Abstract
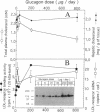
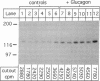
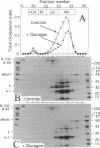
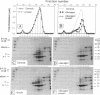
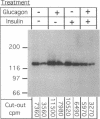
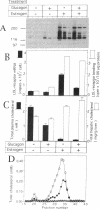
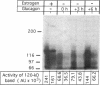
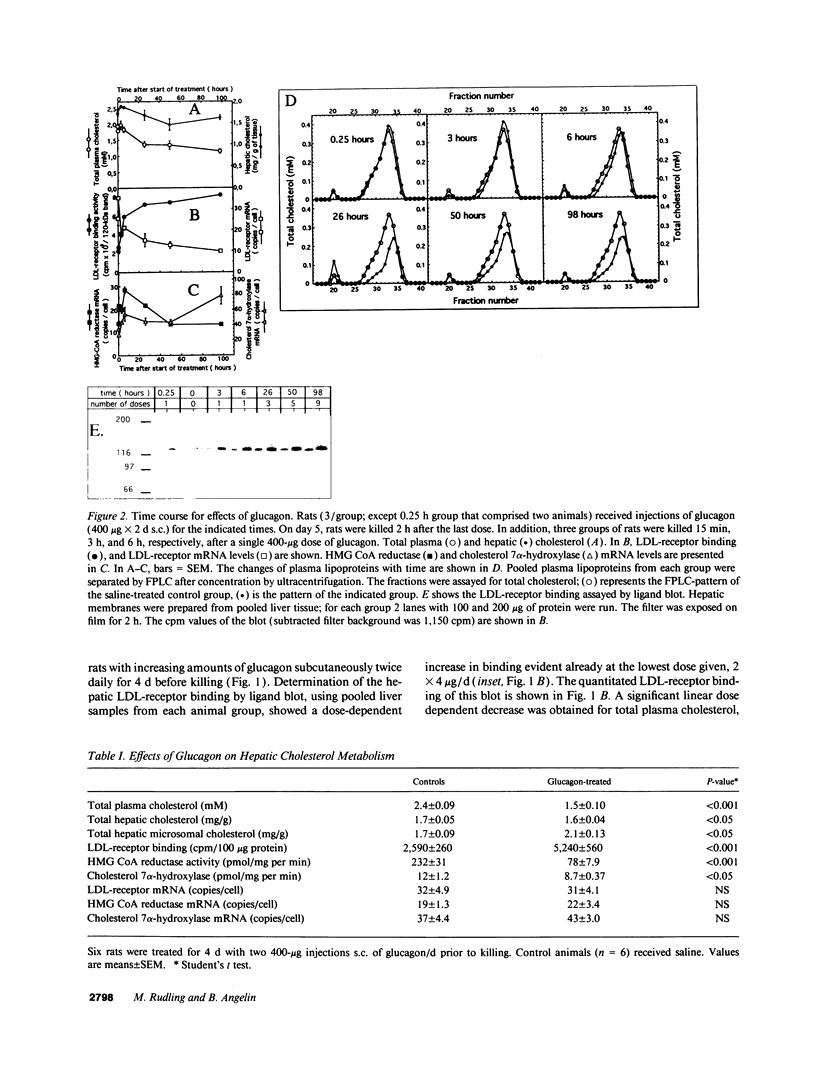
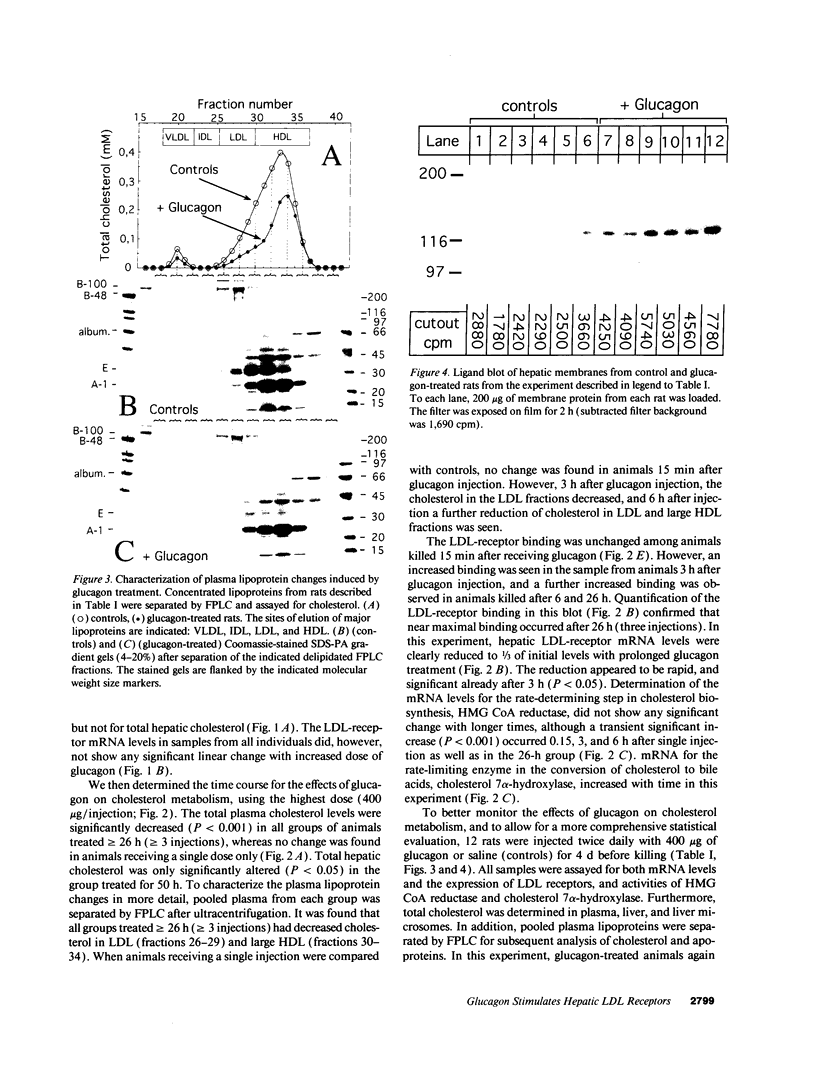
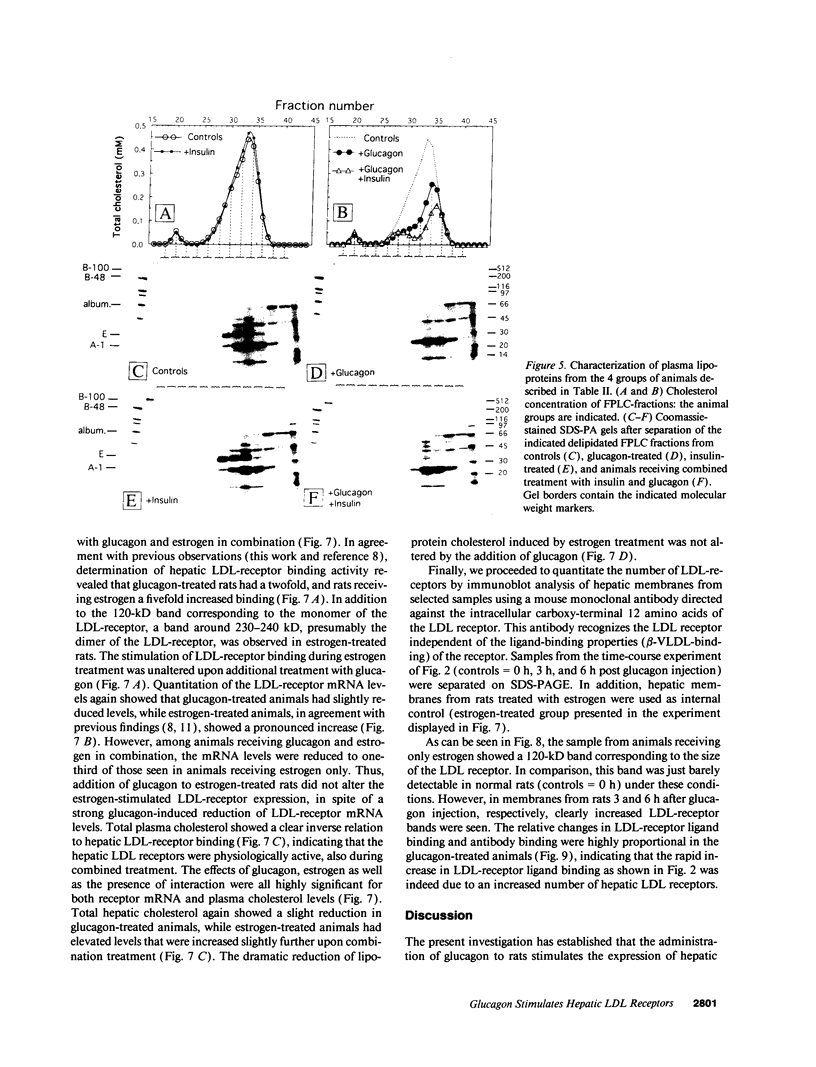
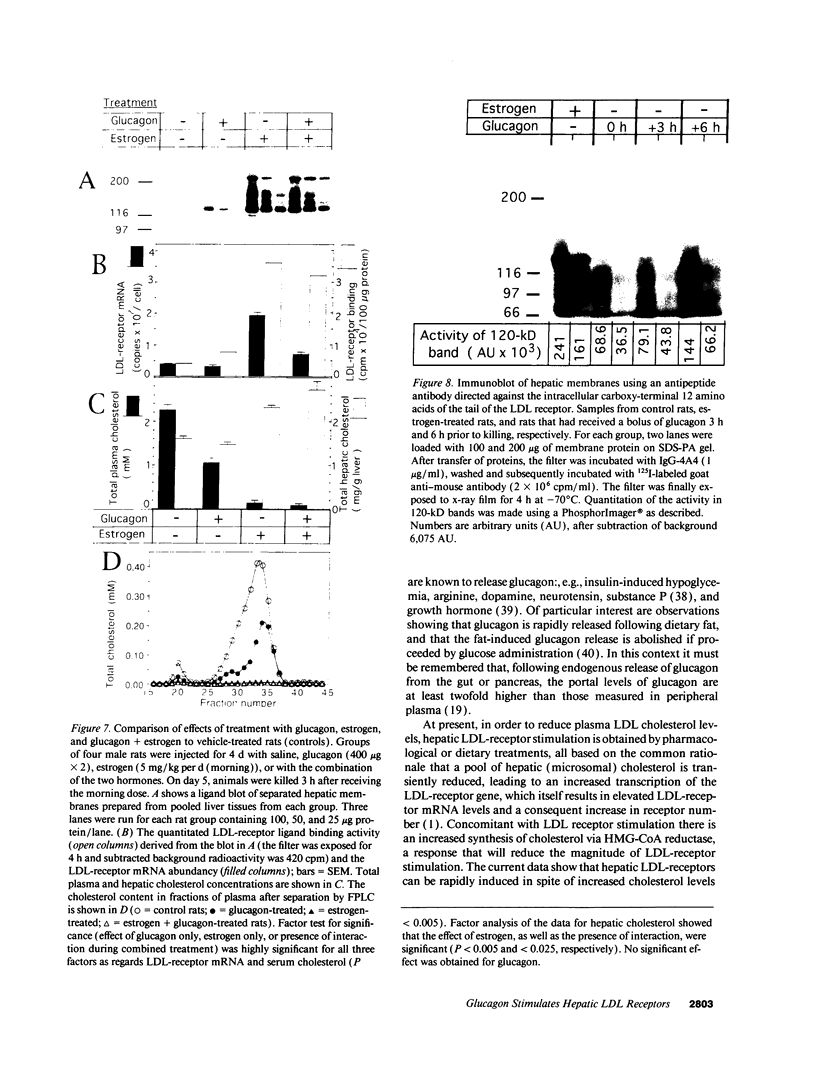
We studied the influence of glucagon on hepatic LDL receptors and plasma lipoproteins in rats. A dose-dependent (maximum, threefold) increase in LDL-receptor binding was evident already at a dose of 2 x 4 micrograms, and detectable 3 h after injection; concomitantly, cholesterol and apolipoprotein (apo) B and apoE within LDL and large HDL decreased in plasma. LDL receptor mRNA levels were however unaltered or reduced. Hepatic microsomal cholesterol was increased and the enzymatic activities of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase in hepatic microsomes were reduced. Insulin alone increased receptor binding and receptor mRNA levels twofold, but plasma cholesterol was unchanged and plasma apoE and apoB increased. Administration of insulin to glucagon-treated animals reduced the LDL-receptor binding to control levels and apoB appeared in LDL particles. Estrogen treatment increased LDL-receptor binding and mRNA levels five- and eightfold, respectively. Combined treatment with glucagon and estrogen reduced the stimulation of LDL-receptor mRNA levels by 80% although LDL-receptor binding was unchanged. Immunoblot analysis showed that glucagon increased the number of hepatic LDL receptors. We conclude that glucagon induces the number of hepatic LDL receptors by a mechanism not related to increased mRNA levels, suggesting the presence of a posttranscriptional regulatory mechanism present in the liver in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMATUZIO D. S., GRANDE F., WADA S. Effect of glucagon on the serum lipids in essential hyperlipemia and in hypercholesterolemia. Metabolism. 1962 Dec;11:1240–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Einarsson K., Liljeqvist L., Nilsell K., Heller R. A. 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in human liver microsomes: active and inactive forms and cross-reactivity with antibody against rat liver enzyme. J Lipid Res. 1984 Nov;25(11):1159–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Olivecrona H., Reihnér E., Rudling M., Ståhlberg D., Eriksson M., Ewerth S., Henriksson P., Einarsson K. Hepatic cholesterol metabolism in estrogen-treated men. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1657–1663. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. F., Salter A. M., Fears R., Brindley D. N. Glucagon, cyclic AMP and adrenaline stimulate the degradation of low-density lipoprotein by cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):425–429. doi: 10.1042/bj2620425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREN R., CARBO L. Pancreatic alpha-cell function in relation to cholesterol metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Apr;16(4):507–516. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-4-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs R., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. Effect of intravenously administered glucose on glucagon and insulin secretion during fat absorption. Metabolism. 1975 Jan;24(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P. Hypolipemic action of glucagon in experimental endogenous lipemia in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1973 May;14(3):312–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Angelin B., Ewerth S., Nilsell K., Björkhem I. Bile acid synthesis in man: assay of hepatic microsomal cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jan;27(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth J. L., Chandrasekaran C., Cooper A. D. Evidence for sterol-independent regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity in Hep-G2 cells. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):175–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2790175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove R. I., Mazzucco C. E., Radka S. F., Shoyab M., Kiener P. A. Oncostatin M up-regulates low density lipoprotein receptors in HepG2 cells by a novel mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18194–18199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guettet C., Rostaqui N., Mathé D., Lecuyer B., Navarro N., Jacotot B. Effect of chronic glucagon administration on lipoprotein composition in normally fed, fasted and cholesterol-fed rats. Lipids. 1991 Jun;26(6):451–458. doi: 10.1007/BF02536072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha Y. C., Barter P. J. Rapid separation of plasma lipoproteins by gel permeation chromatography on agarose gel Superose 6B. J Chromatogr. 1985 May 31;341(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M. L., al-Sheibani S., Riches P. G. Alterations of serum lipids in breast cancer: effects of disease activity, treatment, and hormonal factors. Clin Chem. 1991 Dec;37(12):2093–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Increased binding of low density lipoprotein to liver membranes from rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11367–11373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P. T., Gil G., Südhof T. C., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Mevinolin, an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, induces mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in livers of hamsters and rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8370–8374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P. T., Yamamoto T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Increased mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in livers of rabbits treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):792–796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Basheeruddin K., Ping L., Frazer S., Getz G. S. Mechanism of the growth-related activation of the low density lipoprotein receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1787–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton B., Middleton A. Cyclic AMP stimulates the synthesis and function of the low-density lipoprotein receptor in human vascular smooth-muscle cells and fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):853–861. doi: 10.1042/bj2820853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moltz J. H., Dobbs R. E., McCann S. M., Fawcett C. P. Effects of hypothalamic factors on insulin and glucagon release from the islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1977 Jul;101(1):196–202. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-1-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALOYAN E., HARPER P. V., Jr Glucagon as a regulating factor of plasma lipids. Metabolism. 1961 Apr;10:315–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reihnér E., Rudling M., Ståhlberg D., Berglund L., Ewerth S., Björkhem I., Einarsson K., Angelin B. Influence of pravastatin, a specific inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, on hepatic metabolism of cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):224–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M. J., Reihnér E., Einarsson K., Ewerth S., Angelin B. Low density lipoprotein receptor-binding activity in human tissues: quantitative importance of hepatic receptors and evidence for regulation of their expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3469–3473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M. J. Role of the liver for the receptor-mediated catabolism of low-density lipoprotein in the 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol-treated rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 2;919(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M. Hepatic mRNA levels for the LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase show coordinate regulation in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1992 Apr;33(4):493–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M., Norstedt G., Olivecrona H., Reihnér E., Gustafsson J. A., Angelin B. Importance of growth hormone for the induction of hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6983–6987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter A. M., Hayashi R., al-Seeni M., Brown N. F., Bruce J., Sorensen O., Atkinson E. A., Middleton B., Bleackley R. C., Brindley D. N. Effects of hypothyroidism and high-fat feeding on mRNA concentrations for the low-density-lipoprotein receptor and on acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase activities in rat liver. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 15;276(Pt 3):825–832. doi: 10.1042/bj2760825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey M. F., Miyanohara A., Elam R. L., Friedmann T., Witztum J. L. Post-transcriptional regulation of retroviral vector-transduced low density lipoprotein receptor activity. J Lipid Res. 1990 Dec;31(12):2167–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. P., Brissette L., Ramharack R., Deeley R. G. Differences between the regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and low density lipoprotein receptor in human hepatoma cells and fibroblasts reside primarily at the translational and post-translational levels. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16764–16773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. The Berson memorial lecture. Insulin-glucagon relationships in the defense against hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):575–583. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitkus P., Sirek A., Norwich K. H., Sirek O. V., Unger R. H., Harris V. Rapid changes in hepatic glucose output after a pulse of growth hormone in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):E14–E20. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.1.E14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan G. M., Becker R. A., Unger R. H., Ziegler M. G., Siler-Khodr T. M., Pruitt B. A., Jr, Mason A. D., Jr Nonthyroidal control of metabolism after burn injury: possible role of glucagon. Metabolism. 1985 Jul;34(7):637–641. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade D. P., Knight B. L., Soutar A. K. Regulation of low-density-lipoprotein-receptor mRNA by insulin in human hepatoma Hep G2 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 15;181(3):727–731. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Driel I. R., Goldstein J. L., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S. First cysteine-rich repeat in ligand-binding domain of low density lipoprotein receptor binds Ca2+ and monoclonal antibodies, but not lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17443–17449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]