Abstract
It is not well understood how paracrine communication between basal and luminal cell populations in the mammary gland affects tumorigenesis. During ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis, enriched mammary stem cells that represent a subpopulation of basal cells exhibit enhanced tumorigenic capacity compared to the corresponding luminal progenitors. Transcript profiling of tumors derived from basal and luminal tumor-initiating cells (TIC) revealed preferential loss of the noncanonical Wnt ligand WNT5A in basal TIC-derived tumors. Heterozygous loss of WNT5A was correlated with shorter survival of breast cancer patients. In a mouse model of ErbB2-induced breast cancer, Wnt5a heterozygosity promoted tumor multiplicity and pulmonary metastasis. As a TGFβ substrate, luminal cell-produced WNT5A induced a feed-forward loop to activate SMAD2 in a RYK and TGFβR1-dependent manner to limit the expansion of basal TIC in a paracrine fashion, a potential explanation for the suppressive effect of WNT5A in mammary tumorigenesis. Our results identify the WNT5A/RYK module as a spatial regulator of TGFβ/SMAD signaling pathway in the context of mammary gland development and carcinogenesis, offering a new perspective on tumor suppression provided by basal-luminal crosstalk in normal mammary tissue.
Introduction
The canonical Wnt pathway activates β-catenin and is integral in regulating self-renewal of normal stem cells and the subversion of the canonical Wnt signaling has been implicated in tumorigenesis (1). In contrast, noncanonical Wnt signaling is characterized by a lack of requirement for β-catenin and has been studied for its role in embryonic patterning, gastrulation, and organogenesis (2–6). Moreover, noncanonical Wnt is proposed to antagonize canonical signaling (7). WNT5A is the archetype of noncanonical Wnt ligand and has both tumor-suppressive and -promoting effects. WNT5A is tumor-suppressive in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) (8), colorectal cancer (9), breast cancer (10), and ovarian carcinoma (11); whereas WNT5A increases aggressiveness in various cancers (6). In breast cancer, contradictory results have been reported about the expression of WNT5A in breast cancer based on different methods (12–14). Jönsson and others found the decrease in WNT5A expression through cancer progression (13,14). WNT5A expression in the developing murine gland is highest in terminal end buds where loss of TGFβ signaling correlates with the decrease of WNT5A; in turn, WNT5A mediates the suppressive effect of TGFβ during mammary gland development (15). Inhibition of TGFβ signaling pathway by DNIIR, a dominant negative mutation TGFβ receptor 2 (TGFβR2), led to increased tumor growth and decreased WNT5A expression (10), a similar phenotype as genetic deletion of WNT5A (15), suggesting that WNT5A is a TGFβ-downstream effector and mediates the tumor-suppressive effect of TGFβ.
Several major non-canonical receptors for WNT5A have been studied in development and cancer, including RYK, Ror1/2, and Fzd4 (16–18). RYK is a divergent receptor tyrosine kinase with a shortened extracellular Wnt-inhibitory factor (WIF) domain (19). Due to unusual substitutions in the kinase domain, RYK has an inactive kinase domain and sequesters Wnt ligands from interacting with other receptors (19). Increased expression of RYK has been linked to poor outcomes in ovarian cancer (20). Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor (RORs) have been studied for their role in embryonic patterning, musculoskeletal, and neuronal development (21). ROR1 and ROR2 have growing evidence for their role in the progression of malignancies (18,21).
Our findings demonstrate a novel regulatory mechanism for TGFβ/SMAD signaling pathway via WNT5A. The induction of SMAD2 phosphorylation and activation by WNT5A depends on TGFβR1 kinase activity and RYK. These findings add an avenue to understand the complex environment during mammary tumorigenesis.
Materials and Methods
Mouse Illumina Array
Tumors were generated from our previous study (22). RNAs were isolated from tumors (QIAGEN, Venlo, Limburg, Netherlands) and their quality was assessed. RNA was submitted to the Genomics Division of the University of Iowa for microarray analysis. Microarray data (GEO accession number: GSE64487) was normalized and transformed into log2 expression. Transcriptome heatmap and the heatmap for differentially-expressed genes (DEG) were generated in R using the gplots package. The volcano plot was made in R using the ggplot2 package. Fold change was found by the average log2 expression difference in paired basal-TIC and luminal-TIC tumors. Genes highlighted in the volcano plot have a P-value <0.05 and an average log2 change ≥ 1.58 (equal to linear 3.0-fold change).
TCGA Data Analyses
The UCSC Cancer Genome Browser (https://genome-cancer.ucsc.edu) was used to assess copy number variations (CNV) across all available cancer datasets in the TCGA (23). Level 3 Illumina HiSeq 2000 RNAseq for TCGA BRCA cohort were used. RNAseq expression data was transformed as log2(x+1) Differences in sample numbers between figures were a result of sorting by categorical data.
Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin embedded tissues were deparaffinized and antigens were retrieved with Antigen Unmasking Solution (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) or with S1700 (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). WNT5A antibody (Genetex, Zeeland, MI) was used at a 1:200 dilution. We consulted with Dr. Ryan Askeland who is a clinical pathologist and defined the intensity of WNT5A staining. The staining intensity of WNT5A was given a scoring system as 0, 1+, 2+, 3+. For example, we defined the strongest signal as 3+ (an example would be the Fig. 3A, adjacent normal tissues) and the signals equivalent to IgG non-immune antibody control as 0. We combined 0 and 1+ as low, 2+ as medium and 3+ as high.
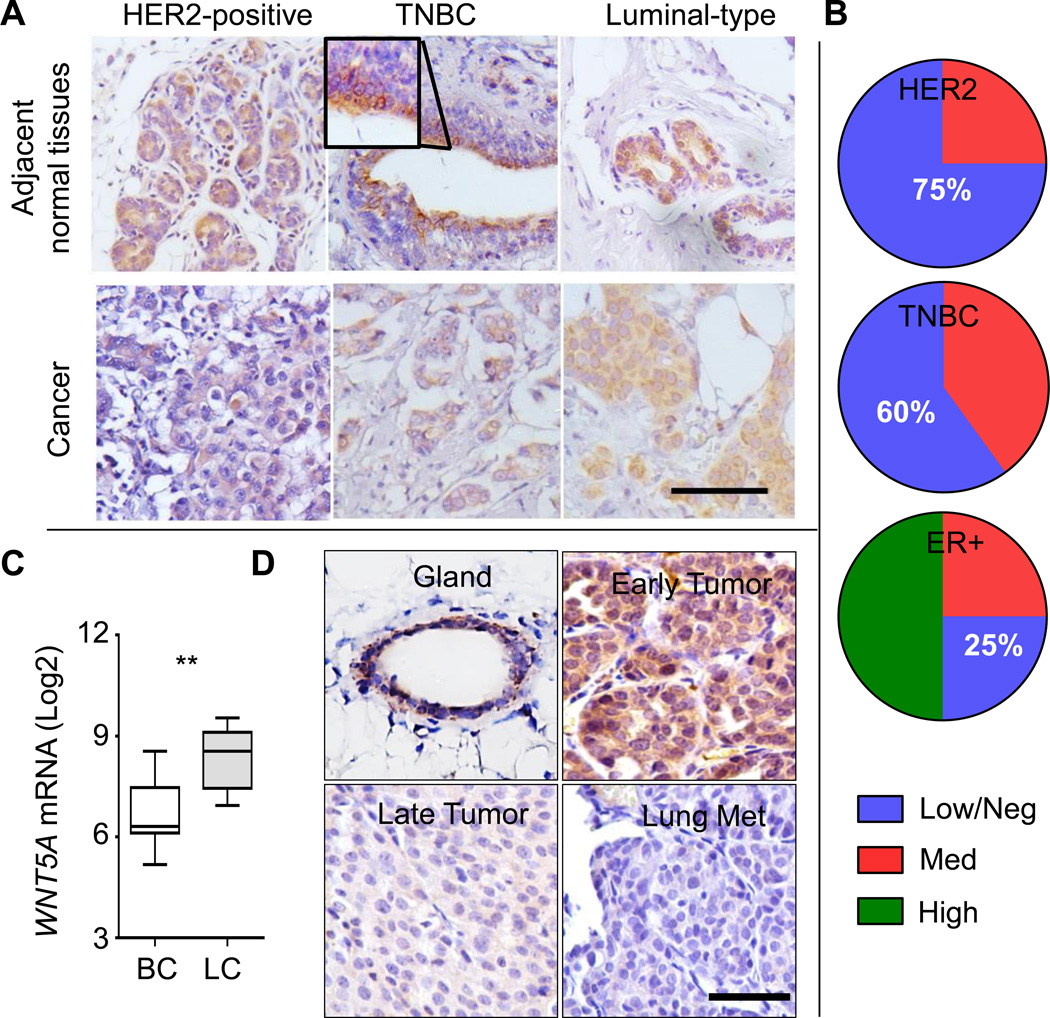
Figure 3. WNT5A protein is lost in more aggressive types of breast cancer.
A. Representative WNT5A immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), HER2+, or estrogen receptor (ER)+ breast cancer specimens (bottom panels) with adjacent normal mammary tissues (top panels) (bar = 100 µm). B. Quantification of WNT5A staining in HER2-positive (n=4), TNBC (n=5), and ER-positive luminal type (n=4) patient tissue samples. C. Microarray dataset GSE37223 deposited in GEO Datasets in Pubmed Central was downloaded and analyzed for the expression of WNT5A in CD49f+EPCAM− human basal mammary epithelial cells and CD49f−EPCAM+ luminal epithelial cells (P = 0.0093, n=7 for each population). D. Representative WNT5A IHC staining from MMTV-ErbB2 mammary glands and tumors. Early tumors were collected at 5–6 months of age when tumors were within 0.5 cm; whereas late tumors (2.5 cm) and paired lung metastases were collected at 7–8 months of age (bar = 50 µm). n=3 for each type.
Separation of Mammary Epithelial cells and spheroid growth in matrigel
We followed previously established protocols (24) and also included the detailed protocol in Supplementary Methods. Briefly, mammary glands were sequentially digested. Single cells were labeled with a cocktail of antibodies for flow cytometry to separate different epithelial cells. For spheroid growth on matrigel (BD Biosciences), 1000 cells were seeded onto matrigel-coated 8-well chamber slide (24). Spheroids were photographed three weeks later as before (22) and the size was quantitated (25).
Cells
HMLE cells (provided by Dr. Jing Yang, University of California, San Diego) and MCF10A cells (purchased from ATCC) were maintained using 10% FBS-containing F12 media (Life Technologies) supplemented with insulin (10 µg/ml), hydrocortisone (2 µg/ml), and EGF (10 ng/ml). For both cell lines, we constantly monitored their morphology, confirmed their epithelial cell feature by positive cytokeratin 5 or 8 staining, and further confirmed their identity with 3-D spheroid growth. Primary mammary epithelial cells, including basal and luminal mammary epithelial cells, were cultured using EpiCult-B medium (StemCell).
shRNA and siRNA
cDNAs of two-independent short hairpin RNAs for RYK were constructed into lentiviral vector pLSLPw-GFP with targeting sequences: shRNA-1: 5’- GC ACA TTT GTC TTC CAG AA -3’; shRNA-2: 5’- CC TGT ACT GGC AAA GTA GA -3’. Viral particles were packaged, following by infection of MCF10A cells and purification of GFP-positive cells using flow cytometry (26). Small interference RNAs for TGFβR1 (siCON, si-1 and si-3 used in Fig. 6B, no targeting information released) were purchased (Sigma-Aldrich).
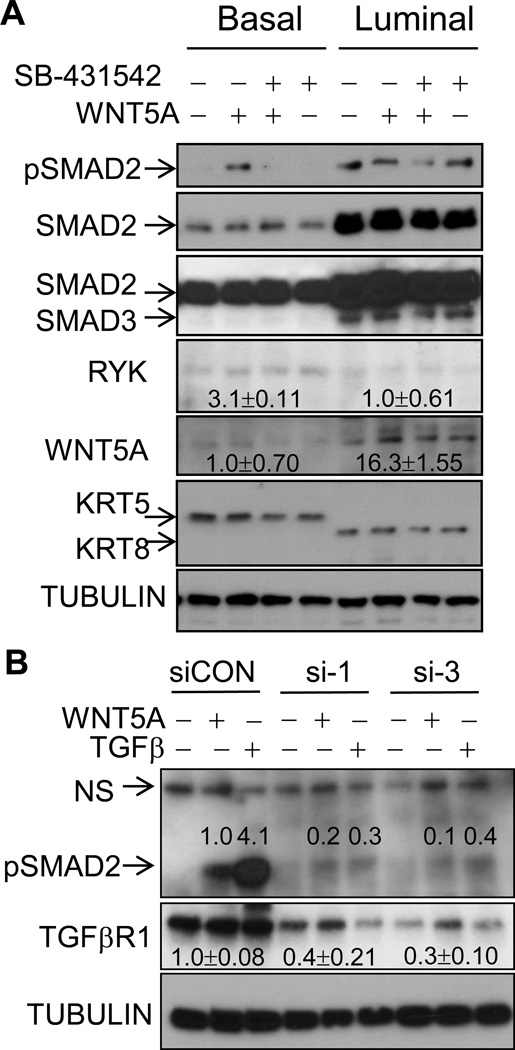
Figure 6. WNT5A induces the phosphorylation of SMAD2 in a TGFβ receptor-dependent fashion.
A. Basal and luminal mammary epithelial cells were purified from pre-neoplastic mammary gland of 5-month-old ErbB2/WNT5A+/− mice and cultured in 24 well plates for 72 hrs. Cells were either mock-treated, treated with WNT5A (100ng/ml), WNT5A+SB-431542 (5 µM), or SB-431542 alone for 1 hr. B. MCF10A cells were transiently transfected with control siRNA (siCON), or two independent siRNAs to TGFβR1 (si-1, si-3). 96 hrs later, cells were either treated with WNT5A (100ng/ml) or TGFβ (5 ng/ml) for 1 hr. For A–B, cell lysates were collected, separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (n=2–3). Band densitometry was measured by Image J.
Cell lysates, immunoprecipitation, immunoblots, and antibodies
Cells were lysed in cell lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCL pH7.5, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Triton X-100, 100 mM KCl, 50 mM NaF, 10 mM Na 2-glycerophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, and supplemented with protease inhibitor set (Roche)). For immunoprecipitation, 1 mg cell lysate was used to incubate with 1µg/ml of antibodies. Immunocomplex was precipitated using protein A/G sepharose (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Antibodies used are as follows: anti-p-SMAD2/3, anti-p-JNK1/2, and anti-TGFβR1 (Cell Signaling Technology); anti-SMAD1/2/3, anti-JNK1/2, and anti-RYK antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies); anti-WNT5A (Genetex); and anti-α-tubulin (Sigma Aldrich); anti-keratin 8 (clone TROMA-I, Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank at the University of Iowa).
Murine Models
All mice were maintained according to University of Iowa IACUC guidelines. Wnt5afl/fl mice in the C57BL/6 background were kindly provided by Dr. Terry Yamaguchi (National Cancer Institute) (27). MMTV-ErbB2 mice in the FVB/N genetic background (FVB/N-Tg(MMTVneu)202Mul/J)) (28) were crossed with Wnt5a+/− mice (B6;129S7-Wnt5atm1Amc/J) in the C57BL/6 background (29) (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, MN). F1 generations of MMTV-ErbB2/Wnt5a+/+ and MMTV-ErbB2/Wnt5a+/− mice were used to isolate mammary epithelial cells and tumorigenesis studies. Tumor onset date was recorded and mice were euthanized when largest tumor reached 2 cm in diameter. Lung metastasis was determined by hematoxylin & eosin staining.
Statistical Analysis and Data Presentation
Data is presented as mean ± s.e.m. for most studies or mean values ± 95% CI for genomic data. Microarray data is reported as log2. TCGA RNAseq data is reported in log2(x+1). Welch’s T-test was used for genomic results. Student’s T-test was used for the remaining experiments. Mantel-Cox log-rank test was used for survival curve analysis (Prism v6, GraphPad, San Diego, CA). Gene expression of human mammary gland cell populations utilized GEO37223 using normalized expression (30).
Results
Transcriptome comparison between ErbB2-induced tumors from different TICs
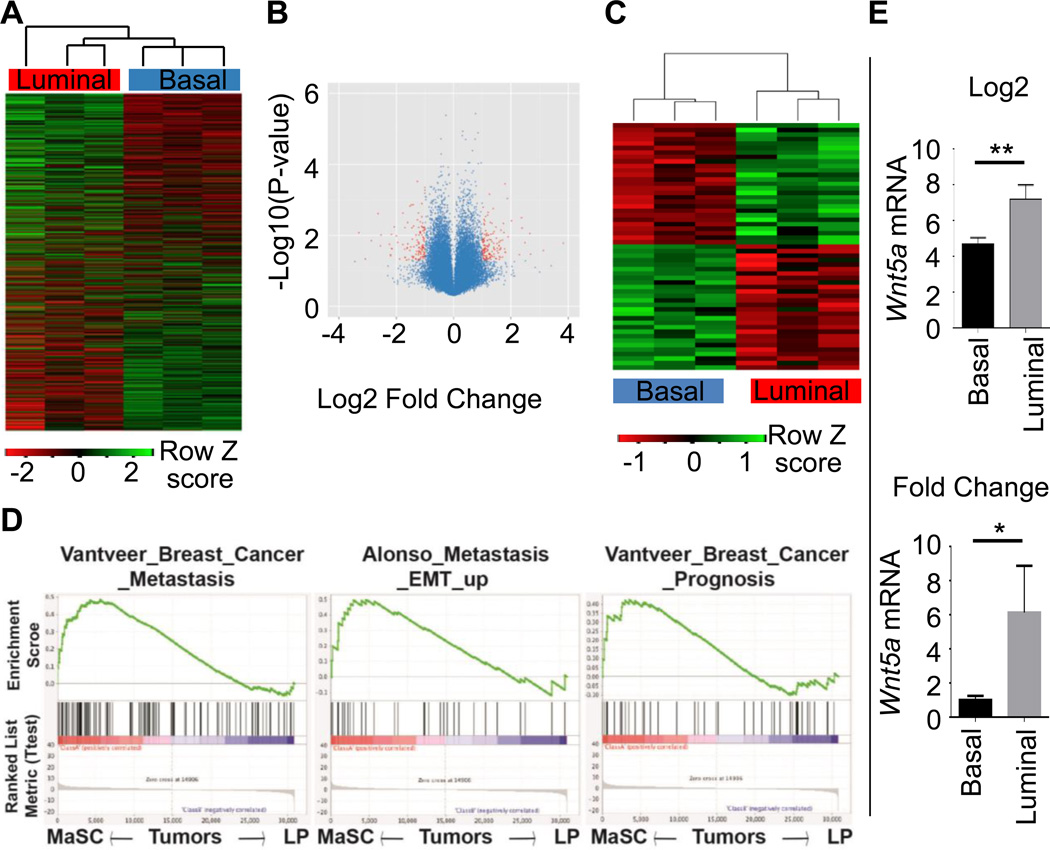
Our previous work has demonstrated a variance in tumorigenic capacity in different mammary epithelial populations of MMTV-ErbB2 mice (22). CD24medCD49fhi basal cells (basal TIC) gave rise to larger tumors at a greater incidence than CD24hiCD49floCD61+ luminal progenitors (luminal TIC). We performed transcript profiling using three paired tumor samples, with each pair of basal TIC-, or luminal TIC-formed tumors from the contralateral inguinal mammary glands of the same mouse in order to minimize differences from the recipient mouse. Basal-TIC tumors were clustered together with similar gene expression pattern and separated from luminal-TIC tumors (Fig. 1A). We used a threshold of 3-fold change (log2 change 1.58) and P value of less than or equal to 0.05, and found 55 genes meeting the criterion as shown in the volcano plot (Fig. 1B). Among these genes, we found 28 up-regulated and 27 down-regulated genes in basal-TIC tumors when compared to their paired luminal-TIC tumors (Supplementary Table S1, Fig. 1C). We validated the array dataset by real-time PCR using a panel of 13 upregulated genes (Supplementary Fig. S1A) and 11 downregulated genes (Supplementary Fig. S1B) in basal-TIC tumors and nearly all examined genes exhibited similar patterns. We searched the literature and found many genes with known function in cancer (Supplementary Table S1). Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (31), a computational method that determines whether a defined set of genes show concordant differences between biological states, revealed that eight pathways related to cell cycle progression, 5 pathways related to RNA/Protein synthesis and processing, and 3 pathways related to metastasis and poor prognosis were upregulated in basal-TIC tumors (Fig. 1D, other pathways not shown). These data suggest that basal-TIC tumors have more aggressive gene signature than luminal-TIC tumors.
Figure 1. Transcriptome comparison between basal-TIC and luminal-TIC tumors.
A. Heatmap for unsupervised clustering of gene profiles from paired tumors derived from basal TICs (Basal, red) and luminal TICs (Luminal, blue). The whole transcriptomes were clustered using R gplots. n=3/group. B. Volcano plot showing differentially-expressed between luminal- and basal-TIC tumors, with P-value < 0.05 and log2 fold-change > 1.58 (linear 3-fold change) highlighted in red. C. 55 genes were identified to fit the criteria in B, with exclusive expression in basal TIC- and luminal TIC-derived tumors. D. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was used to analyze the difference of biological signaling pathways between basal-TIC or luminal-TIC formed tumors based transcriptome data from A. Basal TIC tumors upregulate signaling pathways related to breast cancer metastasis and bad prognosis. Nominal P values < 0.001 for pathways mentioned. E. WNT5A expression in mouse basal-TIC and luminal-TIC tumors. Both Log2 values (Top) and linear fold-change (Bottom) are shown, P = 0.0076, n=3).
Wnt5a is lost in more aggressive mouse basal TIC-tumors and human breast cancer
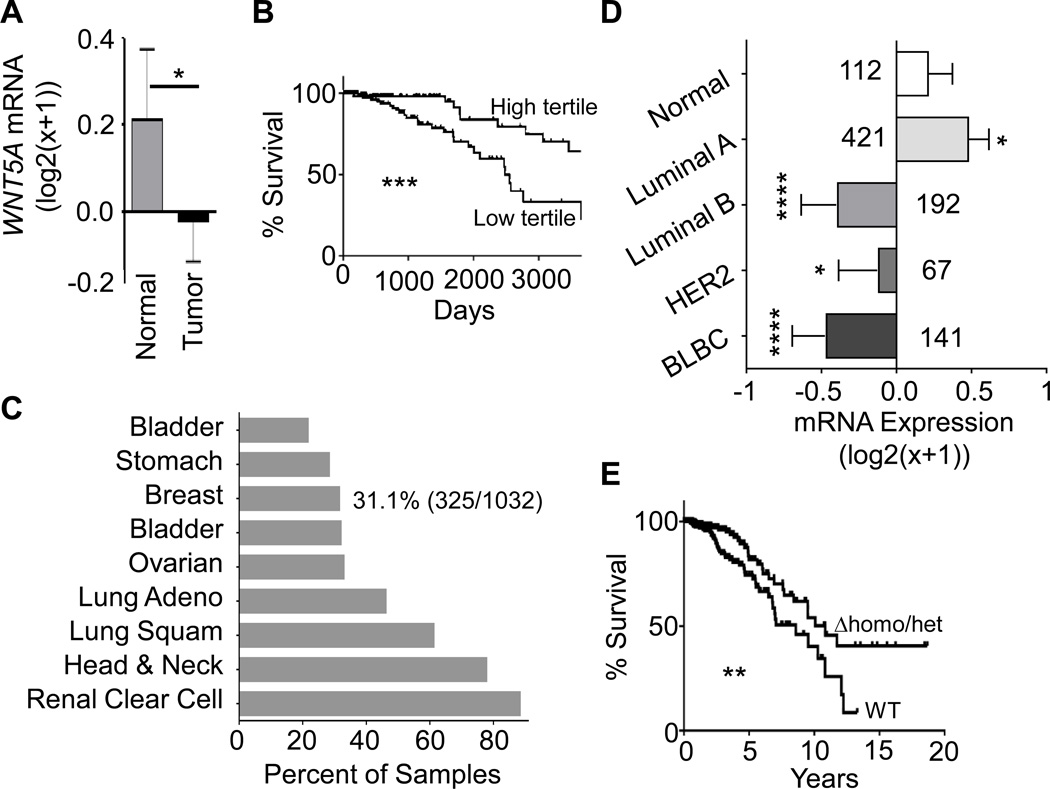
In particular we found Wnt5a to be nearly 6-fold (Log2 difference: 2.534) downregulated in basal-TIC mouse tumors compared with luminal-TIC tumors (Supplementary Table S1, Fig. 1E). We identified a similar WNT5A decrease in human breast cancer samples relative to normal tissues in the breast cancer dataset (BRCA) deposited by TCGA (Fig. 2A). Lower WNT5A mRNA in breast cancer was significantly correlated with shorter patient survival (Fig. 2B). Examining the 58 probes of the Infinium HumanMethylation450 methylation data for WNT5A within the TCGA BRCA, we found no significant correlation between WNT5A expression and DNA methylation (Supplementary Fig.S2A). Rather, we found that mono- or biallelic loss of WNT5A occurs in 31.1% within BRCA dataset and greater than 20% of samples in 8 other cancers from TCGA (Fig. 2C). Loss of WNT5A was seen in more aggressive subtypes, where 60% of basal-like (BLBC), 51% of HER2-positive, and 38% of Luminal B have allelic loss, only 18% have allelic loss in the Luminal A subtype (Supplementary Table S2). The mono- or biallelic loss of WNT5A in breast cancer samples led to decreased WNT5A expression in tumor stages 2–4 of BRCA, but not in stage 1 (Supplementary Fig. S2B). Lower WNT5A mRNA expression was also seen in more aggressive breast cancer subtypes including luminal B, HER2, and basal-like relative to normal and luminal A subtype (Fig. 2D). In addition, we found that patients with loss of one WNT5A-allele possessed significantly shorter overall survival than patients with WNT5A-bialleles (Fig. 2E).
Figure 2. Heterozygous loss of WNT5A is common in cancer.
A. WNT5A expression in TCGA Illumina HiSeq level 3 breast-cancer dataset by sample type (P = 0.0154, n= 112 for normal tissues and n= 1040 for invasive cancer). B. Kaplan-Meier curve to show the overall survival between the highest WNT5A-expressing samples (n=126) and the lowest WNT5A-expressing samples (n=125) among the Agilent G4502A level 3 microarray TCGA BRCA dataset. ***: P = 0.0003. C. Copy number variations (CNV) from different TCGA datasets were analyzed using UCSC cancer genome browser and plotted as percentages of specimens with any loss of WNT5A alleles. D. WNT5A expression in BRCA TCGA Illumina HiSeq level 3 by PAM50 molecular subtype. P values comparing Normal samples (n=60) to Luminal A (n=211, P = 0.0142), Luminal B (n=128, P < 0.0001), HER2 (n=58, P = 0.0389), and basal-like breast cancer (BLBC, n=78, P < 0.0001). E. Kaplan-Meier curve to show the overall survival between WNT5A bialleles (WT, n=519) and either homozygous or heterozygous deletion of WNT5A alleles (Δhomo/het, n=249) among Illumina HiSeq RNAseq level 3 BRCA data. **: P = 0.0098.
We observed strong staining of WNT5A at the normal mammary ducts and acini by immunohistochemistry (IHC) (Fig. 3A). Low WNT5A expression was seen in 75% and 60% of samples of triple-negative (TNBC) and HER2 subtypes, respectively (Fig. 3B). In contrast, 75% of ER+ possessed moderate to high WNT5A staining (Fig. 3A, 3B). We noticed a clear luminal distribution of WNT5A in normal mammary ducts (Fig. 3A). We downloaded GEO dataset GSE37223 (30) and found human luminal cells had ~3-fold increase (Log2 difference: 1.733) in WNT5A mRNA relative to basal epithelial cells (Fig. 3C). We found a similar luminal WNT5A staining in mouse mammary ducts (Fig. 3D, gland). Consistent with WNT5A-loss in human BRCA, WNT5A expression was evident in pre-neoplastic mammary gland and early tumors (less than 0.5 cm in diameter with evident features of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) (Fig. 3D, gland and early tumor) and was decreased in late stage tumors (2 cm in diameter) and lung metastasis (Fig. 3D), in agreement with its tumor-suppressive role (10).
WNT5A suppresses the growth of basal TIC via a paracrine fashion
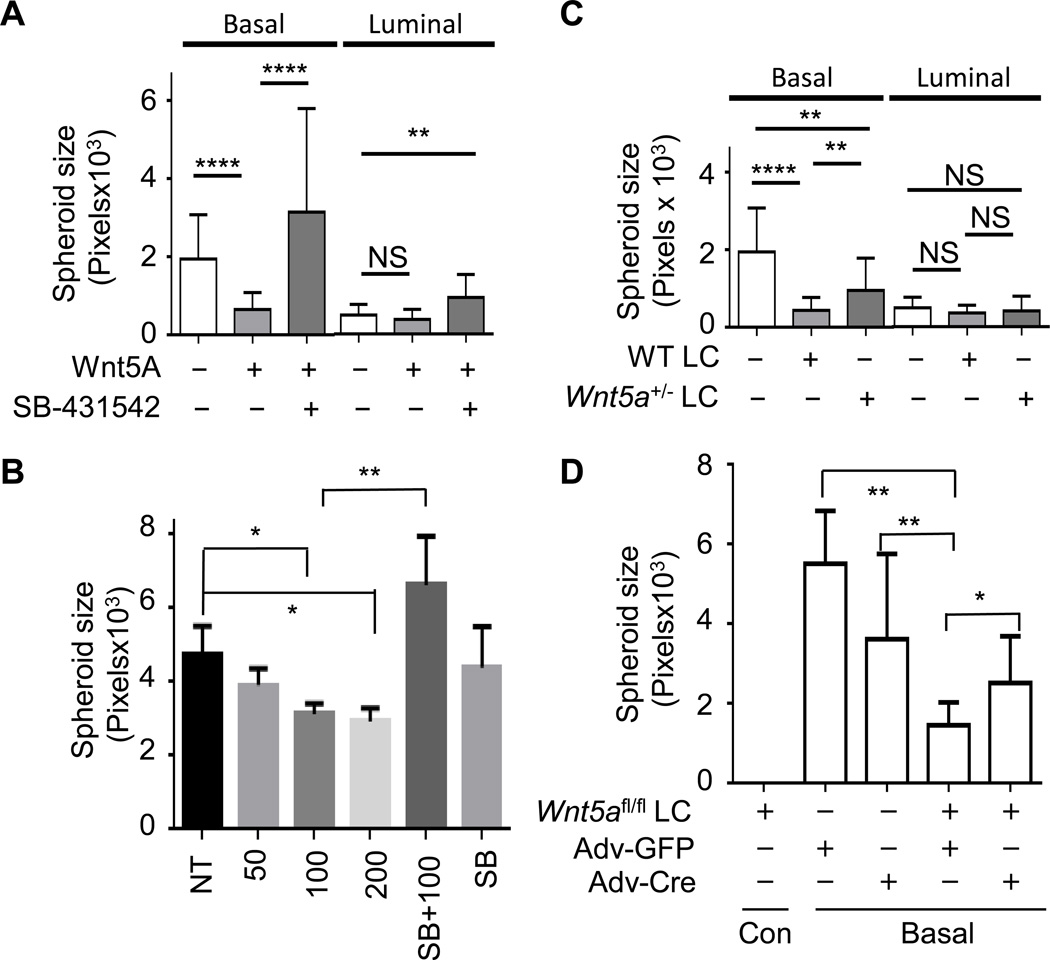
WNT5A is known to suppress breast cancer (10); whereas it is largely unknown how WNT5A inhibits tumorigenesis. We hypothesize that WNT5A is a potential niche component from luminal epithelial cells to suppress basal-TIC expansion, counterbalancing the canonical Wnt ligand in promoting the expansion of basal cells (32,33). We used our established scheme (Supplementary Fig. S3) and isolated lineage−CD24+CD49fhigh basal TIC and lineage−CD24highCD49flowCD61+ luminal TIC from pre-neoplastic mammary gland of 5-month MMTV-ErbB2 female mice (22). We grew them under mammosphere medium to assay the expansion of mammary stem cells or progenitors with or without WNT5A (34). After one-week incubation, untreated cells had an average of 42.3 spheres per well, while WNT5A-treated cells had an average of 11.7 spheres Supplementary Fig. S4A–B). The suspension mammosphere culture system generated significant amount of cell aggregates. Similar phenomenon was noticed in other studies and reviewed (35). We chose to use a well-established matrigel-based system to grow spheroids as a more relevant ex vivo tumor model (24,36). Different doses of WNT5A treatment did not significantly alter the spheroid number from basal TICs (Supplementary Fig. S4C), but significantly reduced the spheroid size from basal TICs not from luminal TICs (Fig. 4A, Supplementary Fig. S4D). We also treated basal TICs with different WNT5A-doses and found a consistent and dose-dependent decrease in spheroid size (Fig. 4B). Next we isolated lineage−CD24highCD49flowCD61− mature luminal cells (mLC) from WT and Wnt5a+/− mice and co-cultured them with basal or luminal TICs. Mature luminal cells did not form spheroid structure (Supplementary Fig. S4E, bottom panels). We found co-culturing basal TICs with WT mLC led to a significant reduction in mean size compared to basal TICs alone (Fig. 4C, Supplementary Fig. S4E). Co-culturing with WT mLC had no impact on luminal TIC-formed spheroids (Fig. 4C, Supplementary Fig. S4E). Co-culturing basal TICs with Wnt5a+/− mLC partially restored spheroid size (Fig. 4C, Supplementary Fig. S4E). We confirmed that WT mLC secreted more WNT5A than Wnt5a+/− mLC (Supplementary Fig. S2C). We also purified mLC from Wnt5afl/fl mice and co-cultured these cells with basal TICs, either treated with adenovirus encoding GFP (Adv-GFP) or adenovirus encoding cre DNA recombinase (Adv-Cre) to deplete WNT5A expression (Supplementary Fig. S4F, right panels). We found mLC from Wnt5afl/fl mice didn’t form discernable spheroids (Fig. 4D, Supplementary Fig. S4F), similarly to mLC from WT mice (Supplementary Fig. S4E, bottom panels). While Adv-GFP- or Adv-Cre-treatment had no significant influence on spheroid growth from basal TICs, co-culturing with Wnt5afl/fl mLC significantly reduced spheroid size (Adv-GFP), which was reversed by the Wnt5a-deletion with Adv-Cre treatment (Fig. 4D, Supplementary Fig. S4F). These data strongly suggest a specific paracrine signaling pathway mediated by WNT5A of luminal origin in suppressing basal TIC growth.
Figure 4. WNT5A suppresses the growth of basal TIC via a paracrine manner.
A. Basal and luminal TICs were purified from pre-neoplastic mammary glands of 5-month old MMTV-ErbB2 female mice and seeded onto matrigel-coated chambers, either mock-treated, or treated with 100 ng/ml of WNT5A alone, or in combination with 5 µM of SB-431542. B. Basal TICs were purified and seeded onto matrigel-coated chambers, either non-treated (NT), treated with different doses of WNT5A (50, 100, or 200 ng/ml), or 100ng/ml WNT5A + 5 µM SB-431542 (SB+100), or 5 µM SB-431542 (SB). C. Basal and luminal TICs were purified and seeded onto matrigel, either alone or co-cultured with purified mature luminal cells (LC) from either WT or WNT5A+/− female mice at 1:5 ratio. D. Basal TICs (basal) and mature luminal cells from WNT5Afl/fl females (WNT5Afl/fl LC) were co-seeded onto matrigel at 1:5 ratio; 24 hrs later, cells were either treated with adenovirus encoding GFP (Adv-GFP) or Cre DNA recombinase (Adv-Cre). Basal TICs alone were also treated with Adv-GFP or Adv-Cre. WNT5Afl/fl LC did not form spheroids under these conditions (WNT5Afl/fl LC, first column). A–D. After 3 weeks, spheroids were photographed and their size in pixels was quantitated with Image J ((*<0.05, ** P ≤ 0.0042, **** P < 0.0001). Mean ± s.e.m., n=10–27 spheroids from two independent experiments).
We stained frozen sections from basal TIC-formed spheroids and confirmed that basal TICs were able to form both hollow acinus-like structures as well as solid DCIS-like structures (Supplementary Fig. S4G) (22). Most of spheroid cells are positive for luminal epithelial cell marker keratin 8 (KRT8), suggesting the differentiation from basal cells to luminal epithelial cells (Supplementary Fig. S4G). WNT5A was expressed by most of KRT8+ luminal cells and was low-to-absent from KRT8-negative cells (Supplementary Fig. S4G).
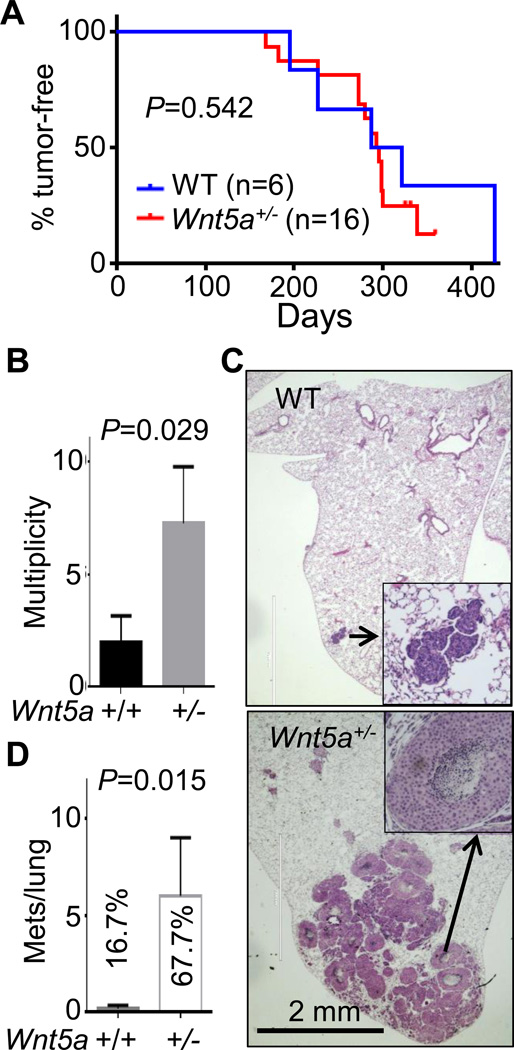
We also compared tumor onset days, multiplicity of tumors, and metastasis between ErbB2/WT and ErbB2/Wnt5a+/− females. Our initial analysis of Wnt5a+/− females showed no phenotype in mammary gland development based on whole mount (Supplementary Fig. S5A), H & E staining (Supplementary Fig. S5B), as well as the litter size and feeding. Heterozygous deletion of Wnt5a did not impact the primary tumor onset in the ErbB2-induced tumorigenesis (Fig. 5A). However, heterozygous Wnt5a deletion increased the tumor incidence (Fig. 5B). We also found that only 1 out of 6 ErbB2/WT females had one small lung metastasis by histological assessment, but 4 out of 6 ErbB2/Wnt5a+/− female mice had lung metastasis with numbers ranging from 2 to 19 (Fig. 5C, 5D).
Figure 5. WNT5A inhibits tumor multiplicity and metastasis in ErbB2-induced mammary cancer.
MMTV-ErbB2 transgenic mice were crossed with WNT5A+/− to produce ErbB2/WT and ErbB2/WNT5A+/− mice. Tumor onset days (A), multiplicity (B), as well as lung metastasis assessed by hematoxylin & eosin staining of paraffin-embedded lung sections (representative images in C and summarized in D) were assessed. % in C indicates the percentage of animals with lung metastasis. Numbers of metastatic nodules were plotted and P values indicated. A. n=6 for ErbB2/WT and n=16 for ErbB2/WNT5A+/−; B, D: n=6 for each group.
WNT5A activates SMAD2 in a TGFβR-dependent manner
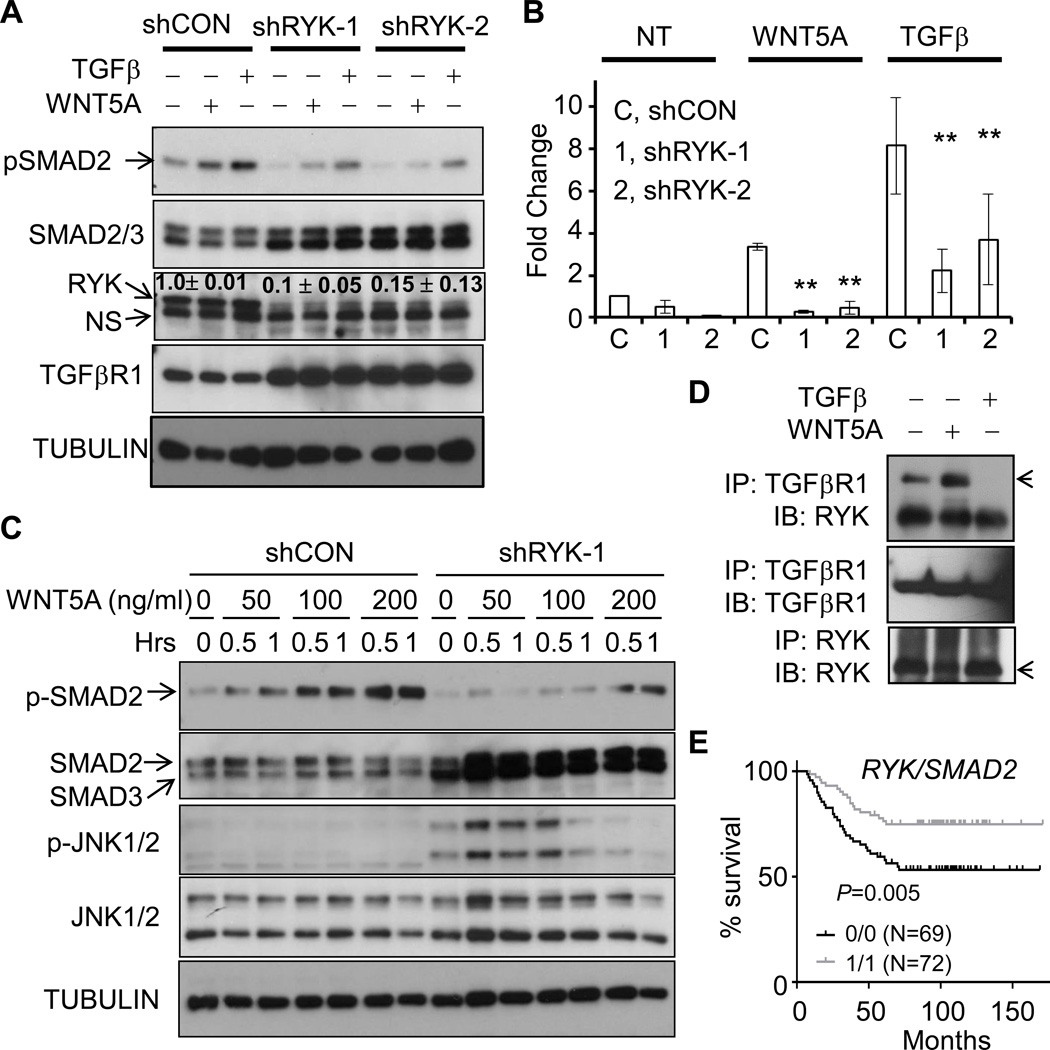
TGFβ/SMAD signaling pathway induces the expression WNT5A and in turn suppresses mammary morphogenesis and carcinogenesis (10,15). We added a TGFβR1 kinase inhibitor SB-431542 together with WNT5A for spheroid growth, with the expectation that WNT5A could suppress spheroid growth when inhibiting TGFβ/SMAD. Unexpectedly, we observed a significant size increase in basal TIC-formed spheroids compared to WNT5A alone (Fig. 4A, 4B, Supplementary Fig. S4D), suggesting that TGFβ/SMAD is either parallel to or downstream of WNT5A. Luminal TIC-formed spheroids were not affected by WNT5A treatment, but inhibition of TGFβ/SMAD significantly increased the mean size from luminal TICs (Fig. 4A, Supplementary Fig. S4D). SB-431542 alone had no significant impact on spheroid size from basal TICs (Fig. 4B, comparing NT and SB). We purified primary basal cells and luminal cells from pre-neoplastic mouse mammary gland and confirmed the purity of basal or luminal cells by using KRT5 as a basal-specific marker and KRT8 as a luminal-specific marker (Fig. 6A). Basal epithelial cells had low level of phosphorylation of SMAD2 (p-SMAD2); whereas luminal cells had constitutively high p-SMAD2 (Fig. 6A). WNT5A induced p-SMAD2 in basal cells in a TGFβR1-dependent manner since SB-431542 inhibited WNT5A-induced p-SMAD2 (Fig. 6A). Luminal cells had higher basal level of p-SMAD2 that was not further induced by WNT5A; SB-431542 treatment, either alone or in combination with WNT5A treatment, did not significantly reduce p-SMAD2 signal (Fig. 6A). We did not observe p-SMAD3 (the lower 52 KD band in third panel, Fig. 6A). WNT5A was expressed stronger in luminal epithelial cells and significantly less in basal epithelial cells (Fig. 6A). We confirmed WNT5A-induced p-SMAD2 in HMLE cells (Supplementary Fig. S6A) and in MCF10A cells (Supplementary Fig. S6B), two immortalized human mammary epithelial lines. TGFβ induced 4–5-fold higher p-SMAD2 than WNT5A in MCF10A cells (Supplementary Fig. S6B, Fig. 6B). We found a similar but delayed WNT5A-induced p-SMAD2 and high basal level of p-SMAD3 in MDA-MB-231 cells, a breast cancer cell line (Supplementary Fig. S6C). We silenced TGFβR1 in MCF10A and found that downregulation of TGFβR1 reduced WNT5A- and TGFβ-induced p-SMAD2 (Fig. 6B) and further confirmed the necessity of TGFβR1 kinase activity by two independent inhibitors SB-341542 and SB-505124 (Supplementary Fig. S6A, S6D). In addition, WNT5A significantly repressed the expression of cyclin D1 and β-catenin; whereas TGFβ increased the expression of cell cycle inhibitors p15 and p21 (Supplementary Fig. S6E). WNT5A and TGFβ induced the repression of some common genes including anti-apoptotic BCL-XL and GATA3 (Supplementary Fig. S6E), further supporting a specific yet different role of WNT5A compared to TGFβ in mammary epithelial cells.
RYK is a co-receptor for WNT5A induced-SMAD2 activation
We examined the expression of WNT5A receptors and found that RYK mRNA was reduced in primary tumors within the TCGA BRCA dataset when compared with normal tissues (Supplementary Fig. S7A). The reduction of RYK mRNA was seen across all four subtypes (Supplementary Fig. S7B). The differential expression of WNT5A receptors from luminal and basal cells were examined using the GSE37223 dataset (30). RYK mRNA was 1.76-fold higher in basal cells than in luminal cells (Supplementary Fig. S7C). We confirmed higher RYK expression in KRT8-negative basal cells from human mammary ducts relative to KRT8-positive luminal cells (Supplementary Fig. S7D), and observed a significantly loss of RYK expression in adjacent invasive cancer cells (Supplementary Fig. S7D). We also found that mouse primary basal cells had higher RYK expression relative to luminal cells (Fig. 6A). ROR1 mRNA was 4-fold higher in basal cells than in luminal cells (Supplementary Fig. S7C). We failed to detect ROR1 protein (data not shown), confirming its nature as a fetal antigen (21). Both ROR2 and FZD4 did not possess significant difference between luminal and basal cells (Supplementary Fig. S7C) (17). As non-relevant FZD members that mediate classical Wnt signaling, FZD6, but not FZD5, was found to be elevated in basal cells relative to luminal cells (Supplementary Fig. S7C), supporting the role of paracrine classic Wnt signaling in mammary epithelium (32,33).
We designed two shRNAs that significantly reduced RYK expression to about 10% relative to MCF10A cells expressing a luciferase-targeting control shRNA (Fig. 7A). WNT5A induced p-SMAD2 that was lower than TGFβ-induced p-SMAD2 (Fig. 7A). Silencing RYK in MCF10A cells led to a significantly reduced p-SMAD2 induced by WNT5A, and to a lesser extent the TGFβ-induced p-SMAD2, relative to parental MCF10A cells (Supplementary Fig. S8A) or MCF10A cells expressing control shRNA (Fig. 7A and quantitated in Fig. 7B). Interestingly, RYK-silencing led to significant increase of TGFβR1 (Fig. 7A) and SMAD2/3 (Fig. 7A, Supplementary Fig. S8A), supporting a potential negative feedback from RYK to SMAD and TGFβR1. We further confirmed a dose-dependent increase of p-SMAD2 in response to WNT5A ranging from 0–200 ng/ml, which agrees with the dose-dependent suppression of spheroid size (Fig. 4B) and was dependent on RYK expression (Fig. 7C). Interestingly, RYK-deficiency led to a significant JNK activation at both basal and WNT5A-induced levels (Fig. 7C). These results suggest that RYK preferentially binds to WNT5A to activate p-SMAD2 and RYK-deficiency leads to other WNT5A receptor-mediated signaling pathways as recently reported (37). Mechanistically, we found a constitutive interaction between TGFβR1 and RYK that was further enhanced by WNT5A treatment (Fig. 7D); however, TGFβ treatment released RYK protein from TGFβR complex (Fig. 7D). Anti-RYK antibody failed to pull down TGFβR (data not shown), possibly due to competitive binding to the similar sites on RYK.
Figure 7. RYK is the co-receptor for WNT5A-induced activation of SMAD2.
A–B. MCF10A cells were infected with lentiviral particles encoding control luciferase shRNA (shCON), or two independent RYK shRNAs with co-expression of GFP. GFP-positive cells were collected by flow cytometry. Parental MCF10A (data not shown here), MCF10A cells with control shRNA, or cells with RYK shRNA1 or shRNA2 were cultured and either left untreated (NT) or treated with WNT5A (100 ng/ml) or TGFβ (5 ng/ml). Cell lysates were collected, separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Representative images were shown in A. and quantitated in B. (P < 0.01, n=3). C. MCF10A cells with control shRNA, or cells with RYK shRNA1 were treated with different amount of WNT5A as indicated for 0.5 or 1 hr. Cell lysates were collected, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. D. MCF10A cells were treated with WNT5A (100ng/ml) or TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 1 hr. Cells were lysed and lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-RYK and anti-TGFβR1 antibodies. Immunocomplex was resolved by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. E. Affymetrix GEO dataset GSE2034 containing 255 human breast cancer specimens with supplemented clinical records was downloaded. 255 specimens in GSE2034 were separated into four groups based on the expression level of RYK and SMAD2. Low (assigned as 0) and high (assigned as 1) expression of RYK or SMAD2 were defined as expression values lower or higher than median values. N numbers and P value comparing 1/1 group VS. 0.0 group is indicated. The correlation between metastasis-free survival and RYK/SMAD2 expression was analyzed and Kaplan-Meier curve was graphed using Prism 6 software.
Consistently, RYK-deficiency in MCF10A cells increased spheroid size and led to an invasive phenotype (Supplementary Fig. S8B, S8C). We analyzed a published GEO dataset GSE2034 including 255 clinical breast-cancer specimens. We equally separated the 255 specimens into 4 groups based on the expression of RYK (Supplementary Fig. S8D) or SMAD2 (Supplementary Fig. S8E), or interaction between RYK and SMAD2 (Supplementary Fig. S8F, Fig. 7E). The expression of either RYK or SMAD2 was not correlated with metastasis-free survival (MFS) (Supplementary Fig. S8D, S8E). We found that patients whose specimens have high expression of both RYK and SMAD2 had the longest time to MFS and those whose specimens have low RYK and SMAD2 had the shortest MFS (Supplementary Fig. S8F, Fig. 7E, P=0.006, comparing groups 1/1 with 0/0). This result suggests the functional interaction between RYK and SMAD2 to suppress the progression and metastasis of human cancer.
Discussion
It is essential for cancer biology and therapy to understand how cancer initiates and how TICs evade the normal suppressive microenvironment. Here we uncover an important paracrine regulation from luminal cell-produced WNT5A, in a TGFβR-dependent manner (10), to suppress the growth of basal TICs thus tumorigenesis (Supplementary Fig. S9). WNT5A induces a specific activation of TGFβR/SMAD2 module in basal cells to suppress their growth. RYK, one of the WNT5A receptors, forms a complex with TGFβR1 upon WNT5A induction and in turn leads to the phosphorylation and activation of SMAD2 (Supplementary Fig. S9). This unique signaling pathway is important for the growth of basal TICs during ErbB2-induced breast cancer.
WNT5A is a downstream effector of TGFβ and mediates the suppressive effect of TGFβ on mammary morphogenesis and carcinogenesis (10,15). Our study identified a feed-forward activation pathway that TGFβ-induces WNT5A within luminal cells and WNT5A further expands the TFGβR/SMAD signaling in basal cells, e.g. basal TIC in the case of breast cancer model, to suppress their growth. It is known that normal tissue microenvironment suppresses uncontrolled proliferation of stem cells and promotes their asymmetrical proliferation (38). Mammary stem cells are known to proliferate during pregnancy and diestrus stage of estrus cycle mediated by classical Wnt signaling and Receptor Activator for NF-κB ligand (RANKL), a process activated by luminal progesterone signaling (32,33). Co-incidentally, both classic Wnt signaling (39) and RANKL (40,41) are critical to promote carcinogen- or oncogene-induced mammary cancer, although the connection between the expansion of mammary stem cells and cancer promotion is difficult to prove and yet to be established. WNT5A, on the other hand, likely serves a “niche” component to counterbalance classical Wnt or RANKL effects on the expansion of mammary stem cells, i.e. the basal TICs and thus suppresses tumorigenesis. WNT5A plays a broader role in tissue stem cells and its ablation increases proliferative intestinal stem cells (27). WNT5A functions as a negative regulator of self-renewal or proliferation in embryonic and hematopoietic stem cells (42,43) through RYK (44). Interestingly, in colon WNT5A induces p-SMAD3 not p-SMAD2 in a ROR1/2-dependent manner, suggesting that WNT5A uses a similar mechanism to regulate the homeostasis of tissue stem cells. Among many WNT5A receptors, RYK is highly expressed in normal mammary tissue and decreased in all breast-cancer subtypes (Supplementary Fig. S7B). Our analysis of Affymetrix array dataset GSE2034 based on 255-human breast cancer specimens further corroborates the role of RYK in suppressing metastasis in conjunction with SMAD2 (Fig. 7E). A recent study showed that WNT5A promotes mammosphere growth via ROR2-mediated JNK activation (37). One potential explanation is that WNT5A preferentially interacts with RYK; in the absence of RYK, WNT5A activates JNK1/2 (Fig. 7C) in a ROR2-dependent manner (37). It is known that WNT5A induces RANKL expression via ROR2-mediated JNK activation during osteoclastogenesis (45), a potential mechanism that might take place in mammary epithelium, when condition permits, to promote mammary stem cells. Another potential explanation is that we used mammary epithelial cells from pre-neoplastic MMTV-ErbB2 female mice. ErbB2 promotes strong activation of MAP kinase Erk1/2 pathway for mammary tumorigenesis thus surpasses the necessity of JNK activation as seen in normal mammary epithelial cells or those from MMTV-Wnt1 transgenic mice (37). Indeed, genetic deletion of JNK in mammary epithelial cells led to increased ductal morphogenesis and mammary tumorigenesis, suggesting its tumor suppressive role in mammary cancer (46).
The paracrine interactions between basal and luminal compartments within the mammary epithelium have broader implications. We reported here that WNT5A is highly expressed in luminal cells and inhibits the growth of basal TICs, which likely needs to evade the WNT5A-mediated or other suppressive microenvironment signals during the oncogenic process. We believe that basal TICs have to undergo luminal differentiation during ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis since all ErbB2-induced tumors express luminal keratins (22). During the basal to luminal differentiation, WNT5A perceivably loses its control on tumor cells as evidenced by the fact that WNT5A failed to induce further p-SMAD2 in ErbB2+ luminal cells (Fig. 6A). It is known that Notch activation leads to the commitment of mammary stem cells to luminal differentiation during Notch-induced tumorigenesis (47). ErbB2 may have a similar function as Notch to initiate tumors from mammary stem cells.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Terry Yamaguchi from the National Cancer Institute for providing the Wnt5afl/fl mice; thank Drs. Hasem Habelhah and Dawn Quelle for technical support and insights; thank Dr. Songhai Chen for providing frozen tissues of human breast cancer; and thank Genetex and Santa Cruz for providing important antibodies. This work was supported by NIH grant K99/R00 CA158055 (W.Z.), NIH T32 GM007337 (N.B., G.V.), NIH T32 AI007260 (R.K.), a V Scholar award from the V Research Foundation for the Cancer (W.Z.). The authors were supported by a Department Startup Grant and Seed Grant from the Department of Pathology, and a Breast Cancer Research Grant for Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine (W.Z.). This work was benefited from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number P30CA086862. Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Center for Research Resources of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number 1S10 RR027219. Lastly, these results here are in whole or part based upon data generated by the TCGA Research Network (http://cancergenome.nih.gov/).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest
All authors possess no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Taipale J, Beachy PA. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature. 2001;411(6835):349–354. doi: 10.1038/35077219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Habas R, Dawid IB, He X. Coactivation of Rac and Rho by Wnt/Frizzled signaling is required for vertebrate gastrulation. Genes Dev. 2003;17(2):295–309. doi: 10.1101/gad.1022203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wansleeben C, Meijlink F. The planar cell polarity pathway in vertebrate development. Developmental Dynamics. 2011;240(3):616–626. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Slusarski DC, Yang-Snyder J, Busa WB, Moon RT. Modulation of Embryonic Intracellular Ca2+Signaling byWnt-5A. Developmental Biology. 1997;182(1):114–120. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.8463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Westfall TA, Brimeyer R, Twedt J, Gladon J, Olberding A, Furutani-Seiki M, et al. Wnt-5/pipetail functions in vertebrate axis formation as a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin activity. J Cell Biol. 2003;162(5):889–898. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200303107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anastas JN, Moon RT. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(1):11–26. doi: 10.1038/nrc3419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yuzugullu H, Benhaj K, Ozturk N, Senturk S, Celik E, Toylu A, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling is antagonized by noncanonical Wnt5a in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Molecular Cancer. 2009;8(1) doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liang H, Chen Q, Coles AH, Anderson SJ, Pihan G, Bradley A, et al. Wnt5a inhibits B cell proliferation and functions as a tumor suppressor in hematopoietic tissue. Cancer Cell. 2003;4(5):349–360. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ying J, Li H, Yu J, Ng KM, Poon FF, Wong SCC, et al. WNT5A Exhibits Tumor-Suppressive Activity through Antagonizing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, and Is Frequently Methylated in Colorectal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(1):55–61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Roarty K, Baxley SE, Crowley MR, Frost AR, Serra R. Loss of TGF-beta or Wnt5a results in an increase in Wnt/beta-catenin activity and redirects mammary tumour phenotype. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(2) doi: 10.1186/bcr2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bitler BG, Nicodemus JP, Li H, Cai Q, Wu H, Hua X, et al. Wnt5a Suppresses Epithelial Ovarian Cancer by Promoting Cellular Senescence. Cancer Res. 2011;71(19):6184–6194. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lejeune S, Huguet EL, Hamby A, Poulsom R, Harris AL. Wnt5a cloning, expression, and up-regulation in human primary breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1(2):215–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jönsson M, Dejmek J, Bendahl P-O, Andersson T. Loss of Wnt-5a Protein Is Associated with Early Relapse in Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2002;62(2):409–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leris ACA, Roberts TR, Jiang WG, Newbold RF, Mokbel K. WNT5A Expression in Human Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(2A):731–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Roarty K, Serra R. Wnt5a is required for proper mammary gland development and TGF-beta-mediated inhibition of ductal growth. Development. 2007;134(21):3929–3939. doi: 10.1242/dev.008250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Keeble TR, Halford MM, Seaman C, Kee N, Macheda M, Anderson RB, et al. The Wnt Receptor Ryk Is Required for Wnt5a-Mediated Axon Guidance on the Contralateral Side of the Corpus Callosum. J Neurosci. 2006;26(21):5840–5848. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1175-06.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mikels AJ, Nusse R. Purified Wnt5a protein activates or inhibits beta-catenin-TCF signaling depending on receptor context. PLoS Biol. 2006;4(4) doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fukuda T, Chen L, Endo T, Tang L, Lu D, Castro JE, et al. Antisera Induced by Infusions of Autologous Ad-CD154-Leukemia B Cells Identify ROR1 as an Oncofetal Antigen and Receptor for Wnt5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(8):3047–3052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712148105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hovens CM, Stacker SA, Andres AC, Harpur AG, Ziemiecki A, Wilks AF. RYK, a receptor tyrosine kinase-related molecule with unusual kinase domain motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(24) doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Katso RMT, Manek S, Ganjavi H, Biddolph S, Charnock MFL, Bradburn M, et al. Overexpression of H-Ryk in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Prognostic Significance of Receptor Expression. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6(8):3271–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Borcherding N, Kusner D, Liu GH, Zhang W. ROR1, an embryonic protein with an emerging role in cancer biology. Protein & cell. 2014;5(7):496–502. doi: 10.1007/s13238-014-0059-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang W, Tan W, Wu X, Poustovoitov M, Strasner A, Li W, et al. A NIK-IKKα Module Expands ErbB2-Induced Tumor-Initiating Cells by Stimulating Nuclear Export of p27/Kip1. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(5):647–659. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.03.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhu J, Sanborn JZ, Benz S, Szeto C, Hsu F, Kuhn RM, et al. The UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser. Nat Meth. 2009;6(4):239–240. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0409-239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Debnath J, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS. Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods. 2003;30(3):256–268. doi: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Meth. 2012;9(7):671–675. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang W, Kater AP, Widhopf GF, Chuang H-Y, Enzler T, James DF, et al. B-cell activating factor and v-Myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (c-Myc) influence progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(44):18956–18960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013420107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miyoshi H, Ajima R, Luo CT, Yamaguchi TP, Stappenbeck TS. Wnt5a Potentiates TGF-β Signaling to Promote Colonic Crypt Regeneration After Tissue Injury. Science. 2012;338(6103):108–113. doi: 10.1126/science.1223821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Muller WJ, Sinn E, Pattengale PK, Wallace R, Leder P. Single-step induction of mammary adenocarcinoma in transgenic mice bearing the activated c-neu oncogene. Cell. 1988;54(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yamaguchi TP, Bradley A, McMahon AP, Jones S. A Wnt5a pathway underlies outgrowth of multiple structures in the vertebrate embryo. Development. 1999;126(6):1211–1223. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.6.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kannan N, Huda N, Tu L, Droumeva R, Aubert G, Chavez E, et al. The Luminal Progenitor Compartment of the Normal Human Mammary Gland Constitutes a Unique Site of Telomere Dysfunction. Stem Cell Reports. 2013;1(1):28–37. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2013.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(43):15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Asselin-Labat ML, Vaillant F, Sheridan JM, Pal B, Wu D, Simpson ER, et al. Control of mammary stem cell function by steroid hormone signalling. Nature. 2010;465(7299):798–802. doi: 10.1038/nature09027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Joshi PA, Jackson HW, Beristain AG, Di Grappa MA, Mote PA, Clarke CL, et al. Progesterone induces adult mammary stem cell expansion. Nature. 2010;465(7299):803–807. doi: 10.1038/nature09091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ, et al. In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev. 2003;17(10):1253–1270. doi: 10.1101/gad.1061803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pastrana E, Silva-Vargas V, Doetsch F. Eyes wide open: a critical review of sphere-formation as an assay for stem cells. Cell stem cell. 2011;8(5):486–498. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Debnath J, Brugge JS. Modelling glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(9):675–688. doi: 10.1038/nrc1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Many AM, Brown AMC. Both Canonical and Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Independently Promote Stem Cell Growth in Mammospheres. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Blanpain C, Fuchs E. Stem cell plasticity. Plasticity of epithelial stem cells in tissue regeneration. Science. 2014;344(6189):1242281. doi: 10.1126/science.1242281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shackleford GM, MacArthur CA, Kwan HC, Varmus HE. Mouse mammary tumor virus infection accelerates mammary carcinogenesis in Wnt-1 transgenic mice by insertional activation of int-2/Fgf-3 and hst/Fgf-4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(2):740–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tan W, Zhang W, Strasner A, Grivennikov S, Cheng JQ, Hoffman RM, et al. Tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells stimulate mammary cancer metastasis through RANKL-RANK signalling. Nature. 2011;470(7335):548–553. doi: 10.1038/nature09707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schramek D, Leibbrandt A, Sigl V, Kenner L, Pospisilik JA, Lee HJ, et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor RANKL controls development of progestin-driven mammary cancer. Nature. 2010;468(7320):98–102. doi: 10.1038/nature09387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nemeth MJ, Topol L, Anderson SM, Yang Y, Bodine DM. Wnt5a inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cells and enhances repopulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(39):15436–15441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704747104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hwang Y-S, Chung BG, Ortmann D, Hattori N, Moeller H-C, Khademhosseini A. Microwell-mediated control of embryoid body size regulates embryonic stem cell fate via differential expression of WNT5a and WNT11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(40):16978–16983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905550106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Povinelli BJ, Nemeth MJ. Wnt5a regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and repopulation through the Ryk receptor. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):105–115. doi: 10.1002/stem.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Maeda K, Kobayashi Y, Udagawa N, Uehara S, Ishihara A, Mizoguchi T, et al. Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling between osteoblast-lineage cells and osteoclast precursors enhances osteoclastogenesis. Nature medicine. 2012;18(3):405–412. doi: 10.1038/nm.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chen P, O'Neal JF, Ebelt ND, Cantrell MA, Mitra S, Nasrazadani A, et al. Jnk2 effects on tumor development, genetic instability and replicative stress in an oncogene-driven mouse mammary tumor model. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(5):e10443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bouras T, Pal B, Vaillant F, Harburg G, Asselin-Labat ML, Oakes SR, et al. Notch signaling regulates mammary stem cell function and luminal cell-fate commitment. Cell stem cell. 2008;3(4):429–441. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.