Seventy imaging trials were taken during a four-hour period (43 trials during the section shown, marked as white dots) and representative trials (1-6) are presented in panels B and C. B. and C. Simultaneous EEG (blue) and optical (black) traces recorded during the theta-dominant (B, trials 2, 3, 6) and delta-dominant periods (C, trials 1, 4, 5). Spiral waves are identified from the 8,192 images of each trial and durations of spiral waves are marked by red lines under each EEG trace. Three example spiral waves (red lines next to green stars) are shown in panel D. D. Phase maps of example spiral waves in sleep-like states. Note that the bottom row images show an example of double spirals with opposite rotating directions. The imaging area is 4 mm in diameter. E. Rate of occurrence of spiral waves during sleep-like states. The occurrence rate was obtained from 70 imaging trials (202 cases of spirals) in this animal based on the EEG spectrum (Panel A shows about half of this data set). Supplemental Figure S2 shows another example from a different animal during sleep-like states.