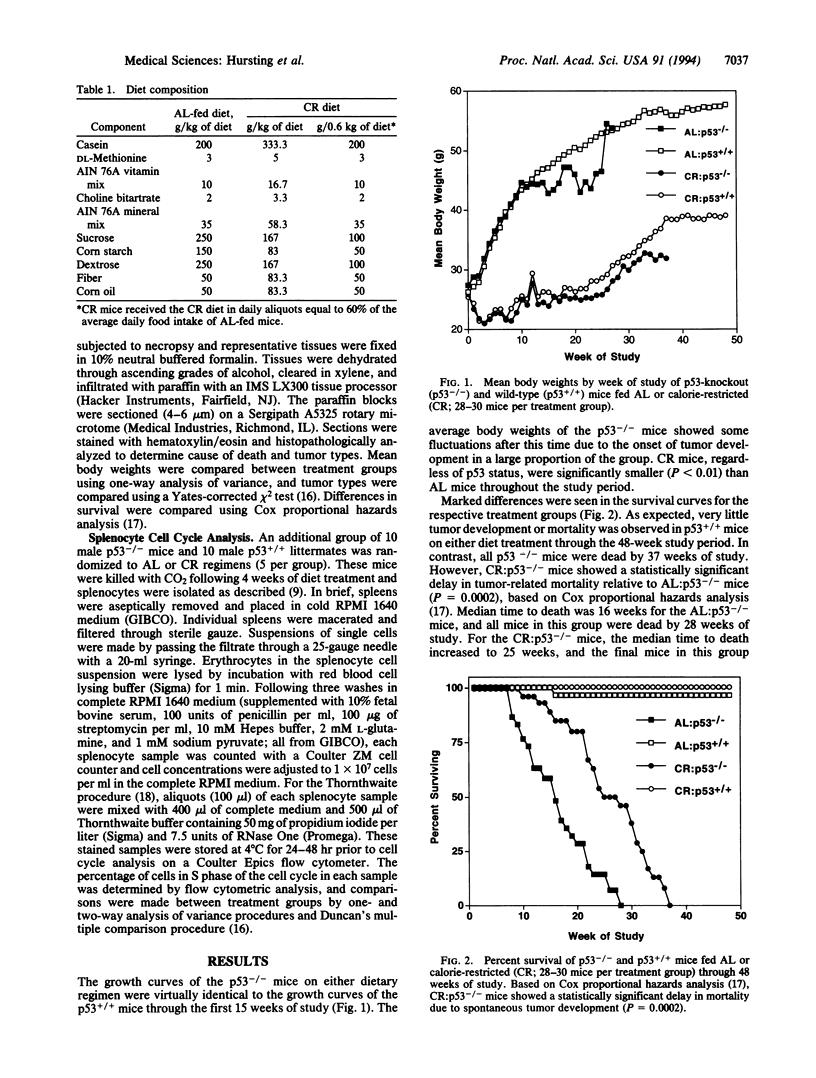
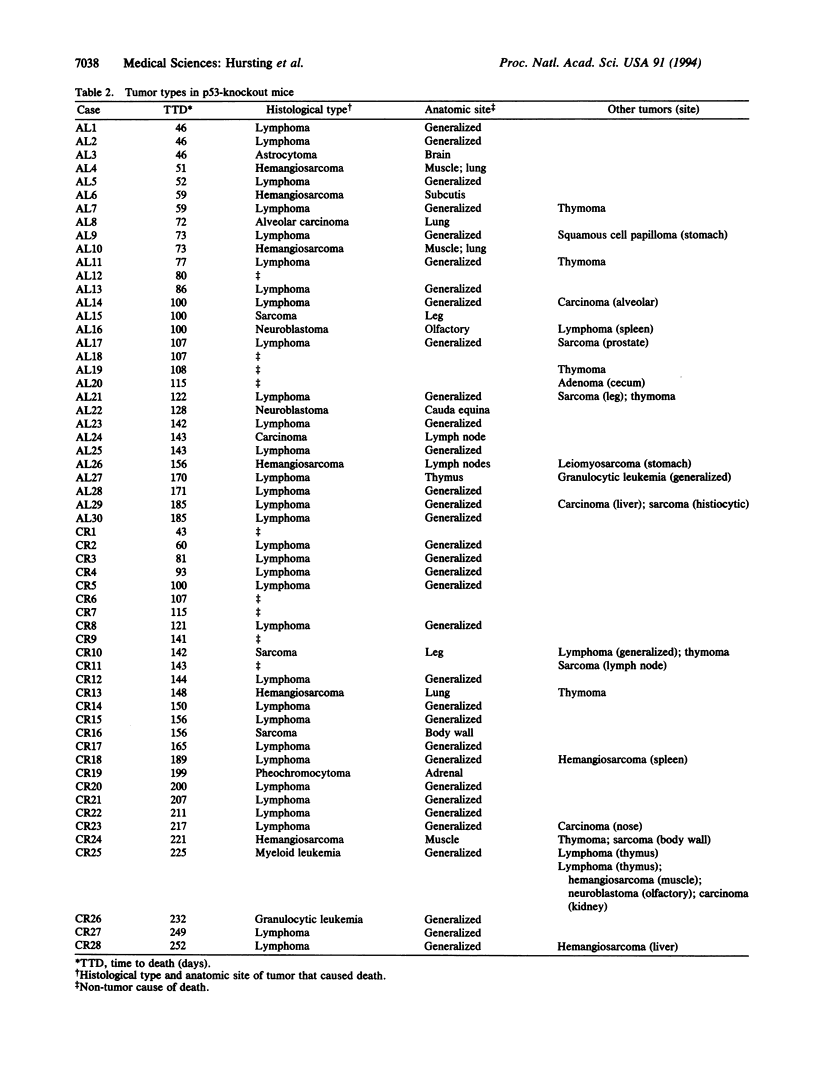
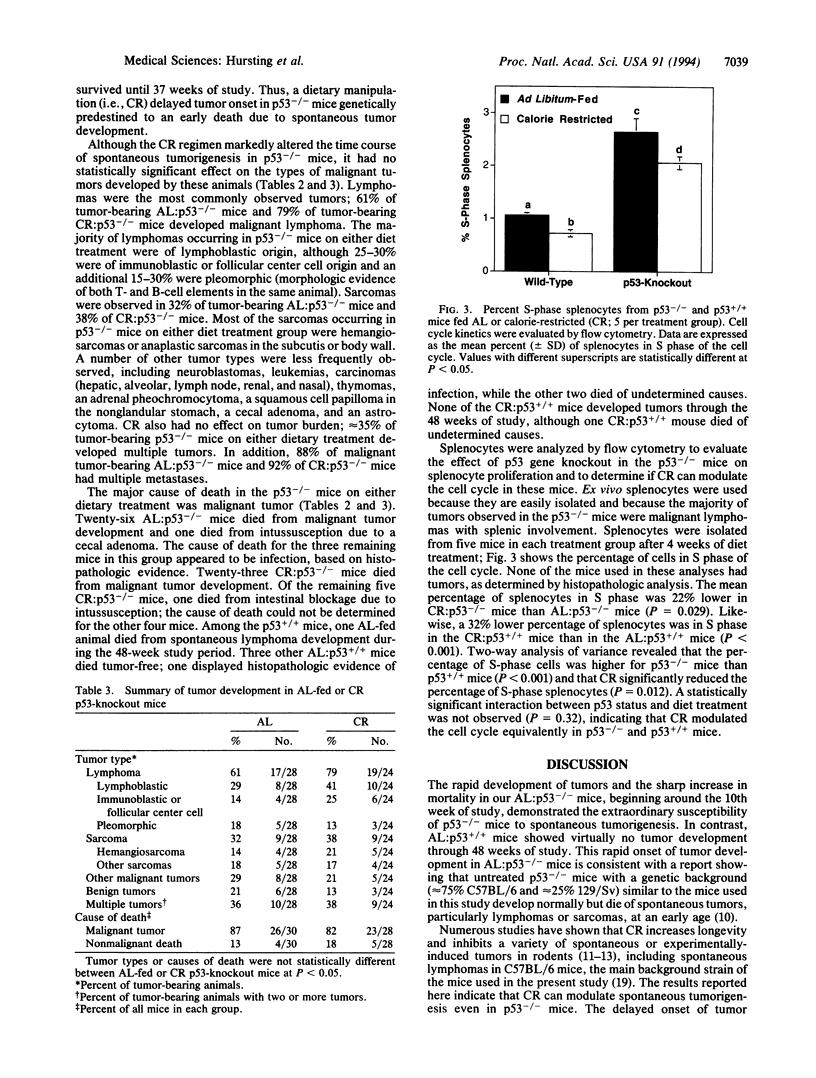
Abstract
Transgenic mice with both alleles of the p53 tumor suppressor gene (frequently mutated in human tumors) knocked out by gene targeting provide a potentially useful tumorigenesis model because these mice rapidly develop spontaneous tumors. To determine whether tumorigenesis in p53-knockout mice is sensitive to experimental manipulation, tumor development in response to calorie restriction (CR; a potent inhibitor of rodent tumors) was evaluated. Tumor development was monitored for 48 weeks in male nullizygous p53-knockout and wild-type littermate mice (28-30 per treatment group) fed ad libitum (AL) or restricted to 60% of AL carbohydrate calorie intake. CR:p53-knockout mice (median survival = 25 weeks) experienced a delay in tumor onset and subsequent mortality (P = 0.0002) relative to AL:p53-knockout mice (median survival = 16 weeks). Tumor development and mortality in wild-type littermates on either diet treatment were < 4% through 48 weeks. Cell cycle analyses were performed on splenocytes from p53-knockout mice and wild-type littermates after 4 weeks of AL feeding or CR (5 per group). The percentage of splenocytes in S phase of the cell cycle was 3-fold higher for p53-knockout mice than wild-type mice (P < 0.001), and CR reduced the percentage of S-phase splenocytes in both p53-knockout and wild-type mice (P = 0.012). These data demonstrate that tumor development in p53-knockout mice genetically predisposed to tumors can be delayed by CR (possibly via cell cycle modulation) and suggest that these mice provide a very useful model of spontaneous tumorigenesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang F., Syrjänen S., Kurvinen K., Syrjänen K. The p53 tumor suppressor gene as a common cellular target in human carcinogenesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;88(2):174–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey M., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Bradley A., Donehower L. A. Genetic background alters the spectrum of tumors that develop in p53-deficient mice. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):938–943. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller T. D., Holt P. R., Richardson A. Food restriction retards age-related histological changes in rat small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90829-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursting S. D., Switzer B. R., French J. E., Kari F. W. The growth hormone: insulin-like growth factor 1 axis is a mediator of diet restriction-induced inhibition of mononuclear cell leukemia in Fischer rats. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2750–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi A., Tsukada M., Wada Y., Masuda H., Weindruch R. Mitotic activity in mice is suppressed by energy restriction-induced torpor. J Nutr. 1992 Jul;122(7):1446–1453. doi: 10.1093/jn/122.7.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok E., Scott F. W., Mongeau R., Nera E. A., Malcolm S., Clayson D. B. Calorie restriction and cellular proliferation in various tissues of the female Swiss Webster mouse. Cancer Lett. 1990 May 15;51(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(90)90232-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Vogelstein B. Tumour suppressor genes. No room at the p53 inn. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):17–18. doi: 10.1038/365017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Peter A., Dobbie L., White S., Howie S. E., Salter D. M., Bird C. C., Wyllie A. H., Hooper M. L. Tumour incidence, spectrum and ploidy in mice with a large deletion in the p53 gene. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):603–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S., Zou Z. Q., Pirollo K., Blattner W., Chang E. H. Germ-line transmission of a mutated p53 gene in a cancer-prone family with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):747–749. doi: 10.1038/348747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. G., Breslow N., Gart J. J. Trend and homogeneity analyses of proportions and life table data. Comput Biomed Res. 1977 Aug;10(4):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(77)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornthwaite J. T., Sugarbaker E. V., Temple W. J. Preparation of tissues for DNA flow cytometric analysis. Cytometry. 1980 Nov;1(3):229–237. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990010309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



