Abstract
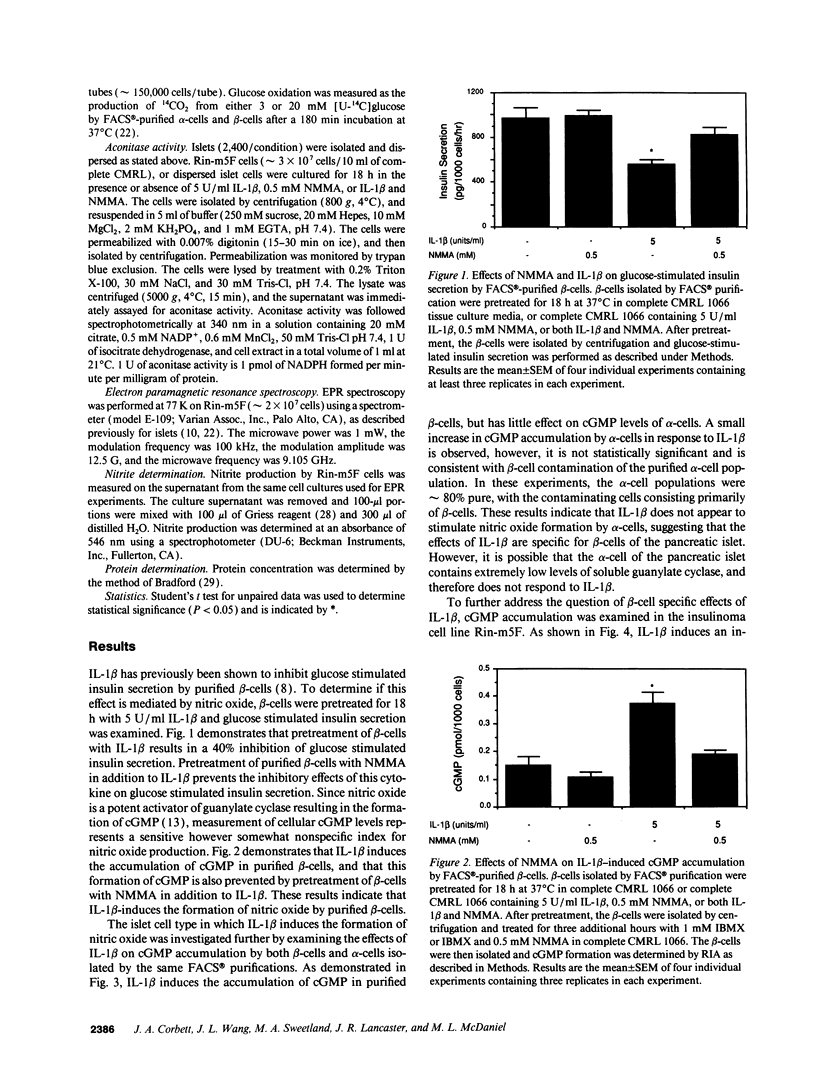
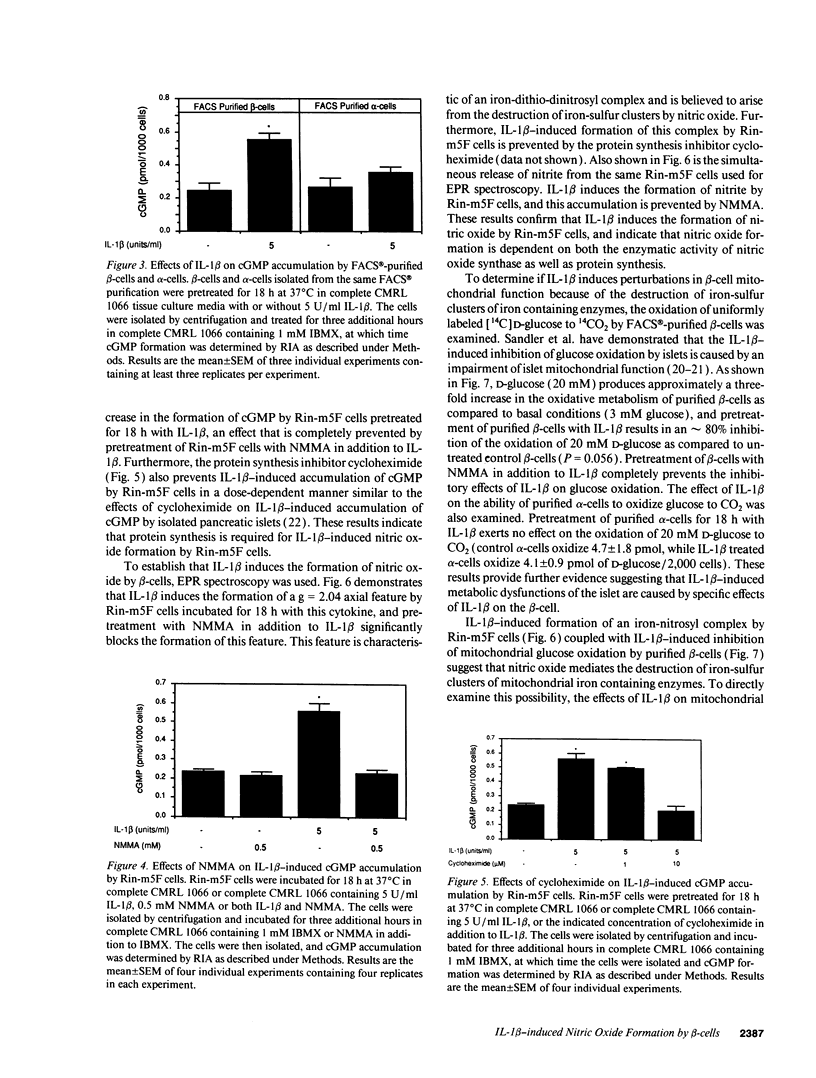
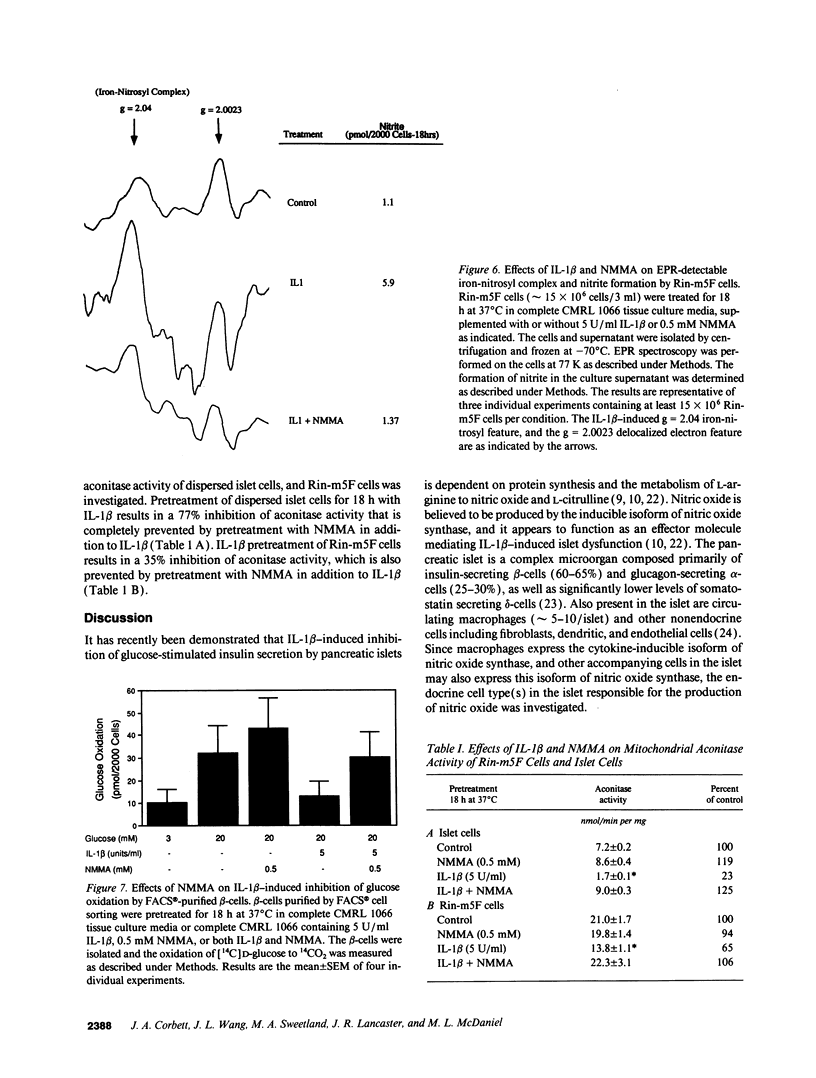
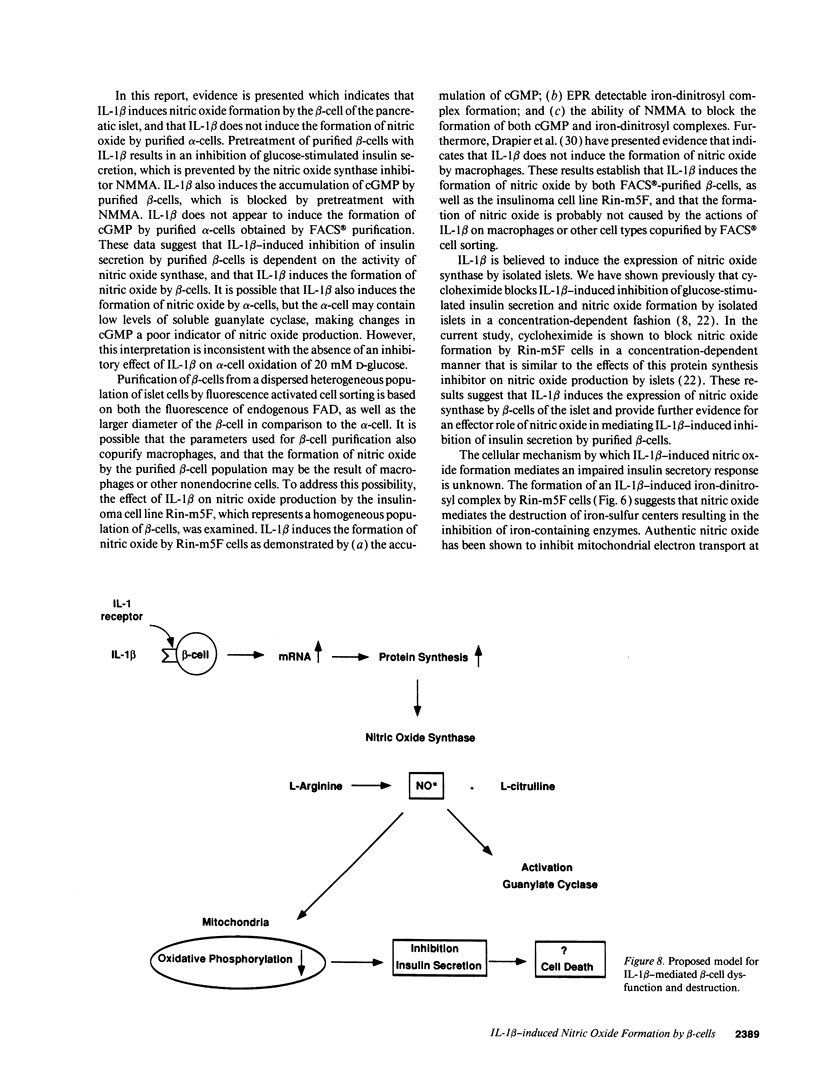
Nitric oxide has recently been implicated as the effector molecule that mediates IL-1 beta-induced inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and beta-cell specific destruction. The pancreatic islet represents a heterogeneous cell population containing both endocrine cells (beta-[insulin], alpha-]glucagon], gamma[somatostatin], and PP-[polypeptide] secreting cells) and non-endocrine cells (fibroblast, macrophage, endothelial, and dendritic cells). The purpose of this investigation was to determine if the beta-cell, which is selectively destroyed during insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, is both a source of IL-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production and also a site of action of this free radical. Pretreatment of beta-cells, purified by FACS with IL-1 beta results in a 40% inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion that is prevented by the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (NMMA). IL-1 beta induces the formation of nitric oxide by purified beta-cells as evidenced by the accumulation of cGMP, which is blocked by NMMA. IL-1 beta also induces the accumulation of cGMP by the insulinoma cell line Rin-m5F, and both NMMA as well as the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide prevent this cGMP accumulation. Iron-sulfur proteins appear to be intracellular targets of nitric oxide. IL-1 beta induces the formation of an iron-dinitrosyl complex by Rin-m5F cells indicating that nitric oxide mediates the destruction of iron-sulfur clusters of iron containing enzymes. This is further demonstrated by IL-1 beta-induced inhibition of glucose oxidation by purified beta-cells, mitochondrial aconitase activity of dispersed islet cells, and mitochondrial aconitase activity of Rin-m5F cells, all of which are prevented by NMMA. IL-1 beta does not appear to affect FACS-purified alpha-cell metabolic activity or intracellular cGMP levels, suggesting that IL-1 beta does not exert any effect on alpha-cells. These results demonstrate that the islet beta-cell is a source of IL-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production, and that beta-cell mitochondrial iron-sulfur containing enzymes are one site of action of nitric oxide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comens P. G., Wolf B. A., Unanue E. R., Lacy P. E., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin 1 is potent modulator of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):963–970. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A. An overview on possible mechanisms of destruction of the insulin-producing beta cell. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;164:125–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75741-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Sweetland M. A., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin-1 beta-induced formation of EPR-detectable iron-nitrosyl complexes in islets of Langerhans. Role of nitric oxide in interleukin-1 beta-induced inhibition of insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21351–21354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Wang J. L., Hughes J. H., Wolf B. A., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, McDaniel M. L. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP formation induced by interleukin 1 beta in islets of Langerhans. Evidence for an effector role of nitric oxide in islet dysfunction. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1;287(Pt 1):229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj2870229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Murine cytotoxic activated macrophages inhibit aconitase in tumor cells. Inhibition involves the iron-sulfur prosthetic group and is reversible. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):790–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI112642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Pellat C., Henry Y. Generation of EPR-detectable nitrosyl-iron complexes in tumor target cells cocultured with activated macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10162–10167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Wietzerbin J., Hibbs J. B., Jr Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor induce the L-arginine-dependent cytotoxic effector mechanism in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1587–1592. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Tracey D. E., Bendtzen K., Sandler S. An interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein protects insulin-producing beta cells against suppressive effects of interleukin-1 beta. Diabetologia. 1991 Jun;34(6):445–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00403185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):619–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Lehninger A. L. Sites of inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport in macrophage-injured neoplastic cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):527–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds P., Beggs M., Beresford G., Espinal J., Clarke J., Mertz R. J. Insulin-secreting beta-cells possess specific receptors for interleukin-1 beta. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80645-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helqvist S., Polla B. S., Johannesen J., Nerup J. Heat shock protein induction in rat pancreatic islets by recombinant human interleukin 1 beta. Diabetologia. 1991 Mar;34(3):150–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00418268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Vavrin Z., Taintor R. R. L-arginine is required for expression of the activated macrophage effector mechanism causing selective metabolic inhibition in target cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. H., Colca J. R., Easom R. A., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin 1 inhibits insulin secretion from isolated rat pancreatic islets by a process that requires gene transcription and mRNA translation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):856–863. doi: 10.1172/JCI114785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. H., Watson M. A., Easom R. A., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin-1 induces rapid and transient expression of the c-fos proto-oncogene in isolated pancreatic islets and in purified beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81499-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Kolb-Bachofen V., Berschick B., Burkart V., Kolb H. Activated macrophages kill pancreatic syngeneic islet cells via arginine-dependent nitric oxide generation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):752–758. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91630-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Gilker C., Griffith O. W., Matthews D. E., Stuehr D. J. L-citrulline production from L-arginine by macrophage nitric oxide synthase. The ureido oxygen derives from dioxygen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13442–13445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr EPR demonstration of iron-nitrosyl complex formation by cytotoxic activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1223–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G., Modica M. E., Cavanaugh C. T. L-arginine stimulates cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in rat islets of Langerhans and RINm5F insulinoma cells: evidence for L-arginine:nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3043–3052. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Bendtzen K., Nerup J., Egeberg J., Nielsen J. H. Mechanisms of pancreatic islet cell destruction. Dose-dependent cytotoxic effect of soluble blood mononuclear cell mediators on isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy. 1986 May;41(4):250–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1986.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Bendtzen K., Nielsen J. H., Bendixen G., Nerup J. Cytokines cause functional and structural damage to isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy. 1985 Aug;40(6):424–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb02681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Helqvist S., Wogensen L. D., Mølvig J., Pociot F., Johannesen J., Nerup J. Cytokine and free radicals as effector molecules in the destruction of pancreatic beta cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;164:169–193. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75741-9_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., Lacy P. E. A subcellular fractionation approach for studying insulin release mechanisms and calcium metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:182–200. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Mølvig J. The HLA-IDDM association: implications for etiology and pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jul;3(3):779–802. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellat C., Henry Y., Drapier J. C. IFN-gamma-activated macrophages: detection by electron paramagnetic resonance of complexes between L-arginine-derived nitric oxide and non-heme iron proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91919-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., in't Veld P. A., Van de Winkel M., Maes E., Schuit F. C., Gepts W. A new in vitro model for the study of pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):806–816. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S., Andersson A., Hellerström C. Inhibitory effects of interleukin 1 on insulin secretion, insulin biosynthesis, and oxidative metabolism of isolated rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1424–1431. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S., Bendtzen K., Borg L. A., Eizirik D. L., Strandell E., Welsh N. Studies on the mechanisms causing inhibition of insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets exposed to human interleukin-1 beta indicate a perturbation in the mitochondrial function. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1492–1501. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Warner T. D., Ishii K., Sheng H., Murad F. Insulin secretion from pancreatic B cells caused by L-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):721–723. doi: 10.1126/science.1371193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setum C. M., Serie J. R., Hegre O. D. Confocal microscopic analysis of the nonendocrine cellular component of isolated adult rat islets of Langerhans. Transplantation. 1991 May;51(5):1131–1133. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199105000-00043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern C., Schulster D., Green I. C. Inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha via an L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide generating mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80502-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Stuehr D. J., Ochoa J. B., Simmons R. L. Effect of exogenous and endogenous nitric oxide on mitochondrial respiration of rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):C910–C916. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.5.C910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Cho H. J., Kwon N. S., Weise M. F., Nathan C. F. Purification and characterization of the cytokine-induced macrophage nitric oxide synthase: an FAD- and FMN-containing flavoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., McDaniel M. L. Secretagogue-induced oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in single beta and alpha-cells obtained from pancreatic islets by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 30;166(2):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90882-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


