Abstract
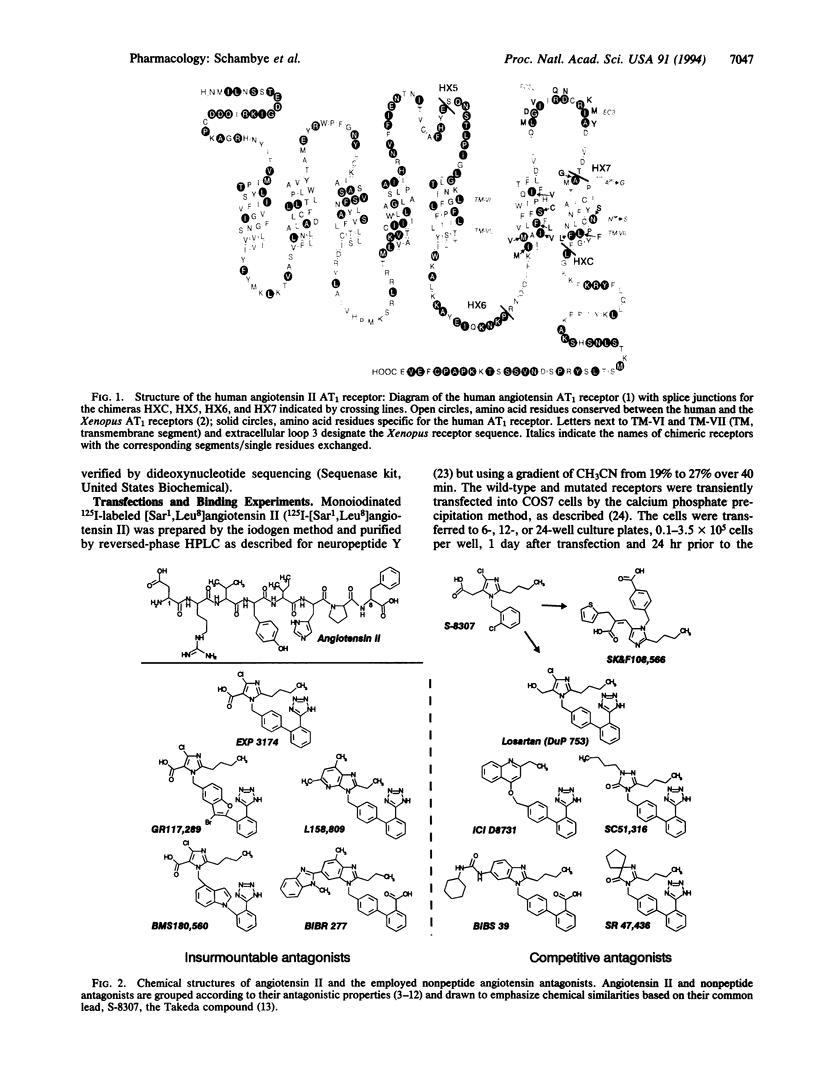
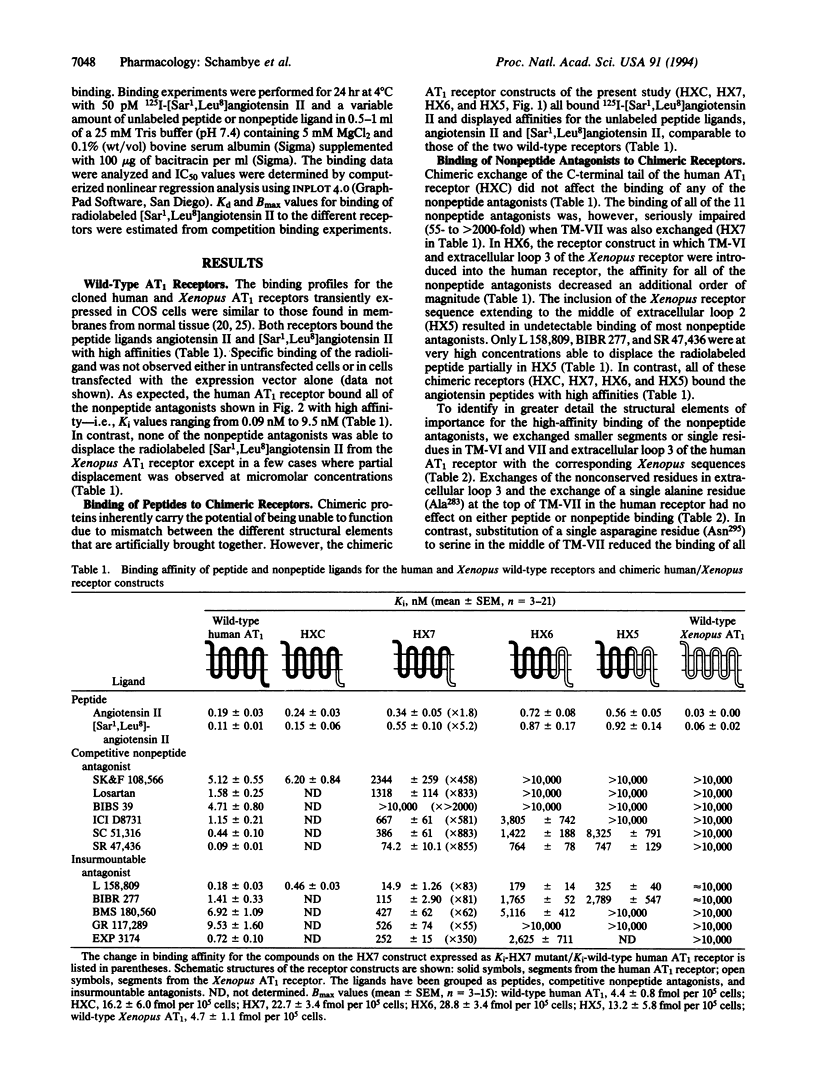
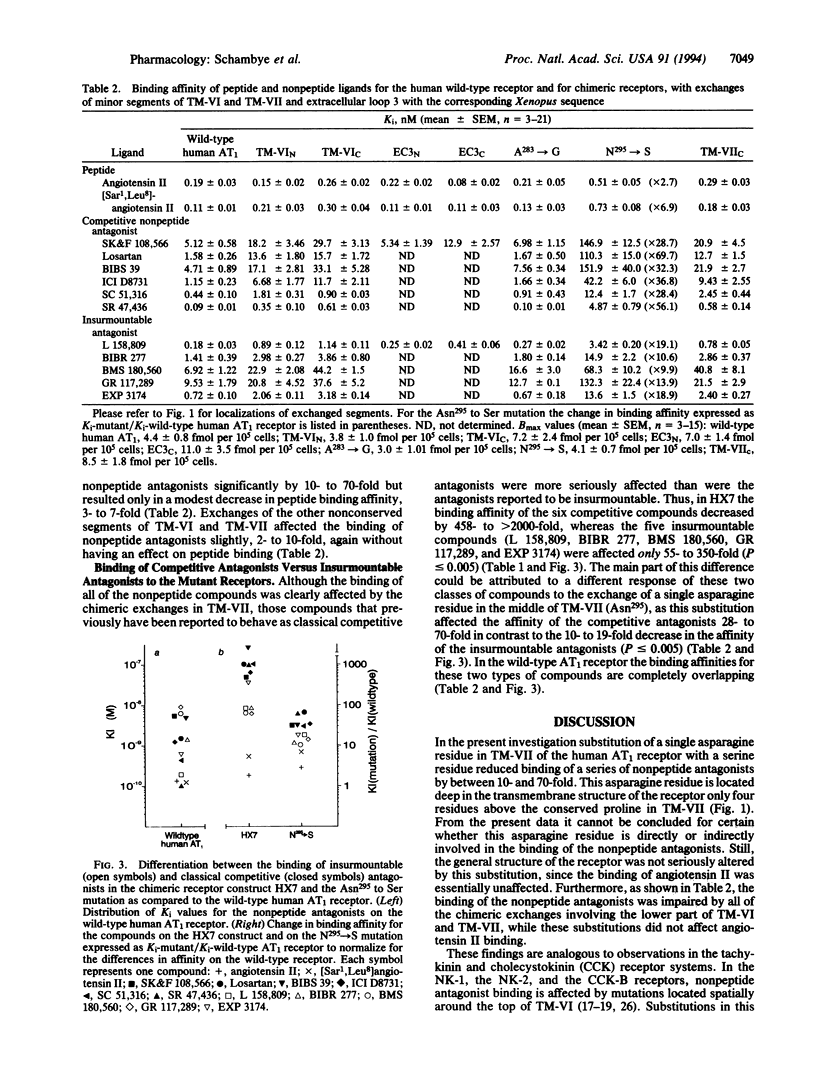
To characterize binding sites for nonpeptide angiotensin antagonists on the human angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1 receptor) we have systematically exchanged segments of the human receptor with corresponding segments from a homologous Xenopus laevis receptor, which does not bind the nonpeptide compounds. Substitution of transmembrane segment VII of the human AT1 receptor dramatically reduced the binding affinity of all of the 11 nonpeptide antagonists tested (55- to > 2000-fold) with no effect on the binding of angiotensin. The affinity for the nonpeptide compounds decreased additionally one order of magnitude when transmembrane segment VI and the connecting extracellular loop 3 from the Xenopus receptor were also introduced into the human AT1 receptor. Exchanges of smaller segments and single residues in transmembrane segments VI and VII and extracellular loop 3 revealed that the binding of nonpeptide antagonists was dependent on nonconserved residues located deep within the transmembrane segments VI and VII, in particular Asn295 in transmembrane segment VII. Surprisingly, all exchanges in transmembrane segment VII, including the Asn295 to Ser substitution, had a more pronounced effect on the binding of the competitive antagonists relative to the insurmountable antagonists. It is concluded that the binding mode for peptide and nonpeptide ligands on the AT1 receptor is rather different and that competitive and insurmountable antagonists presumably bind to overlapping but distinct sites located in transmembrane segments VI and VII.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beinborn M., Lee Y. M., McBride E. W., Quinn S. M., Kopin A. S. A single amino acid of the cholecystokinin-B/gastrin receptor determines specificity for non-peptide antagonists. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):348–350. doi: 10.1038/362348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Ellis C., Kumar C., Nuthulaganti P., Kersten H., Elshourbagy N., Griffin E., Stadel J. M., Aiyar N. Cloning and characterization of a human angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):989–995. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Ellis C., Nuthulaganti P. R., Nambi P., Scaife K., Kumar C., Aiyar N. Isolation and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor from Xenopus laevis heart. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;44(2):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury R. H., Allott C. P., Dennis M., Fisher E., Major J. S., Masek B. B., Oldham A. A., Pearce R. J., Rankine N., Revill J. M. New nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. 2. Synthesis, biological properties, and structure-activity relationships of 2-alkyl-4-(biphenylylmethoxy)quinoline derivatives. J Med Chem. 1992 Oct 30;35(22):4027–4038. doi: 10.1021/jm00100a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carini D. J., Duncia J. V., Aldrich P. E., Chiu A. T., Johnson A. L., Pierce M. E., Price W. A., Santella J. B., 3rd, Wells G. J., Wexler R. R. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: the discovery of a series of N-(biphenylylmethyl)imidazoles as potent, orally active antihypertensives. J Med Chem. 1991 Aug;34(8):2525–2547. doi: 10.1021/jm00112a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Lotti V. J. Two distinct angiotensin II receptor binding sites in rat adrenal revealed by new selective nonpeptide ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Siegl P. K., Clineschmidt B. V., Mantlo N. B., Chakravarty P. K., Greenlee W. J., Patchett A. A., Lotti V. J. In vitro pharmacology of L-158,809, a new highly potent and selective angiotensin II receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu A. T., McCall D. E., Price W. A., Wong P. C., Carini D. J., Duncia J. V., Wexler R. R., Yoo S. E., Johnson A. L., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VII. Cellular and biochemical pharmacology of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):711–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Cascieri M. A., Yu H., Bansal A., Swain C., Strader C. D. Amino-aromatic interaction between histidine 197 of the neurokinin-1 receptor and CP 96345. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):350–353. doi: 10.1038/362350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Huang R. R., Strader C. D. Localization of agonist and antagonist binding domains of the human neurokinin-1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25664–25667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gether U., Johansen T. E., Schwartz T. W. Chimeric NK1 (substance P)/NK3 (neurokinin B) receptors. Identification of domains determining the binding specificity of tachykinin agonists. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7893–7898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gether U., Johansen T. E., Snider R. M., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Nakanishi S., Schwartz T. W. Different binding epitopes on the NK1 receptor for substance P and non-peptide antagonist. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):345–348. doi: 10.1038/362345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gether U., Yokota Y., Emonds-Alt X., Brelière J. C., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Snider R. M., Nakanishi S., Schwartz T. W. Two nonpeptide tachykinin antagonists act through epitopes on corresponding segments of the NK1 and NK2 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6194–6198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. K., Feldman P. L., Schuster S. V., Bilotta J. M., Brackeen M. F., Leighton H. J. Opioid receptor activity of GI 87084B, a novel ultra-short acting analgesic, in isolated tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Nov;259(2):712–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Leung M., Zhang Y., Catt K. J., Sandberg K. Differential structural requirements for specific binding of nonpeptide and peptide antagonists to the AT1 angiotensin receptor. Identification of amino acid residues that determine binding of the antihypertensive drug losartan. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16533–16536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Sandberg K., Catt K. J. Novel angiotensin II antagonists distinguish amphibian from mammalian angiotensin II receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T. E., Schøller M. S., Tolstoy S., Schwartz T. W. Biosynthesis of peptide precursors and protease inhibitors using new constitutive and inducible eukaryotic expression vectors. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 16;267(2):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80947-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogletree M. L., Harris D. N., Schumacher W. A., Webb M. L., Misra R. N. Pharmacological profile of BMS 180,291: a potent, long-acting, orally active thromboxane A2/prostaglandin endoperoxide receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):570–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins G. M., Corpus V. M., McMahon E. G., Palomo M. A., Schuh J. R., Blehm D. J., Huang H. C., Reitz D. B., Manning R. E., Blaine E. H. In vitro pharmacology of a nonpeptidic angiotensin II receptor antagonist, SC-51316. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jun;261(3):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh S. P., O'Hare M. M., Tortora O., Schwartz T. W. Binding of monoiodinated neuropeptide Y to hippocampal membranes and human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6648–6654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock J., Keenan R. M., Samanen J., Hempel J., Finkelstein J. A., Franz R. G., Gaitanopoulos D. E., Girard G. R., Gleason J. G., Hill D. T. 1-(carboxybenzyl)imidazole-5-acrylic acids: potent and selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1991 Apr;34(4):1514–1517. doi: 10.1021/jm00108a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienen W., Hauel N., Van Meel J. C., Narr B., Ries U., Entzeroth M. Pharmacological characterization of the novel nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, BIBR 277. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienen W., Mauz A. B., Van Meel J. C., Entzeroth M. Different types of receptor interaction of peptide and nonpeptide angiotensin II antagonists revealed by receptor binding and functional studies. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;41(6):1081–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Chiu A. T., Price W. A., Thoolen M. J., Carini D. J., Johnson A. L., Taber R. I., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. I. Pharmacological characterization of 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-1-(2-chlorobenzyl)imidazole-5-acetic acid, sodium salt (S-8307). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Oct;247(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Entzeroth M., Wienen W., Van Meel J. C. Characterization of BIBS 39 and BIBS 222: two new nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 21;218(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90144-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoffmann S., Gether U., Schwartz T. W. Conserved HisVI-17 of the NK-1 receptor is involved in binding of non-peptide antagonists but not substance P. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80865-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]