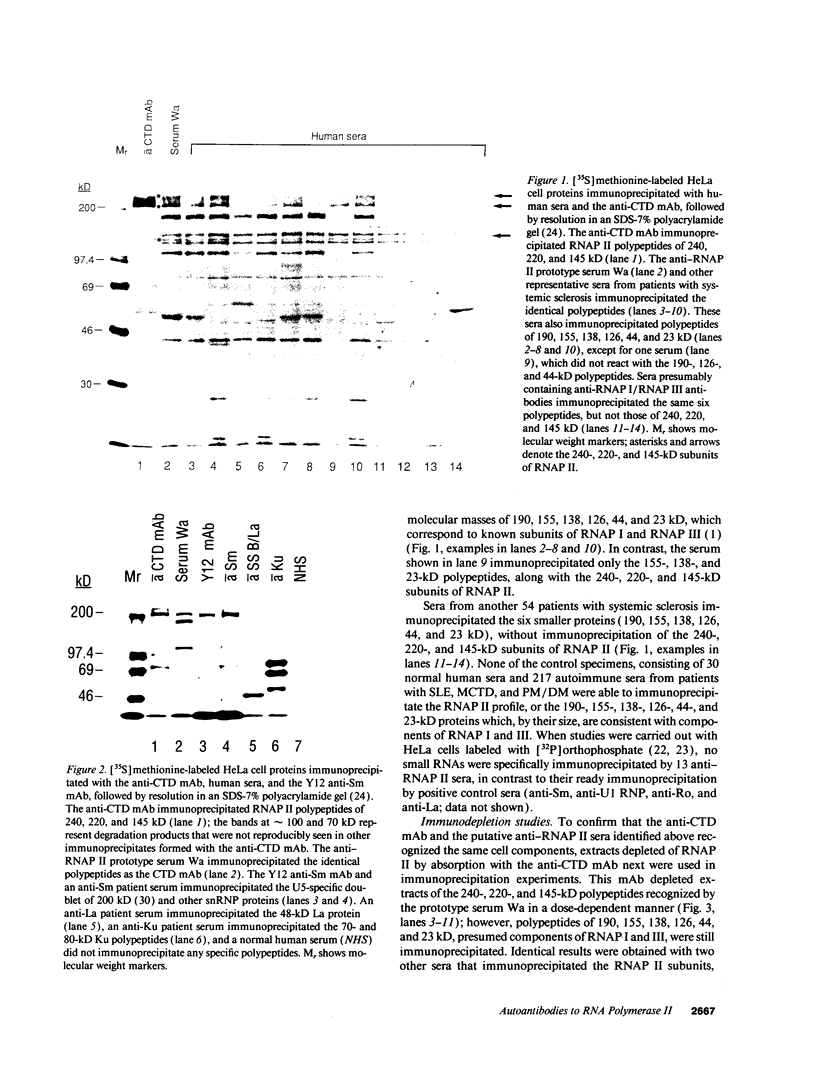
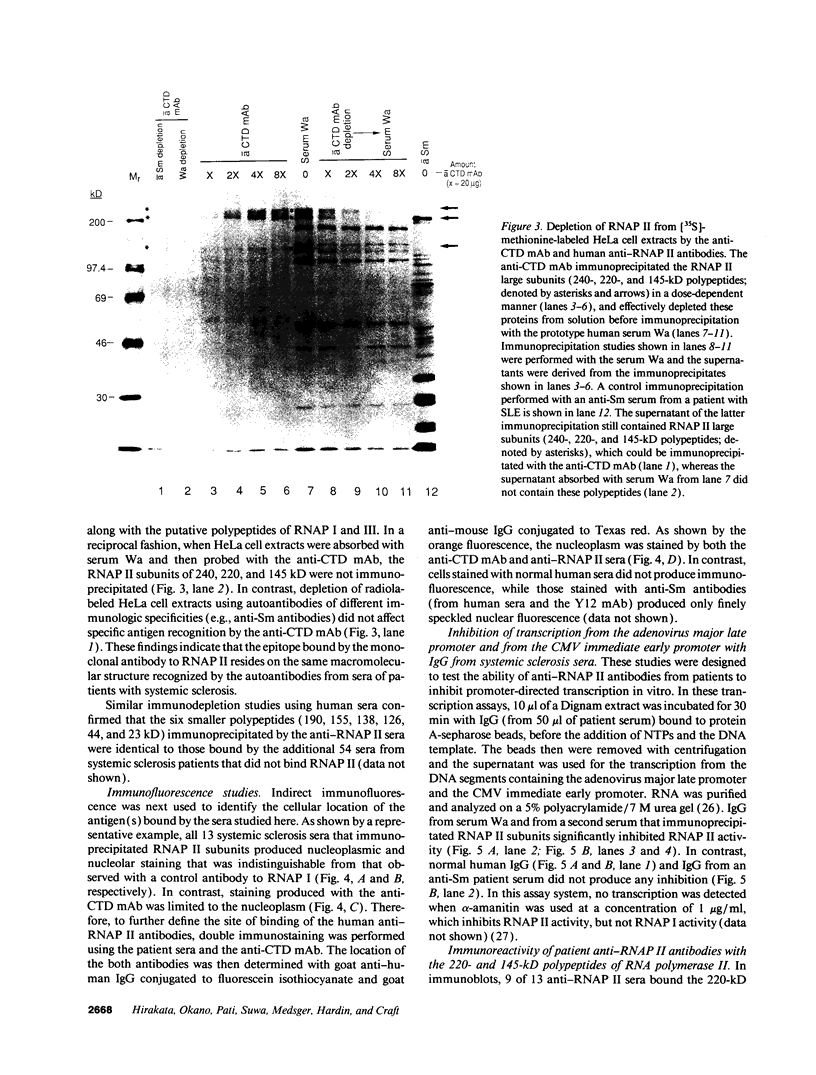
Abstract
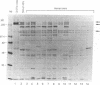
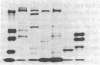
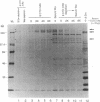
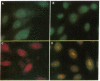
In this study, autoantibodies to RNA polymerase II from sera of patients with systemic sclerosis have been identified and characterized. These antibodies immunoprecipitated polypeptides of 220 kD (IIA) and 145 kD (IIC), the two largest subunits of RNA polymerase II, and bound both subunits in immunoblots. These polypeptides were immunoprecipitated by the anti-RNA polymerase II monoclonal antibody 8WG16, which recognizes the carboxyl-terminal domain of the 220-kD subunit, and their identity to the proteins bound by human sera was confirmed in immunodepletion studies. Sera with anti-RNA polymerase II antibodies also immunoprecipitated proteins that were consistent with components of RNA polymerases I and III. In vitro transcription experiments showed that the human antibodies were an effective inhibitor of RNA polymerase II activity. In indirect immunofluorescence studies, anti-RNA polymerase II autoantibodies stained the nucleoplasm, as expected from the known location of RNA polymerase II, and colocalized with the anti-RNA polymerase II monoclonal antibody. The human sera also stained the nucleolus, the location of RNA polymerase I. From a clinical perspective, these antibodies were found in 13 of 278 patients with systemic sclerosis, including 10 with diffuse and three with limited cutaneous disease, but were not detected in sera from patients with other connective tissue diseases and from normal controls. We conclude that anti-RNA polymerase II antibodies are specific to patients with systemic sclerosis, and that they are apparently associated with antibodies to RNA polymerases I and III. These autoantibodies may be useful diagnostically and as a probe for further studies of the biological function of RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M., Winkelmann G., Lührmann R. 20S small nuclear ribonucleoprotein U5 shows a surprisingly complex protein composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6038–6042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 13;292(7):344–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmann J. L., Dahmus M. E. Monoclonal antibody specific for calf thymus RNA polymerases IIO and IIA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11798–11803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J., Mimori T., Olsen T. L., Hardin J. A. The U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle as an autoantigen. Analysis with sera from patients with overlap syndromes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1716–1724. doi: 10.1172/JCI113511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E., Kedinger C. Transcription of adenovirus-2 major late promoter inhibited by monoclonal antibody directed against RNA polymerases IIO and IIA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2303–2307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E. Structural relationship between the large subunits of calf thymus RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle T. J., Hagen G., Malcolm S. Size heterogeneity of the largest subunit of nuclear RNA polymerase II. An immunological analysis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):649–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A. The lupus autoantigens and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):457–460. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata M., Mimori T., Akizuki M., Craft J., Hardin J. A., Homma M. Autoantibodies to small nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins in Japanese patients with inflammatory muscle disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Apr;35(4):449–456. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodo H. G., 3rd, Blatti S. P. Purification using polyethylenimine precipitation and low molecular weight subunit analyses of calf thymus and wheat germ DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2334–2343. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipnis R. J., Craft J., Hardin J. A. The analysis of antinuclear and antinucleolar autoantibodies of scleroderma by radioimmunoprecipitation assays. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Sep;33(9):1431–1437. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémet S., Saurin W., Sentenac A. RNA polymerases B and C are more closely related to each other than to RNA polymerase A. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10048–10051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M. L., Young R. A. Intragenic and extragenic suppressors of mutations in the heptapeptide repeat domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):715–724. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Medsger T. A., Jr Autoantibody to Th ribonucleoprotein (nucleolar 7-2 RNA protein particle) in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;33(12):1822–1828. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Steen V. D., Medsger T. A., Jr Autoantibody to U3 nucleolar ribonucleoprotein (fibrillarin) in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jan;35(1):95–100. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pati U. K., Weissman S. M. Isolation and molecular characterization of a cDNA encoding the 23-kDa subunit of human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13114–13121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Rose K. M., Scheer U., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to RNA polymerase I in scleroderma sera. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):65–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI112809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase II from the mouse plasmacytoma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3221–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Reichlin M., Berlin C. M., Jacob S. T. Autoantibodies against RNA polymerase I in scleroderma and Sjögren's syndrome sera. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 14;144(3):1296–1302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Rose K. M., Wenger M. E., Berlin C. M., Jacob S. T. Antibodies to distinct polypeptides of RNA polymerase I in sera from patients with rheumatic autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7499–7503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Purification of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II by immunoaffinity chromatography. Elution of active enzyme with protein stabilizing agents from a polyol-responsive monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7069–7077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Steinberg T. H., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11511–11520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintzerith M., Acker J., Vicaire S., Vigneron M., Kedinger C. Complete sequence of the human RNA polymerase II largest subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):910–910. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Liao S. M., Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Subunits shared by eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):313–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]