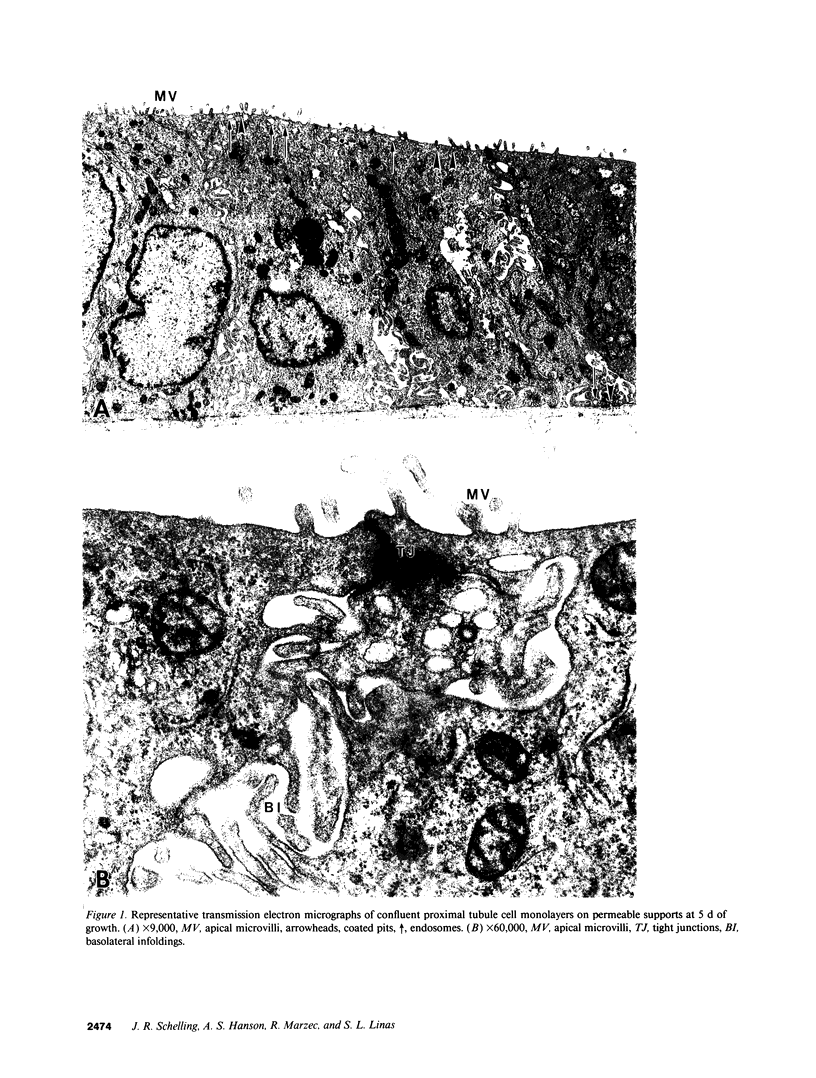
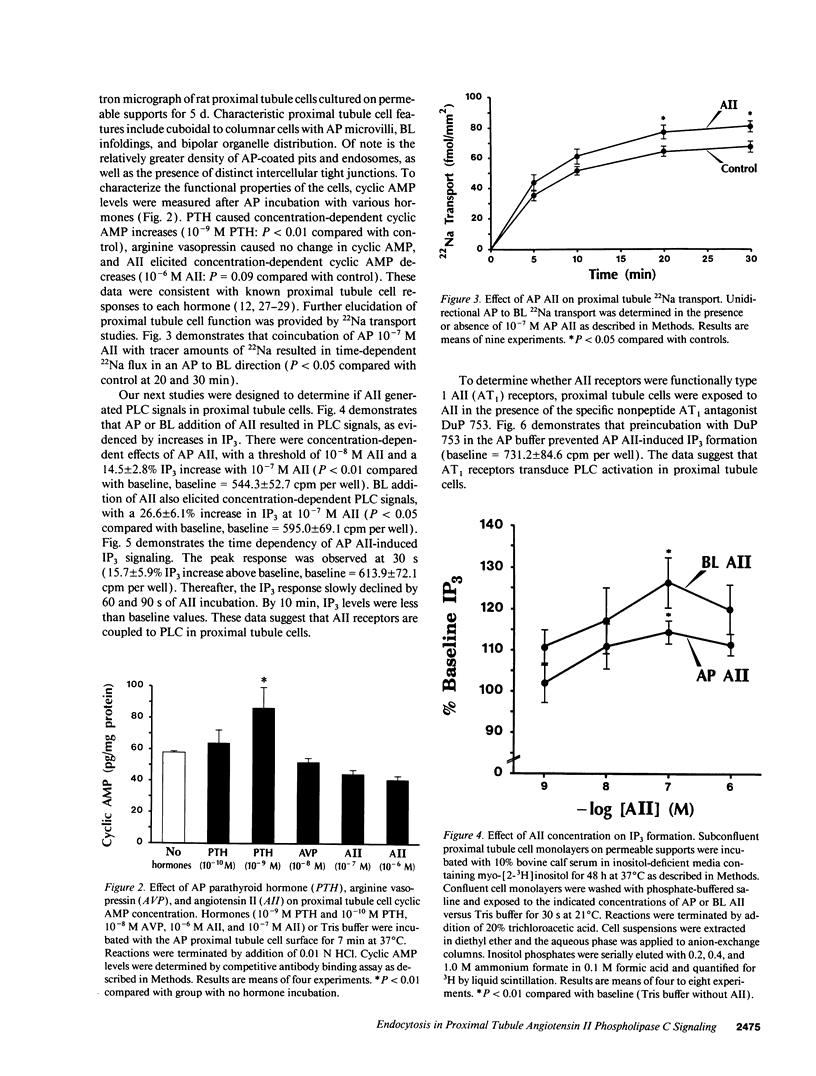
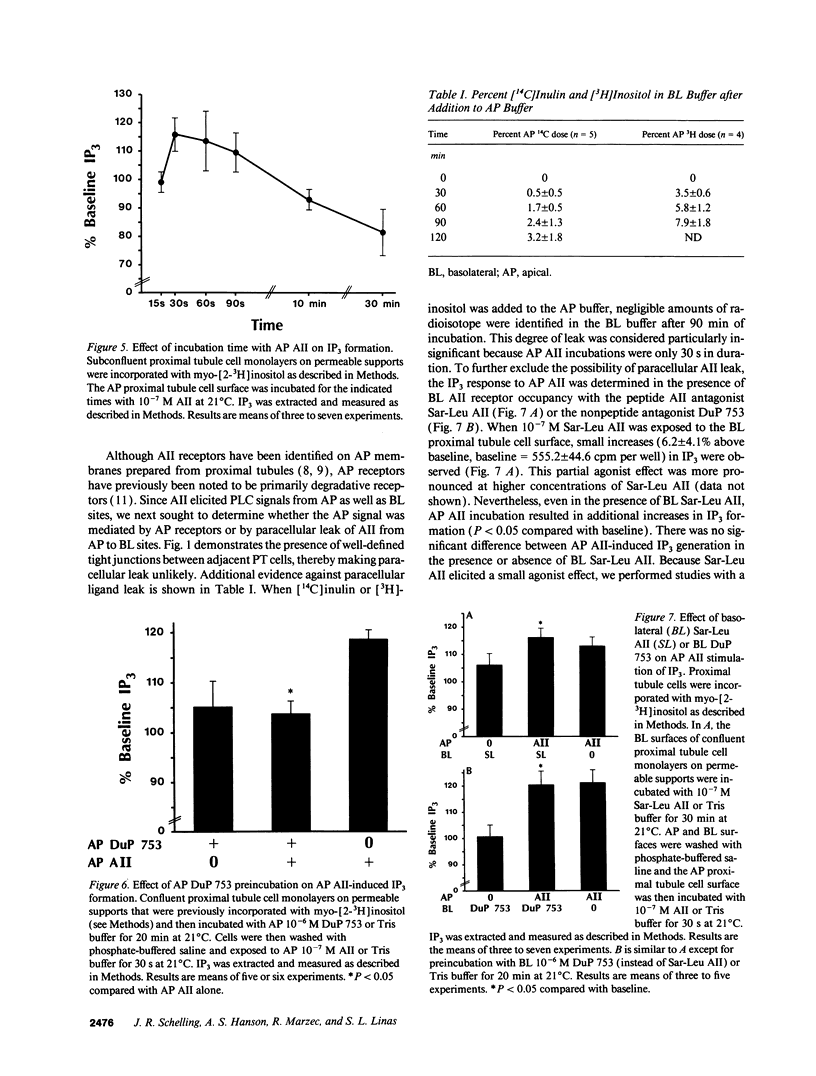
Abstract
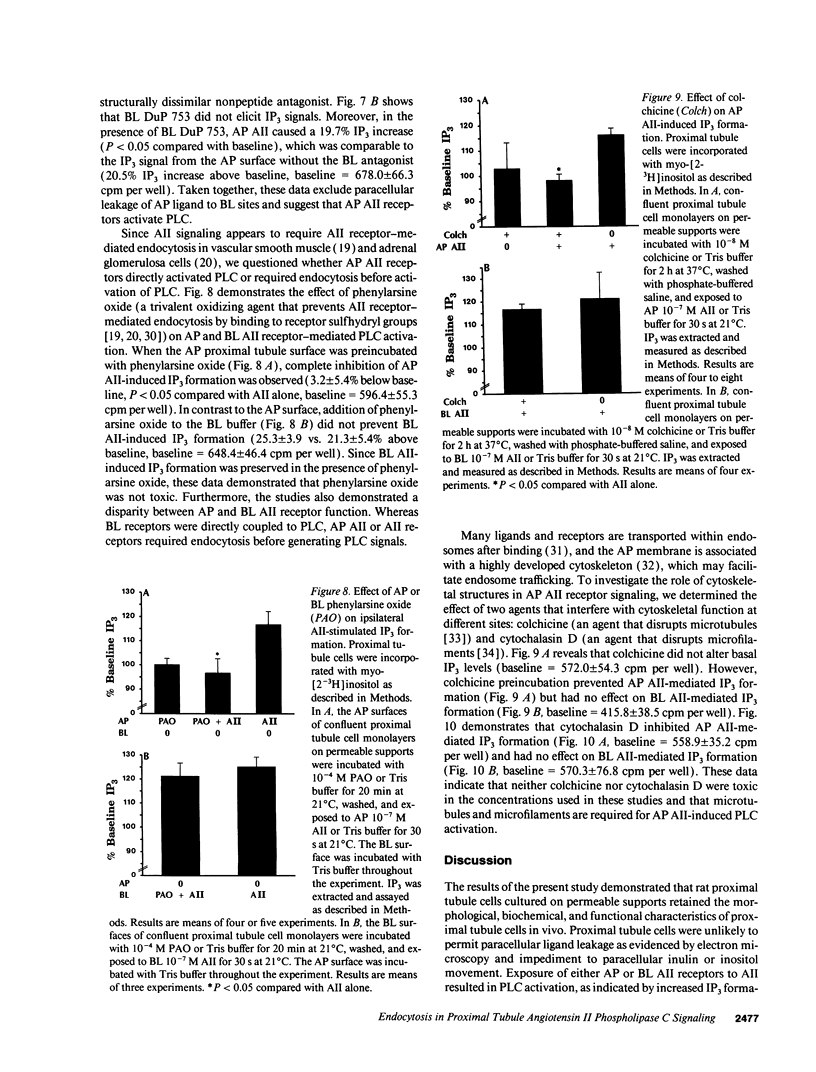
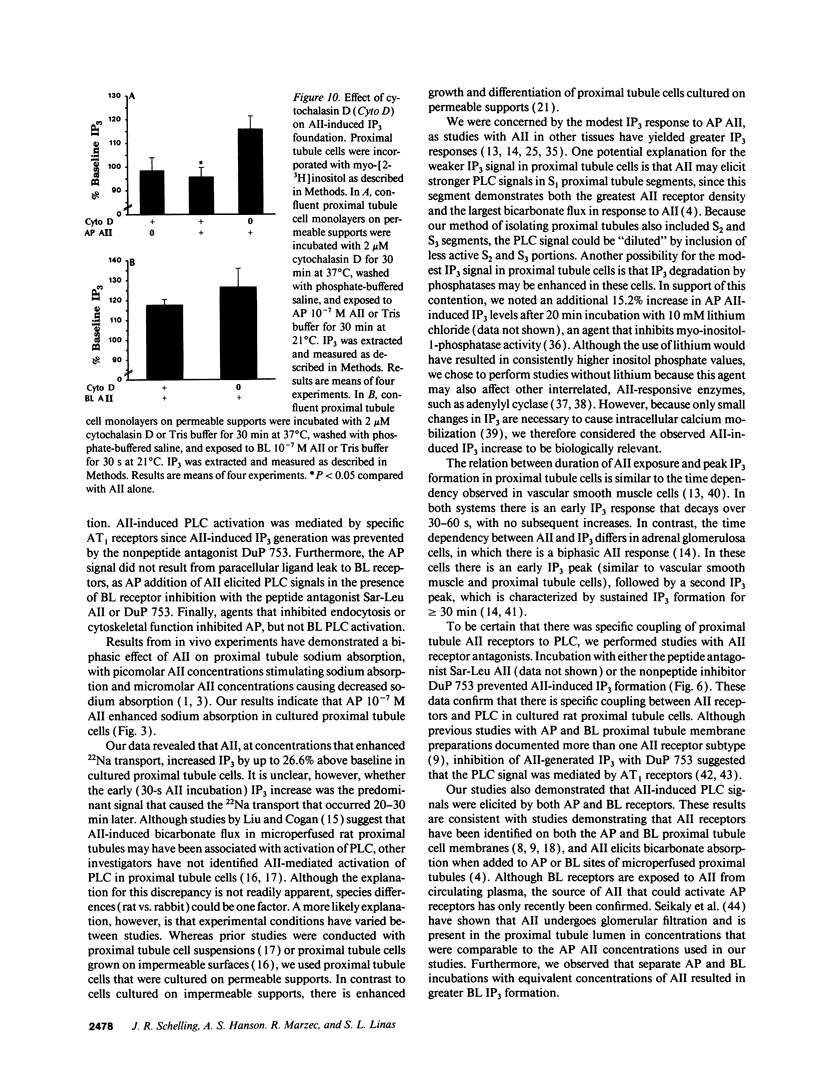
Renal proximal tubule sodium reabsorption is enhanced by apical or basolateral angiotensin II (AII). Although AII activates phospholipase C (PLC) in other tissues, AII coupling to PLC on either apical or basolateral surfaces of proximal tubule cells is unclear. To determine if AII causes PLC activation, and the differences between apical and basolateral AII receptor function, receptors were unilaterally activated in rat proximal tubule cells cultured on permeable, collagen-coated supports. Apical AII incubation resulted in concentration- and time-dependent inositol trisphosphate (IP3) formation. Basolateral AII caused greater IP3 responses. Apical AII-induced IP3 generation was inhibited by DuP 753, suggesting that the type 1 AII receptor subtype mediated proximal tubule PLC activation. Apical AII signaling did not result from paracellular ligand leak to basolateral receptors since AII-induced PLC activation occurred when basolateral AII receptors were occupied by Sar-Leu AII or DuP 753. Inhibition of endocytosis with phenylarsine oxide prevented apical (but not basolateral) AII-induced IP3 formation. Cytoskeletal disruption with colchicine or cytochalasin D also prevented apical AII-induced IP3 generation. These results demonstrate that in cultured rat proximal tubule cells, AII is coupled to PLC via type 1 AII receptors and cytoskeleton-dependent endocytosis is required for apical (but not basolateral) AII receptor-mediated PLC activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. W., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Rittenhouse S. E. Angiotensin increases inositol trisphosphate and calcium in vascular smooth muscle. Hypertension. 1985 May-Jun;7(3 Pt 1):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balla T., Baukal A. J., Guillemette G., Catt K. J. Multiple pathways of inositol polyphosphate metabolism in angiotensin-stimulated adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4083–4091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benabe J. E., Spry L. A., Morrison A. R. Effects of angiotensin II on phosphatidylinositol and polyphosphoinositide turnover in rat kidney. Mechanism of prostaglandin release. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7430–7434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R. Inhibition of glucose transport in the human erythrocyte by cytochalasin B. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4799–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitfeld P. P., McKinnon W. C., Mostov K. E. Effect of nocodazole on vesicular traffic to the apical and basolateral surfaces of polarized MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2365–2373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. P., Douglas J. G. Angiotensin II binding sites on isolated rat renal brush border membranes. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1830–1836. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. P., Douglas J. G. Angiotensin II-binding sites in rat and primate isolated renal tubular basolateral membranes. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2007–2014. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carone F. A., Peterson D. R. Hydrolysis and transport of small peptides by the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):F151–F158. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.3.F151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu A. T., McCall D. E., Aldrich P. E., Timmermans P. B. [3H]DUP 753, a highly potent and specific radioligand for the angiotensin II-1 receptor subtype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1195–1202. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91575-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. D., Alavi N., Livingston D., Hiller S., Taub M. Characterization of primary rabbit kidney cultures that express proximal tubule functions in a hormonally defined medium. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):118–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan E., Abramow M. Inhibition by lithium of the hydroosmotic action of vasopressin in the isolated perfused cortical collecting tubule of the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1507–1514. doi: 10.1172/JCI112465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. G. Angiotensin receptor subtypes of the kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):F1–F7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dousa T. P. Cellular action of antidiuretic hormone in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Mar;49(3):188–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley D. T., Panek R. L., Major T. C., Lu G. H., Bruns R. F., Klinkefus B. A., Hodges J. C., Weishaar R. E. Subclasses of angiotensin II binding sites and their functional significance. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;38(3):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. M., Williams P. D., Grassl S., Holohan P. D. Transepithelial acidification by cultures of rabbit proximal tubules grown on filters. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C103–C109. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geibel J., Giebisch G., Boron W. F. Angiotensin II stimulates both Na(+)-H+ exchange and Na+/HCO3- cotransport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7917–7920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesek F. A., Schoolwerth A. C. Hormonal interactions with the proximal Na(+)-H+ exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F514–F521. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesek F. A., Wolff D. W., Strandhoy J. W. Improved separation method for rat proximal and distal renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F358–F365. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Delafontaine P., Rittenhouse S. E., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Correlation of receptor sequestration with sustained diacylglycerol accumulation in angiotensin II-stimulated cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14555–14562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E. J., Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Brown D. Colchicine-induced redistribution of an apical membrane glycoprotein (gp330) in proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):C397–C407. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.2.C397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E. Control of sodium excretion by angiotensin II: intrarenal mechanisms and blood pressure regulation. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):R960–R972. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.6.R960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S. Studies of kidney cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1986 Aug;30(2):208–215. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Navar L. G. Tubular transport responses to angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 2):F621–F630. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.5.F621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunyady L., Merelli F., Baukal A. J., Balla T., Catt K. J. Agonist-induced endocytosis and signal generation in adrenal glomerulosa cells. A potential mechanism for receptor-operated calcium entry. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2783–2788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachadorian W. A., Ellis S. J., Muller J. Possible roles for microtubules and microfilaments in ADH action on toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):F14–F20. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.1.F14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. S., Blain P. L., Park J. H., Tuma D. J. Altered role of microtubules in asialoglycoprotein trafficking in developing liver. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):G129–G137. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.1.G129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Kojima K., Kreutter D., Rasmussen H. The temporal integration of the aldosterone secretory response to angiotensin occurs via two intracellular pathways. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14448–14457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II stimulates early proximal bicarbonate absorption in the rat by decreasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):83–91. doi: 10.1172/JCI114174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II stimulation of hydrogen ion secretion in the rat early proximal tubule. Modes of action, mechanism, and kinetics. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):601–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI113638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Role of protein kinase C in proximal bicarbonate absorption and angiotensin signaling. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 2):F927–F933. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.4.F927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F. Sites of hormone action in the mammalian nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):F159–F164. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.3.F159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojakian G. K., Schwimmer R. The polarized distribution of an apical cell surface glycoprotein is maintained by interactions with the cytoskeleton of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2377–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Lorenzen M. Antidiuretic hormone-dependent membrane capacitance and water permeability in the toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):F195–F204. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.2.F195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl M., Taylor A. Actin filaments and vasopressin-stimulated water flow in toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C28–C39. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Sabatini D. D. Microtubule-acting drugs lead to the nonpolarized delivery of the influenza hemagglutinin to the cell surface of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):231–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Selective modulation of the endocytic uptake of ricin and fluid phase markers without alteration in transferrin endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6382–6388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Angiotensin II directly stimulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):507–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI111237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seikaly M. G., Arant B. S., Jr, Seney F. D., Jr Endogenous angiotensin concentrations in specific intrarenal fluid compartments of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1352–1357. doi: 10.1172/JCI114846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekar M. C., Yang M., Meezan E., Pillion D. J. Angiotensin II and bradykinin stimulate phosphoinositide breakdown in intact rat kidney glomeruli but not in proximal tubules: glomerular response modulated by phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91955-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Smith L., Brown E. R., Barnes D., Sabir M. A., Davis J. S., Farese R. V. Angiotensin II rapidly increases phosphatidate-phosphoinositide synthesis and phosphoinositide hydrolysis and mobilizes intracellular calcium in cultured arterial muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7812–7816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Schwartz A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):657–662. doi: 10.1172/JCI112359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlicht E., Barnard R. J., Grimditch G. K. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):E633–E638. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.5.E633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullian M. E., Linas S. L. Angiotensin II surface receptor coupling to inositol trisphosphate formation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullian M. E., Linas S. L. Role of receptor cycling in the regulation of angiotensin II surface receptor number and angiotensin II uptake in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):840–846. doi: 10.1172/JCI114244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenti G., Hugon J. S., Bourguet J. To what extent is microtubular network involved in antidiuretic response? Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1098–F1106. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinay P., Gougoux A., Lemieux G. Isolation of a pure suspension of rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F403–F411. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh C., Dubyak G., Douglas J. G. Relationship between phospholipase C activation and prostaglandin E2 and cyclic adenosine monophosphate production in rabbit tubular epithelial cells. Effects of angiotensin, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):710–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI113376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. D., Dillingham M. A., Breckon R., Anderson R. J. Defined human renal tubular epithelia in culture: growth, characterization, and hormonal response. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 2):F436–F443. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.3.F436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Harada F., Sekita S., Yoshihira K., Natori S. Correlation between effects of 24 different cytochalasins on cellular structures and cellular events and those on actin in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):69–78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]