Abstract
Rotaviruses are an important cause of gastroenteritis in human infants. In vivo, rotavirus displays striking cell tropism with viral replication generally restricted to the villus tip enterocytes of the small intestine. We studied a panel of cell lines that vary significantly in their permissivity to rotavirus infection. L cells and HEp2 cells were relatively resistant to rotavirus infection compared with permissive Ma104 cells and HT29 cells. RNA transcription among the cell lines was proportional to antigen synthesis making a translational or posttranslational block an unlikely source of observed differences in susceptibility. All of the cell lines bound and internalized radiolabeled virus equally well, as measured by escape from surface protease treatment. Analysis of the escape of cell bound virus from neutralizing monoclonal antibody revealed that rotavirus did not immediately enter an eclipse phase in nonpermissive cells, but was internalized in an infectious form for several hours, possibly sequestered within endocytic vacuoles. L cells and HEp2 cells were as permissive as Ma104 and HT29 cells when rotavirus infection was mediated by transfection of single- or double-shelled rotavirus particles with cationic liposomes (Lipofectin). Rotavirus cell tropism in tissue culture cells is determined by the ability of infecting virions to traverse the plasma membrane of the cells into the cytoplasmic compartment.
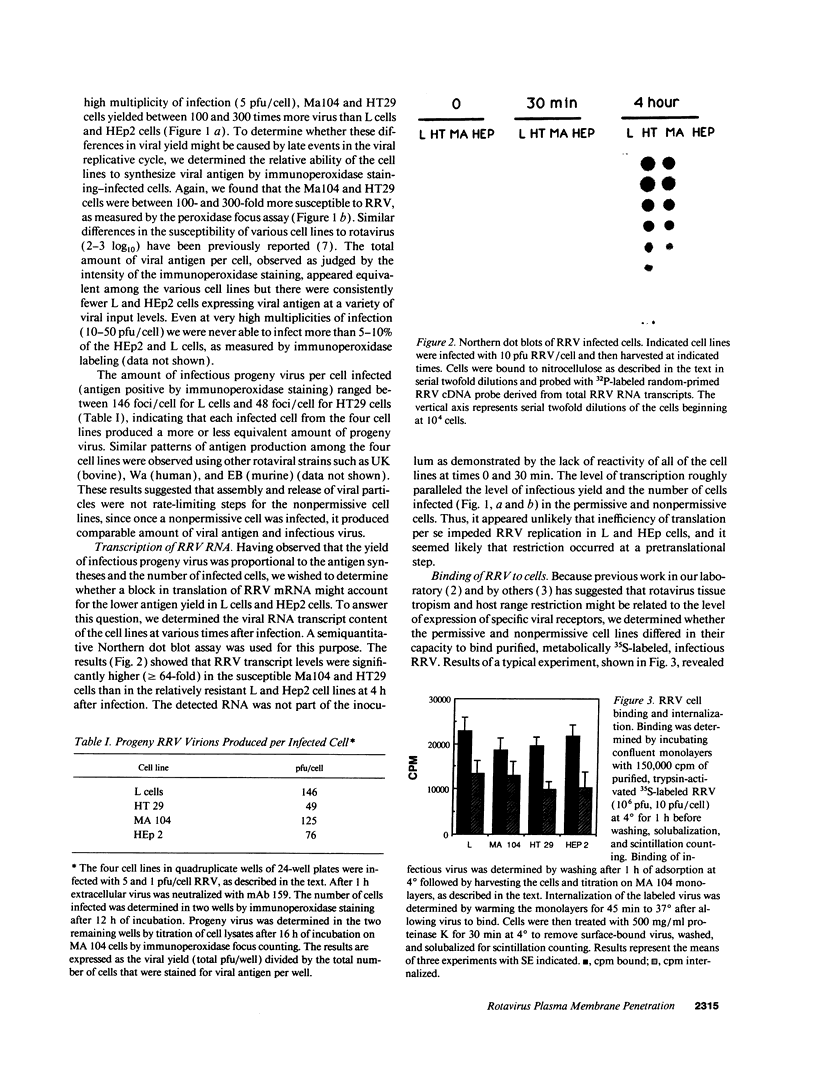
Full text
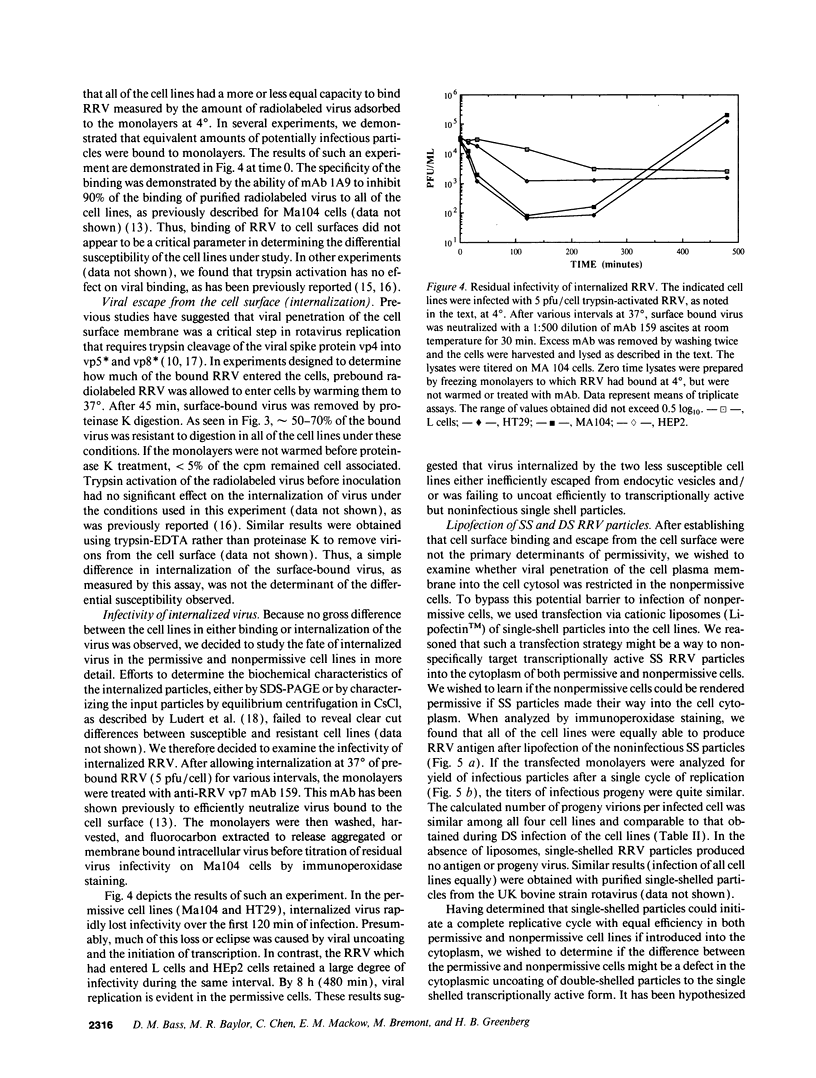
PDF

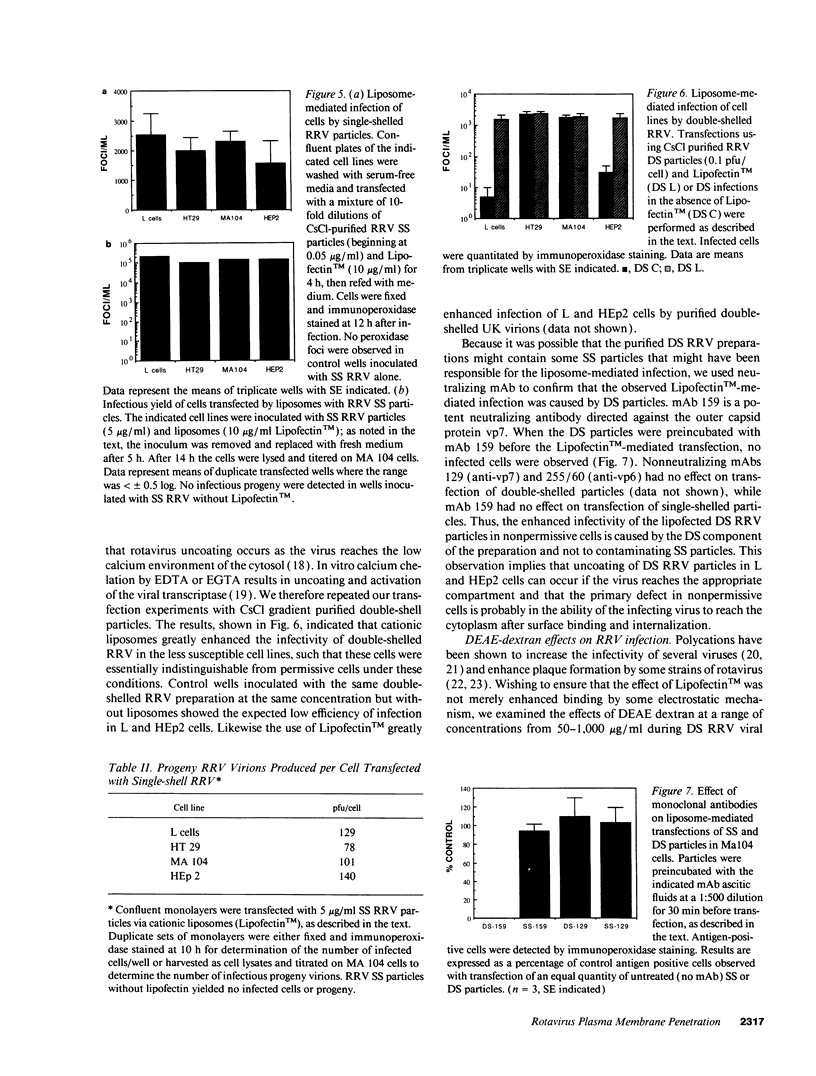



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey C. A., Miller D. K., Lenard J. Effects of DEAE-dextran on infection and hemolysis by VSV. Evidence that nonspecific electrostatic interactions mediate effective binding of VSV to cells. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. M., Baylor M., Broome R., Greenberg H. B. Molecular basis of age-dependent gastric inactivation of rhesus rotavirus in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1741–1745. doi: 10.1172/JCI115776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. M., Mackow E. R., Greenberg H. B. Identification and partial characterization of a rhesus rotavirus binding glycoprotein on murine enterocytes. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):602–610. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90989-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. M., Roth J. R., Clark M. L., Barnett B. B., Spendlove R. S. Trypsin enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: mechanism of enhancement. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):816–822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.816-822.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. B., Spier R. E. An investigation into causes of resistance of a cloned line of BHK cells to a strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Jun;8(3):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Laporte J., Charpilienne A., Scherrer R. Activation of rotavirus RNA polymerase by calcium chelation. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):177–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01317489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Lefevre F., Estes M. K., Bremont M. Cloning of bovine rotavirus (RF strain): nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major capsid protein. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Shanley J. D., Damiano-Burbach P. Encephalomyocarditis virus can bind to and transfect non-permissive cells. Arch Virol. 1986;88(3-4):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF01310884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Ringold G. M. Cationic liposome-mediated transfection. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):387–388. doi: 10.1038/337387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuhara N., Yoshie O., Kitaoka S., Konno T. Role of VP3 in human rotavirus internalization after target cell attachment via VP7. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2209–2218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2209-2218.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. Gene coding assignments for growth restriction, neutralization and subgroup specificities of the W and DS-1 strains of human rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):313–320. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Sato F., Ono K., Murakami T., Matumoto M. A sensitive plaque assay for bovine rotavirus in cultures of the bovine cell line GBK. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Apr;13(4):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath J., Weber J. M. Nonpermissivity of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to adenovirus type 2 infection. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):341–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.341-345.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innes C. L., Smith P. B., Langenbach R., Tindall K. R., Boone L. R. Cationic liposomes (Lipofectin) mediate retroviral infection in the absence of specific receptors. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):957–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.957-961.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Flores J., Greenberg H. B. Identification of the rotaviral gene that codes for hemagglutination and protease-enhanced plaque formation. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaljot K. T., Shaw R. D., Rubin D. H., Greenberg H. B. Infectious rotavirus enters cells by direct cell membrane penetration, not by endocytosis. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1136–1144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1136-1144.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keljo D. J., Kuhn M., Smith A. Acidification of endosomes is not important for the entry of rotavirus into the cell. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Mar-Apr;7(2):257–263. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198803000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooi C., Mizzen L., Alderson C., Daya M., Anderson R. Early events of importance in determining host cell permissiveness to mouse hepatitis virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1125–1135. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludert J. E., Michelangeli F., Gil F., Liprandi F., Esparza J. Penetration and uncoating of rotaviruses in cultured cells. Intervirology. 1987;27(2):95–101. doi: 10.1159/000149726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludert J. E., Michelangeli F., Gil F., Liprandi F., Esparza J. Penetration and uncoating of rotaviruses in cultured cells. Intervirology. 1987;27(2):95–101. doi: 10.1159/000149726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E. R., Shaw R. D., Matsui S. M., Vo P. T., Dang M. N., Greenberg H. B. The rhesus rotavirus gene encoding protein VP3: location of amino acids involved in homologous and heterologous rotavirus neutralization and identification of a putative fusion region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):645–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Inouye S., Kono R. Plaque assay of neonatal calf diarrhea virus and the neutralizing antibody in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.1-4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi P., Charpilienne A., Cohen J. Interaction of rotavirus particles with liposomes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3363-3367.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G., Greenberg H. B., Clark H. F. Molecular basis of rotavirus virulence: role of gene segment 4. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.46-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paeratakul U., De Stasio P. R., Taylor M. W. A fast and sensitive method for detecting specific viral RNA in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1132-1135.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B. V., Burns J. W., Marietta E., Estes M. K., Chiu W. Localization of VP4 neutralization sites in rotavirus by three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):476–479. doi: 10.1038/343476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan C. M., Doane F. W. Ultrastructural evidence for the cellular uptake of rotavirus by endocytosis. Intervirology. 1983;20(4):223–231. doi: 10.1159/000149395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Galle K. L. Rotavirus genome segment 4 determines viral replication phenotype in cultured liver cells (HepG2). J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1044–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1044-1049.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Lee P. C., Carmody P. J., Barrett H. J., Ogra P. L. Age-dependent rotavirus-enterocyte interactions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jun;170(2):146–154. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri F. M., Greenberg H. B. Antibodies to the trypsin cleavage peptide VP8 neutralize rotavirus by inhibiting binding of virions to target cells in culture. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2211–2219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2211-2219.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kitaoka S., Konno T., Sato T., Ishida N. Two modes of human rotavirus entry into MA 104 cells. Arch Virol. 1985;85(1-2):25–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01317003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kitaoka S., Konno T., Sato T., Ishida N. Two modes of human rotavirus entry into MA 104 cells. Arch Virol. 1985;85(1-2):25–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01317003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kitaoka S., Sato T., Konno T., Iwasaki Y., Numazaki Y., Ishida N. Further investigation on the mode of entry of human rotavirus into cells. Arch Virol. 1986;91(1-2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF01316734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dinter S., Flintoff W. F. Rat glial C6 cells are defective in murine coronavirus internalization. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1677–1685. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderfecht S. L., Miskuff R. L., Wee S. B., Sato S., Tidwell R. R., Geratz J. D., Yolken R. H. Protease inhibitors suppress the in vitro and in vivo replication of rotavirus. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2011–2016. doi: 10.1172/JCI113821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Tsurudome M., Hishiyama M., Ito Y. Abortive infection of mumps virus in murine cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):973–980. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




