Abstract
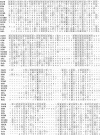
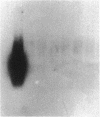
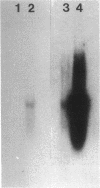
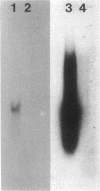
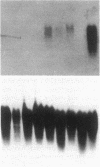
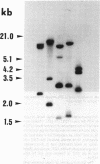
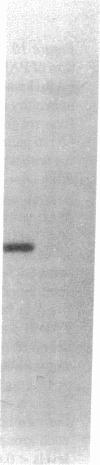
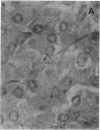
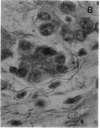
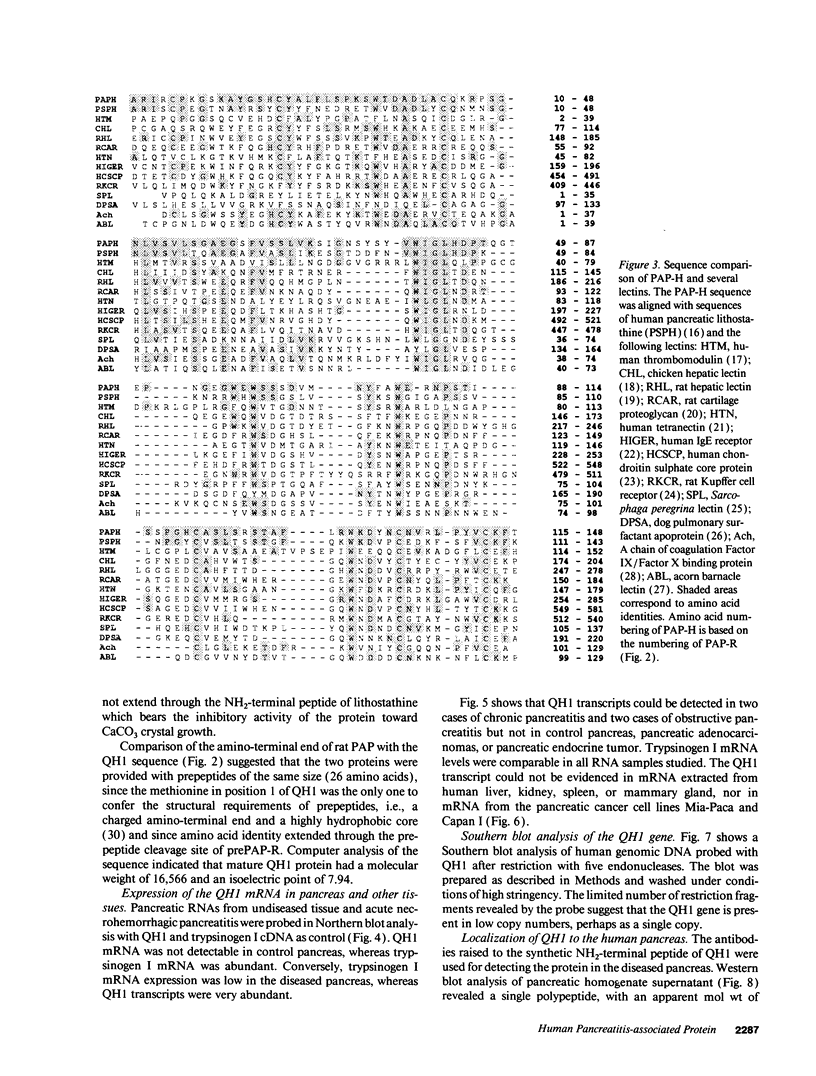
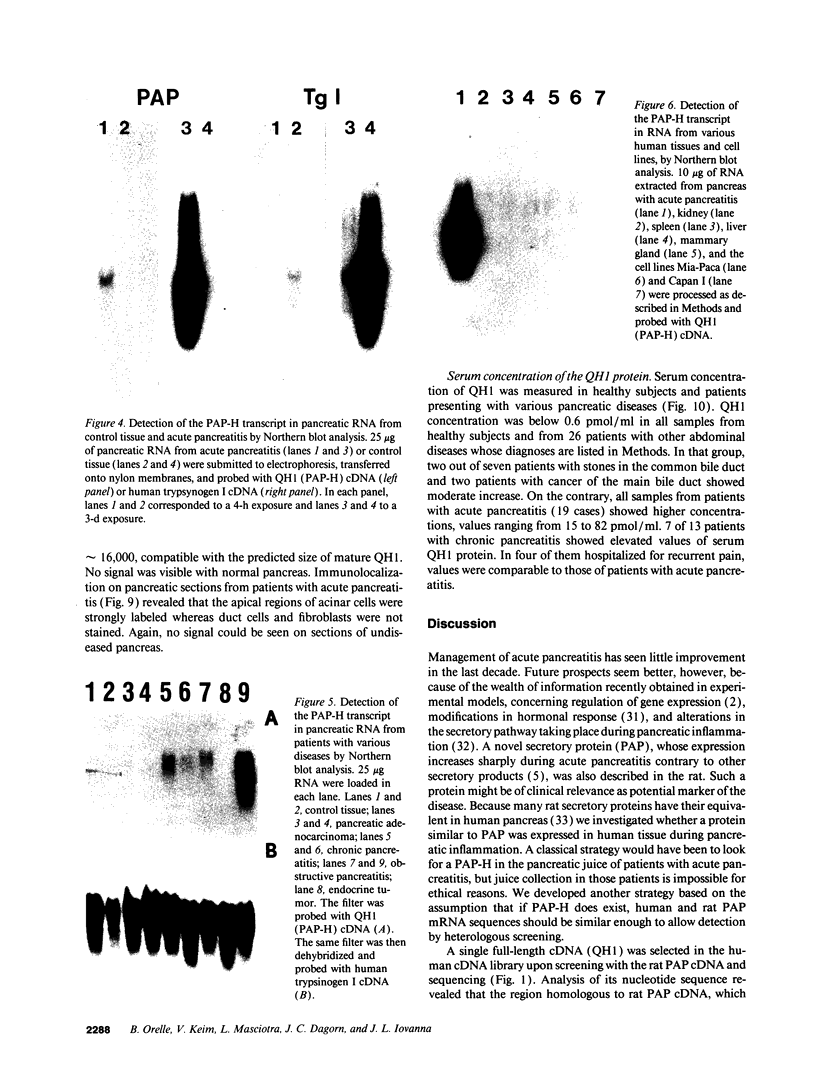
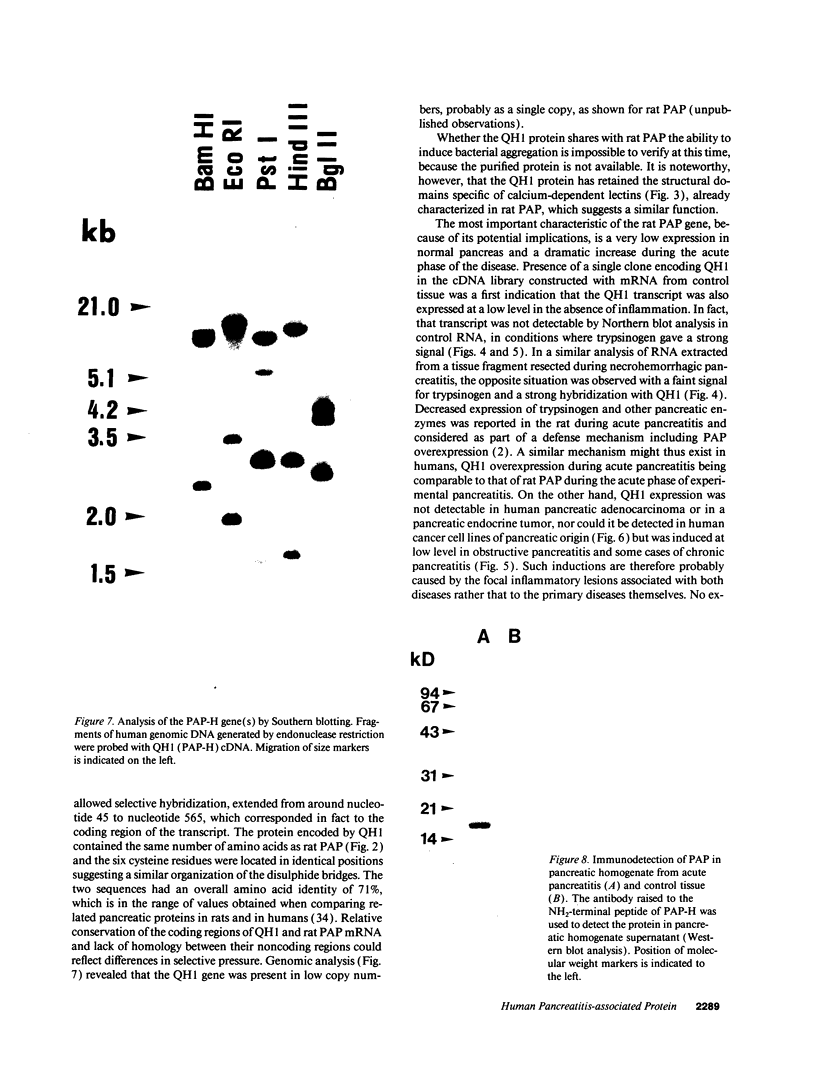
A human pancreatic cDNA library was screened with the cDNA encoding rat "pancreatitis-associated protein" (PAP). The selected clone encoded a secretory protein structurally related to rat PAP. The protein had the same size as rat PAP and showed 71% amino acid identity, the six half-cystines being in identical positions. Domains of the proteins showing homologies with calcium-dependent lectins were also conserved. In addition, expression in pancreas of the genes encoding the human protein and rat PAP showed similar characteristics: both were expressed at very low levels in control tissue and overexpressed during the acute phase of pancreatitis, contrary to most secretory products. The human protein was therefore named human pancreatitis-associated protein (PAP-H). Antibodies raised to a synthetic peptide of PAP-H detected a single band with an M(r) compatible with PAP-H in Western blot analysis of proteins extracted from a pancreas presenting with acute pancreatitis. In that tissue, the protein could be immunolocalized to the apical regions of acinar cells. An immunoassay was also constructed to quantify the protein in serum. Elevated PAP-H levels were observed in patients with acute pancreatitis and in some patients with chronic pancreatitis. Values were close to background in healthy subjects and in patients with other abdominal diseases. These results confirm that PAP-H synthesis increases during inflammation and suggest a possible use of the protein as biological marker of acute pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atoda H., Hyuga M., Morita T. The primary structure of coagulation factor IX/factor X-binding protein isolated from the venom of Trimeresurus flavoviridis. Homology with asialoglycoprotein receptors, proteoglycan core protein, tetranectin, and lymphocyte Fc epsilon receptor for immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14903–14911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson B., Hawgood S., Schilling J., Clements J., Damm D., Cordell B., White R. T. Structure of canine pulmonary surfactant apoprotein: cDNA and complete amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K., Fernandez P., Hassell J. R., Sasaki M., Yamada Y. Partial cDNA sequence encoding a globular domain at the C terminus of the rat cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8108–8111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman D. M., Zon L. I., Orkin S. H. Rapid amplification of lambda gt11 bacteriophage library inserts from plaques using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Biotechniques. 1989 Jun;7(6):568–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., Mamon J. F., Binns G., Leung J. O. Primary structure of the rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor. Structural evidence for multiple polypeptide species. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):770–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Two distinct classes of carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9557–9560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlendorff J., Clemmensen I., Magnusson S. Primary structure of tetranectin, a plasminogen kringle 4 binding plasma protein: homology with asialoglycoprotein receptors and cartilage proteoglycan core protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6757–6764. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi D., Bernard J. P., Rouquier S., Iovanna J., Sarles H., Dagorn J. C. Secretory pancreatic stone protein messenger RNA. Nucleotide sequence and expression in chronic calcifying pancreatitis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):100–106. doi: 10.1172/JCI114128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad W. B., Kanehisa M. I. Pattern recognition in nucleic acid sequences. I. A general method for finding local homologies and symmetries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):247–263. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle G. W., Hill R. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for a carbohydrate binding receptor unique to rat Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7487–7492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iovanna J. L., Keim V., Michel R., Dagorn J. C. Pancreatic gene expression is altered during acute experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):G485–G489. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.3.G485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iovanna J., Orelle B., Keim V., Dagorn J. C. Messenger RNA sequence and expression of rat pancreatitis-associated protein, a lectin-related protein overexpressed during acute experimental pancreatitis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24664–24669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim V., Iovanna J. L., Rohr G., Usadel K. H., Dagorn J. C. Characterization of a rat pancreatic secretory protein associated with pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Mar;100(3):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)80025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Inui S., Sato R., Barsumian E. L., Owaki H., Yamasaki K., Kaisho T., Uchibayashi N., Hardy R. R., Hirano T. Molecular structure of human lymphocyte receptor for immunoglobulin E. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Gehlsen K. R., Ruoslahti E. A fibroblast chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan core protein contains lectin-like and growth factor-like sequences. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13120–13125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Niederau M., Lüthen R., Strohmeyer G., Ferrell L. D., Grendell J. H. Pancreatic exocrine secretion in acute experimental pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1120–1127. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90633-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouquier S., Verdier J. M., Iovanna J., Dagorn J. C., Giorgi D. Rat pancreatic stone protein messenger RNA. Abundant expression in mature exocrine cells, regulation by food content, and sequence identity with the endocrine reg transcript. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):786–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer M. L., Meldolesi J. The cell biology of experimental pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 15;316(3):144–150. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701153160306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Z., Dittman W. A., Ye R. D., Deaven L. L., Majerus P. W., Sadler J. E. Human thrombomodulin: complete cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4350–4357. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Analysis of the distribution of charged residues in the N-terminal region of signal sequences: implications for protein export in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2315–2318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]