Abstract
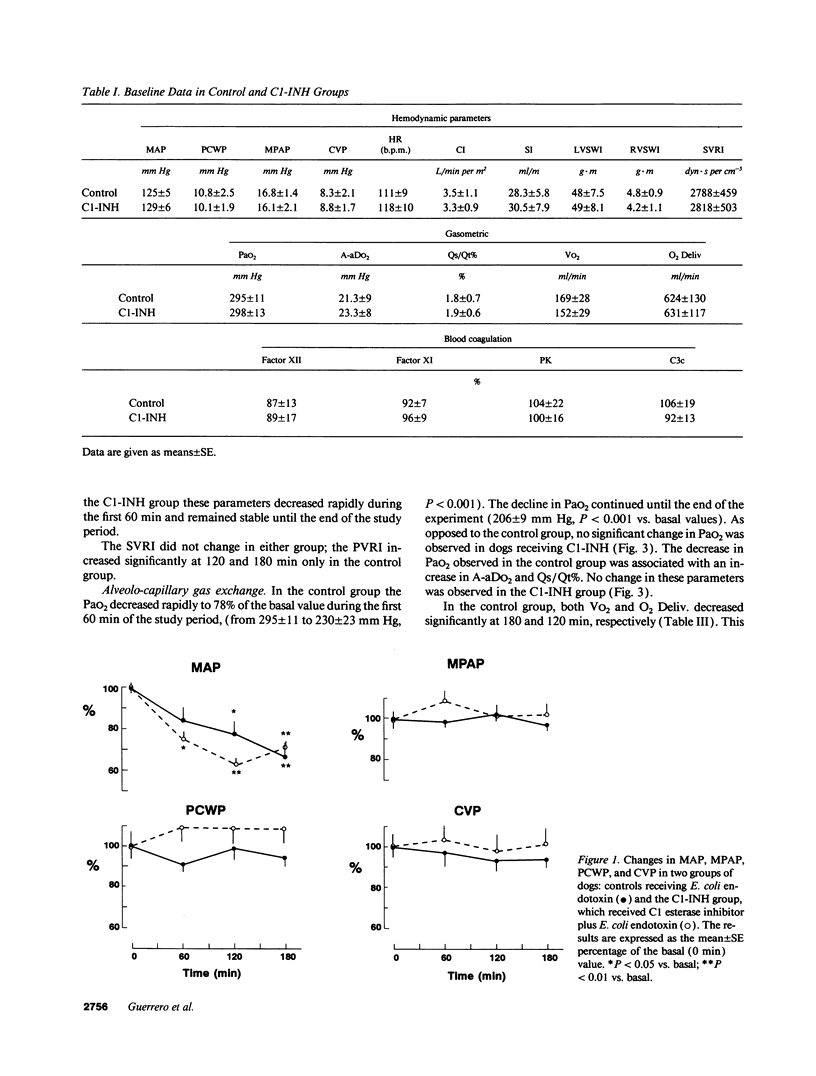
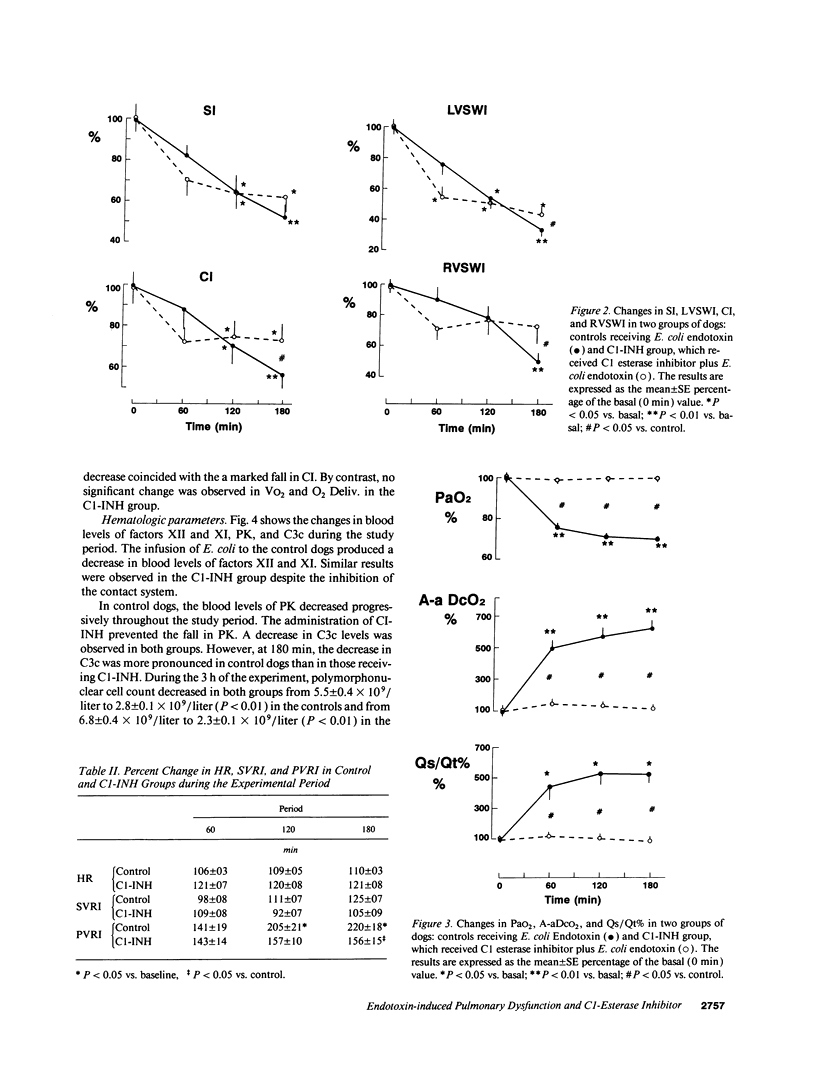
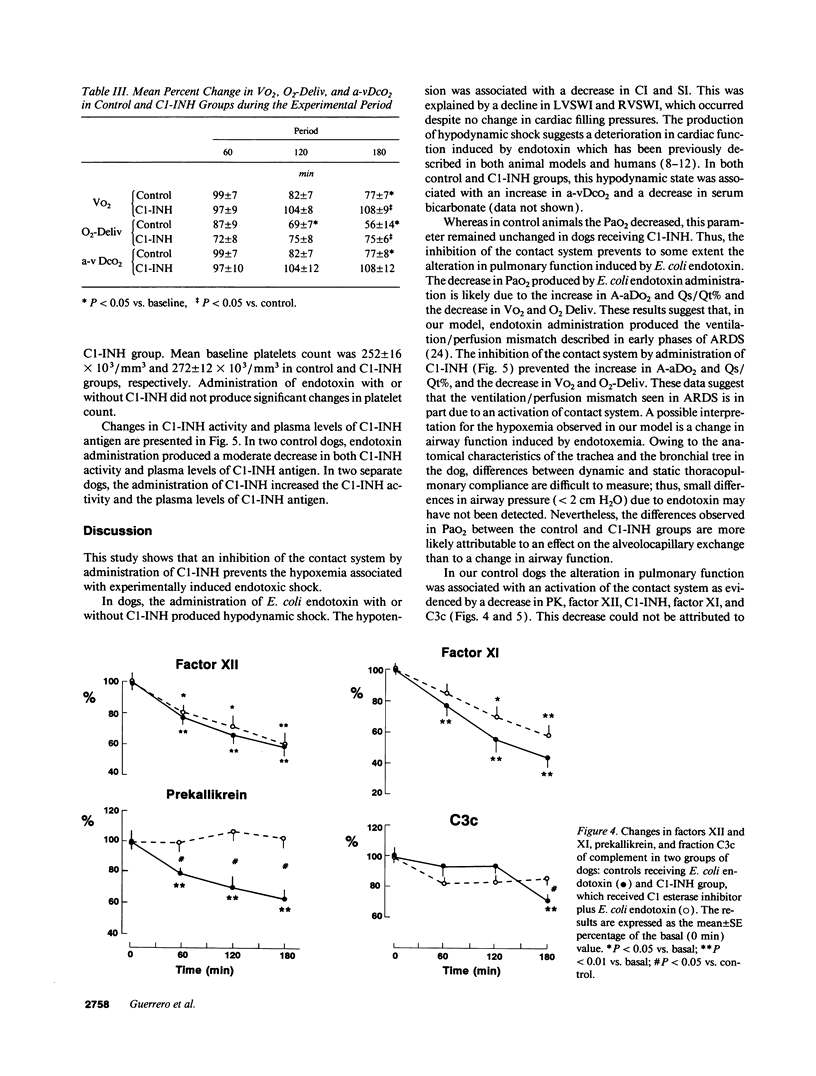
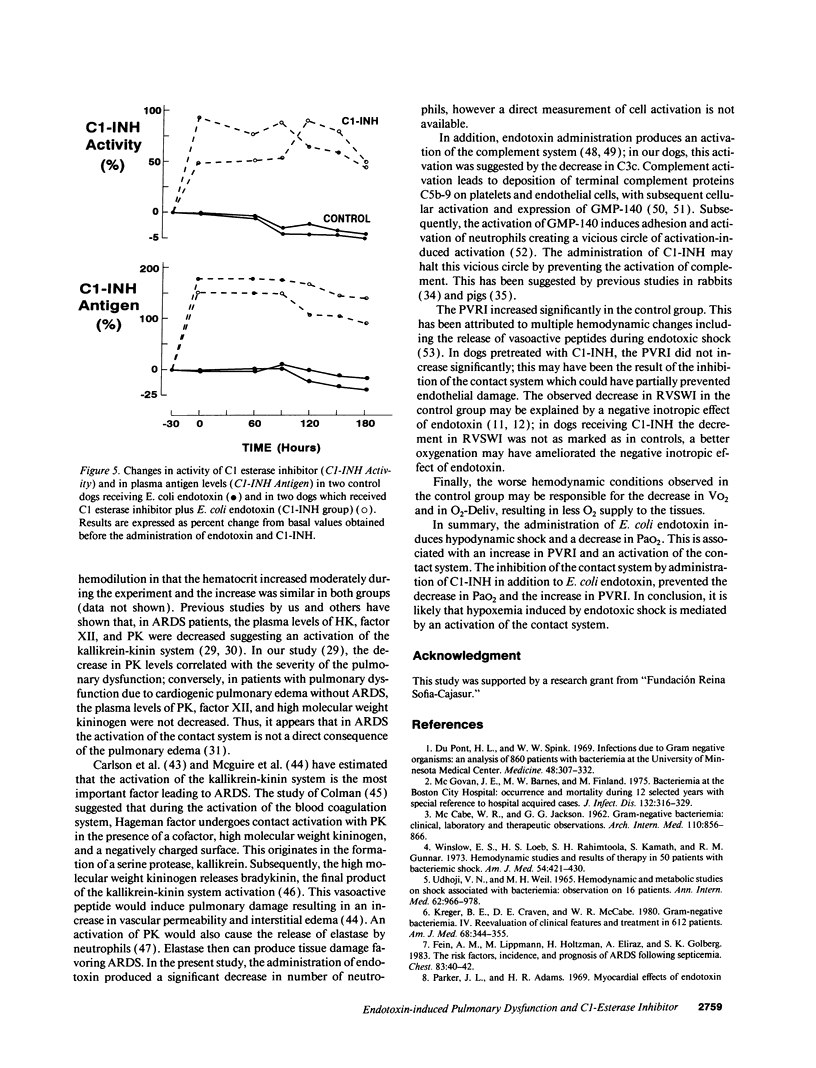
In septic shock, hypotension, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and neutrophil activation are related to the activation of the blood coagulation contact system. This study evaluates in dogs the effect of the C1-esterase inhibitor (C1-INH), a main inhibitor of the blood coagulation contact system, on the cardiovascular and respiratory dysfunction associated with endotoxic shock. Two groups were included: controls, which received Escherichia coli endotoxin, and a C1-INH group in which C1-INH was infused before E. coli endotoxin administration. In both groups, endotoxin produced hypodynamic shock; however, the decrease in the systolic index and the ventricular systolic work indexes were greater in controls than the C1-INH group. In controls, the arterial O2 partial pressure decreased by 30% and the alveolo-arterial O2 difference increased by 625%, these parameters remained unchanged in the C1-INH group. Hypoxemia was associated with increased intrapulmonary shunt, decreased blood coagulation contact factors, and decreased C3c. In contrast, C1-INH administration prevented endotoxin-induced hypoxemia, the increase in intrapulmonary shunt, and the decrease in blood coagulation contact factors. This study shows that, in dogs with endotoxic shock, pulmonary dysfunction is associated with an activation of the blood coagulation contact phase system. An inhibition of this system by C1-INH prevented the hypoxemia induced by endotoxic shock.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasen A. O., Frolich W., Saugstad O. D., Amundsen E. Plasma kallikrein activity and prekallikrein levels during endotoxin shock in dogs. Eur Surg Res. 1978;10(1):50–62. doi: 10.1159/000127992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aasen A. O., Ohlsson K., Larsbraaten M., Amundsen E. Changes in plasminogen levels, plasmin activity and activity of antiplasmins during endotoxin shock in dogs. Eur Surg Res. 1978;10(1):63–72. doi: 10.1159/000127993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Oct;116(4):589–615. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertozzi P., Astedt B., Zenzius L., Lynch K., LeMaire F., Zapol W., Chapman H. A., Jr Depressed bronchoalveolar urokinase activity in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):890–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Schaeffer R. C., Jr, Carpio M., Weil M. H. Edema fluid and coagulation changes during fulminant pulmonary edema. Chest. 1981 Jan;79(1):43–49. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho A. C., DeMarinis S., Scott C. F., Silver L. D., Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W. Activation of the contact system of plasma proteolysis in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Aug;112(2):270–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Surface-mediated defense reactions. The plasma contact activation system. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1249–1253. doi: 10.1172/JCI111326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. The role of plasma proteases in septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1207–1209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Spink W. W. Infections due to gram-negative organisms: an analysis of 860 patients with bacteremia at the University of Minnesota Medical Center, 1958-1966. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jul;48(4):307–332. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellrodt A. G., Riedinger M. S., Kimchi A., Berman D. S., Maddahi J., Swan H. J., Murata G. H. Left ventricular performance in septic shock: reversible segmental and global abnormalities. Am Heart J. 1985 Aug;110(2):402–409. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein A. M., Lippmann M., Holtzman H., Eliraz A., Goldberg S. K. The risk factors, incidence, and prognosis of ARDS following septicemia. Chest. 1983 Jan;83(1):40–42. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funkhouser E. A. Synthesis of Nitrate Reductase in Chlorella: II. EVIDENCE FOR SYNTHESIS IN AMMONIA-GROWN CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):944–948. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANS H., KRIVIT W. Effect of endotoxin shock on the clotting mechanism of dogs. Ann Surg. 1960 Jul;152:69–76. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196007000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore M. J., Amundsen E., Larsbraaten M., Lyngaas K., Fareid E. Studies on plasma inhibitors of plasma kallikrein using chromogenic peptide substrate assays. Thromb Res. 1979;16(5-6):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori R., Hamilton K. K., McEver R. P., Sims P. J. Complement proteins C5b-9 induce secretion of high molecular weight multimers of endothelial von Willebrand factor and translocation of granule membrane protein GMP-140 to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9053–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera C., Velasco F., Guerrero A., Guerrero R., Alvarez F., Torres A. Contact phase of blood coagulation in cardiogenic pulmonary oedema (CPO) and adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Intensive Care Med. 1989;15(2):99–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00295985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idell S., James K. K., Levin E. G., Schwartz B. S., Manchanda N., Maunder R. J., Martin T. R., McLarty J., Fair D. S. Local abnormalities in coagulation and fibrinolytic pathways predispose to alveolar fibrin deposition in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):695–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI114217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P. Initiation of the intrinsic coagulation and fibrinolytic pathways of man: the role of surfaces, hageman factor, prekallikrein, high molecular weight kininogen, and factor XI. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1978;4:127–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. L., Sahn S. A., Petty T. L. Incidence and outcome of the respiratory distress syndrome in gram-negative sepsis. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Aug;139(8):867–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger B. E., Craven D. E., McCabe W. R. Gram-negative bacteremia. IV. Re-evaluation of clinical features and treatment in 612 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):344–355. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACROIX E., LEUSEN I. LA CIRCULATION H'EPATIQUE ET SPLANCHNIQUE. J Physiol (Paris) 1965 Jan-Feb;57:115–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. W., Kleeberg U., Dolan P., Colman R. W. Plasma kallikrein and Hageman factor in Gram-negative bacteremia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Oct;73(4):545–551. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-4-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Barnes M. W., Finland M. Bacteremia at Boston City Hospital: Occurrence and mortality during 12 selected years (1935-1972), with special reference to hospital-acquired cases. J Infect Dis. 1975 Sep;132(3):316–335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.3.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. W., Spragg R. G., Cohen A. B., Cochrane C. G. Studies on the pathogenesis of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):543–553. doi: 10.1172/JCI110480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natanson C., Fink M. P., Ballantyne H. K., MacVittie T. J., Conklin J. J., Parrillo J. E. Gram-negative bacteremia produces both severe systolic and diastolic cardiac dysfunction in a canine model that simulates human septic shock. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):259–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI112559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A. S., Forsyth R. P., Williams H. E., Melmon K. L. Contribution of kinins to endotoxin shock in unanesthetized Rhesus monkeys. Circ Res. 1968 Feb;22(2):155–164. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell T. F., Jr, Clowes G. H., Jr, Talamo R. C., Colman R. W. Kinin activation in the blood of patients with sepsis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Oct;143(4):539–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. M., Shelhamer J. H., Bacharach S. L., Green M. V., Natanson C., Frederick T. M., Damske B. A., Parrillo J. E. Profound but reversible myocardial depression in patients with septic shock. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):483–490. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. D., Zimmerman G. A., Prescott S. M., McEver R. P., McIntyre T. M. Oxygen radicals induce human endothelial cells to express GMP-140 and bind neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):749–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Fromm R. E., Parker M. M., Brenner M., Kovacs J. A., Wesley R. A., Parrillo J. E. The cardiovascular response of normal humans to the administration of endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 3;321(5):280–287. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908033210503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllopoulos D. C., Cho M. S. Effect of injection of C1 inactivator on the platelet count and blood coagulation in rabbits infused with endotoxin. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):293–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDHOJI V. N., WEIL M. H. HEMODYNAMIC AND METABOLIC STUDIES ON SHOCK ASSOCIATED WITH BACTEREMIA. OBSERVATIONS ON 16 PATIENTS. Ann Intern Med. 1965 May;62:966–978. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-5-966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco F., Torres A., Guerrero A., Andres P., Guerrero R., Aljama P., Alvarez F. Behaviour of the contact phase of blood coagulation in the adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Thromb Haemost. 1986 Jun 30;55(3):357–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vito L., Dennis R. C., Weisel R. D., Hechtman H. B. Sepsis presenting as acute respiratory insufficiency. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974 Jun;138(6):896–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtfogel Y. T., Kucich U., James H. L., Scott C. F., Schapira M., Zimmerman M., Cohen A. B., Colman R. W. Human plasma kallikrein releases neutrophil elastase during blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1172/JCI111126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmer T., Ando B., Sims P. J. Complement C5b-9-stimulated platelet secretion is associated with a Ca2+-initiated activation of cellular protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13674–13681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow E. J., Loeb H. S., Rahimtoola S. H., Kamath S., Gunnar R. M. Hemodynamic studies and results of therapy in 50 patients with bacteremic shock. Am J Med. 1973 Apr;54(4):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., Morris A. H., Cengiz M. Cardiovascular alterations in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Med. 1982 Jul;73(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90920-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Bouma B. N. Inactivation of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



