Abstract
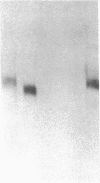
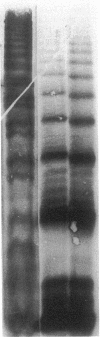
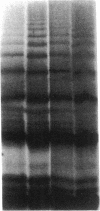
By transfecting the full-length cDNA for human von Willebrand factor (vWf) into a line of Chinese hamster ovary cells with a defect in carbohydrate metabolism, we have prepared recombinant vWf specifically lacking O-linked carbohydrates. We have compared this under-glycosylated protein to fully glycosylated recombinant vWf with respect to several structural and binding properties. vWf deficient in O-linked glycans was synthesized, assembled into multimers, and secreted in an apparently normal manner and was not prone to degradation in the extracellular milieu. It did not differ from fully glycosylated vWf in ability to bind to heparin or to collagen type I but did interact less well with glycoprotein 1b on formalin-fixed platelets. This decreased interaction was evidenced in both a lessened overall binding to platelets and in diminished capacity to promote platelet agglutination, in the presence of ristocetin. In contrast, no difference was seen in platelet binding in the presence of botrocetin. These data indicate a possible role for O-linked carbohydrates in the vWf-glycoprotein 1b interaction promoted by ristocetin and suggest that abnormalities in carbohydrate modification might contribute to the altered ristocetin-dependent reactivity between vWf and platelets described for some variant forms of von Willebrand disease.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. K., Booth W. J., Gorman J. J., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Purification of botrocetin from Bothrops jararaca venom. Analysis of the botrocetin-mediated interaction between von Willebrand factor and the human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8317–8326. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. K., Gorman J. J., Booth W. J., Corino G. L., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Cross-linking of a monomeric 39/34-kDa dispase fragment of von Willebrand factor (Leu-480/Val-481-Gly-718) to the N-terminal region of the alpha-chain of membrane glycoprotein Ib on intact platelets with bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8326–8336. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. D., Federici A. B. Sialic acid prevents loss of large von Willebrand factor multimers by protecting against amino-terminal proteolytic cleavage. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1790–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockenstedt P., Greenberg J. M., Handin R. I. Structural basis of von Willebrand factor binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib and collagen. Effects of disulfide reduction and limited proteolysis of polymeric von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):743–749. doi: 10.1172/JCI112369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S., Fricke W. A., Wagner R. H. Botrocetin (venom coagglutinin): reaction with a broad spectrum of multimeric forms of factor VIII macromolecular complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1463–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew J. A., Browning P. J., Lynch D. C. Sulfation of von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2530–2539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney K. A., Nichols W. C., Bruck M. E., Bahou W. F., Shapiro A. D., Bowie E. J., Gralnick H. R., Ginsburg D. The molecular defect in type IIB von Willebrand disease. Identification of four potential missense mutations within the putative GpIb binding domain. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1227–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI115123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzucato M., De Roia D., Casonato A., Federici A. B., Girolami A., Ruggeri Z. M. Distinct abnormalities in the interaction of purified types IIA and IIB von Willebrand factor with the two platelet binding sites, glycoprotein complexes Ib-IX and IIb-IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):785–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Shapiro S. S. Properties of human asialo-factor VIII. A ristocetin-independent platelet-aggregating agent. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):321–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI110259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debeire P., Montreuil J., Samor B., Mazurier C., Goudemand M., van Halbeek H., Vliegenthart J. F. Structure determination of the major asparagine-linked sugar chain of human factor VIII--von Willebrand factor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 10;151(1):22–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Kawai Y., Wagner D. D., Ginsburg D., Bonthron D., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Chavin S. I., Abraham G. N., Handin R. I., Orkin S. H. Propolypeptide of von Willebrand factor circulates in blood and is identical to von Willebrand antigen II. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):995–998. doi: 10.1126/science.3486471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Marti T., Titani K., Zimmerman T. S. A major factor VIII binding domain resides within the amino-terminal 272 amino acid residues of von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8443–8446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Holland L. Z., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The von willebrand factor domain-mediating botrocetin-induced binding to glycoprotein IB lies between Val449 and Lys728. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):985–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Kostel P., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. A heparin-binding domain of human von Willebrand factor. Characterization and localization to a tryptic fragment extending from amino acid residue Val-449 to Lys-728. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Usami Y., Suzuki M., Oyama R., Matsui T., Fukui H., Sugimoto M., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and chemical characterization of two structurally and functionally distinct forms of botrocetin, the platelet coagglutinin isolated from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1957–1964. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Usami Y., Titani K., Niinomi K., Nishio K., Takase T., Yoshioka A., Fukui H. Studies on anti-von Willebrand factor (vWF) monoclonal antibody NMC-4, which inhibits both ristocetin- and botrocetin-induced vWF binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Meyer D., Verweij C. L., Pannekoek H., Sixma J. J. Structure-function relationship of human von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):605–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Takahashi Y., Yoshioka A., Diaz J., Meyer D. Ristocetin and botrocetin involve two distinct domains of von Willebrand factor for binding to platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Oct 22;64(2):326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Takahashi Y., Yoshioka A., Diaz J., Meyer D. Ristocetin and botrocetin involve two distinct domains of von Willebrand factor for binding to platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Oct 22;64(2):326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin--a new tool in the investigation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins C. S., Phillips D. R., Clemetson K. J., Meyer D., Larrieu M. J., Lüscher E. F. Platelet membrane glycoproteins implicated in ristocetin-induced aggregation. Studies of the proteins on platelets from patients with Bernard-Soulier syndrome and von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):112–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Kozarsky K. F., Hobbie L., Krieger M. Reversible defects in O-linked glycosylation and LDL receptor expression in a UDP-Gal/UDP-GalNAc 4-epimerase deficient mutant. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):749–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90841-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarsky K. F., Call S. M., Dower S. K., Krieger M. Abnormal intracellular sorting of O-linked carbohydrate-deficient interleukin-2 receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3357–3363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene R. B., Booyse F. M., Chediak J., Zimmerman T. S., Livingston D. M., Lynch D. C. Expression of abnormal von Willebrand factor by endothelial cells from a patient with type IIA von Willebrand disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. C., Zimmerman T. S., Kirby E. P., Livingston D. M. Subunit composition of oligomeric human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12757–12760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S. E., Bruck M. E., Bowie E. J., Ginsburg D. Impaired intracellular transport produced by a subset of type IIA von Willebrand disease mutations. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4424–4430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti T., Rösselet S. J., Titani K., Walsh K. A. Identification of disulfide-bridged substructures within human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8099–8109. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzuk M. M., Krieger M., Corless C. L., Boime I. Effects of preventing O-glycosylation on the secretion of human chorionic gonadotropin in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier C., Dieval J., Jorieux S., Delobel J., Goudemand M. A new von Willebrand factor (vWF) defect in a patient with factor VIII (FVIII) deficiency but with normal levels and multimeric patterns of both plasma and platelet vWF. Characterization of abnormal vWF/FVIII interaction. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll D. R., Levin E. G., Montgomery R. R. Endothelial cell synthesis of von Willebrand antigen II, von Willebrand factor, and von Willebrand factor/von Willebrand antigen II complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1089–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI111802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Fujimura Y., Shima M., Yoshioka A., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Structure of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17901–17904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Yoshioka A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib, heparin, and collagen and characterization of its three distinct functional sites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17361–17367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino M., Girma J. P., Rothschild C., Fressinaud E., Meyer D. New variant of von Willebrand disease with defective binding to factor VIII. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1591–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh-eda M., Hasegawa M., Hattori K., Kuboniwa H., Kojima T., Orita T., Tomonou K., Yamazaki T., Ochi N. O-linked sugar chain of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor protects it against polymerization and denaturation allowing it to retain its biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11432–11435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareti F. I., Fujimura Y., Dent J. A., Holland L. Z., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and characterization of a collagen binding domain in human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15310–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piétu G., Meulien P., Cherel G., Diaz J., Baruch D., Courtney M., Meyer D. Production in Escherichia coli of a biologically active subfragment of von Willebrand factor corresponding to the platelet glycoprotein Ib, collagen and heparin binding domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91816-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randi A. M., Rabinowitz I., Mancuso D. J., Mannucci P. M., Sadler J. E. Molecular basis of von Willebrand disease type IIB. Candidate mutations cluster in one disulfide loop between proposed platelet glycoprotein Ib binding sequences. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1220–1226. doi: 10.1172/JCI115122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Shermer R. W., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin: an activator of platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Smith S. V., Lamb M. A., Brinkhous K. M. Role of botrocetin in platelet agglutination: formation of an activated complex of botrocetin and von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1989 Aug 15;74(3):1031–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Caras I., Krieger M. Effects of O-linked glycosylation on the cell surface expression and stability of decay-accelerating factor, a glycophospholipid-anchored membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17329–17336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samor B., Michalski J. C., Mazurier C., Goudemand M., De Waard P., Vliegenthart J. F., Strecker G., Montreuil J. Primary structure of the major O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate unit of human von Willebrand factor. Glycoconj J. 1989;6(3):263–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01047846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. P., Montgomery R. R., Retzinger G. S. Dimeric ristocetin flocculates proteins, binds to platelets, and mediates von Willebrand factor-dependent agglutination of platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8149–8155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shogren R., Gerken T. A., Jentoft N. Role of glycosylation on the conformation and chain dimensions of O-linked glycoproteins: light-scattering studies of ovine submaxillary mucin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5525–5536. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn L. A., Marder V. J., Wagner D. D. Inducible secretion of large, biologically potent von Willebrand factor multimers. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90735-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Kumar S., Takio K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Ashida K., Walsh K. A., Chopek M. W., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3171–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Hart M., Pannekoek H. Expression of variant von Willebrand factor (vWF) cDNA in heterologous cells: requirement of the pro-polypeptide in vWF multimer formation. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2885–2890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Fay P. J., Sporn L. A., Sinha S., Lawrence S. O., Marder V. J. Divergent fates of von Willebrand factor and its propolypeptide (von Willebrand antigen II) after secretion from endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1955–1959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells. Identification of a large precursor polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2065–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells: processing steps and their intracellular localization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Pittman D. D., Handin R. I., Kaufman R. J., Orkin S. H. The propeptide of von Willebrand factor independently mediates the assembly of von Willebrand multimers. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanni E. E., Kouvatsi A., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Krieger M., Zannis V. I. Expression of ApoE gene in Chinese hamster cells with a reversible defect in O-glycosylation. Glycosylation is not required for apoE secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9137–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot P. G., Federici A. B., de Boer H. C., d'Alessio P., Mannucci P. M., Sixma J. J. von Willebrand factor synthesized by endothelial cells from a patient with type IIB von Willebrand disease supports platelet adhesion normally but has an increased affinity for platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3793–3797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]